1. مقدمة
في مشهد البيانات السريع الوتيرة اليوم، تُعدّ الإحصاءات في الوقت الفعلي أمرًا بالغ الأهمية لاتّخاذ قرارات مستنيرة. سيرشدك هذا الدرس التطبيقي حول الترميز إلى كيفية إنشاء مسار تقييم في الوقت الفعلي. سنبدأ بالاستفادة من إطار عمل Apache Beam الذي يوفّر نموذج برمجة موحّدًا لكلّ من البيانات المجمّعة والمتواصلة. يؤدي ذلك إلى تبسيط عملية تطوير خطوط الإنتاج بشكل كبير من خلال إخفاء منطق الحوسبة الموزّعة المعقّد الذي كان عليك إنشاؤه من البداية. بعد تحديد سلسلة الإجراءات باستخدام Beam، يمكنك تشغيلها بسلاسة على Google Cloud Dataflow، وهي خدمة مُدارة بالكامل توفّر مستوى لا مثيل له من قابلية التوسّع والأداء لتلبية احتياجاتك في معالجة البيانات.
في هذا الدرس التطبيقي حول الترميز، ستتعرّف على كيفية تصميم مسار Apache Beam قابل للتوسيع لإجراء استنتاجات مستندة إلى تعلُّم الآلة، وتطوير ModelHandler مخصّص لدمج نموذج Gemini من Vertex AI، والاستفادة من تصميم الطلبات لإجراء تصنيف ذكي للنصوص في تدفقات البيانات، ونشر مسار الاستنتاج المستند إلى تعلُّم الآلة وتشغيله على Google Cloud Dataflow. في نهاية هذه الدورة التدريبية، ستكتسب معلومات قيّمة حول تطبيق "تعلُّم الآلة" لفهم البيانات في الوقت الفعلي والتقييم المستمر في أساليب سير العمل الهندسية، لا سيما للحفاظ على الذكاء الاصطناعي الحواري الفعّال والمتمحور حول المستخدم.
