1. 简介
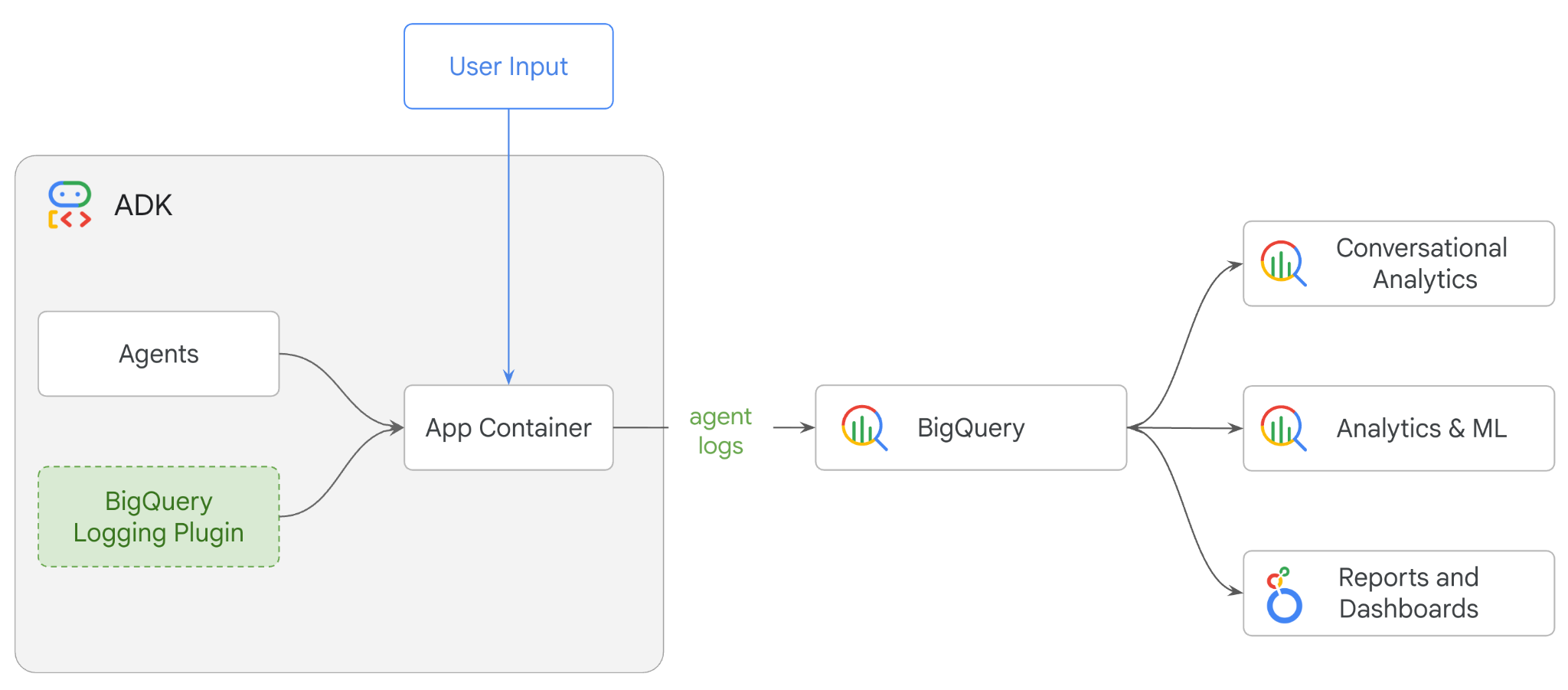
在此 Codelab 中,您将使用智能体开发套件 (ADK) 构建多智能体系统,并使用 BigQuery 智能体分析插件启用智能体可观测性。您将向智能体提出一系列问题,然后使用 BigQuery 分析对话轨迹和智能体工具使用情况。
实践内容
- 使用 ADK 构建多智能体零售助理
- 初始化 BigQuery Agent Analytics Plugin,以捕获和存储有关此代理执行的轨迹数据到 BigQuery
- 在 BigQuery 中分析代理日志数据
所需条件
- 网络浏览器,例如 Chrome
- 启用了结算功能的 Google Cloud 项目,或者
- Gmail 账号。下一部分将介绍如何兑换此 Codelab 的 5 美元免费赠金并设置新项目
本 Codelab 适用于各种水平的开发者,包括新手。您将使用 Google Cloud Shell 中的命令行界面和 Python 代码进行 ADK 开发。您无需成为 Python 专家,但对如何读取代码有基本的了解有助于您理解这些概念。
2. 准备工作
创建 Google Cloud 项目
- 在 Google Cloud 控制台的项目选择器页面上,选择或创建一个 Google Cloud 项目。
- 确保您的 Cloud 项目已启用结算功能。了解如何检查项目是否已启用结算功能。
启动 Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell 是在 Google Cloud 中运行的命令行环境,预加载了必要的工具。
- 点击 Google Cloud 控制台顶部的激活 Cloud Shell:

- 连接到 Cloud Shell 后,运行以下命令以验证您在 Cloud Shell 中的身份验证:
gcloud auth list
- 运行以下命令,确认您的项目已配置为可与 gcloud 搭配使用:
gcloud config get project
- 如果您的项目未按预期配置,请使用以下命令设置项目:
export PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
启用 API
- 运行以下命令以启用所有必需的 API 和服务:
gcloud services enable bigquery.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com
- 成功执行该命令后,您应该会看到类似如下所示的消息:
Operation "operations/..." finished successfully.
3. 安装和设置
返回到 Cloud Shell,并确保您位于主目录中。
在 Cloud Shell 中运行以下命令,在 BigQuery 中创建一个名为 adk_logs 的新数据集:
bq mk --dataset --location=US adk_logs
现在,我们来创建虚拟 Python 环境并安装所需的软件包。
- 在 Cloud Shell 中打开新的终端标签页,然后运行以下命令来创建并前往名为
adk-agent-observability的文件夹:
mkdir adk-agent-observability
cd adk-agent-observability
- 创建虚拟 Python 环境:
python -m venv .venv
- 激活此虚拟环境:
source .venv/bin/activate
- 安装 ADK:
pip install --upgrade google-adk
4. 创建 ADK 应用
现在,我们来创建零售助理代理。此代理将设计为 ...
- 运行 adk create 实用程序命令,以搭建包含必要文件夹和文件的新代理应用:
adk create retail_assistant_app
按照提示操作:
- 为模型选择 gemini-2.5-flash。
- 选择 Vertex AI 作为后端。
- 确认您的默认 Google Cloud 项目 ID 和区域。
下面展示了互动示例:

- 点击 Cloud Shell 中的“打开编辑器”按钮,打开 Cloud Shell 编辑器,然后查看新创建的文件夹和文件:

请注意生成的文件:
retail_assistant_app/
