1. Introduzione
Questo codelab fornisce una guida per il deployment di AlloyDB con operatori AI e il loro utilizzo per attività come la ricerca semantica, i join e il ranking dei risultati.
Prerequisiti
- Una conoscenza di base di Google Cloud e della console
- Competenze di base nell'interfaccia a riga di comando e in Cloud Shell
Cosa imparerai a fare
- Come eseguire il deployment del cluster e dell'istanza principale di AlloyDB
- Come attivare gli operatori AI di AlloyDB
- Come utilizzare diversi operatori AI di AlloyDB
- Come utilizzare il ranking negli operatori AI di AlloyDB per migliorare l'output dei risultati
Che cosa ti serve
- Un account Google Cloud e un progetto Google Cloud
- Un browser web come Chrome che supporta la console Google Cloud e Cloud Shell
2. Configurazione e requisiti
Configurazione del progetto
- Accedi alla console Google Cloud. Se non hai ancora un account Gmail o Google Workspace, devi crearne uno.
Utilizza un account personale anziché un account di lavoro o della scuola.
- Crea un nuovo progetto o riutilizzane uno esistente. Per creare un nuovo progetto nella console Google Cloud, fai clic sul pulsante Seleziona un progetto nell'intestazione per aprire una finestra popup.

Nella finestra Seleziona un progetto, premi il pulsante Nuovo progetto per aprire una finestra di dialogo per il nuovo progetto.
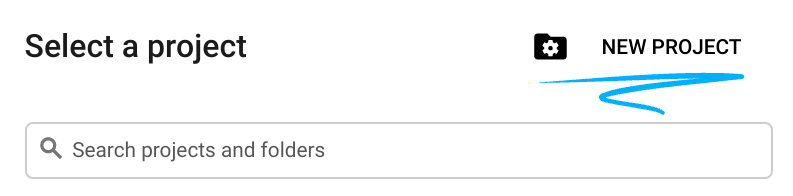
Nella finestra di dialogo, inserisci il nome del progetto che preferisci e scegli la posizione.
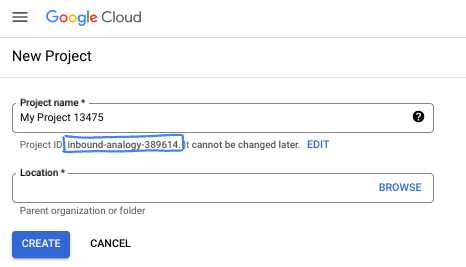
- Il nome del progetto è il nome visualizzato per i partecipanti a questo progetto. Il nome del progetto non viene utilizzato dalle API Google e può essere modificato in qualsiasi momento.
- L'ID progetto è univoco in tutti i progetti Google Cloud ed è immutabile (non può essere modificato dopo l'impostazione). La console Google Cloud genera automaticamente un ID univoco, ma puoi personalizzarlo. Se non ti piace l'ID generato, puoi generarne un altro casuale o fornire il tuo per verificarne la disponibilità. Nella maggior parte dei codelab, devi fare riferimento all'ID progetto, in genere identificato con il segnaposto PROJECT_ID.
- Per tua informazione, esiste un terzo valore, un numero di progetto, utilizzato da alcune API. Scopri di più su tutti e tre questi valori nella documentazione.
Abilita fatturazione
Per attivare la fatturazione, hai due opzioni. Puoi utilizzare il tuo account di fatturazione personale o riscattare i crediti seguendo questi passaggi.
Riscatta 5 $di crediti Google Cloud (facoltativo)
Per partecipare a questo workshop, devi disporre di un account di fatturazione con del credito. Se prevedi di utilizzare la tua fatturazione, puoi saltare questo passaggio.
- Fai clic su questo link e accedi con un Account Google personale.
- Visualizzerai un riquadro simile al seguente:

- Fai clic sul pulsante CLICCA QUI PER ACCEDERE AI TUOI CREDITI. Verrà visualizzata una pagina per configurare il tuo profilo di fatturazione. Se viene visualizzata una schermata di registrazione alla prova senza costi, fai clic su Annulla e continua a collegare la fatturazione.
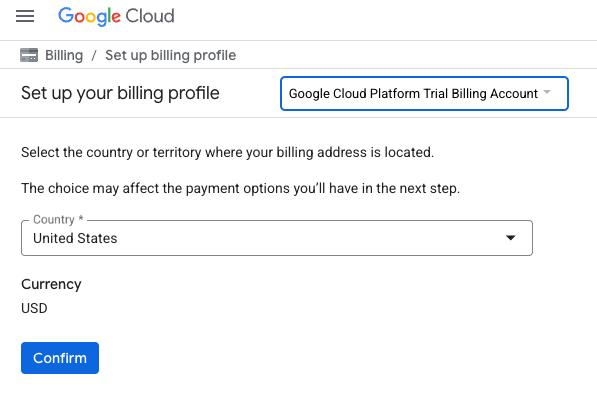
- Fai clic su Conferma. Ora sei connesso a un account di fatturazione di prova di Google Cloud.
Configurare un account di fatturazione personale
Se hai configurato la fatturazione utilizzando i crediti Google Cloud, puoi saltare questo passaggio.
Per configurare un account di fatturazione personale, vai qui per abilitare la fatturazione nella console Cloud.
Alcune note:
- Il completamento di questo lab dovrebbe costare meno di 3 $in risorse cloud.
- Per evitare ulteriori addebiti, puoi seguire i passaggi alla fine di questo lab per eliminare le risorse.
- I nuovi utenti hanno diritto alla prova senza costi di 300$.
Avvia Cloud Shell
Sebbene Google Cloud possa essere gestito da remoto dal tuo laptop, in questo codelab utilizzerai Google Cloud Shell, un ambiente a riga di comando in esecuzione nel cloud.
Nella console Google Cloud, fai clic sull'icona di Cloud Shell nella barra degli strumenti in alto a destra:
In alternativa, puoi premere G e poi S. Questa sequenza attiverà Cloud Shell se ti trovi nella console Google Cloud o utilizza questo link.
Bastano pochi istanti per eseguire il provisioning e connettersi all'ambiente. Al termine, dovresti vedere un risultato simile a questo:
Questa macchina virtuale è caricata con tutti gli strumenti per sviluppatori di cui avrai bisogno. Offre una home directory permanente da 5 GB e viene eseguita su Google Cloud, migliorando notevolmente le prestazioni e l'autenticazione della rete. Tutto il lavoro in questo codelab può essere svolto all'interno di un browser. Non devi installare nulla.
3. Prima di iniziare
Abilita l'API
Per utilizzare AlloyDB, Compute Engine, Servizi di rete e Vertex AI, devi abilitare le rispettive API nel tuo progetto Google Cloud.
All'interno del terminale Cloud Shell, assicurati che l'ID progetto sia configurato:
gcloud config set project [YOUR-PROJECT-ID]
Imposta la variabile di ambiente PROJECT_ID:
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
Attiva tutti i servizi necessari:
gcloud services enable alloydb.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
discoveryengine.googleapis.com
Output previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud config set project test-project-001-402417
Updated property [core/project].
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
Your active configuration is: [cloudshell-14650]
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud services enable alloydb.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com \
servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
discoveryengine.googleapis.com
Operation "operations/acat.p2-4470404856-1f44ebd8-894e-4356-bea7-b84165a57442" finished successfully.
Introduzione alle API
- L'API AlloyDB (
alloydb.googleapis.com) consente di creare, gestire e scalare i cluster AlloyDB per PostgreSQL. Fornisce un servizio di database completamente gestito e compatibile con PostgreSQL progettato per carichi di lavoro transazionali e analitici aziendali impegnativi. - L'API Compute Engine (
compute.googleapis.com) consente di creare e gestire macchine virtuali (VM), dischi permanenti e impostazioni di rete. Fornisce le basi di Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) necessarie per eseguire i carichi di lavoro e ospitare l'infrastruttura sottostante per molti servizi gestiti. - L'API Cloud Resource Manager (
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com) ti consente di gestire in modo programmatico i metadati e la configurazione del tuo progetto Google Cloud. Consente di organizzare le risorse, gestire i criteri IAM (Identity and Access Management) e convalidare le autorizzazioni nella gerarchia dei progetti. - L'API Service Networking (
servicenetworking.googleapis.com) ti consente di automatizzare la configurazione della connettività privata tra la tua rete Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) e i servizi gestiti di Google. È necessario in particolare per stabilire l'accesso IP privato per servizi come AlloyDB, in modo che possano comunicare in modo sicuro con le altre risorse. - L'API Vertex AI (
aiplatform.googleapis.com) consente alle tue applicazioni di creare, eseguire il deployment e scalare modelli di machine learning. Fornisce l'interfaccia unificata per tutti i servizi di AI di Google Cloud, incluso l'accesso ai modelli di AI generativa (come Gemini) e l'addestramento di modelli personalizzati.