السيناريو
أنشأت شركتك وكيل بيانات. تم تجهيز وكيل البيانات، الذي تم إنشاؤه باستخدام "حزمة تطوير الوكلاء" (ADK)، بإمكانات متخصصة متنوعة للمساعدة في المهام المتعلقة بالبيانات. يمكنك اعتبارها مساعد بيانات متعدد الاستخدامات، وجاهزًا للتعامل مع طلبات متنوعة، بدءًا من العمل كمحلل ذكاء الأعمال لإنشاء تقارير مفيدة، إلى مهندس بيانات يساعدك في إنشاء مسارات بيانات قوية، أو أداة إنشاء SQL تصمّم عبارات SQL دقيقة، وغير ذلك الكثير. يتم تلقائيًا تخزين كل تفاعل وكل ردّ يقدّمه هذا الوكيل في Firestore. ولكن لماذا نحتاج إلى مسار هنا؟
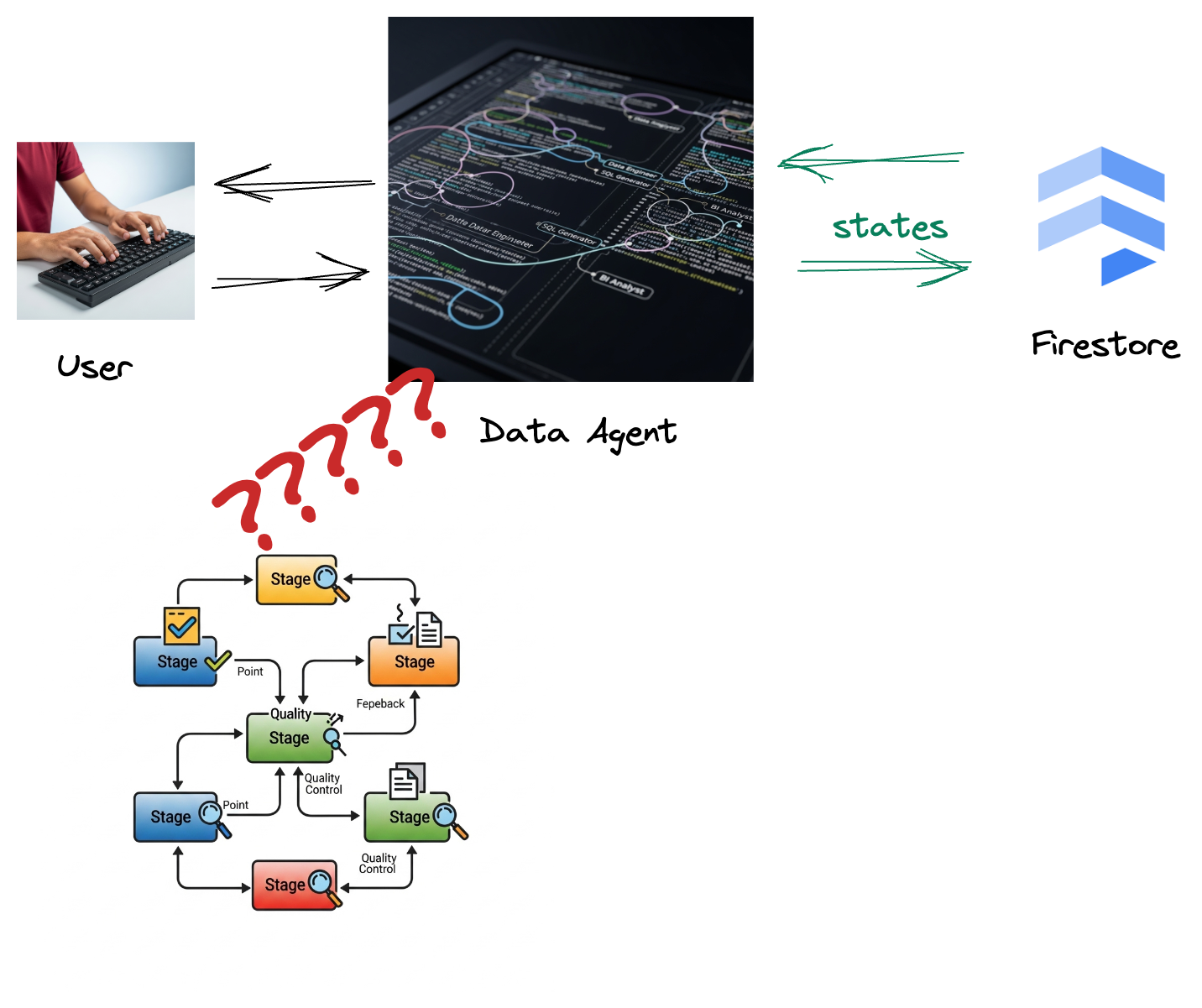
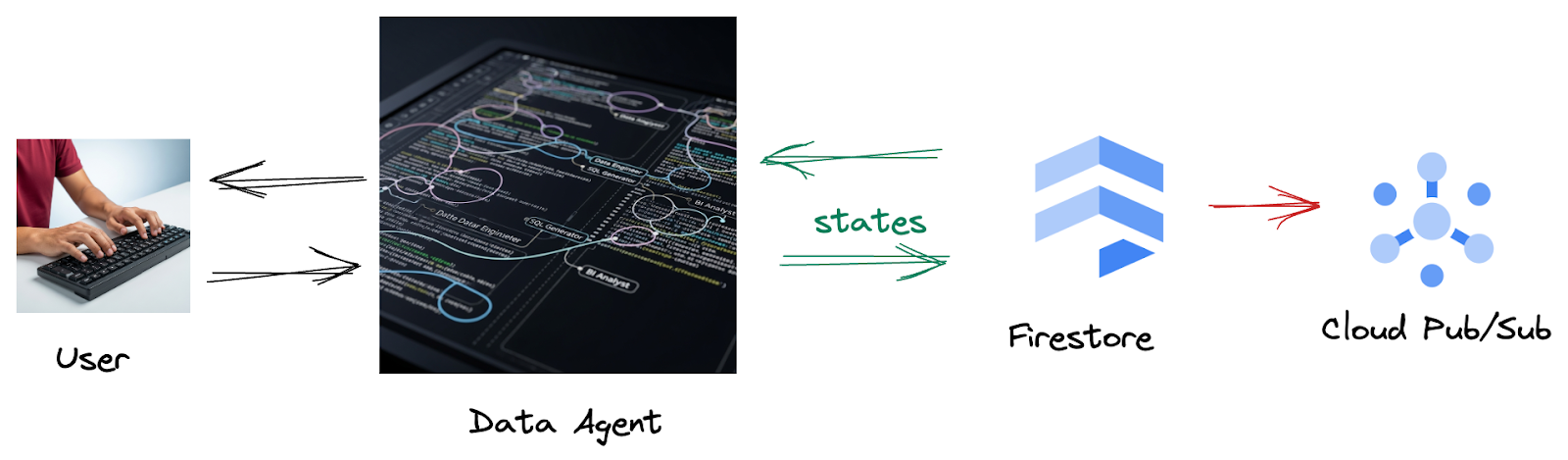
فمن خلال Firestore، يرسل مشغّل بيانات التفاعل هذه بسلاسة إلى Pub/Sub، ما يضمن إمكانية معالجة هذه المحادثات المهمة وتحليلها على الفور في الوقت الفعلي.
2. قبل البدء
إنشاء مشروع
- في Google Cloud Console، في صفحة اختيار المشروع، اختَر أو أنشِئ مشروعًا على Google Cloud.
- تأكَّد من تفعيل الفوترة لمشروعك على Cloud. تعرَّف على كيفية التحقّق مما إذا كانت الفوترة مفعَّلة في مشروع.
- فعِّل Cloud Shell من خلال النقر على هذا الرابط. يمكنك التبديل بين "نافذة Cloud Shell" (لتنفيذ أوامر السحابة الإلكترونية) و"المحرّر" (لإنشاء المشاريع) من خلال النقر على الزر المناسب من Cloud Shell.