├── .venv/
└── retail_assistant_app/
├── __init__.py
├── agent.py
└── .env
- init.py::将相应文件夹标记为 Python 模块。
- agent.py::包含初始代理定义。
- .env:您可能需要依次点击“查看”>“显示/不显示隐藏文件”才能查看此文件
- .env 文件包含项目的环境变量,请更新提示中未正确设置的任何变量:
GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI=1
GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=<YOUR_GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID>
GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION=<YOUR_GOOGLE_CLOUD_REGION>
5. 定义代理
现在,我们来定义一个分层多智能体系统。
- 实时趋势代理:使用 Google 搜索查找当前的时尚趋势。
- 库存数据代理:使用 BigQuery 工具集查询公共 thelook_ecommerce 数据集中的可用商品。
- 零售助理(根)智能体:通过向趋势智能体咨询建议并向库存智能体咨询匹配的产品来编排工作流。
将 retail_assistant_app/agent.py 的全部内容替换为以下代码。
import os
import uuid
import asyncio
import google.auth
import dotenv
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.agents import Agent
from google.adk.apps import App
from google.adk.runners import InMemoryRunner
from google.adk.tools import AgentTool, google_search
from google.adk.tools.bigquery import BigQueryCredentialsConfig, BigQueryToolset
from google.adk.plugins.bigquery_agent_analytics_plugin import BigQueryAgentAnalyticsPlugin
dotenv.load_dotenv()
# --- Configuration ---
PROJECT_ID = os.getenv('GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT', 'project_not_set')
DATASET_ID = "adk_logs"
TABLE_ID = "retail_assistant_agent_logs"
APP_NAME = "retail_assistant_agent"
USER_ID = "test_user"
# --- Toolsets ---
credentials, _ = google.auth.default()
credentials_config = BigQueryCredentialsConfig(credentials=credentials)
bigquery_toolset = BigQueryToolset(
credentials_config=credentials_config
)
# --- Agents ---
# 1. Trend Spotter
real_time_agent = Agent(
name="real_time_agent",
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
description="Researches external factors like weather, local events, and current fashion trends.",
instruction="""
You are a real-time research agent.