4. Esegui il deployment di AlloyDB
Crea il cluster AlloyDB e l'istanza principale. Puoi eseguirne il deployment utilizzando uno script preparato che eseguirà il deployment di tutte le risorse necessarie oppure puoi farlo passo dopo passo in autonomia.
Eseguire il deployment di AlloyDB utilizzando lo script automatico
Questo approccio utilizza uno script automatizzato per eseguire il deployment del cluster AlloyDB e fornisce le informazioni necessarie per iniziare a lavorare con le risorse di cui è stato eseguito il deployment.
In Cloud Shell, termina il comando di esecuzione per clonare lo script di deployment.
REPO_NAME="codelabs"
REPO_URL="https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/$REPO_NAME"
SOURCE_DIR="alloydb-ai-operators"
git clone --no-checkout --filter=blob:none --depth=1 $REPO_URL
cd $REPO_NAME
git sparse-checkout set $SOURCE_DIR
git checkout
cd $SOURCE_DIR
Esegui lo script di deployment.
./deploy_alloydb.sh
L'esecuzione dello script richiede un po' di tempo, in genere circa 5-7 minuti. Dovrebbe quindi fornire informazioni sul cluster AlloyDB di cui è stato eseguito il deployment. Tieni presente che la password sarà diversa. Registrala da qualche parte per un uso futuro.
... <redacted> ... Creating primary instance: alloydb-aip-01-pr (8 vCPUs for TRIAL cluster) Operation ID: operation-1765988049916-646282264938a-bddce198-9f248715 Creating instance...done. ---------------------------------------- Deployment Process Completed Cluster: alloydb-aip-01 (TRIAL) Instance: alloydb-aip-01-pr Region: us-central1 Initial Password: JBBoDTgixzYwYpkF (if new cluster) ----------------------------------------
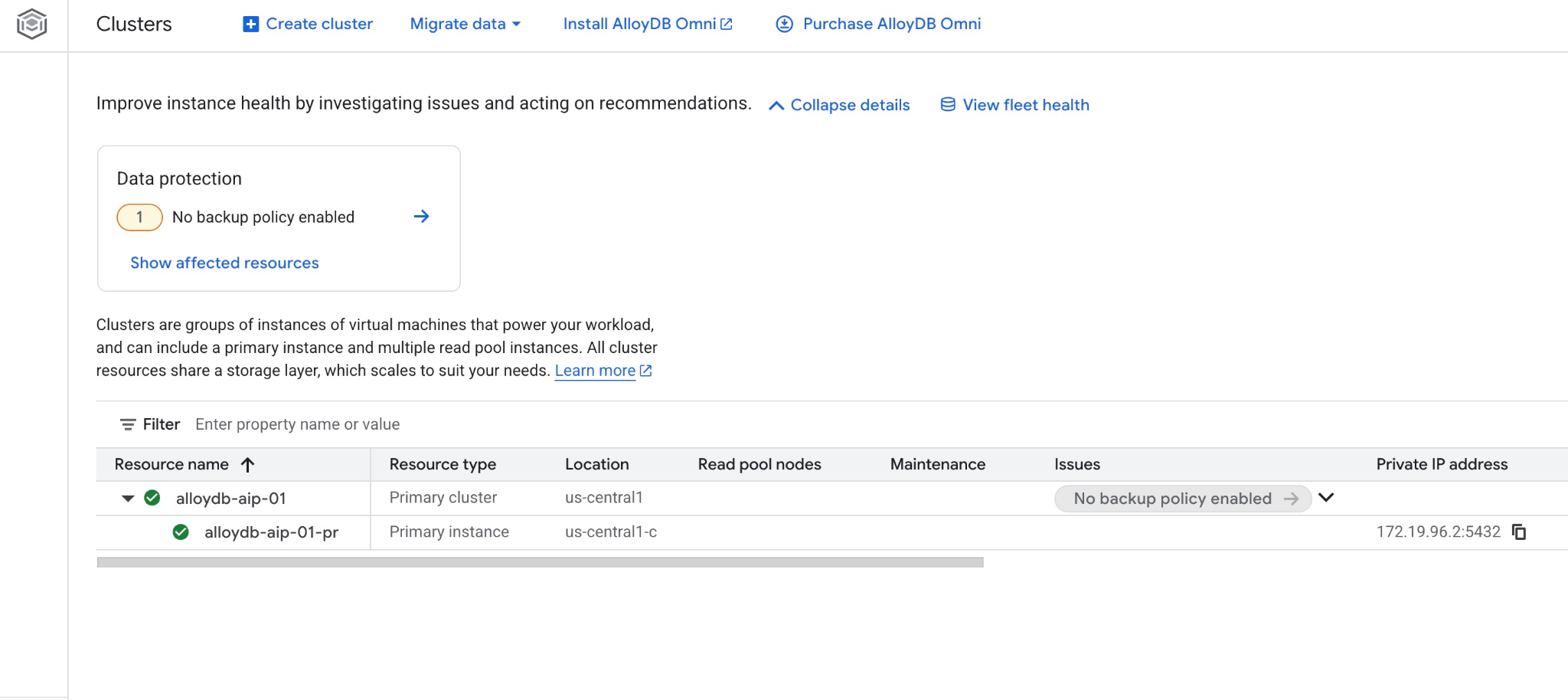
Puoi visualizzarlo anche nella console web.
Esegui il deployment di AlloyDB passo passo utilizzando Google Cloud SDK
La seguente procedura descrive come creare un cluster e un'istanza AlloyDB utilizzando Google Cloud SDK. Ignoralo se l'hai già eseguito tramite lo script nel passaggio precedente e vai direttamente a "Prepara il database".
Se preferisci l'approccio della console GUI web, puoi seguire la documentazione qui.
Prima di creare un cluster AlloyDB, abbiamo bisogno di un intervallo di IP privati disponibile nel nostro VPC da utilizzare per la futura istanza AlloyDB. Se non lo abbiamo, dobbiamo crearlo, assegnarlo per l'utilizzo da parte dei servizi Google interni e solo dopo potremo creare il cluster e l'istanza.
Crea un intervallo IP privato
Dobbiamo configurare la configurazione dell'accesso privato ai servizi nel nostro VPC per AlloyDB. Il presupposto è che nel progetto sia presente la rete VPC "predefinita" e che verrà utilizzata per tutte le azioni.
Crea l'intervallo IP privato:
gcloud compute addresses create psa-range \
--global \
--purpose=VPC_PEERING \
--prefix-length=24 \
--description="VPC private service access" \
--network=default
Crea una connessione privata utilizzando l'intervallo IP allocato:
gcloud services vpc-peerings connect \
--service=servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
--ranges=psa-range \
--network=default
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud compute addresses create psa-range \
--global \
--purpose=VPC_PEERING \
--prefix-length=24 \
--description="VPC private service access" \
--network=default
Created [https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/test-project-402417/global/addresses/psa-range].
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud services vpc-peerings connect \
--service=servicenetworking.googleapis.com \
--ranges=psa-range \
--network=default
Operation "operations/pssn.p24-4470404856-595e209f-19b7-4669-8a71-cbd45de8ba66" finished successfully.
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$
Crea cluster AlloyDB
In questa sezione creiamo un cluster AlloyDB nella regione us-central1.
Definisci la password per l'utente postgres. Puoi definire una password personalizzata o utilizzare una funzione casuale per generarla.
export PGPASSWORD=`openssl rand -hex 12`
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ export PGPASSWORD=`openssl rand -hex 12`
Prendi nota della password PostgreSQL per utilizzarla in futuro.
echo $PGPASSWORD
Avrai bisogno di questa password in futuro per connetterti all'istanza come utente postgres. Ti consiglio di annotarlo o copiarlo da qualche parte per poterlo utilizzare in un secondo momento.