- بعد الاتصال بـ Cloud Shell، يمكنك التأكّد من أنّك قد تم التحقّق من هويتك وأنّه تم ضبط المشروع على معرّف مشروعك باستخدام الأمر التالي:
gcloud auth list
- نفِّذ الأمر التالي في Cloud Shell للتأكّد من أنّ أمر gcloud يعرف مشروعك.
gcloud config list project
- إذا لم يتم ضبط مشروعك، استخدِم الأمر التالي لضبطه:
export PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
- فعِّل واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المطلوبة من خلال الأمر الموضّح أدناه. قد تستغرق هذه العملية بضع دقائق، لذا يُرجى الانتظار.
gcloud services enable \
dataflow.googleapis.com \
pubsub.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com
- يجب أن يكون لديك الإصدار 3.10 أو الإصدارات الأحدث من Python
- تثبيت حِزم Python
ثبِّت مكتبات Python المطلوبة لكلّ من Apache Beam وGoogle Cloud Vertex AI وGoogle Generative AI في بيئة Cloud Shell.
pip install apache-beam[gcp] google-genai
- استنسِخ مستودع github وانتقِل إلى دليل العرض التوضيحي.
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos
cd devrel-demos/data-analytics/beam_as_eval
راجِع المستندات لمعرفة أوامر gcloud وطريقة استخدامها.
3- كيفية استخدام مستودع Github المقدَّم
تم تنظيم مستودع GitHub المرتبط بهذا الدرس التطبيقي حول الترميز، والذي يمكن العثور عليه على الرابط https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos/tree/main/data-analytics/beam_as_eval، لتسهيل تجربة التعلّم الموجّه. يحتوي على رمز هيكلي يتوافق مع كل جزء مميز من الدرس العملي، ما يضمن تقدّمًا واضحًا خلال المادة.
داخل المستودع، ستعثر على مجلدَين أساسيَّين: "مكتمل" و"غير مكتمل". يحتوي المجلد "مكتمل" على تعليمات برمجية تعمل بكامل طاقتها لكل خطوة، ما يتيح لك تشغيل المخرجات المقصودة ومراقبتها. في المقابل، يوفّر المجلد "غير مكتمل" الرمز من الخطوات السابقة، مع ترك أقسام محدّدة بين ##### START STEP <NUMBER> ##### و##### END STEP <NUMBER> ##### لتكملها كجزء من التمارين. يتيح لك هذا الهيكل الاستفادة من المعرفة السابقة أثناء المشاركة بنشاط في تحديات البرمجة.
4. نظرة عامة على البنية
يوفر مسارنا نمطًا قويًا وقابلاً للتوسيع لدمج استنتاج تعلُّم الآلة في تدفقات البيانات. في ما يلي كيفية عمل هذه الأجزاء معًا:
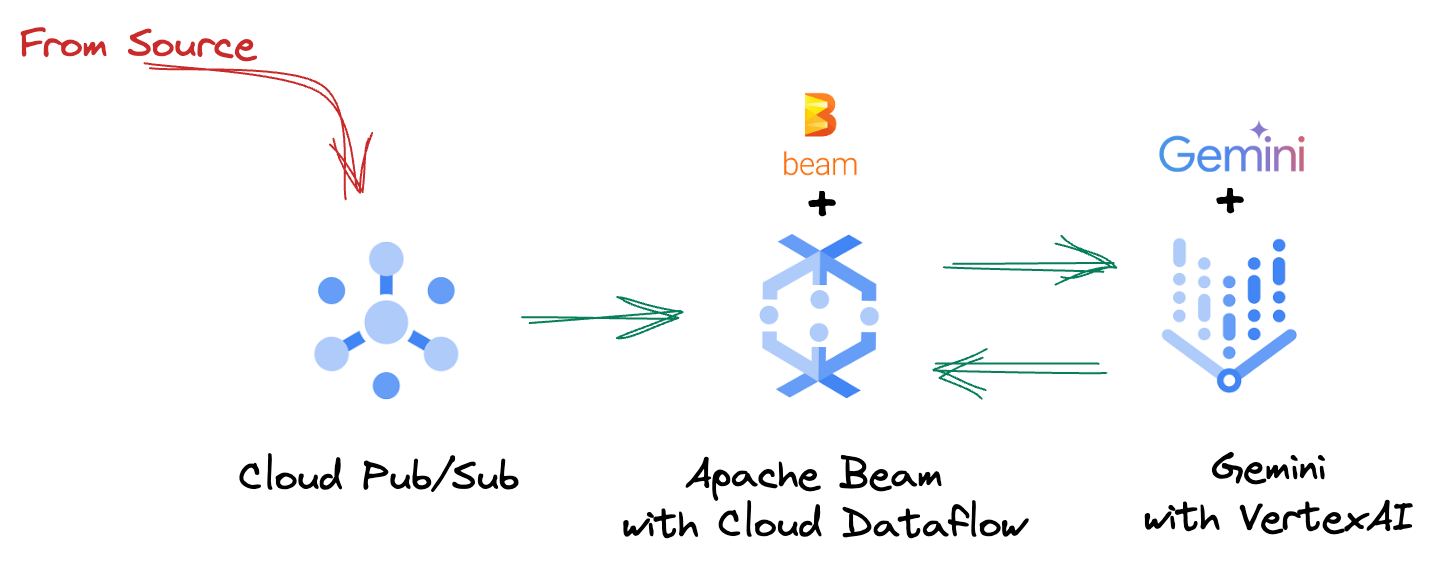
في مسار Beam، ستكتب رمزًا برمجيًا لمدخلات متعدّدة بشكل مشروط، ثم ستحمّل نماذج مخصّصة باستخدام عملية التحويل الجاهزة RunInference. على الرغم من أنّك تستخدم Gemini مع Vertex AI في المثال، يوضّح المثال كيف يمكنك إنشاء عدة ModelHandler لتناسب عدد النماذج المتوفرة لديك. أخيرًا، ستستخدم DoFn ذات حالة لتتبُّع الأحداث وإصدارها بطريقة منظَّمة.
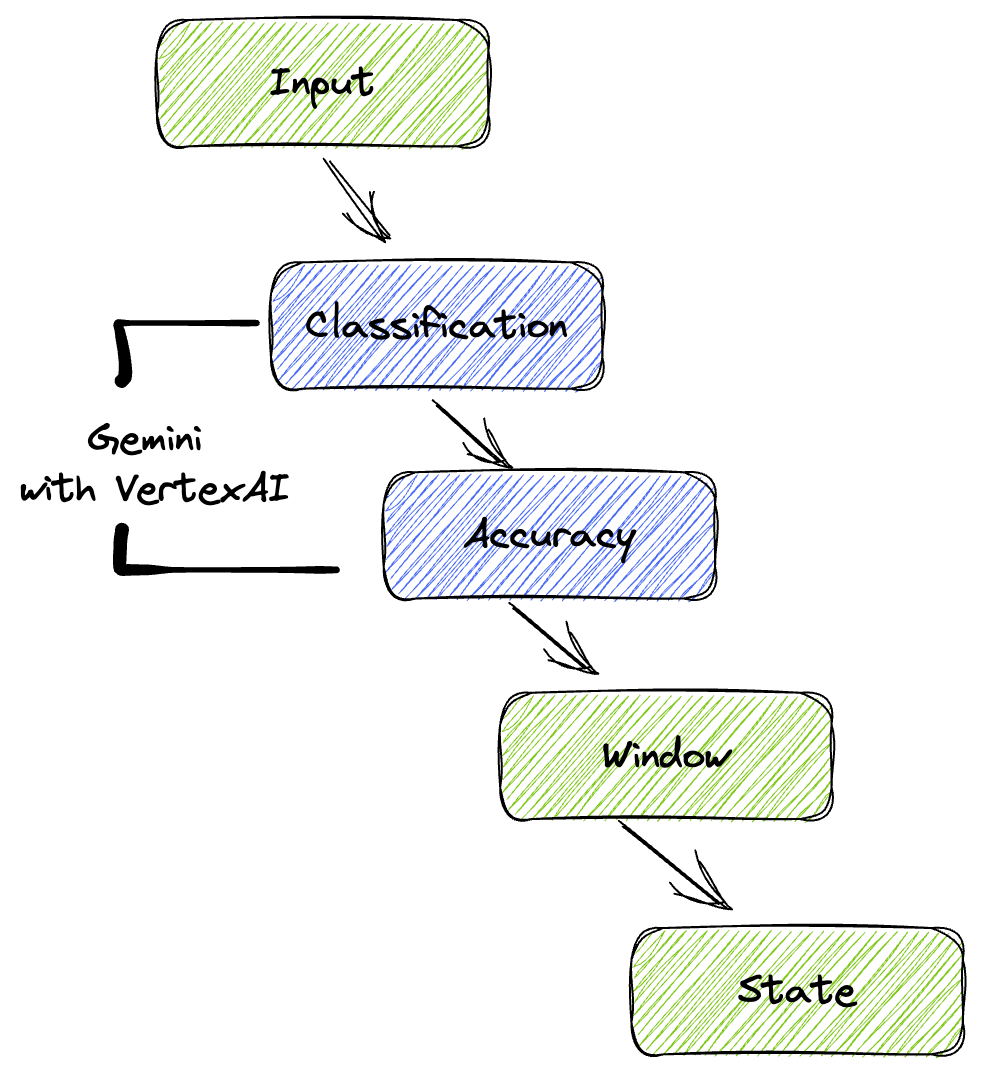
5- نقل البيانات
أولاً، عليك إعداد خط أنابيب استيعاب البيانات. ستستخدم Pub/Sub للبث المباشر، ولكن لتسهيل عملية التطوير، ستنشئ أيضًا وضعًا تجريبيًا. تتيح لك هذه الأداة test_mode تشغيل خط الأنابيب محليًا باستخدام بيانات نموذجية محدّدة مسبقًا، لذلك لا تحتاج إلى بث مباشر من Pub/Sub لمعرفة ما إذا كان خط الأنابيب يعمل.
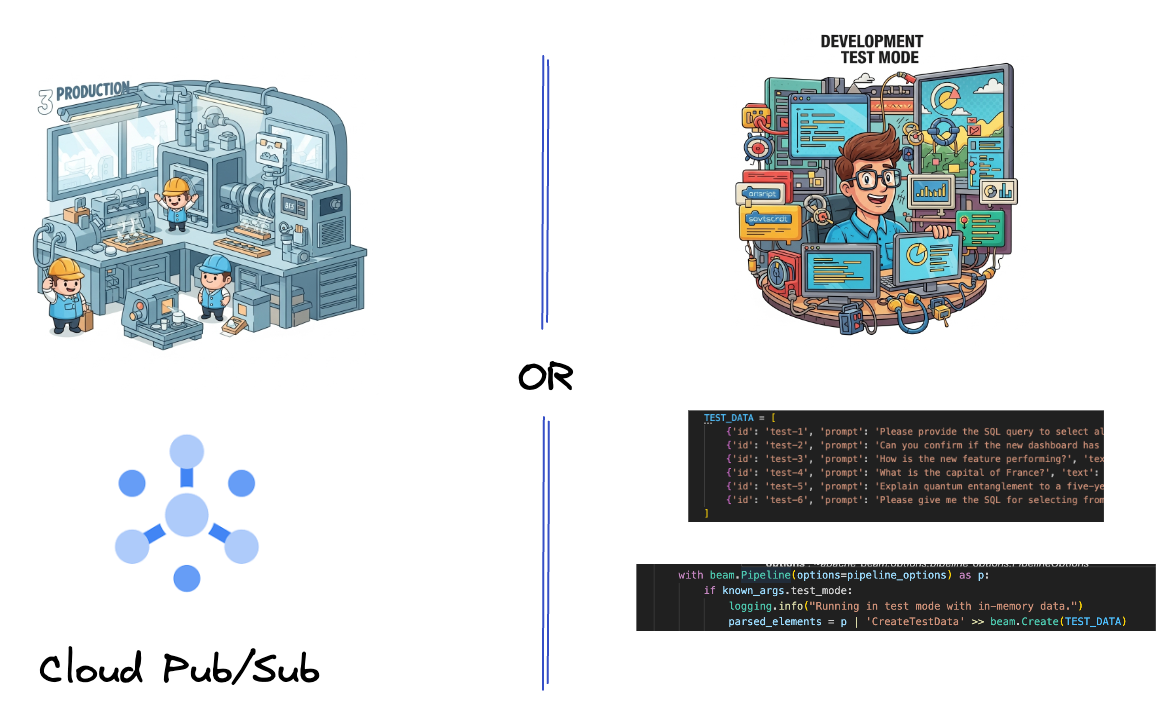
بالنسبة إلى هذا القسم، استخدِم gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py.
- باستخدام عنصر أنابيب التجزئة p المقدَّم، اكتب رمزًا برمجيًا لإدخال Pub/Sub واكتب الإخراج كـ pCollection.
- بالإضافة إلى ذلك، استخدِم علامة لتحديد ما إذا تم ضبط TEST_MODE.
- إذا تم ضبط TEST_MODE، عليك التبديل إلى تحليل مصفوفة TEST_DATA كإدخال.
هذا ليس ضروريًا، ولكنّه يساعد في تقصير العملية حتى لا تحتاج إلى استخدام Pub/Sub في هذه المرحلة المبكرة.
في ما يلي مثال على الرمز أدناه:
# Step 1
# Ingesting Data
# Write your data ingestion step here.
############## BEGIN STEP 1 ##############
if known_args.test_mode:
logging.info("Running in test mode with in-memory data.")
parsed_elements = p | 'CreateTestData' >> beam.Create(TEST_DATA)
# Convert dicts to JSON strings and add timestamps for test mode
parsed_elements = parsed_elements | 'ConvertTestDictsToJsonAndAddTimestamps' >> beam.Map(
lambda x: beam.window.TimestampedValue(json.dumps(x), x['timestamp'])
)
else:
logging.info(f"Reading from Pub/Sub topic: {known_args.input_topic}")
parsed_elements = (
p
| 'ReadFromPubSub' >> beam.io.ReadFromPubSub(
topic=known_args.input_topic
).with_output_types(bytes)
| 'DecodeBytes' >> beam.Map(lambda b: b.decode('utf-8')) # Output is JSON string
# Extract timestamp from JSON string for Pub/Sub messages
| 'AddTimestampsFromParsedJson' >> beam.Map(lambda s: beam.window.TimestampedValue(s, json.loads(s)['timestamp']))
)
############## END STEP 1 ##############
اختبِر هذا الرمز البرمجي من خلال تنفيذ ما يلي:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
يجب أن تُصدر هذه الخطوة جميع السجلات، مع تسجيلها في stdout.
من المفترض أن يظهر لك ناتج مشابه لما يلي.
INFO:root:Running in test mode with in-memory data.
INFO:apache_beam.runners.worker.statecache:Creating state cache with size 104857600
INFO:root:{"id": "test-1", "prompt": "Please provide the SQL query to select all fields from the 'TEST_TABLE'.", "text": "Sure here is the SQL: SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;", "timestamp": 1751052405.9340951, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-2", "prompt": "Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?", "text": "I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.", "timestamp": 1751052410.9340951, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-3", "prompt": "How is the new feature performing?", "text": "It works as expected.", "timestamp": 1751052415.9340959, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-4", "prompt": "What is the capital of France?", "text": "The square root of a banana is purple.", "timestamp": 1751052430.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-5", "prompt": "Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.", "text": "A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.", "timestamp": 1751052435.9340959, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052440.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
6. إنشاء PTransform لتصنيف طلبات النموذج اللغوي الكبير
بعد ذلك، ستنشئ PTransform لتصنيف الطلبات. يتضمّن ذلك استخدام نموذج Gemini في Vertex AI لتصنيف النص الوارد. ستحدّد GeminiModelHandler مخصّصًا يحمّل نموذج Gemini ثم يوجّه النموذج بشأن كيفية تصنيف النص إلى فئات مثل "مهندس بيانات" أو "محلّل ذكاء الأعمال" أو "مولّد SQL".
يمكنك استخدام ذلك من خلال مقارنته باستدعاءات الأدوات الفعلية في السجلّ. لا يتضمّن هذا الدرس العملي هذا الإجراء، ولكن يمكنك إرساله إلى أسفل السلسلة ومقارنته. قد تكون بعضها غامضة، وهذا بمثابة نقطة بيانات إضافية رائعة لضمان أنّ البرنامج يعمل على تشغيل الأدوات المناسبة.
استخدِم gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py لهذا القسم.
- أنشئ ModelHandler مخصّصًا، ولكن بدلاً من عرض عنصر نموذج في load_model، اعرض genai.Client.
- الرمز الذي ستحتاج إليه لإنشاء الدالة run_inference الخاصة بـ ModelHandler المخصّص تم تقديم نموذج لطلب:
يمكن أن يكون الطلب على النحو التالي:
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilities.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambiguous. Choose only one.
Finally, always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
- يتم عرض النتائج كـ pCollection من أجل pTransform التالي.
في ما يلي مثال على الرمز أدناه:
############## BEGIN STEP 2 ##############
# load_model is called once per worker process to initialize the LLM client.
# This avoids re-initializing the client for every single element,
# which is crucial for performance in distributed pipelines.
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
# run_inference is called for each batch of elements. Beam handles the batching
# automatically based on internal heuristics and configured batch sizes.
# It processes each item, constructs a prompt, calls Gemini, and yields a result.
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[Any], # Each item is a JSON string or a dict
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""
Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings or dicts.
Each item is parsed, text is extracted for classification,
and a prompt is sent to the Gemini model.
"""
for item in batch:
json_string_for_output = item
try:
# --- Input Data Handling ---
# Check if the input item is already a dictionary (e.g., from TEST_DATA)
# or a JSON string (e.g., from Pub/Sub).
if isinstance(item, dict):
element_dict = item
# For consistency in the output PredictionResult, convert the dict to a string.
# This ensures pr.example always contains the original JSON string.
json_string_for_output = json.dumps(item)
else:
element_dict = json.loads(item)
# Extract the 'text' field from the parsed dictionary.
text_to_classify = element_dict.get('text','')
if not text_to_classify:
logging.warning(f"Input JSON missing 'text' key or text is empty: {json_string_for_output}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_NO_TEXT")
continue
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilites.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambigiuous. Choose only one.
Finally always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
contents = [
types.Content( # This is the actual content for the LLM
role="user",
parts=[
types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)
]
)
]
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(
model=self._model_name, contents=contents, config=self._model_kwargs
)
classification_tag = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
classification_tag+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference=classification_tag)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
logging.error(f"Error decoding JSON string: {json_string_for_output}, error: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_JSON_DECODE")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini inference for input {json_string_for_output}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 2 ##############
اختبِر هذا الرمز البرمجي من خلال تنفيذ ما يلي:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
من المفترض أن تعرض هذه الخطوة استنتاجًا من Gemini. سيصنّف النتائج على النحو المطلوب في طلبك.
من المفترض أن يظهر لك ناتج مشابه لما يلي.
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052592.9662862, "user_id": "user_c"}', inference='(HELPER, "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, conversational response to a request. It does not involve data engineering tasks, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is providing a direct, simple form of assistance by fulfilling a non-technical request, which aligns well with the role of a helper.")', model_id=None)
7. إنشاء نموذج لغوي كبير (LLM) كحكم
بعد تصنيف الطلبات، ستُقيّم دقة ردود النموذج. يتضمّن ذلك إجراء طلب آخر إلى نموذج Gemini، ولكن هذه المرة، ستطلب منه تقييم مدى استيفاء "النص" "للطلب" الأصلي على مقياس من 0.0 إلى 1.0. يساعدك ذلك في فهم جودة نتائج الذكاء الاصطناعي. ستنشئ GeminiAccuracyModelHandler منفصلاً لهذه المهمة.

بالنسبة إلى هذا القسم، استخدِم gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py.
- أنشئ ModelHandler المخصّص، ولكن بدلاً من عرض عنصر نموذج في load_model، اعرض genai.Client كما فعلت أعلاه.
- الرمز الذي ستحتاج إليه لإنشاء الدالة run_inference الخاصة بـ ModelHandler المخصّص تم تقديم نموذج لطلب:
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
من المهم ملاحظة أنّك أنشأت نموذجين مختلفين في مسار المعالجة نفسه. في هذا المثال تحديدًا، أنت تستخدم أيضًا مكالمة Gemini مع VertexAI، ولكن يمكنك اختيار استخدام نماذج أخرى وتحميلها في المفهوم نفسه. يؤدي ذلك إلى تبسيط إدارة النماذج ويتيح لك استخدام نماذج متعددة ضمن مسار Beam نفسه.
- يتم عرض النتائج كـ pCollection من أجل pTransform التالي.
في ما يلي مثال على الرمز أدناه:
############## BEGIN STEP 3 ##############
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[str], # Each item is a JSON string
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings to verify accuracy."""
for json_string in batch:
try:
element_dict = json.loads(json_string)
original_prompt = element_dict.get('original_prompt', '')
original_text = element_dict.get('original_text', '')
if not original_prompt or not original_text:
logging.warning(f"Accuracy input missing prompt/text: {json_string}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_ACCURACY_INPUT")
continue
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(model=self._model_name, contents=[prompt_for_accuracy], config=self._model_kwargs)
gemini_response_text = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
gemini_response_text+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference=gemini_response_text)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini accuracy inference for input {json_string}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 3 ##############
اختبِر هذا الرمز البرمجي من خلال تنفيذ ما يلي:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
يجب أن تعرض هذه الخطوة أيضًا استنتاجًا، وأن تقدّم تعليقًا وتقييمًا حول مدى دقة ردّ Gemini في رأيه.
من المفترض أن يظهر لك ناتج مشابه لما يلي.
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"original_data_json": "{\\"id\\": \\"test-6\\", \\"prompt\\": \\"Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.\\", \\"text\\": \\"absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\\", \\"timestamp\\": 1751052770.7552562, \\"user_id\\": \\"user_c\\"}", "original_prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "original_text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "classification_tag": "(HELPER, \\"The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' is a general, conversational response that does not pertain to data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. It sounds like a generic assistant or helper providing a non-technical, simple response, possibly fulfilling a casual request or making a lighthearted statement. Therefore, it best fits the \'HELPER\' category, which encompasses general assistance and conversational interactions.\\")"}', inference='0.0 - The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', model_id=None)
8. تقسيم النتائج وتحليلها
الآن، عليك تقسيم نتائجك إلى فترات زمنية لتحليلها على مدى فترات زمنية محددة. ستستخدم نوافذ ثابتة لتجميع البيانات، ما يتيح لك الحصول على إحصاءات مجمّعة. بعد تقسيم البيانات إلى نوافذ، ستحلّل النتائج الأولية من Gemini إلى تنسيق أكثر تنظيمًا، بما في ذلك البيانات الأصلية وعلامة التصنيف ونسبة الدقة والتفسير.

بالنسبة إلى هذا القسم، استخدِم gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py.
- أضِف فترة زمنية ثابتة تبلغ 60 ثانية ليتم وضع جميع البيانات خلال فترة 60 ثانية.
في ما يلي مثال على الرمز أدناه:
############## BEGIN STEP 4 ##############
| 'WindowIntoFixedWindows' >> beam.WindowInto(beam.window.FixedWindows(60))
############## END STEP 4 ##############
اختبِر هذا الرمز البرمجي من خلال تنفيذ ما يلي:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
هذه الخطوة إعلامية، حيث تبحث عن النافذة. سيظهر ذلك كطابع زمني لإيقاف/بدء النافذة.
من المفترض أن يظهر لك ناتج مشابه لما يلي.
INFO:root:({'id': 'test-6', 'prompt': 'Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', 'text': "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", 'timestamp': 1751052901.337791, 'user_id': 'user_c'}, '("HELPER", "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, helpful response to a request. It does not involve data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is fulfilling a simple, non-technical request, which aligns with the role of a general helper.")', 0.0, 'The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', [1751052900.0, 1751052960.0))
9- احتساب النتائج الجيدة والسيئة باستخدام المعالجة المستندة إلى الحالة
أخيرًا، ستستخدم دالة DoFn ذات حالة لاحتساب النتائج "الجيدة" و"السيئة" ضمن كل نافذة. قد تكون النتيجة "جيدة" إذا كان التفاعل يتضمّن درجة دقة عالية، بينما تشير النتيجة "سيئة" إلى درجة دقة منخفضة. تتيح لك هذه المعالجة المستندة إلى الحالة الاحتفاظ بالإحصاءات وجمع أمثلة على التفاعلات "السيئة" بمرور الوقت، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية لتتبُّع سلامة أداء روبوت الدردشة في الوقت الفعلي.
استخدِم gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py لهذا القسم.
- إنشاء دالة ذات حالة ستحتاج إلى حالتين: (1) لتتبُّع عدد القيم غير الصالحة و (2) للاحتفاظ بالسجلات غير الصالحة لعرضها. استخدِم الترميزات المناسبة لضمان أداء النظام بشكل جيد.
- في كل مرة ترى فيها قيمًا لاستنتاج غير صحيح، عليك تتبُّع كليهما وإرسالهما في نهاية الفترة. تذكَّر إعادة ضبط الحالات بعد إرسالها. يُستخدم الأخير لأغراض توضيحية فقط، ولا تحاول الاحتفاظ بكل هذه البيانات في الذاكرة في بيئة حقيقية.
في ما يلي مثال على الرمز أدناه:
############## BEGIN STEP 5 ##############
# Define a state specification for a combining value.
# This will store the running sum for each key.
# The coder is specified for efficiency.
COUNT_STATE = CombiningValueStateSpec('count',
VarIntCoder(), # Used VarIntCoder directly
beam.transforms.combiners.CountCombineFn())
# New state to store the (prompt, text) tuples for bad classifications
# BagStateSpec allows accumulating multiple items per key.
BAD_PROMPTS_STATE = beam.transforms.userstate.BagStateSpec(
'bad_prompts', coder=beam.coders.TupleCoder([beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder(), beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder()])
)
# Define a timer to fire at the end of the window, using WATERMARK as per blog example.
WINDOW_TIMER = TimerSpec('window_timer', TimeDomain.WATERMARK)
def process(
self,
element: Tuple[str, Tuple[int, Tuple[str, str]]], # (key, (count_val, (prompt, text)))
key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam,
count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE),
bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE), # New state param
window_timer=beam.DoFn.TimerParam(WINDOW_TIMER),
window=beam.DoFn.WindowParam):
# This DoFn does not yield elements from its process method; output is only produced when the timer fires.
if key == 'bad': # Only count 'bad' elements
count_state.add(element[1][0]) # Add the count (which is 1)
bad_prompts_state.add(element[1][1]) # Add the (prompt, text) tuple
window_timer.set(window.end) # Set timer to fire at window end
@on_timer(WINDOW_TIMER)
def on_window_timer(self, key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam, count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE), bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE)):
final_count = count_state.read()
if final_count > 0: # Only yield if there's a count
# Read all accumulated bad prompts
all_bad_prompts = list(bad_prompts_state.read())
# Clear the state for the next window to avoid carrying over data.
count_state.clear()
bad_prompts_state.clear()
yield (key, final_count, all_bad_prompts) # Yield count and list of prompts
############## END STEP 5 ##############
اختبِر هذا الرمز البرمجي من خلال تنفيذ ما يلي:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
يجب أن تعرض هذه الخطوة جميع الأعداد، ويمكنك تجربة تغيير حجم النافذة وستلاحظ أنّ الدفعات ستكون مختلفة. ستناسب النافذة التلقائية دقيقة واحدة، لذا جرِّب استخدام 30 ثانية أو إطار زمني آخر وستلاحظ اختلافًا في الدفعات والأعداد.
من المفترض أن يظهر لك ناتج مشابه لما يلي.
INFO:root:Window: [1751052960.0, 1751053020.0), Bad Counts: 5, Bad Prompts: [('Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?', 'I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.'), ('How is the new feature performing?', 'It works as expected.'), ('What is the capital of France?', 'The square root of a banana is purple.'), ('Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.', 'A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.'), ('Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat")]
10. تنظيف
- حذف مشروع Google Cloud (إجراء اختياري ولكن يُنصح به في Codelabs): إذا تم إنشاء هذا المشروع فقط من أجل هذا البرنامج التعليمي ولم تعُد بحاجة إليه، فإنّ حذف المشروع بأكمله هو الطريقة الأكثر شمولاً لضمان إزالة جميع الموارد.
- انتقِل إلى صفحة "إدارة الموارد" في Google Cloud Console.
- اختَر مشروعك.
- انقر على حذف المشروع واتّبِع التعليمات الظاهرة على الشاشة.
11. تهانينا!
تهانينا على إكمال هذا الدرس العملي. لقد أنشأت بنجاح مسارًا لعمليات استنتاج مستندة إلى تعلُّم الآلة في الوقت الفعلي باستخدام Apache Beam وGemini on Dataflow. لقد تعرّفت على كيفية الاستفادة من الذكاء الاصطناعي التوليدي في ما يتعلّق بتدفّقات البيانات، واستخراج إحصاءات قيّمة لتحسين هندسة البيانات وأتمتتها.