Use Google Search to find real-time information relevant to the user's request,
such as the current weather in their location or trending styles.
""",
tools=[google_search]
)
# 2. Inventory Manager
inventory_data_agent = Agent(
name="inventory_data_agent",
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
description="Oversees product inventory in the BigQuery `thelook_ecommerce` dataset to find available items and prices.",
instruction=f"""
You manage the inventory. You have access to the `bigquery-public-data.thelook_ecommerce` dataset via the BigQuery toolset.
Run all BigQuery queries the project id of: '{PROJECT_ID}'
Your workflow:
1. Look at the products table.
2. Find items that match the requirements, factor in the results from the trend_setter agent if there are any.
3. Return with a user friendly response, including the list of specific products and prices.
""",
tools=[bigquery_toolset]
)
# 3. Root Orchestrator
root_agent = Agent(
name="retail_assistant",
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
description="The primary orchestrator, responsible for handling user input, delegating to sub-agents, and synthesizing the final product recommendation.",
instruction="""
You are a Retail Assistant.
You can ask the 'real_time_agent' agent for any realtime information needed, or style advice, include any information provided by the user.
You should ask the 'inventory_data_agent' agent to find a maximum of 3 available items matching that style.
Combine the results into a recommendation.
""",
tools=[AgentTool(agent=real_time_agent)],
sub_agents=[inventory_data_agent]
)
6. 使用 BigQuery Agent Analytics 插件生成日志
现在,我们来配置 BigQuery Agent Analytics 插件以捕获执行数据。
为此,您将创建 App 类的实例。此类用作代理的运行时容器;它管理对话循环、处理用户状态,并协调任何附加的插件(例如我们的代理分析记录器)。
以下代码:
- 初始化 Logging 插件:使用所需的连接详细信息创建
BigQueryAgentAnalyticsPlugin。 - 集成插件:将初始化的 BigQuery 插件传递到
App构造函数中,确保自动捕获并记录代理执行事件。 - 运行并记录代理执行情况:通过
runner.run_async执行对话流程,同时插件会收集整个事件序列并将其发送到 BigQuery,然后关闭其资源。
将此代码复制并粘贴到 agent.py 文件中的代理定义下方:
async def main(prompt: str):
"""Runs a conversation with the BigQuery agent using the ADK Runner."""
bq_logger_plugin = BigQueryAgentAnalyticsPlugin(
project_id=PROJECT_ID, dataset_id=DATASET_ID, table_id=TABLE_ID
)
app = App(name=APP_NAME, root_agent=root_agent, plugins=[bq_logger_plugin])
runner = InMemoryRunner(app=app)
try:
session_id = f"{USER_ID}_{uuid.uuid4().hex[:8]}"
my_session = await runner.session_service.create_session(
app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=session_id
)
async for event in runner.run_async(
user_id=USER_ID,
new_message=types.Content(
role="user", parts=[types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)]
),
session_id=my_session.id,
):
if event.content.parts and event.content.parts[0].text:
print(f"** {event.author}: {event.content.parts[0].text}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error in main: {e}")
finally:
print("Closing BQ Plugin...")
await bq_logger_plugin.close()
print("BQ Plugin closed.")
async def run_all_prompts():
"""Runs all prompts in a single event loop."""
prompts = [
"what outfits do you have available that are suitable for the weather in london this week?",
"You are such a cool agent! I need a gift idea for my friend who likes yoga.",
"I'd like to complain - the products sold here are not very good quality!"
]
for prompt in prompts:
await main(prompt)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(run_all_prompts())
完成插桩后,接下来就可以查看代理的实际运行情况了。运行脚本以触发对话工作流。
python retail_assistant_app/agent.py
您应该会看到零售助理编排工作流程:
- 它会要求 Real Time Trend Agent (real_time_agent) 识别伦敦的天气并搜索合适的时尚趋势。
- 然后,它会委托给 Inventory Data Agent (inventory_data_agent) 查询
thelook_ecommerceBigQuery 数据集,以查找符合这些趋势的特定产品。 - 最后,根 Orchestrator 会将结果合成最终推荐。
与此同时,插件会将代理的执行轨迹流式传输到 BigQuery。
7. 分析代理日志
使用工具
现在,我们可以看到代理在后台做了什么!数据已流式传输到 BigQuery,可供分析:
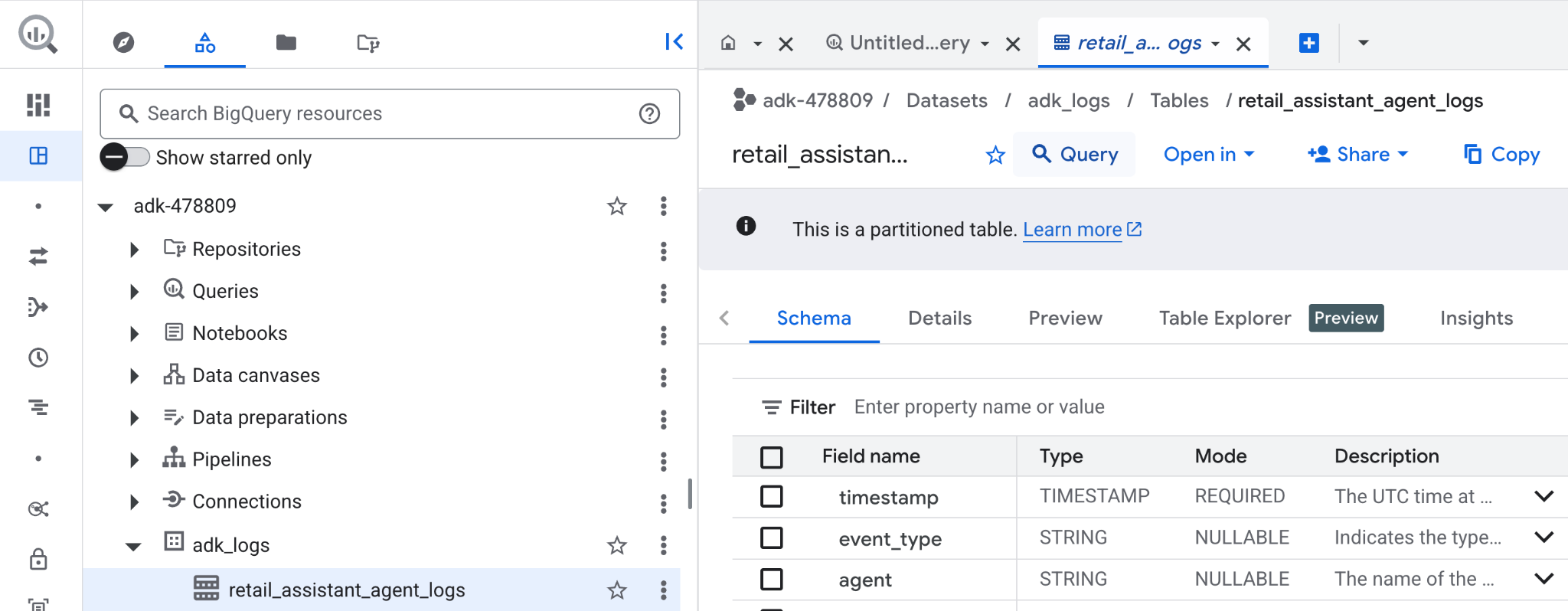
- 在 Google Cloud 控制台中,搜索 BigQuery。
- 在探索器窗格中,找到您的项目。
- 展开
adk_logs数据集。 - 打开
retail_assitant_agent_logs表,然后点击查询。
如需查看代理发出的工具调用,并捕获任何工具错误,请在 BigQuery 编辑器中运行以下查询:
SELECT
-- Extract the tool name directly from the JSON key "tool"
JSON_VALUE(content, '$.tool') AS tool_name,
-- Count every time a tool finished (successfully or with an error)
COUNT(*) AS total_finished_runs,
-- Count as a failure if event_type is ERROR, result object contains a status of 'ERROR', or error_details exist
COUNTIF(
event_type = 'TOOL_ERROR' OR
JSON_VALUE(content, '$.result.status') = 'ERROR' OR
JSON_VALUE(content, '$.result.error_details') IS NOT NULL
) AS failure_count
FROM
`adk_logs.retail_assistant_agent_logs`
WHERE
event_type IN ('TOOL_COMPLETED', 'TOOL_ERROR')
GROUP BY
1;
点击“可视化图表”,以图表形式查看结果(您的结果可能有所不同):
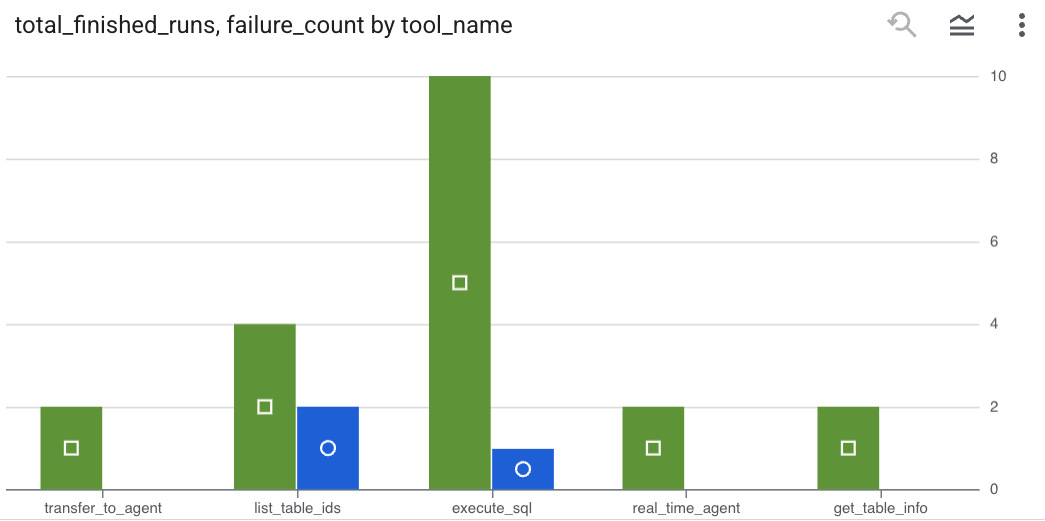
token 用量
如需推断代理的费用,您可以汇总每个不同代理消耗的提示词元和候选词元:
SELECT
t.agent,
SUM(LAX_INT64(t.content.usage.prompt)) AS prompt_tokens,
SUM(LAX_INT64(t.content.usage.completion)) AS completion_tokens
FROM
`adk_logs.retail_assistant_agent_logs` AS t
WHERE
t.event_type = 'LLM_RESPONSE'
-- Filter for records that actually contain usage metadata
AND t.content.usage IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY 1;
点击“可视化图表”,以图表形式查看结果(您的结果可能有所不同):
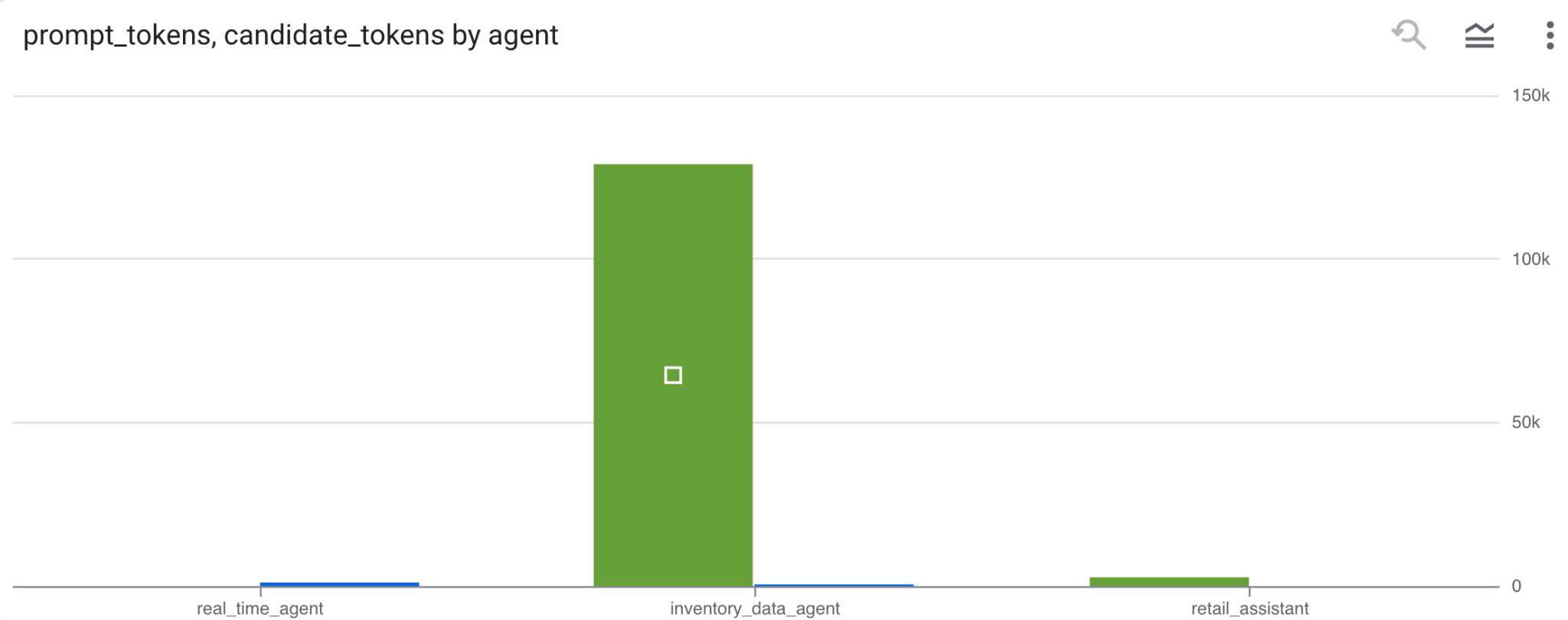
8. [奖励] 分析用户情绪
现在,我们来分析用户向代理提供的输入的语气。
- 在 Cloud Shell 中,创建 Cloud 资源连接,以使 BigQuery 能够与 Vertex AI 服务进行交互:
bq mk --connection --location=us \
--connection_type=CLOUD_RESOURCE test_connection
您应该会看到如下所示的响应:
已成功创建连接 517325854360.us.test_connection
- 创建 Cloud 资源连接:
export SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL=$(bq show --format=prettyjson --connection us.test_connection | grep "serviceAccountId" | cut -d '"' -f 4)
- 运行以下命令以验证服务账号是否已成功创建:
echo $SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL
您应该会看到显示的服务账号:

- 向资源连接服务账号授予与 Vertex AI 交互所需的项目级权限:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $(gcloud config get-value project) \
--member="serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL" \
--role='roles/bigquery.connectionUser' && \
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $(gcloud config get-value project) \
--member="serviceAccount:$SERVICE_ACCOUNT_EMAIL" \
--role='roles/aiplatform.user'
请等待几分钟,让系统传播权限。然后返回到 BigQuery,并运行包含 AI.SCORE 函数的以下查询来分析用户情绪:
SELECT
timestamp,
user_id,
content,
AI.SCORE((
'What is the sentiment of the user in this text:', JSON_VALUE(content.text_summary),
'Use a scale from 1 to 5.'),
connection_id => 'us.test_connection') AS user_sentiment
FROM
`adk_logs.retail_assistant_agent_logs`
WHERE
event_type = 'USER_MESSAGE_RECEIVED'
ORDER BY
user_sentiment DESC;
AI.SCORE 函数将为每项用户输入分配一个介于 1 到 5 之间的情绪值。您应该会看到类似如下所示的结果:
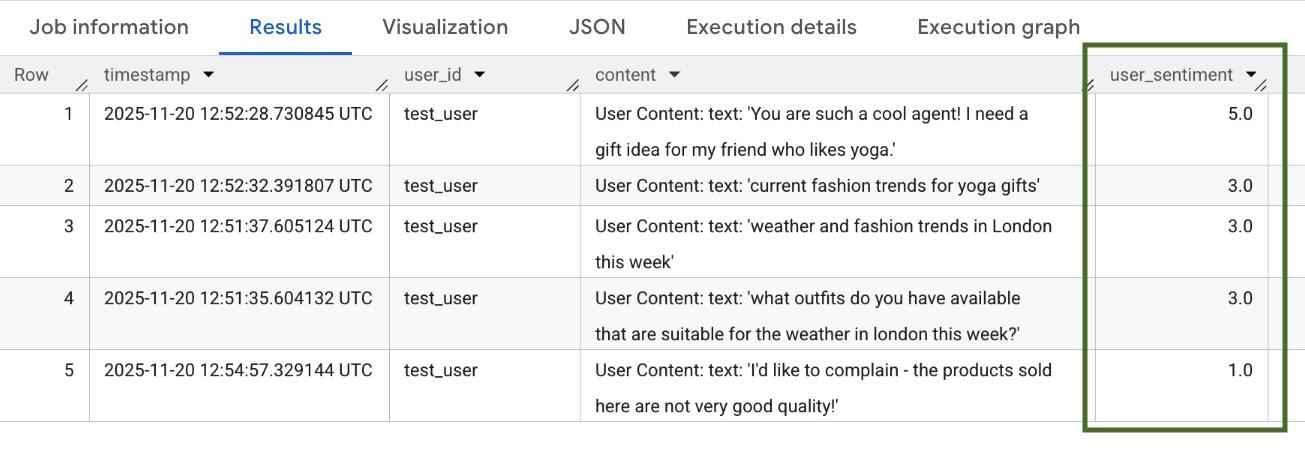
9. 清理
为避免系统向您的 Google Cloud 账号持续收取费用,请删除本次研讨会期间创建的资源。
删除脚本创建的日志记录数据集:
bq rm -r -f -d $PROJECT_ID:adk_logs
删除云资源连接:
bq rm --connection --project_id=$PROJECT_ID --location=us test_connection
如需移除 bigquery-adk-codelab 目录及其内容,请执行以下操作:
cd ..
rm -rf adk-agent-observability
10. 恭喜
恭喜!您已使用智能体开发套件 (ADK) 构建了一个多智能体系统,并成功集成了 BigQuery Agent Analytics 插件,以跟踪和审核智能体的行为。