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ echo $PGPASSWORD bbefbfde7601985b0dee5723 (Note: Yours will be different!)
Creare un cluster di prova senza costi
Se non hai mai utilizzato AlloyDB, puoi creare un cluster di prova senza costi:
Definisci la regione e il nome del cluster AlloyDB. Utilizzeremo la regione us-central1 e alloydb-aip-01 come nome del cluster:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
Esegui il comando per creare il cluster:
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION \
--subscription-type=TRIAL
Output console previsto:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION \
--subscription-type=TRIAL
Operation ID: operation-1697655441138-6080235852277-9e7f04f5-2012fce4
Creating cluster...done.
Crea un'istanza principale AlloyDB per il nostro cluster nella stessa sessione della shell Cloud. Se la connessione viene interrotta, dovrai definire di nuovo le variabili di ambiente del nome della regione e del cluster.
gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=8 \
--region=$REGION \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=8 \
--region=$REGION \
--availability-type ZONAL \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
Operation ID: operation-1697659203545-6080315c6e8ee-391805db-25852721
Creating instance...done.
Crea un cluster AlloyDB Standard
Se non è il tuo primo cluster AlloyDB nel progetto, procedi con la creazione di un cluster standard. Se hai già creato un cluster di prova senza costi nel passaggio precedente, salta questo passaggio.
Definisci la regione e il nome del cluster AlloyDB. Utilizzeremo la regione us-central1 e alloydb-aip-01 come nome del cluster:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
Esegui il comando per creare il cluster:
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION
Output console previsto:
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
gcloud alloydb clusters create $ADBCLUSTER \
--password=$PGPASSWORD \
--network=default \
--region=$REGION
Operation ID: operation-1697655441138-6080235852277-9e7f04f5-2012fce4
Creating cluster...done.
Crea un'istanza principale AlloyDB per il nostro cluster nella stessa sessione della shell Cloud. Se la connessione viene interrotta, dovrai definire di nuovo le variabili di ambiente del nome della regione e del cluster.
gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=2 \
--region=$REGION \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-402417)$ gcloud alloydb instances create $ADBCLUSTER-pr \
--instance-type=PRIMARY \
--cpu-count=2 \
--region=$REGION \
--availability-type ZONAL \
--cluster=$ADBCLUSTER
Operation ID: operation-1697659203545-6080315c6e8ee-391805db-25852721
Creating instance...done.
5. Prepara il database
Dobbiamo creare un database, abilitare l'integrazione di Vertex AI, creare oggetti di database e importare i dati.
Concedere le autorizzazioni necessarie ad AlloyDB
Aggiungi le autorizzazioni Vertex AI al service agent AlloyDB.
Apri un'altra scheda di Cloud Shell utilizzando il segno "+" in alto.
Nella nuova scheda di Cloud Shell, esegui:
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:service-$(gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format="value(projectNumber)")@gcp-sa-alloydb.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/aiplatform.user"
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \
--member="serviceAccount:service-$(gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format="value(projectNumber)")@gcp-sa-alloydb.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role="roles/discoveryengine.viewer"
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project) Your active configuration is: [cloudshell-11039] student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $PROJECT_ID \ --member="serviceAccount:service-$(gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format="value(projectNumber)")@gcp-sa-alloydb.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/aiplatform.user" Updated IAM policy for project [test-project-001-402417]. bindings: - members: - serviceAccount:service-4470404856@gcp-sa-alloydb.iam.gserviceaccount.com role: roles/aiplatform.user - members: ... etag: BwYIEbe_Z3U= version: 1
Chiudi la scheda con il comando di esecuzione "exit":
exit
Connettersi ad AlloyDB Studio
Nei capitoli seguenti, tutti i comandi SQL che richiedono la connessione al database possono essere eseguiti in AlloyDB Studio. T
Vai alla pagina Cluster in AlloyDB per PostgreSQL.
Apri l'interfaccia della console web per il cluster AlloyDB facendo clic sull'istanza principale.
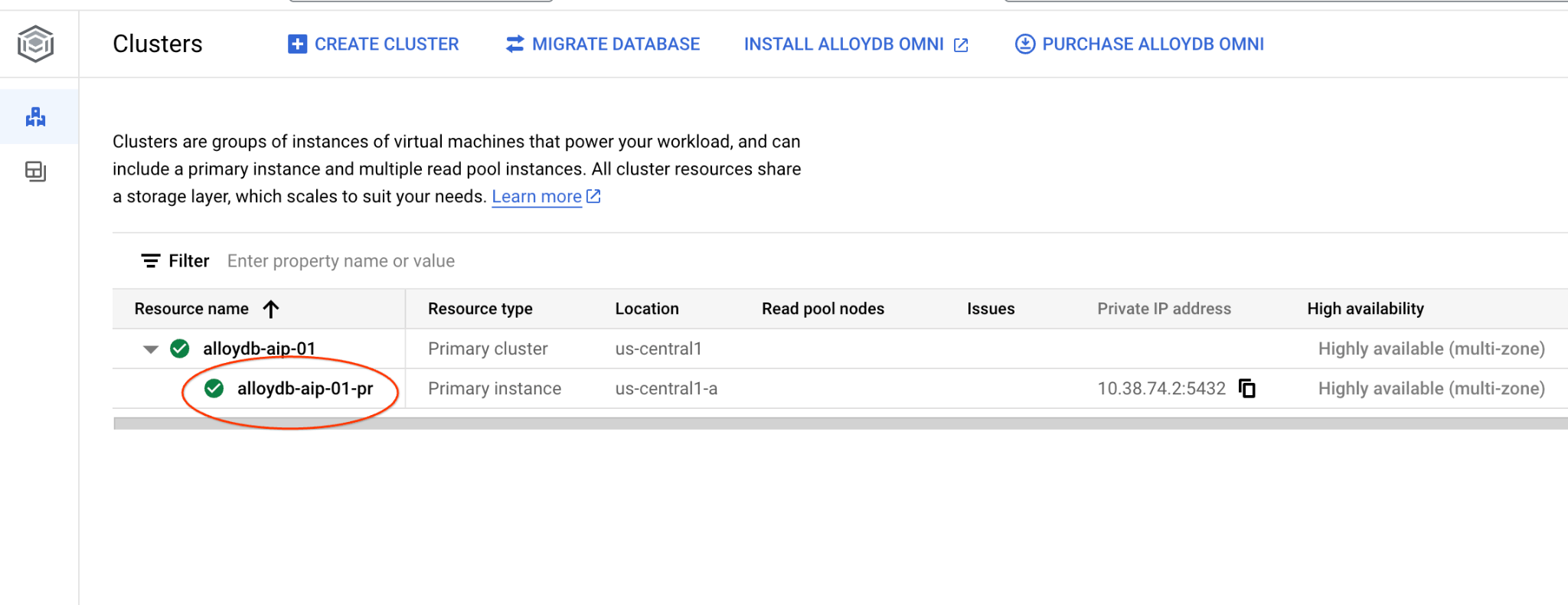
Quindi, fai clic su AlloyDB Studio a sinistra:
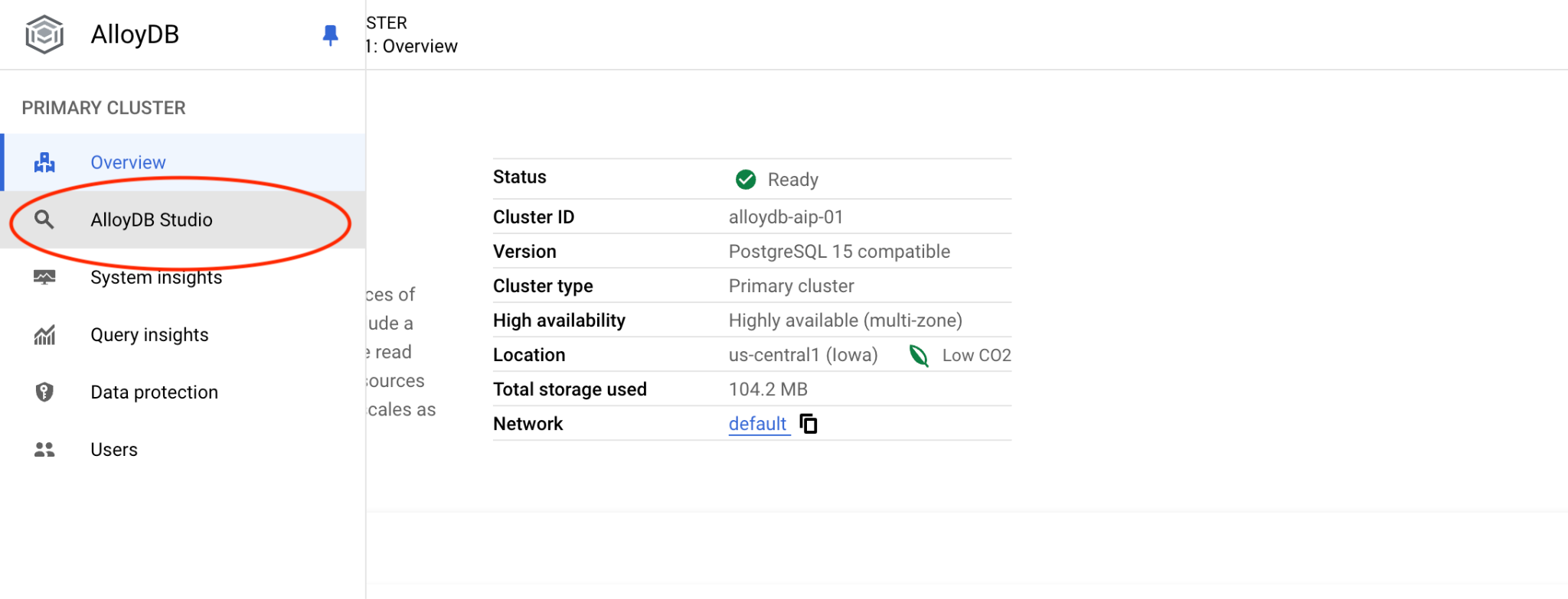
Scegli il database Postgres, l'utente Postgres e fornisci la password annotata durante la creazione del cluster. A questo punto, fai clic sul pulsante "Autentica".
Se la password non funziona o hai dimenticato di annotarla, puoi cambiarla. Consulta la documentazione per scoprire come fare.
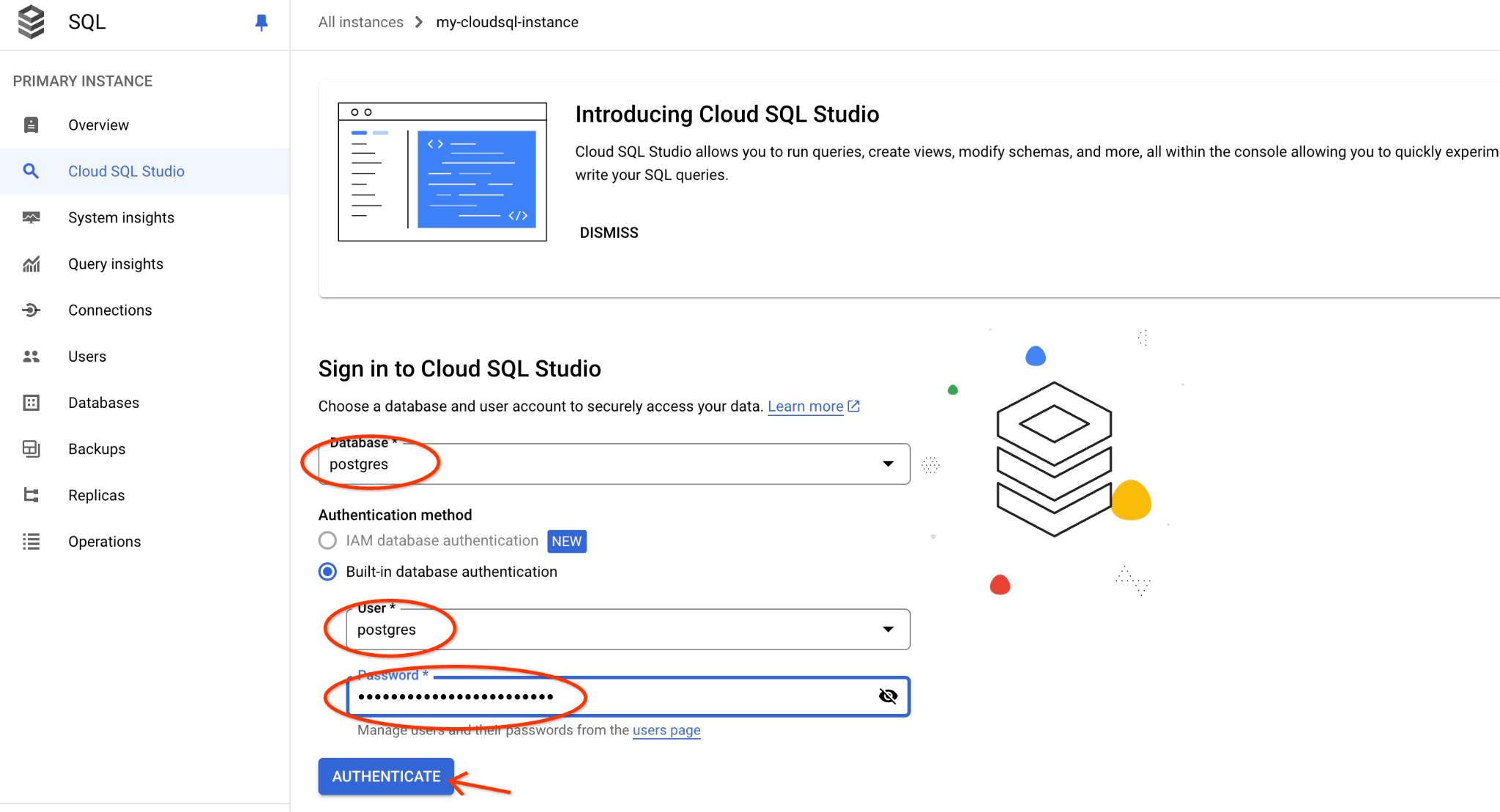
Si aprirà l'interfaccia di AlloyDB Studio. Per eseguire i comandi nel database, fai clic sulla scheda "Query senza titolo" a destra.
Si apre l'interfaccia in cui puoi eseguire i comandi SQL
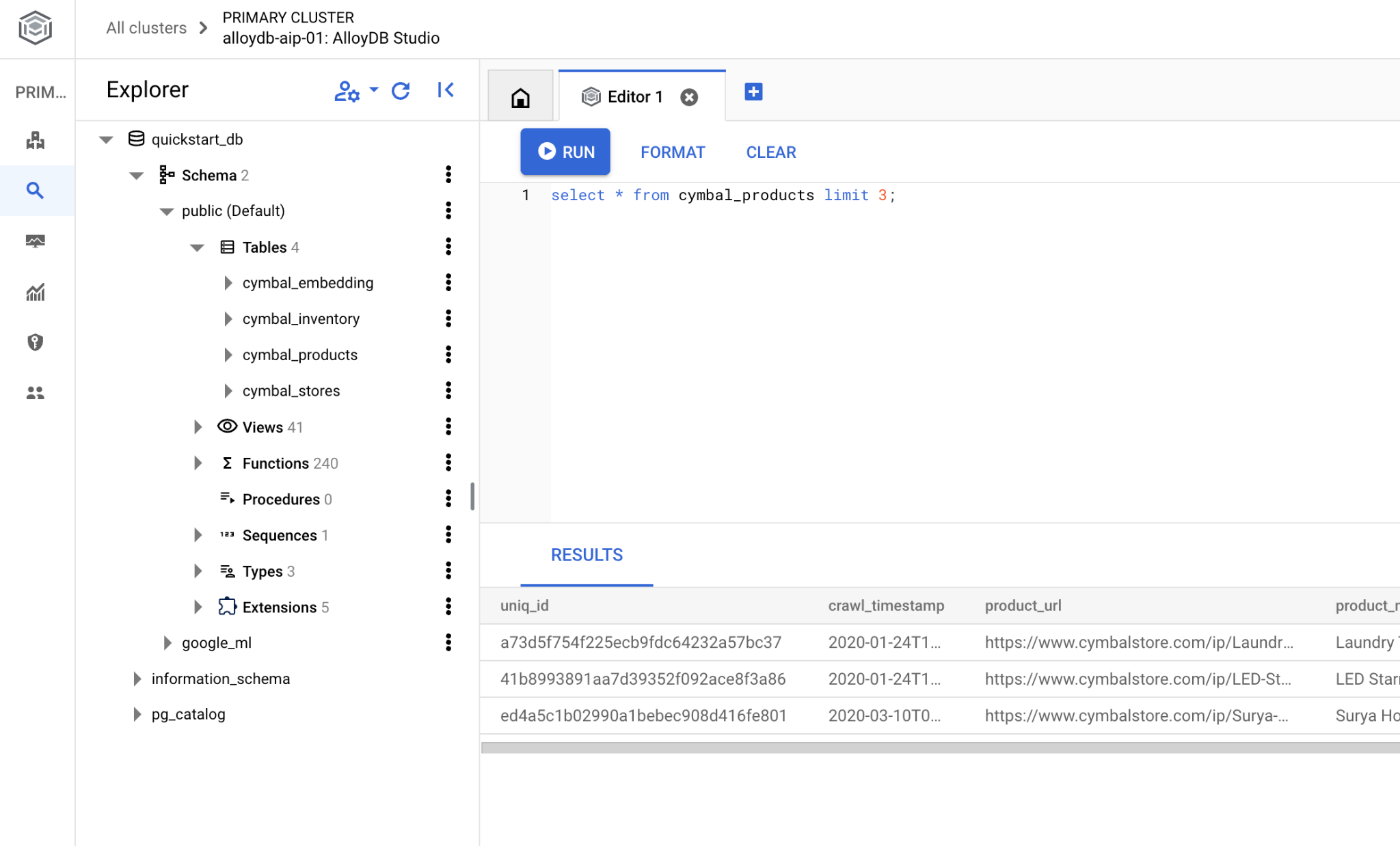
Crea database
Guida rapida alla creazione di un database.
Nell'editor di AlloyDB Studio, esegui questo comando.
Crea database:
CREATE DATABASE quickstart_db
Output previsto:
Statement executed successfully
Connettiti a quickstart_db
Riconnettiti allo studio utilizzando il pulsante per cambiare utente/database.
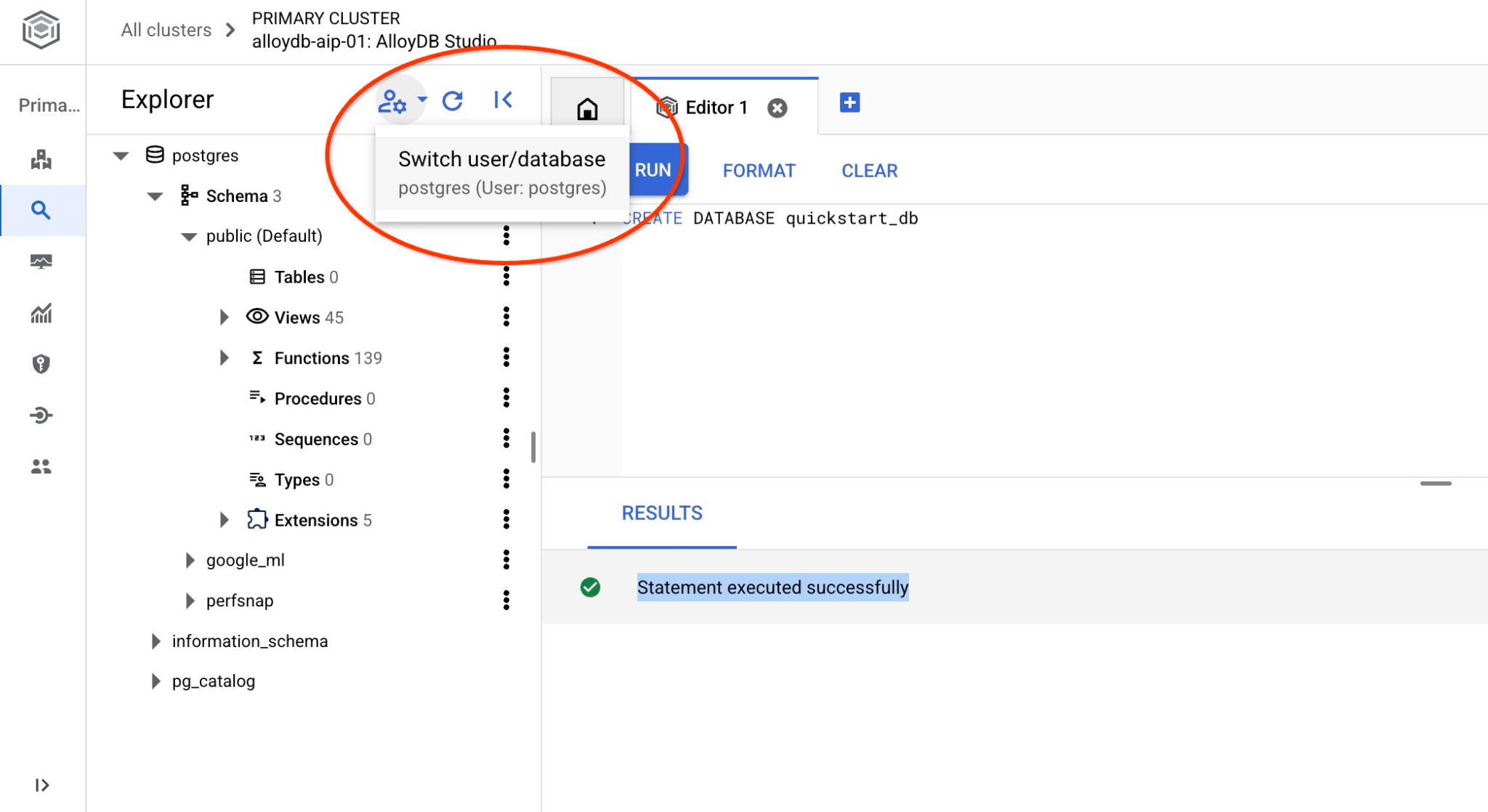
Seleziona il nuovo database quickstart_db dall'elenco a discesa e utilizza lo stesso utente e la stessa password di prima.
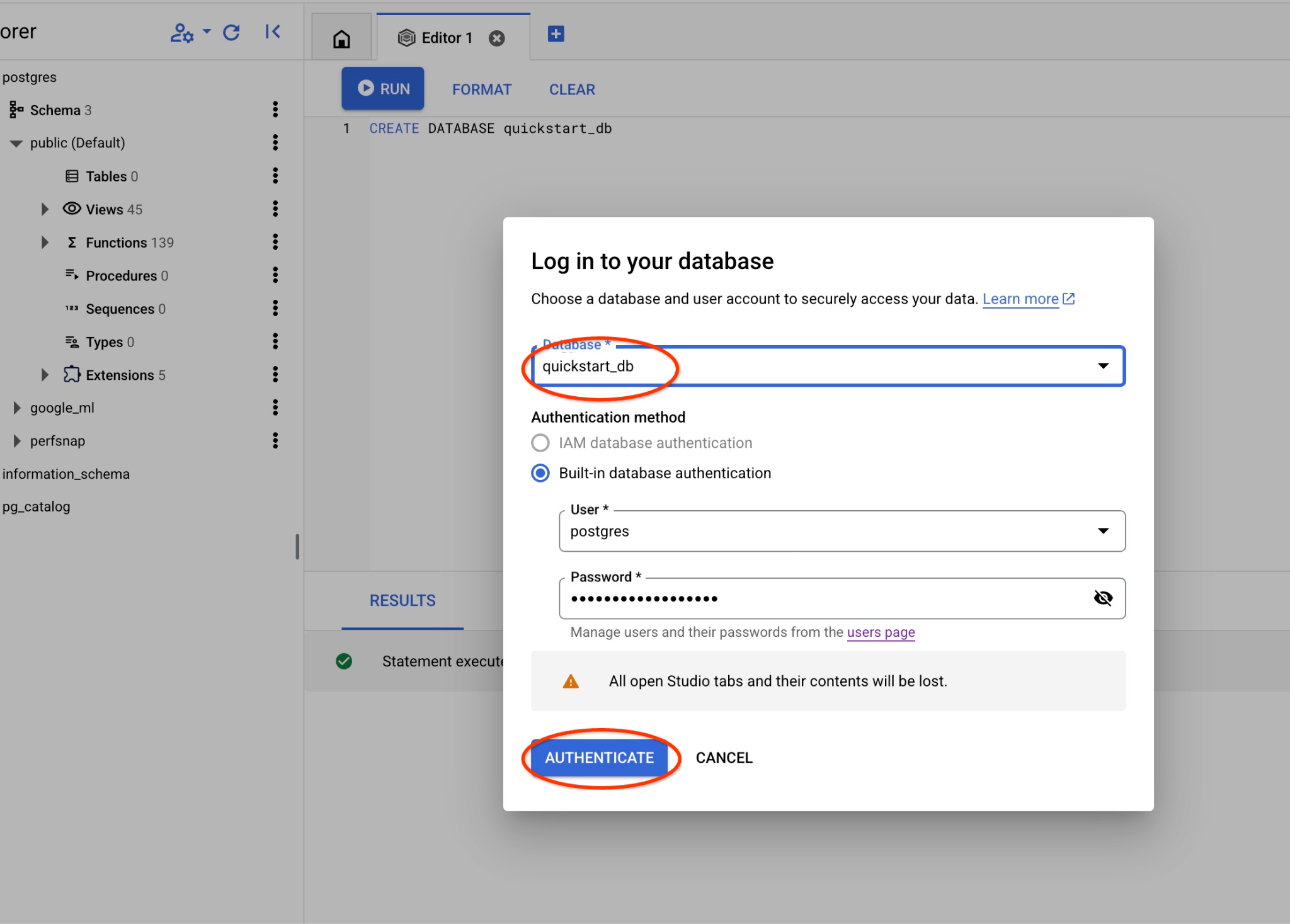
Si aprirà una nuova connessione in cui potrai lavorare con gli oggetti del database quickstart_db.
Verifica l'estensione google_ml
Controlla la versione dell'estensione google_ml per assicurarti che sia 1.5.2 o versioni successive per poter utilizzare il motore di query AI.
In AlloyDB Studio, mentre sei connesso a quickstart_db, esegui:
SELECT extversion FROM pg_extension WHERE extname = 'google_ml_integration';
Output previsto:
1.5.2
Se la versione è precedente a quella richiesta, aggiorna l'estensione.
In AlloyDB Studio, mentre sei connesso a quickstart_db, esegui:
CALL google_ml.upgrade_to_preview_version();
Output previsto:
Statement executed successfully
Dopo l'esecuzione, verifica di nuovo la versione.
In AlloyDB Studio, mentre sei connesso a quickstart_db, esegui:
SELECT extversion FROM pg_extension WHERE extname = 'google_ml_integration';
Output previsto:
1.5.2
Dobbiamo anche attivare le funzionalità del motore di query AI nel nostro database. Può essere eseguito aggiornando il flag per istanza per tutti i database dell'istanza o abilitandolo solo per il nostro database. Esegui il seguente comando in AlloyDB Studio per abilitarlo per il database quickstart_db.
ALTER DATABASE quickstart_db SET google_ml_integration.enable_ai_query_engine = 'on';
6. Dati di esempio
Ora dobbiamo creare oggetti nel database e caricare i dati. Utilizzeremo un set di dati fittizio sui film con poche righe.
Copia le seguenti istruzioni nell'editor di AlloyDB Studio e premi il pulsante "Esegui".
-- Drop tables if they exist to prevent errors on re-running the script
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS movie_reviews;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS movies;
-- Create the 'movies' table
-- This table stores information about each movie.
CREATE TABLE movies (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY, -- Unique identifier for the movie
title TEXT NOT NULL, -- Title of the movie
description TEXT, -- A brief description or synopsis of the movie
genres TEXT, -- Comma-separated list of genres (e.g., "Action, Adventure, Sci-Fi")
actors TEXT -- Comma-separated list of main actors
);
-- Create the 'movie_reviews' table
-- This table stores reviews for the movies.
CREATE TABLE movie_reviews (
review_id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY, -- Unique identifier for the review
movie_id BIGINT NOT NULL, -- Foreign key referencing the movie being reviewed
reviewer_name TEXT, -- Name of the person who wrote the review
rating INT CHECK (rating >= 1 AND rating <= 5), -- Rating from 1 to 5 stars
review_text TEXT, -- The content of the review
review_date DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE, -- Date when the review was submitted
FOREIGN KEY (movie_id) REFERENCES movies(id) ON DELETE CASCADE -- Ensures referential integrity; if a movie is deleted, its reviews are also deleted.
);
-- Insert sample data into the 'movies' table (20 rows)
INSERT INTO movies (id, title, description, genres, actors) VALUES
(1, 'Inception', 'A thief who steals information by entering people''s dreams.', 'Sci-Fi, Thriller, Action', 'Leonardo DiCaprio, Joseph Gordon-Levitt, Elliot Page'),
(2, 'The Matrix', 'A computer hacker learns about the true nature of his reality.', 'Sci-Fi, Action', 'Keanu Reeves, Laurence Fishburne, Carrie-Anne Moss'),
(3, 'Interstellar', 'A team of explorers journey through a cosmic passage beyond our world in an attempt to ensure humanity''s survival.', 'Sci-Fi, Drama, Adventure', 'Matthew McConaughey, Anne Hathaway, Jessica Chastain'), -- Updated description
(4, 'The Dark Knight', 'When the menace known as the Joker wreaks havoc and chaos on the people of Gotham, Batman must accept one of the greatest psychological and physical tests of his ability to fight injustice.', 'Action, Crime, Drama', 'Christian Bale, Heath Ledger, Aaron Eckhart'),
(5, 'Pulp Fiction', 'The lives of two mob hitmen, a boxer, a gangster and his wife, and a pair of diner bandits intertwine in four tales of violence and redemption.', 'Crime, Drama', 'John Travolta, Uma Thurman, Samuel L. Jackson'),
(6, 'Forrest Gump', 'The presidencies of Kennedy and Johnson, the Vietnam War, the Watergate scandal and other historical events unfold from the perspective of an Alabama man with an IQ of 75.', 'Drama, Romance', 'Tom Hanks, Robin Wright, Gary Sinise'),
(7, 'The Shawshank Redemption', 'Two imprisoned men bond over a number of years, finding solace and eventual redemption through acts of common decency.', 'Drama', 'Tim Robbins, Morgan Freeman, Bob Gunton'),
(8, 'Gladiator', 'A former Roman General sets out to exact vengeance against the corrupt emperor who murdered his family and sent him into slavery.', 'Action, Adventure, Drama', 'Russell Crowe, Joaquin Phoenix, Connie Nielsen'),
(9, 'Fight Club', 'An insomniac office worker looking for a way to change his life crosses paths with a devil-may-care soap maker and they form an underground fight club that evolves into something much, much more.', 'Drama', 'Brad Pitt, Edward Norton, Meat Loaf'),
(10, 'The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King', 'Gandalf and Aragorn lead the World of Men against Sauron''s army to draw his gaze from Frodo and Sam as they approach Mount Doom with the One Ring.', 'Action, Adventure, Drama', 'Elijah Wood, Viggo Mortensen, Ian McKellen'),
(11, 'Spirited Away', 'During her family''s move to the suburbs, a sullen 10-year-old girl wanders into a world ruled by gods, witches, and spirits, and where humans are changed into beasts.', 'Animation, Adventure, Family', 'Daveigh Chase, Suzanne Pleshette, Miyu Irino'),
(12, 'Parasite', 'Greed and class discrimination threaten the newly formed symbiotic relationship between the wealthy Park family and the destitute Kim clan.', 'Comedy, Drama, Thriller', 'Song Kang-ho, Lee Sun-kyun, Cho Yeo-jeong'),
(13, 'The Godfather', 'The aging patriarch of an organized crime dynasty transfers control of his clandestine empire to his reluctant son.', 'Crime, Drama', 'Marlon Brando, Al Pacino, James Caan'),
(14, 'Avengers: Endgame', 'After the devastating events of Avengers: Infinity War, the universe is in ruins. With the help of remaining allies, the Avengers assemble once more in order to reverse Thanos'' actions and restore balance to the universe.', 'Action, Adventure, Drama', 'Robert Downey Jr., Chris Evans, Mark Ruffalo'),
(15, 'Joker', 'In Gotham City, mentally troubled comedian Arthur Fleck is disregarded and mistreated by society. He then embarks on a downward spiral of revolution and bloody crime.', 'Crime, Drama, Thriller', 'Joaquin Phoenix, Robert De Niro, Zazie Beetz'),
(16, 'Mad Max: Fury Road', 'In a post-apocalyptic wasteland, a woman rebels against a tyrannical ruler in search for her homeland with the help of a group of female prisoners, a psychotic worshiper, and a drifter named Max.', 'Action, Adventure, Sci-Fi', 'Tom Hardy, Charlize Theron, Nicholas Hoult'),
(17, 'Coco', 'Aspiring musician Miguel, confronted with his family''s ancestral ban on music, enters the Land of the Dead to find his great-great-grandfather, a legendary singer.', 'Animation, Adventure, Family', 'Anthony Gonzalez, Gael García Bernal, Benjamin Bratt'),
(18, 'Whiplash', 'A promising young drummer enrolls at a cut-throat music conservatory where his dreams of greatness are mentored by an instructor who will stop at nothing to realize a student''s potential.', 'Drama, Music', 'Miles Teller, J.K. Simmons, Paul Reiser'),
(19, 'The Grand Budapest Hotel', 'The adventures of Gustave H, a legendary concierge at a famous hotel from the fictional Republic of Zubrowka between the first and second World Wars, and Zero Moustafa, the lobby boy who becomes his most trusted friend.', 'Adventure, Comedy, Drama', 'Ralph Fiennes, F. Murray Abraham, Mathieu Amalric'),
(20, 'Blade Runner 2049', 'Young Blade Runner K''s discovery of a long-buried secret leads him to track down former Blade Runner Rick Deckard, who''s been missing for thirty years.', 'Action, Drama, Mystery', 'Ryan Gosling, Harrison Ford, Ana de Armas');
-- Insert sample data into the 'movie_reviews' table (30 rows)
-- Reviews are linked to movies via movie_id. Includes a mix of positive and negative reviews.
-- Movie title is prepended to the review text.
INSERT INTO movie_reviews (review_id, movie_id, reviewer_name, rating, review_text) VALUES
(1, 1, 'Alice Wonderland', 5, 'Inception: Absolutely mind-bending! A masterpiece of sci-fi.'),
(2, 1, 'Bob The Critic', 2, 'Inception: Too confusing and pretentious. Didn''t enjoy it.'),
(3, 2, 'Charlie Reviewer', 5, 'The Matrix: Revolutionary visuals and a compelling story.'),
(4, 3, 'Diana Prince', 5, 'Interstellar: Visually stunning and emotionally powerful. A must-see.'),
(5, 3, 'Edward Nigma', 4, 'Interstellar: Long, but worth it for the spectacle and ideas.'),
(6, 4, 'Fiona Glenanne', 5, 'The Dark Knight: Heath Ledger''s Joker is iconic. Dark and thrilling.'),
(7, 5, 'George Costanza', 5, 'Pulp Fiction: Quirky, violent, and endlessly quotable.'),
(8, 5, 'Hannah Montana', 1, 'Pulp Fiction: Way too violent and the timeline was confusing. Hated it.'),
(9, 6, 'Ian Malcolm', 4, 'Forrest Gump: A heartwarming story with a great performance by Hanks.'),
(10, 7, 'Jane Doe', 5, 'The Shawshank Redemption: An uplifting story of hope and friendship. Perfect.'),
(11, 7, 'John Smith', 5, 'The Shawshank Redemption: Morgan Freeman is amazing. Truly a classic.'),
(12, 8, 'Kyle Broflovski', 2, 'Gladiator: Generic plot and boring action scenes. Overrated.'),
(13, 9, 'Laura Palmer', 5, 'Fight Club: Provocative and thought-provoking. Norton and Pitt are fantastic.'),
(14, 10, 'Michael Scott', 5, 'The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King: A fitting and epic conclusion to a legendary trilogy.'),
(15, 11, 'Nancy Drew', 5, 'Spirited Away: Beautiful animation and a magical story for all ages.'),
(16, 12, 'Oscar Martinez', 5, 'Parasite: A brilliant satire with unexpected twists. Loved it!'),
(17, 12, 'Pam Beesly', 4, 'Parasite: Very intense, but incredibly well-directed and acted.'),
(18, 13, 'Quentin Coldwater', 5, 'The Godfather: A cinematic masterpiece. Brando is unforgettable.'),
(19, 14, 'Rachel Green', 3, 'Avengers: Endgame: It was okay, but felt bloated and had too many characters.'),
(20, 14, 'Steve Rogers', 5, 'Avengers: Endgame: The culmination of a decade of storytelling. Perfect ending.'),
(21, 15, 'Tony Stark', 4, 'Joker: A dark and disturbing character study. Phoenix is mesmerizing.'),
(22, 16, 'Uma Thurman', 5, 'Mad Max: Fury Road: Non-stop action and incredible practical effects. What a ride!'),
(23, 17, 'Victor Frankenstein', 5, 'Coco: A heartwarming and visually stunning celebration of family and culture.'),
(24, 18, 'Walter White', 5, 'Whiplash: Intense and gripping. J.K. Simmons is terrifyingly good.'),
(25, 19, 'Xena Warrior', 2, 'The Grand Budapest Hotel: Too quirky for its own good. Style over substance.'),
(26, 20, 'Ygritte Snow', 5, 'Blade Runner 2049: A worthy sequel that expands on the original in meaningful ways. Visually breathtaking.'),
(27, 1, 'Zack Morris', 4, 'Inception: Kept me on the edge of my seat. Very clever.'),
(28, 4, 'Buffy Summers', 5, 'The Dark Knight: The best superhero movie ever made. Ledger is a legend.'),
(29, 8, 'Clark Kent', 3, 'Gladiator: Decent action, but the story felt predictable and dragged a bit.'),
(30, 15, 'Diana Troy', 3, 'Joker: Hard to watch at times, but a powerful performance. Felt it was a bit one-note though.');
Se disponi di dati di esempio e di file CSV compatibili con lo strumento di importazione Cloud SQL disponibile in Cloud Console, puoi utilizzarli al posto dell'approccio presentato.
7. Utilizzare l'operatore IF
Proviamo prima la ricerca classica utilizzando gli approcci PostgreSQL standard.
Se proviamo a cercare un film sulle avventure spaziali, possiamo provare la seguente query
SELECT title,description AS movies_about_space
FROM movies
WHERE description like '%space%' OR title like '%space%';
Non ha restituito alcun risultato. Ma sono sicuro che abbiamo almeno un film che rientra in questa categoria. Possiamo provare a utilizzare un approccio di ricerca a testo intero.
SELECT title,description
FROM movies
WHERE to_tsvector('english', description) @@ to_tsquery('english', 'space');
E potremmo non ottenere alcun risultato. Pertanto, dobbiamo conoscere alcune parole o frasi chiave per poter utilizzare le tecniche "classiche" della ricerca PostgreSQL.
Ora possiamo provare a utilizzare il filtro semantico basato sull'AI con la funzione google_ml.if. Utilizzerà l'AI in background per eseguire il filtro semantico in base alla nostra richiesta in linguaggio naturale.
SELECT title,description AS movies_about_space
FROM movies
WHERE
google_ml.if(
prompt => 'Here are descriptions of movies, can you return the ones about space adventures: '||description);
Stiamo recuperando il film "Interstellar" in base al significato semantico della richiesta, anche se non contiene il termine "spazio" né nel titolo né nella descrizione. Come avrai notato, non abbiamo creato nulla in anticipo e ci siamo affidati esclusivamente a funzioni automatiche integrate.
8. Utilizzare JOIN con l'operatore IF
E se volessimo unire due tabelle utilizzando il filtro semantico basato sull'AI? Ad esempio, possiamo provare ad abbinare le recensioni degli utenti ai film in base alle recensioni degli utenti se il film è stato menzionato nella recensione.
Esegui in una nuova scheda dell'editor di AlloyDB Studio:
SELECT title, rating, movie_reviews
FROM movies
JOIN
movie_reviews ON
google_ml.if(
prompt => 'Does the following reviews talk about a movie mentioned? The review: ' || review_text||' and the movie title is: '||title)
AND
title='Interstellar';
Riceviamo due recensioni corrispondenti alla nostra richiesta in base al nome del film menzionato nel titolo. Possiamo semplificare ulteriormente la richiesta:
SELECT title, rating, movie_reviews
FROM movies
JOIN
movie_reviews ON
google_ml.if(
prompt => 'Do we have the movie in the review?: ' || review_text||' and the movie title is: '||title)
AND
title='Interstellar';
9. Punteggio dei risultati in base ai contenuti
La tabella movie_reviews contiene le valutazioni dei film, ma se vogliamo implementare una nostra valutazione possiamo utilizzare la funzione google_ml.rank. Possiamo assegnare un punteggio alle recensioni in base a condizioni definite da un linguaggio naturale e ottenere, ad esempio, le 5 recensioni migliori per i film e mostrare la valutazione originale a scopo di confronto.
SELECT rating,review_text AS top_five
FROM movie_reviews
ORDER BY google_ml.rank('Score of 7 to 10 if the review says the movie was really good, 3 to 6 if the review says it''s alright is and 1 to 2 if the review says it was not worth of time. Review: ' || review_text) DESC
LIMIT 5;
Se vogliamo mostrare la nuova valutazione accanto a quella originale, possiamo aggiungerla all'elenco delle colonne.
SELECT rating,
google_ml.rank('Score of 7 to 10 if the review says the movie was really good, 3 to 6 if the review says it''s alright is and 1 to 2 if the review says it was not worth of time. Review: ' || review_text) AS ml_rank,
review_text AS top_five
FROM movie_reviews
ORDER BY ml_rank DESC
LIMIT 5;
Ecco le prime 5 recensioni.
rating | ml_rank | top_five
--------+---------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------
5 | 9 | The Dark Knight: Heath Ledger's Joker is iconic. Dark and thrilling.
5 | 9 | The Matrix: Revolutionary visuals and a compelling story.
5 | 9 | Interstellar: Visually stunning and emotionally powerful. A must-see.
5 | 9 | Inception: Absolutely mind-bending! A masterpiece of sci-fi.
5 | 9 | Pulp Fiction: Quirky, violent, and endlessly quotable.
(5 rows)
5 rows in set (0.13 sec)
La valutazione scelta è stata 9 su 10 per le recensioni migliori.
Scopri di più sugli operatori di AlloyDB AI nella documentazione.
10. Migliorare la ricerca semantica utilizzando il ranking
Possiamo combinare la nostra ricerca semantica con la classificazione per ottenere risultati più precisi.
Accesso al modello di riposizionamento
Per utilizzare i modelli di ranking, dobbiamo abilitare l'API Discovery Engine e concedere il ruolo "discoveryengine.viewer" al service account AlloyDB. L'API e il ruolo sono stati abilitati nei primi passaggi del nostro lab. La funzione ai.rank trova e utilizza automaticamente il modello di ranking più recente su Vertex AI.
Utilizzare il modello di riposizionamento nelle query
Ora possiamo utilizzare il nostro modello di riassegnazione del ranking nelle query per migliorare i risultati della ricerca semantica, rendendoli più specifici e scegliendo le opzioni migliori.
Troviamo film d'azione e classifichiamoli utilizzando "computer e futuro" come condizioni.
WITH
action_movies AS (
SELECT
title,
description,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (ORDER BY title, description) AS ref_number
FROM
movies
WHERE
google_ml.if(
prompt => 'The following movies are action movies. The movie title: ' || title || ' and the description is: ' || description
)
),
ranked_documents_array AS (
SELECT
ARRAY_AGG(description ORDER BY ref_number) AS docs
FROM
action_movies
),
reranked_results AS (
SELECT
r.index,
r.score
FROM
ranked_documents_array,
ai.rank(
model_id => 'semantic-ranker-default',
search_string => 'Computers and future',
documents => ranked_documents_array.docs
) AS r
)
SELECT
am.title,
left(am.description,80) as description,
rr.score
FROM
action_movies am
JOIN
reranked_results rr ON am.ref_number = rr.index
ORDER BY
rr.score DESC;
I risultati elencheranno i film d'azione, mettendo in primo piano quelli sul futuro e sui computer.
title | description | score
-----------------------------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+--------
The Matrix | A computer hacker learns about the true nature of his reality. | 0.1197
Inception | A thief who steals information by entering people's dreams. | 0.0646
Blade Runner 2049 | Young Blade Runner K's discovery of a long-buried secret leads him to track down | 0.022
Mad Max: Fury Road | In a post-apocalyptic wasteland, a woman rebels against a tyrannical ruler in se | 0.0206
Gladiator | A former Roman General sets out to exact vengeance against the corrupt emperor w | 0.0189
Avengers: Endgame | After the devastating events of Avengers: Infinity War, the universe is in ruins | 0.0175
Fight Club | An insomniac office worker looking for a way to change his life crosses paths wi | 0.0162
The Dark Knight | When the menace known as the Joker wreaks havoc and chaos on the people of Gotha | 0.0095
The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King | Gandalf and Aragorn lead the World of Men against Sauron's army to draw his gaze | 0.0056
(9 rows)
Prova con condizioni diverse e vedi in che modo la classificazione influisce sull'ordine di output.
Scopri di più sulle opzioni e sul ranking nella documentazione.
11. Pulizia dell'ambiente
Elimina le istanze e il cluster AlloyDB al termine del lab.
Elimina il cluster AlloyDB e tutte le istanze
Se hai utilizzato la versione di prova di AlloyDB. Non eliminare il cluster di prova se prevedi di testare altri lab e risorse utilizzando il cluster di prova. Non potrai creare un altro cluster di prova nello stesso progetto.
Il cluster viene eliminato con l'opzione force, che elimina anche tutte le istanze appartenenti al cluster.
In Cloud Shell definisci le variabili di progetto e di ambiente se la connessione è stata interrotta e tutte le impostazioni precedenti sono andate perse:
gcloud config set project <your project id>
export REGION=us-central1
export ADBCLUSTER=alloydb-aip-01
export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project)
Elimina il cluster:
gcloud alloydb clusters delete $ADBCLUSTER --region=$REGION --force
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ gcloud alloydb clusters delete $ADBCLUSTER --region=$REGION --force All of the cluster data will be lost when the cluster is deleted. Do you want to continue (Y/n)? Y Operation ID: operation-1697820178429-6082890a0b570-4a72f7e4-4c5df36f Deleting cluster...done.
Elimina i backup di AlloyDB
Elimina tutti i backup AlloyDB per il cluster:
for i in $(gcloud alloydb backups list --filter="CLUSTER_NAME: projects/$PROJECT_ID/locations/$REGION/clusters/$ADBCLUSTER" --format="value(name)" --sort-by=~createTime) ; do gcloud alloydb backups delete $(basename $i) --region $REGION --quiet; done
Output console previsto:
student@cloudshell:~ (test-project-001-402417)$ for i in $(gcloud alloydb backups list --filter="CLUSTER_NAME: projects/$PROJECT_ID/locations/$REGION/clusters/$ADBCLUSTER" --format="value(name)" --sort-by=~createTime) ; do gcloud alloydb backups delete $(basename $i) --region $REGION --quiet; done Operation ID: operation-1697826266108-60829fb7b5258-7f99dc0b-99f3c35f Deleting backup...done.
12. Complimenti
Congratulazioni per aver completato il codelab.
Percorso di apprendimento di Google Cloud
Questo lab fa parte del percorso di apprendimento per l'AI pronta per la produzione con Google Cloud.
- Esplora il curriculum completo per colmare il divario tra prototipo e produzione.
- Condividi i tuoi progressi con l'hashtag
#ProductionReadyAI.
Argomenti trattati
- Come eseguire il deployment del cluster e dell'istanza principale di AlloyDB
- Come abilitare gli operatori AlloyDB AI
- Come utilizzare diversi operatori AI di AlloyDB
- Come utilizzare il ranking negli operatori AI di AlloyDB per migliorare l'output dei risultati
13. Sondaggio
Output:
