1. 简介
在此 Codelab 中,您将学习如何构建和部署 AI 赋能的代理饮食规划器。对于使用 Streamlit 的界面,LLM 模型使用 Gemini Pro 2.5,Agentic AI Engine Orchestrator 使用 Vertex AI 进行开发 Agentic AI,BigQuery 用于存储数据,Cloud Run 用于部署。
在此 Codelab 中,您将采用以下分步方法:
- 准备好您的 Google Cloud 项目,并在其中启用所有必需的 API
- 使用 Streamlit、Vertex AI 和 BigQuery 构建 Agentic AI 饮食规划器
- 将应用部署到 Cloud Run
架构概览
前提条件
- 启用了结算功能的 Google Cloud Platform (GCP) 项目。
- Python 基础知识
学习内容
- 如何使用 Streamlit 和 Vertex AI 构建 Agentic AI 饮食规划器,并将数据存储到 BigQuery
- 如何将应用部署到 Cloud Run
所需条件
- Chrome 网络浏览器
- Gmail 账号
- 启用了结算功能的 Cloud 项目
2. 基本设置和要求
自定进度的环境设置
- 登录 Google Cloud 控制台,然后创建一个新项目或重复使用现有项目。如果您还没有 Gmail 或 Google Workspace 账号,则必须创建一个。

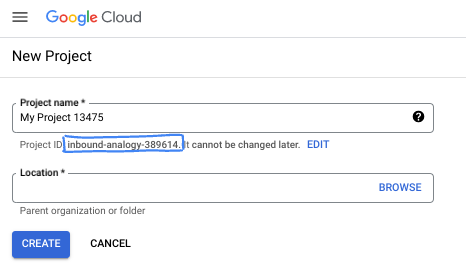
- 项目名称是此项目参与者的显示名称。它是 Google API 尚未使用的字符串。您可以随时对其进行更新。
- 项目 ID 在所有 Google Cloud 项目中是唯一的,并且是不可变的(一经设置便无法更改)。Cloud 控制台会自动生成一个唯一字符串;通常情况下,您无需关注该字符串。在大多数 Codelab 中,您都需要引用项目 ID(通常用
PROJECT_ID标识)。如果您不喜欢生成的 ID,可以再随机生成一个 ID。或者,您也可以尝试自己的项目 ID,看看是否可用。完成此步骤后便无法更改该 ID,并且此 ID 在项目期间会一直保留。 - 此外,还有第三个值,即部分 API 使用的项目编号,供您参考。如需详细了解所有这三个值,请参阅文档。
- 接下来,您需要在 Cloud 控制台中启用结算功能,以便使用 Cloud 资源/API。运行此 Codelab 应该不会产生太多的费用(如果有的话)。若要关闭资源以避免产生超出本教程范围的结算费用,您可以删除自己创建的资源或删除项目。Google Cloud 新用户符合参与 300 美元免费试用计划的条件。
3. 准备工作
在 Cloud Shell 编辑器中设置 Cloud 项目
此 Codelab 假设您已拥有一个启用了结算功能的 Google Cloud 项目。如果您还没有,可以按照以下说明开始使用。
- 在 Google Cloud Console 的项目选择器页面上,选择或创建一个 Google Cloud 项目。
- 确保您的 Cloud 项目已启用结算功能。了解如何检查项目是否已启用结算功能。
- 您将使用 Cloud Shell,这是一个在 Google Cloud 中运行的命令行环境,它预加载了 bq。点击 Google Cloud 控制台顶部的“激活 Cloud Shell”。
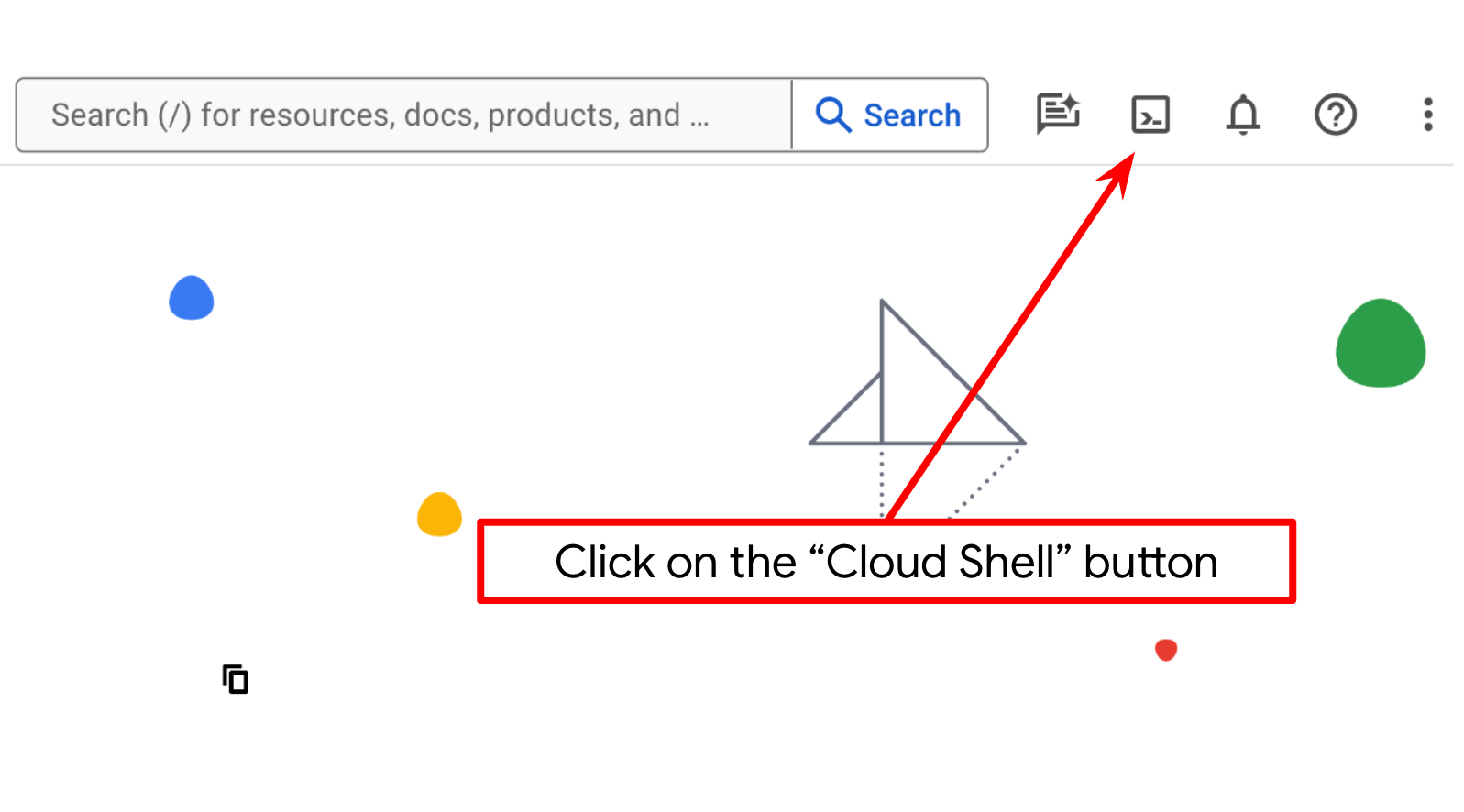
- 连接到 Cloud Shell 后,您可以使用以下命令检查自己是否已通过身份验证,以及项目是否已设置为您的项目 ID:
gcloud auth list
- 在 Cloud Shell 中运行以下命令,以确认 gcloud 命令了解您的项目。
gcloud config list project
- 如果项目未设置,请使用以下命令进行设置:
gcloud config set project <YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
或者,您也可以在控制台中看到 PROJECT_ID ID
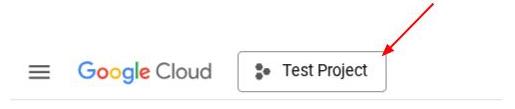
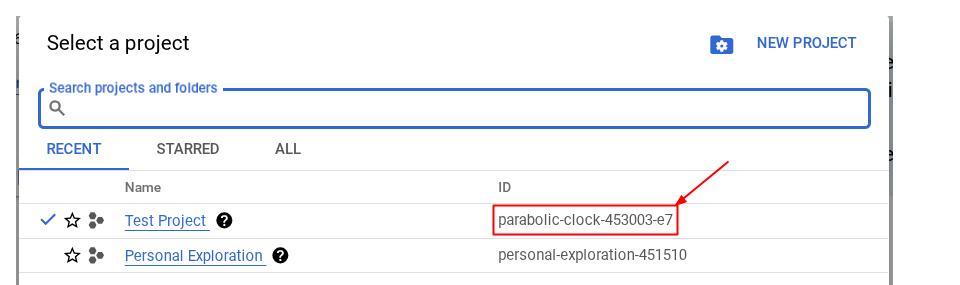
点击该项目,您将在右侧看到您的所有项目和项目 ID
- 通过以下命令启用必需的 API。这可能需要几分钟的时间,请耐心等待。
gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com \
run.googleapis.com \
cloudbuild.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
bigquery.googleapis.com
成功执行该命令后,您应该会看到类似于以下消息的消息:
Operation "operations/..." finished successfully.
除了使用 gcloud 命令,您还可以通过控制台搜索每个产品或使用此链接。
如果遗漏了任何 API,您始终可以在实施过程中启用它。
如需了解 gcloud 命令和用法,请参阅文档。
设置应用工作目录
- 点击“打开编辑器”按钮,系统会打开 Cloud Shell 编辑器,我们可以在这里编写代码
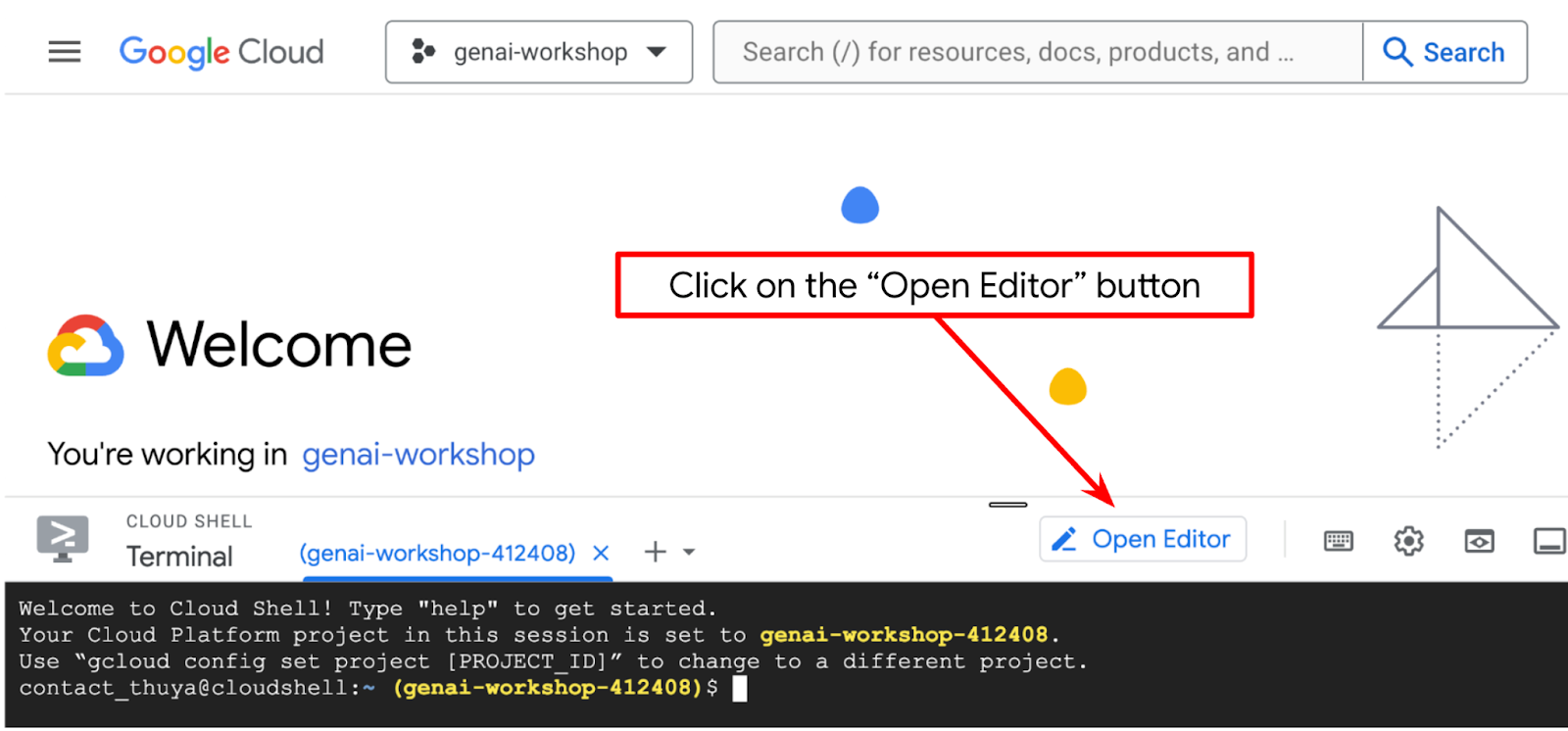
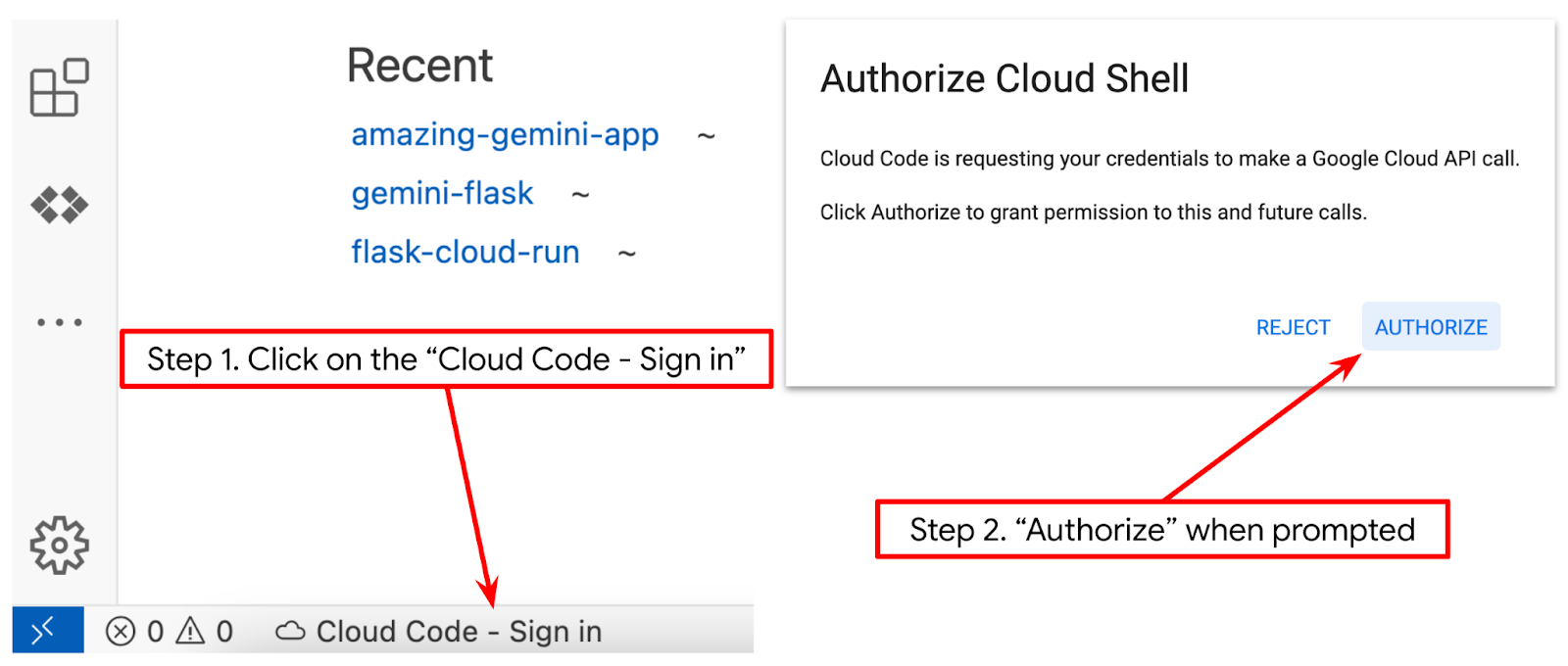
- 确保 Cloud Shell 编辑器的左下角(状态栏)已设置 Cloud Code 项目,如下图中突出显示的那样,并且已设置为已启用结算的有效 Google Cloud 项目。如果系统提示,请点击授权。初始化 Cloud Shell 编辑器后,Cloud Code - 登录按钮可能需要一段时间才会显示,请耐心等待。
接下来,我们将准备 Python 环境
环境设置
准备 Python 虚拟环境
下一步是准备开发环境。在此 Codelab 中,我们将使用 Python 3.12,并使用 Python virtualenv 来简化创建和管理 Python 版本和虚拟环境的需求
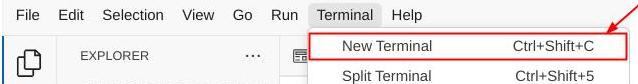
- 如果您尚未打开终端,请依次点击 Terminal -> New Terminal 将其打开,或者使用 Ctrl + Shift + C
- 运行以下命令,创建新文件夹并将位置更改为该文件夹
mkdir agent_diet_planner
cd agent_diet_planner
- 运行以下命令创建新的 virtualenv
python -m venv .env
- 使用以下命令激活 virtualenv
source .env/bin/activate
- 创建
requirements.txt。依次点击“文件”→“新建文本文件”,然后填充以下内容。然后将其保存为requirements.txt
streamlit==1.33.0
google-cloud-aiplatform
google-cloud-bigquery
pandas==2.2.2
db-dtypes==1.2.0
pyarrow==16.1.0
- 然后,运行以下命令,从 requirements.txt 安装所有依赖项
pip install -r requirements.txt
- 输入以下命令,检查是否已安装所有 Python 库依赖项
pip list
设置配置文件
现在,我们需要为此项目设置配置文件。配置文件用于存储变量和服务账号凭据。
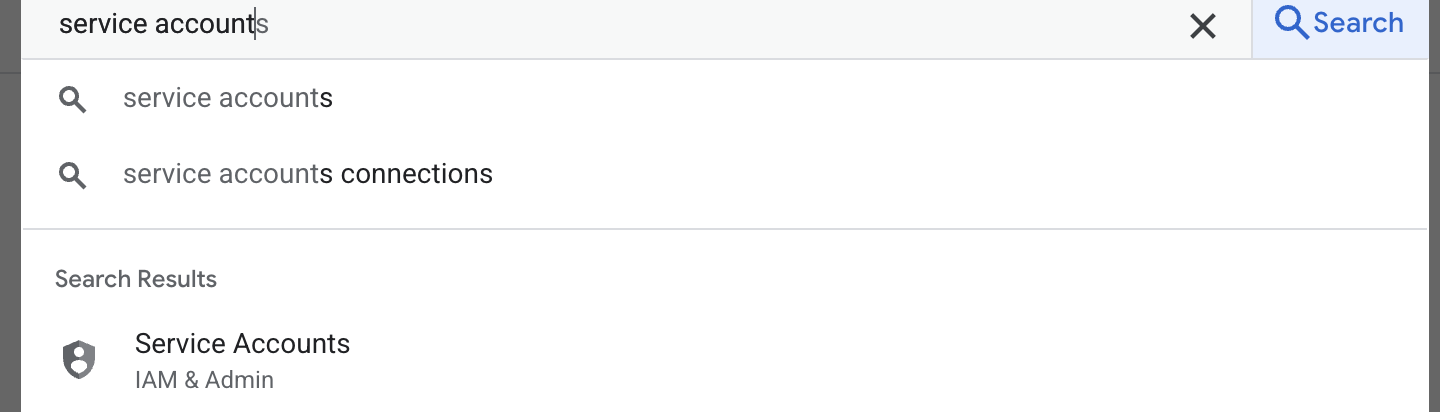
- 第一步是创建服务账号。在搜索框中输入“服务账号”,然后点击“服务账号”。
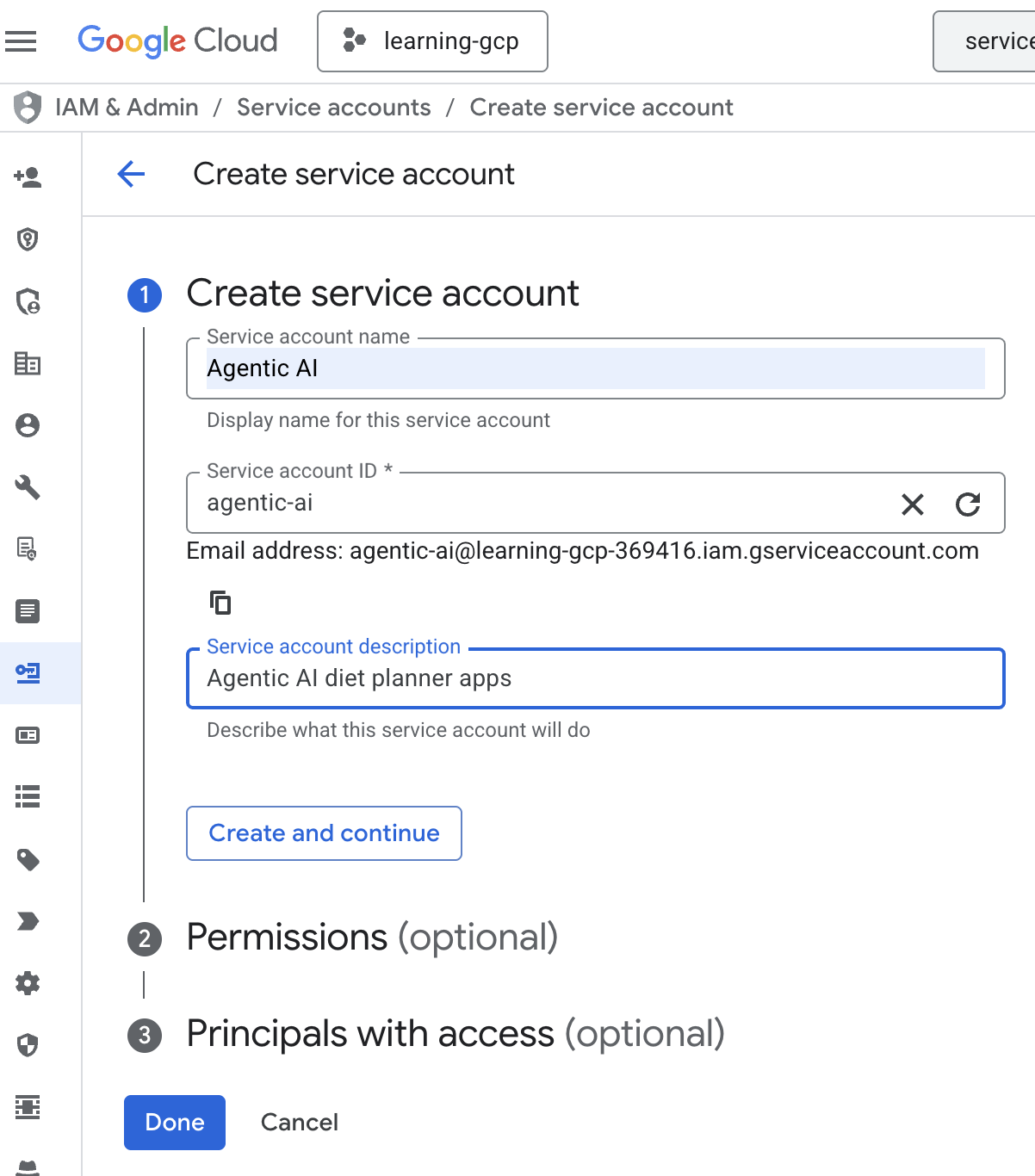
- 点击“+ 创建服务账号”。输入服务账号名称,然后点击“创建并继续”。
- 在“权限”中,选择“Service Account User”角色。依次点击“+ 添加其他角色”和 IAM 角色:“BigQuery Admin”“Cloud Run Admin”“Cloud Run Invoker”“Vertex AI Service Agent”和“Vertex AI User”,然后点击“完成”图标
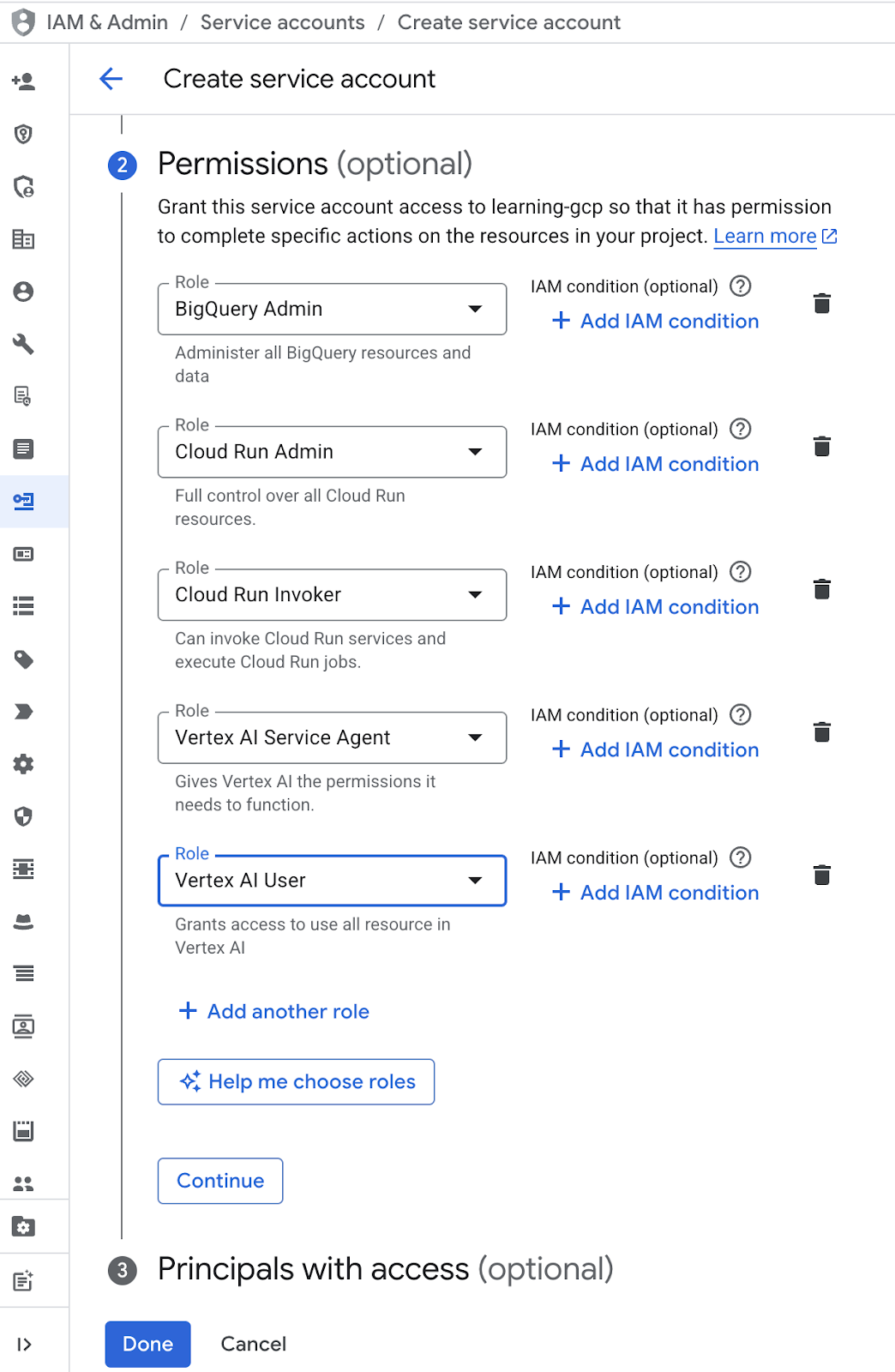
- 依次点击“服务账号电子邮件地址”“Tab”键、“添加密钥”→“创建新密钥”。
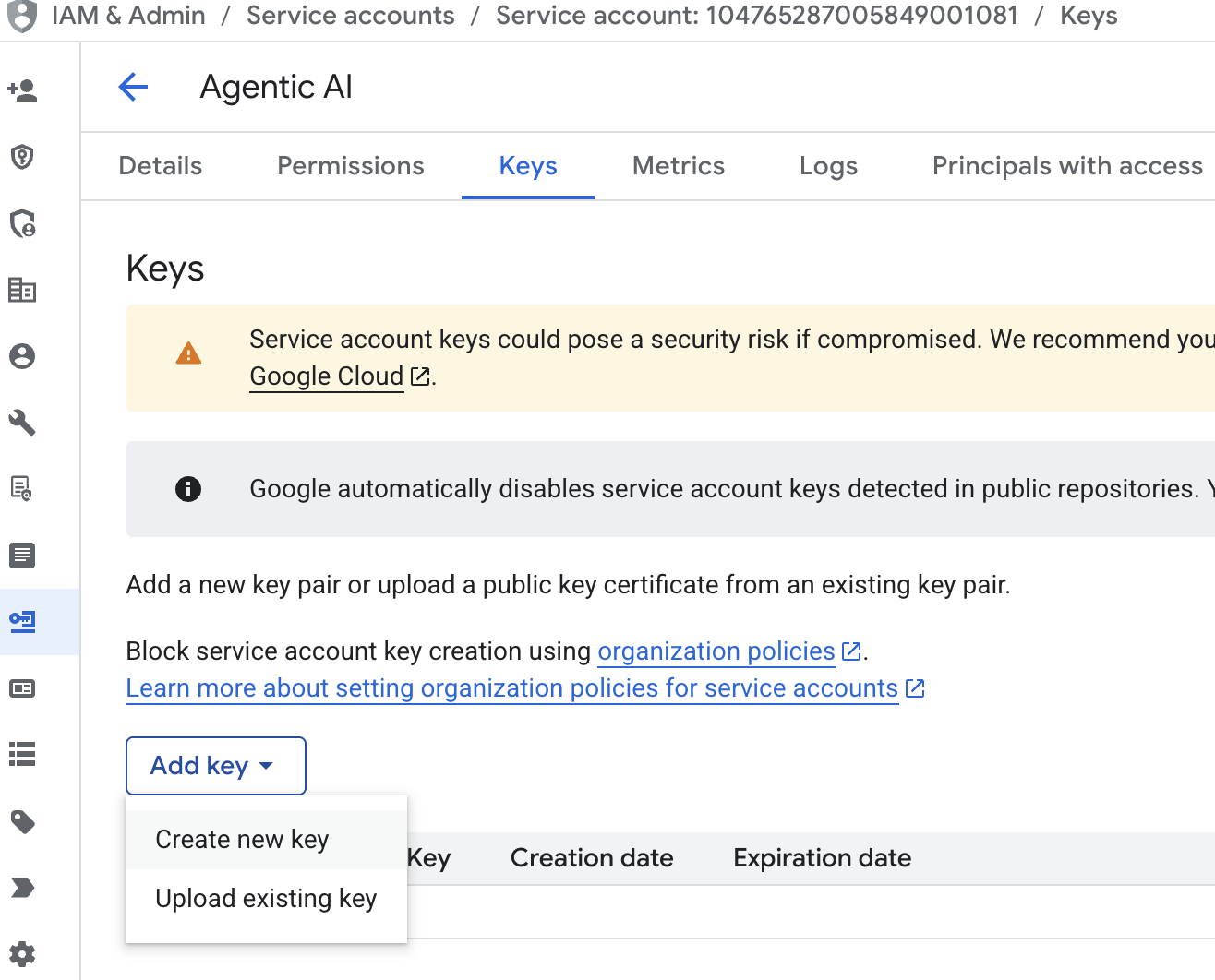
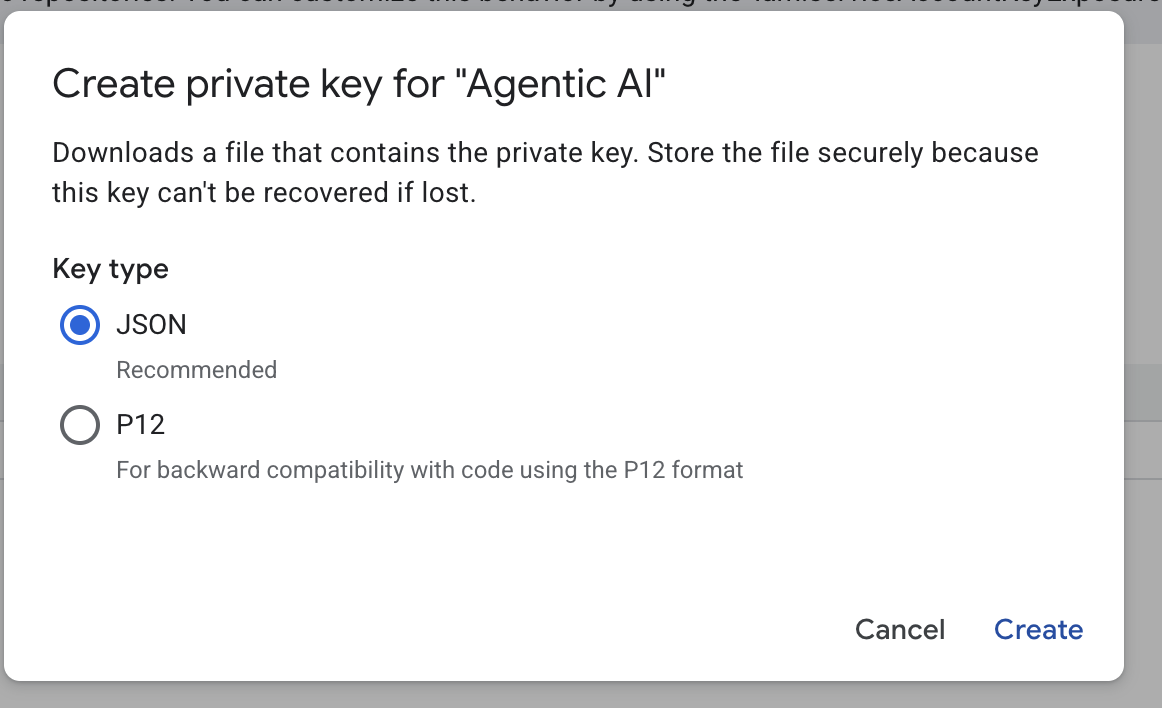
- 选择 json,然后点击“创建”。将此服务账号文件保存到本地,以供在下一步中使用
- 创建一个名为 .streamlit 的文件夹,其中包含以下配置。右键点击鼠标,点击“新建文件夹”,然后输入文件夹名称
.streamlit - 在文件夹
.streamlit中点击右键,然后点击“新建文件”,并填写以下值。然后将其保存为secrets.toml
# secrets.toml (for Streamlit sharing)
# Store in .streamlit/secrets.toml
[gcp]
project_id = "your_gcp_project"
location = "us-central1"
[gcp_service_account]
type = "service_account"
project_id = "your-project-id"
private_key_id = "your-private-key-id"
private_key = '''-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY_HERE
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----'''
client_email = "your-sa@project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
client_id = "your-client-id"
auth_uri = "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth"
token_uri = "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token"
auth_provider_x509_cert_url = "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs"
client_x509_cert_url = "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/your-sa%40project-id.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
- 根据您在上一步中创建的服务账号,更新
project_id、private_key_id、private_key、client_email、client_id , and auth_provider_x509_cert_url的值
准备 BigQuery 数据集
下一步是创建 BigQuery 数据集,以便将生成结果保存到 BigQuery。
- 在搜索框中输入“BigQuery”,然后点击“BigQuery”。
- 点击
 ,然后点击“创建数据集”
,然后点击“创建数据集” - 输入数据集 ID
diet_planner_data,然后点击“创建数据集”图标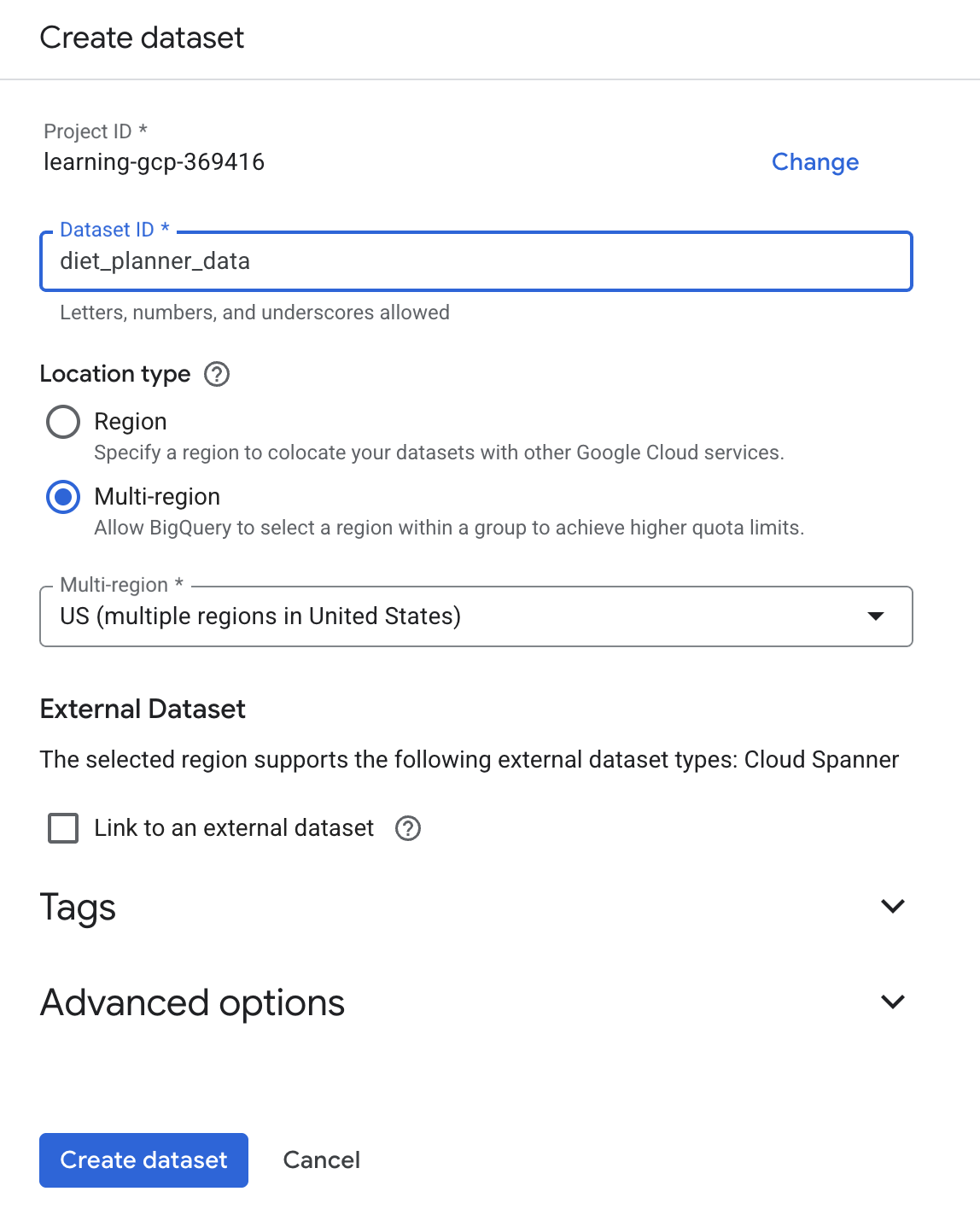
4. 构建 Agent 饮食规划应用
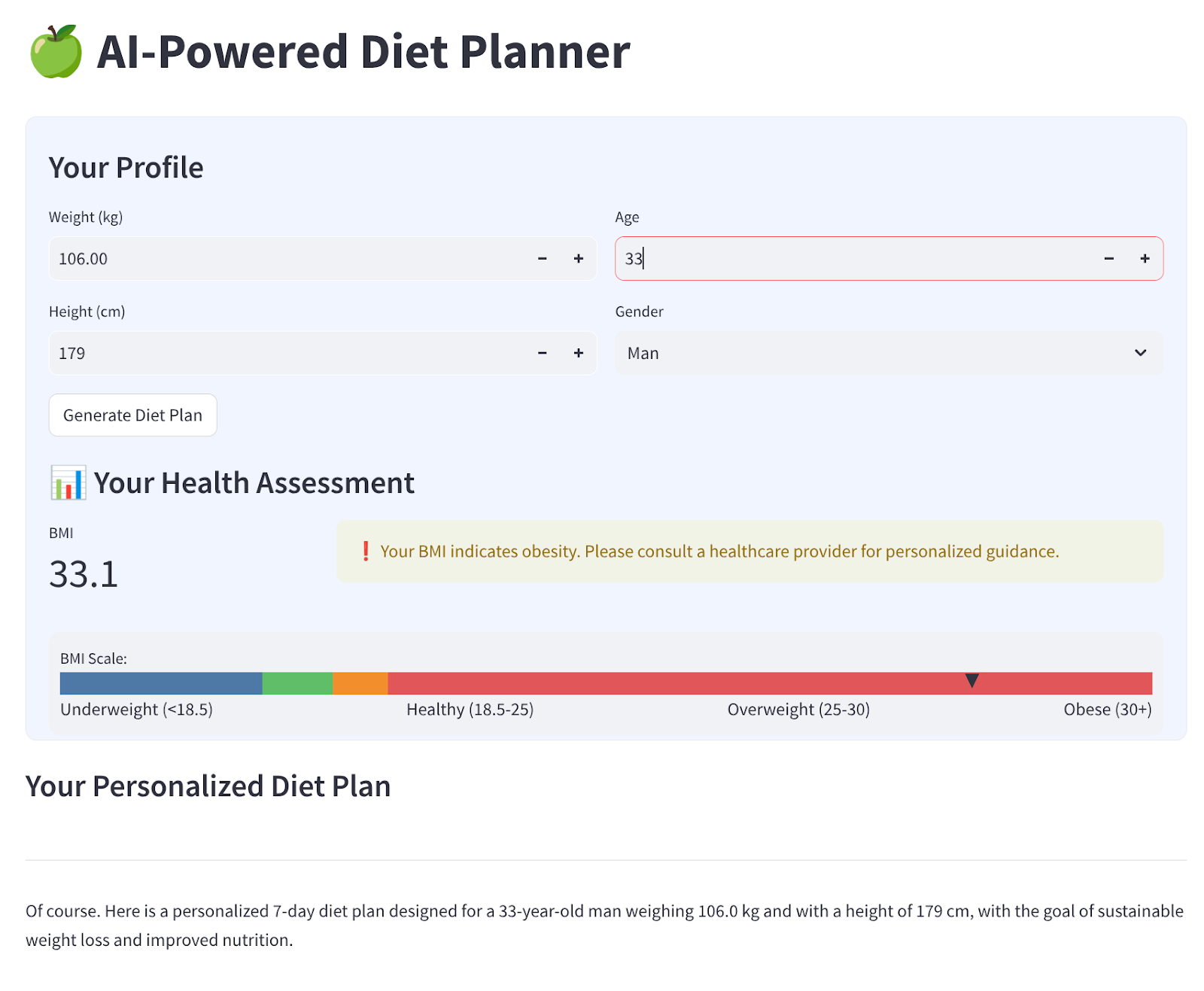
我们将构建一个包含 4 个输入的简单网页界面,如下所示
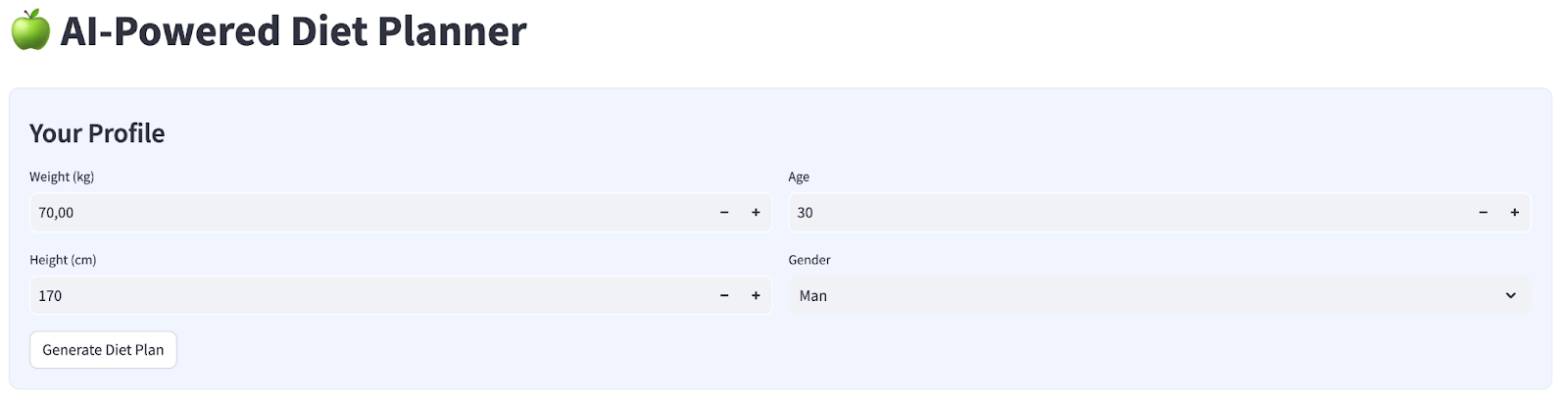
根据您的个人资料更改体重、身高、年龄和性别,然后点击“生成”。它将调用 Vertex AI 库中的 LLM 模型 Gemini Pro 2.5,并将生成的结果存储到 BigQuery 中。
为了避免代码过长,系统会将其分成 6 个部分。
创建函数来计算 BMI 状态
- 右键点击
agent_diet_planner文件夹 → 新建文件 .. → 输入文件名bmi_calc.py,然后按 Enter 键 - 使用以下代码填充代码
# Add this function to calculate BMI and health status
def calculate_bmi_status(weight, height):
"""
Calculate BMI and return status message
"""
height_m = height / 100 # Convert cm to meters
bmi = weight / (height_m ** 2)
if bmi < 18.5:
status = "underweight"
message = "⚠️ Your BMI suggests you're underweight. Consider increasing calorie intake with nutrient-dense foods."
elif 18.5 <= bmi < 25:
status = "normal"
message = "✅ Your BMI is in the healthy range. Let's maintain this balance!"
elif 25 <= bmi < 30:
status = "overweight"
message = "⚠️ Your BMI suggests you're overweight. Focus on gradual weight loss through balanced nutrition."
else:
status = "obese"
message = "❗ Your BMI indicates obesity. Please consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance."
return {
"value": round(bmi, 1),
"status": status,
"message": message
}
创建代理饮食规划器主应用
- 右键点击
agent_diet_planner文件夹 → 新建文件 .. → 输入文件名app.py,然后按 Enter 键。 - 使用以下代码填充代码
import os
from google.oauth2 import service_account
import streamlit as st
from google.cloud import bigquery
from vertexai.preview.generative_models import GenerativeModel
import vertexai
import datetime
import time
import pandas as pd
from bmi_calc import calculate_bmi_status
# Get configuration from environment
PROJECT_ID = os.environ.get("GCP_PROJECT_ID", "your_gcp_project_id")
LOCATION = os.environ.get("GCP_LOCATION", "us-central1")
#CONSTANTS Dataset and table in BigQuery
DATASET = "diet_planner_data"
TABLE = "user_plans"
# Initialize Vertex AI
vertexai.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=LOCATION)
# Initialize BigQuery client
try:
# For Cloud Run, use default credentials
bq_client = bigquery.Client()
except:
# For local development, use service account from secrets
if "gcp_service_account" in st.secrets:
service_account_info = dict(st.secrets["gcp_service_account"])
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_info(service_account_info)
bq_client = bigquery.Client(credentials=credentials, project=PROJECT_ID)
else:
st.error("BigQuery client initialization failed")
st.stop()
将值 your_gcp_project_id 替换为您的项目 ID。
创建代理饮食规划器主应用 - setup_bq_tables
在本部分中,我们将创建一个名为 setup_bq_table 的函数,该函数具有 1 个输入形参 bq_client。此函数将在 BigQuery 表中定义架构,并在表不存在时创建表。
在 app.py 中,使用以下代码填充代码
# Create BigQuery table if not exists
def setup_bq_table(bq_client):
dataset_id = f"{st.secrets['gcp']['project_id']}.{DATASET}"
table_id = f"{dataset_id}.{TABLE}"
schema = [
bigquery.SchemaField("user_id", "STRING", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("timestamp", "TIMESTAMP", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("weight", "FLOAT", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("height", "INTEGER", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("age", "INTEGER", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("gender", "STRING", mode="REQUIRED"),
bigquery.SchemaField("diet_plan", "STRING", mode="REQUIRED")
]
try:
bq_client.get_table(table_id)
except:
table = bigquery.Table(table_id, schema=schema)
bq_client.create_table(table)
st.toast("BigQuery table created successfully")
创建代理饮食规划器主应用 - generate_diet_plan
在本部分中,我们将创建一个名为 generate_diet_plan 且带有 1 个输入参数的函数。此函数将使用定义的提示调用 LLM 模型 Gemini Pro 2.5 并生成结果。
在 app.py 中,使用以下代码填充代码
# Generate diet plan using Gemini Pro
def generate_diet_plan(params):
try:
model = GenerativeModel("gemini-2.5-pro")
prompt = f"""
Create a personalized 7-day diet plan for:
- {params['gender']}, {params['age']} years old
- Weight: {params['weight']} kg
- Height: {params['height']} cm
Include:
1. Daily calorie target
2. Macronutrient breakdown (carbs, protein, fat)
3. Meal timing and frequency
4. Food recommendations
5. Hydration guidance
Make the plan:
- Nutritionally balanced
- Practical for daily use
- Culturally adaptable
- With portion size guidance
"""
response = model.generate_content(prompt)
return response.text
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"AI generation error: {str(e)}")
return None
创建代理饮食规划器主应用 - save_to_bq
在此部分中,我们将创建一个名为 save_to_bq 的函数,该函数具有 3 个输入参数:bq_client、user_id 和 plan。此函数会将生成的结果保存到 BigQuery 表中
在 app.py 中,使用以下代码填充代码
# Save user data to BigQuery
def save_to_bq(bq_client, user_id, plan):
try:
dataset_id = f"{st.secrets['gcp']['project_id']}.{DATASET}"
table_id = f"{dataset_id}.{TABLE}"
row = {
"user_id": user_id,
"timestamp": datetime.datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
"weight": st.session_state.user_data["weight"],
"height": st.session_state.user_data["height"],
"age": st.session_state.user_data["age"],
"gender": st.session_state.user_data["gender"],
"diet_plan": plan
}
errors = bq_client.insert_rows_json(table_id, [row])
if errors:
st.error(f"BigQuery error: {errors}")
else:
return True
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"Data saving error: {str(e)}")
return False
创建代理饮食规划器主应用 - main
在本部分中,我们将创建一个名为 main 且不带输入参数的函数。此函数主要用于处理 Streamlit 界面脚本、显示生成的结果、显示来自 BigQuery 表的历史生成结果,以及将数据下载到 Markdown 文件。
在 app.py 中,使用以下代码填充代码
# Streamlit UI
def main():
st.set_page_config(page_title="AI Diet Planner", page_icon="🍏", layout="wide")
# Initialize session state
if "user_data" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.user_data = None
if "diet_plan" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.diet_plan = None
# Initialize clients
#bq_client = init_clients()
setup_bq_table(bq_client)
st.title("🍏 AI-Powered Diet Planner")
st.markdown("""
<style>
.stProgress > div > div > div > div {
background-color: #4CAF50;
}
[data-testid="stForm"] {
background: #f0f5ff;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
border: 1px solid #e6e9ef;
}
</style>
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
# User input form
with st.form("user_profile", clear_on_submit=False):
st.subheader("Your Profile")
col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
with col1:
weight = st.number_input("Weight (kg)", min_value=30.0, max_value=200.0, value=70.0)
height = st.number_input("Height (cm)", min_value=100, max_value=250, value=170)
with col2:
age = st.number_input("Age", min_value=18, max_value=100, value=30)
gender = st.selectbox("Gender", ["Man", "Woman"])
submitted = st.form_submit_button("Generate Diet Plan")
if submitted:
user_data = {
"weight": weight,
"height": height,
"age": age,
"gender": gender
}
st.session_state.user_data = user_data
# Calculate BMI
bmi_result = calculate_bmi_status(weight, height)
# Display BMI results in a visually distinct box
with st.container():
st.subheader("📊 Your Health Assessment")
col1, col2 = st.columns([1, 3])
with col1:
st.metric("BMI", bmi_result["value"])
with col2:
if bmi_result["status"] != "normal":
st.warning(bmi_result["message"])
else:
st.success(bmi_result["message"])
# Add BMI scale visualization
st.markdown(f"""
<div style="background:#f0f2f6;padding:10px;border-radius:10px;margin-top:10px">
<small>BMI Scale:</small><br>
<div style="display:flex;height:20px;background:linear-gradient(90deg,
#4e79a7 0%,
#4e79a7 18.5%,
#60bd68 18.5%,
#60bd68 25%,
#f28e2b 25%,
#f28e2b 30%,
#e15759 30%,
#e15759 100%);position:relative">
<div style="position:absolute;left:{min(100, max(0, (bmi_result["value"]/40)*100))}%;top:-5px">
▼
</div>
</div>
<div style="display:flex;justify-content:space-between">
<span>Underweight (<18.5)</span>
<span>Healthy (18.5-25)</span>
<span>Overweight (25-30)</span>
<span>Obese (30+)</span>
</div>
</div>
""", unsafe_allow_html=True)
# Store BMI in session state
st.session_state.bmi = bmi_result
# Plan generation and display
if submitted and st.session_state.user_data:
with st.spinner("🧠 Generating your personalized diet plan using Gemini AI..."):
#diet_plan = generate_diet_plan(st.session_state.user_data)
diet_plan = generate_diet_plan({**st.session_state.user_data,"bmi": bmi_result["value"],
"bmi_status": bmi_result["status"]
})
if diet_plan:
st.session_state.diet_plan = diet_plan
# Generate unique user ID
user_id = f"user_{int(time.time())}"
# Save to BigQuery
if save_to_bq(bq_client, user_id, diet_plan):
st.toast("✅ Plan saved to database!")
# Display generated plan
if st.session_state.diet_plan:
st.subheader("Your Personalized Diet Plan")
st.markdown("---")
st.markdown(st.session_state.diet_plan)
# Download button
st.download_button(
label="Download Plan",
data=st.session_state.diet_plan,
file_name="my_diet_plan.md",
mime="text/markdown"
)
# Show history
st.subheader("Your Plan History")
try:
query = f"""
SELECT timestamp, weight, height, age, gender
FROM `{st.secrets['gcp']['project_id']}.{DATASET}.{TABLE}`
WHERE user_id LIKE 'user_%'
ORDER BY timestamp DESC
LIMIT 5
"""
history = bq_client.query(query).to_dataframe()
if not history.empty:
history["timestamp"] = pd.to_datetime(history["timestamp"])
st.dataframe(history.style.format({
"weight": "{:.1f} kg",
"height": "{:.0f} cm"
}))
else:
st.info("No previous plans found")
except Exception as e:
st.error(f"History load error: {str(e)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
将代码保存为 app.py。
5. 使用 Cloud Build 将应用部署到 Cloud Run
当然,我们希望向其他人展示这款出色的应用。为此,我们可以将此应用打包并将其部署到 Cloud Run,使其成为可供他人访问的公共服务。为此,我们来回顾一下架构

首先,我们需要 Dockerfile,点击文件->新建文本文档,然后复制粘贴以下代码并将其另存为 Dockerfile
# Use official Python image
FROM python:3.12-slim
# Set environment variables
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE 1
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1
ENV PORT 8080
# Install system dependencies
RUN apt-get update && \
apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends \
build-essential \
libpq-dev \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Copy requirements
COPY requirements.txt .
# Install Python dependencies
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# Copy application files
COPY . .
# Expose port
EXPOSE $PORT
# Run the application
CMD ["streamlit", "run", "app.py", "--server.port", "8080", "--server.address", "0.0.0.0"]
接下来,我们将创建 cloudbuild.yaml,以构建应用并将其转换为 Docker 映像,然后将其推送到 Artifact Registry 并部署到 Cloud Run。
点击文件->新建文本文件,然后复制并粘贴以下代码,并将其另存为 cloudbuild.yaml
steps:
# Build Docker image
- name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker'
args: ['build', '-t', 'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/diet-planner:$BUILD_ID', '--no-cache',
'--progress=plain',
'.']
id: 'Build'
timeout: 1200s
waitFor: ['-']
dir: '.'
# Push to Container Registry
- name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker'
args: ['push', 'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/diet-planner:$BUILD_ID']
id: 'Push'
waitFor: ['Build']
# Deploy to Cloud Run
- name: 'gcr.io/google.com/cloudsdktool/cloud-sdk'
entrypoint: gcloud
args:
- 'run'
- 'deploy'
- 'diet-planner-service'
- '--image=gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/diet-planner:$BUILD_ID'
- '--port=8080'
- '--region=us-central1'
- '--platform=managed'
- '--allow-unauthenticated'
- '--set-env-vars=GCP_PROJECT_ID=$PROJECT_ID,GCP_LOCATION=us-central1'
- '--cpu=1'
- '--memory=1Gi'
- '--timeout=300'
waitFor: ['Push']
options:
logging: CLOUD_LOGGING_ONLY
machineType: 'E2_HIGHCPU_8'
diskSizeGb: 100
images:
- 'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/diet-planner:$BUILD_ID'
至此,我们已拥有构建应用以生成 Docker 映像、推送到 Artifact Registry 并部署到 Cloud Run 所需的所有文件,接下来我们来部署它。前往 Cloud Shell 终端,确保当前项目已配置为您的有效项目。如果不是,您可以使用 gcloud configure 命令设置项目 ID:
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]
然后,运行以下命令来构建应用,使其成为 Docker 映像,并将其推送到 Artifact Registry 并部署到 Cloud Run
gcloud builds submit --config cloudbuild.yaml
它将根据我们之前提供的 Dockerfile 构建 Docker 容器,并将其推送到 Artifact Registry。之后,我们将构建的映像部署到 Cloud Run。整个流程在 cloudbuild.yaml 步骤中定义。
请注意,我们在此处允许未经身份验证的访问,因为这是一个演示应用。建议为企业应用和生产应用使用适当的身份验证。
部署完成后,我们可以在 Cloud Run 页面中查看部署情况。在顶部 Cloud 控制台搜索栏中搜索 Cloud Run,然后点击 Cloud Run 产品
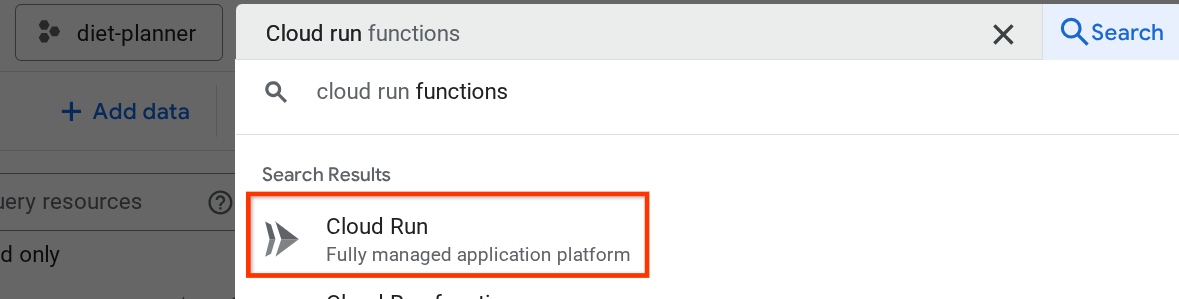
之后,您可以检查 Cloud Run 服务页面中列出的已部署服务,点击该服务以获取服务网址
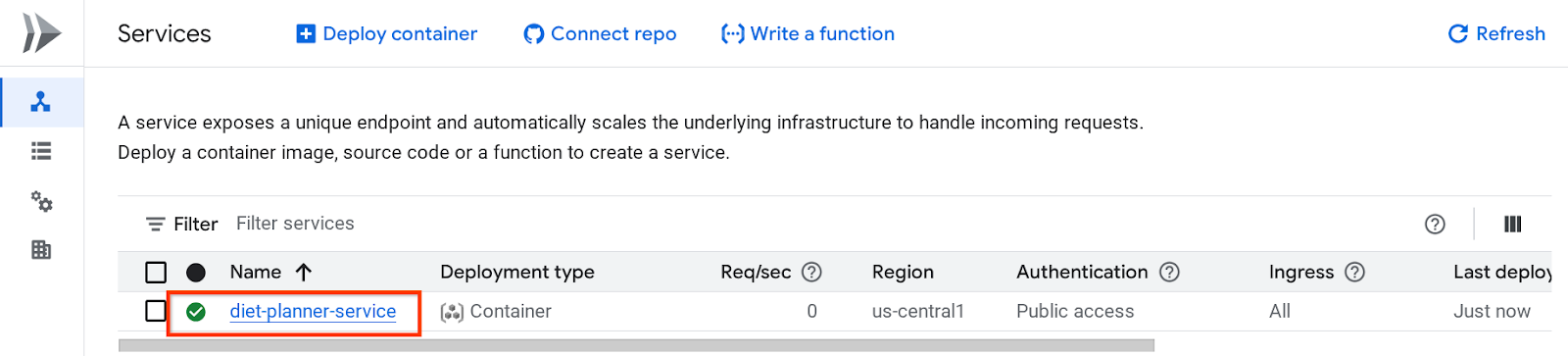
服务网址将显示在顶部栏中
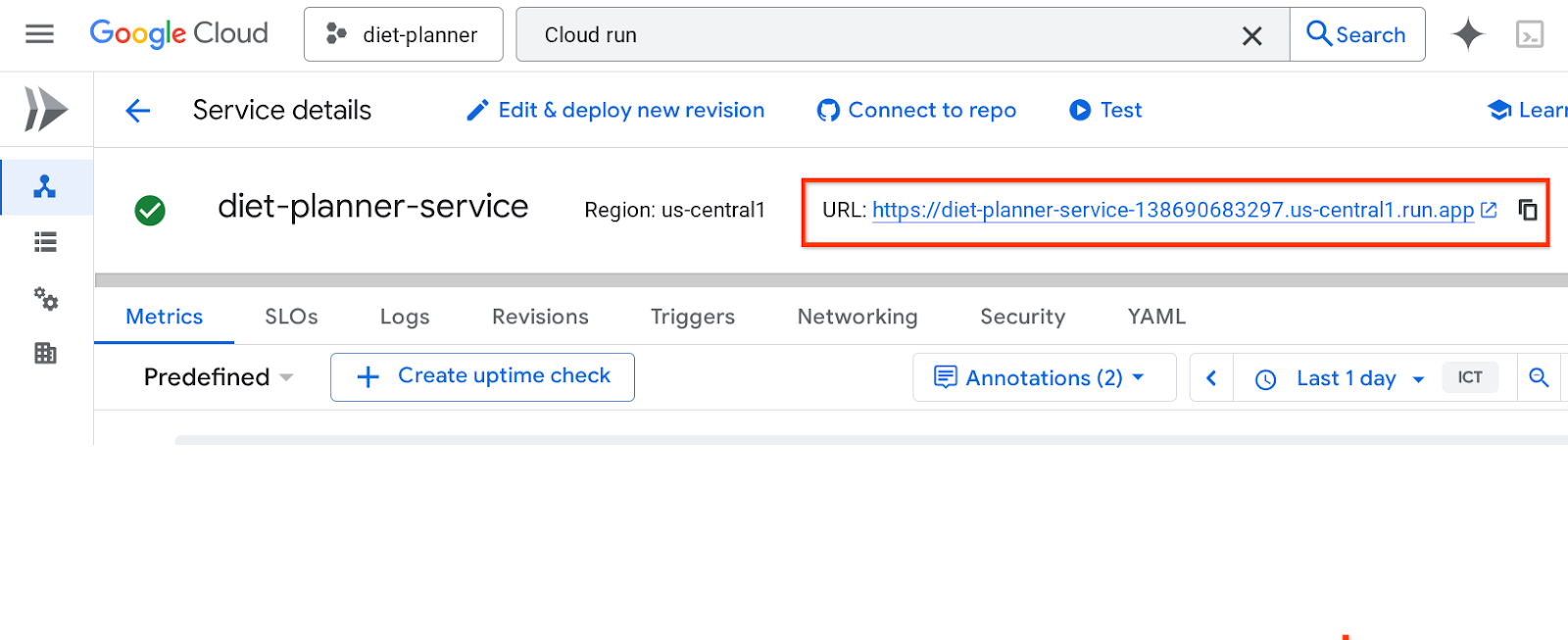 接下来,您可以在无痕式窗口或移动设备上使用该应用。该功能应该已经上线。
接下来,您可以在无痕式窗口或移动设备上使用该应用。该功能应该已经上线。
6. 清理
为避免系统因本 Codelab 中使用的资源向您的 Google Cloud 账号收取费用,请按照以下步骤操作:
