1. Pengantar
Dalam lanskap data yang bergerak cepat saat ini, insight real-time sangat penting untuk membuat keputusan yang tepat. Codelab ini akan memandu Anda dalam membuat pipeline evaluasi real-time. Kita akan mulai dengan memanfaatkan framework Apache Beam, yang menawarkan model pemrograman terpadu untuk data batch dan streaming. Hal ini menyederhanakan pengembangan pipeline secara signifikan dengan menghilangkan logika komputasi terdistribusi yang kompleks yang harus Anda buat dari awal. Setelah pipeline ditentukan menggunakan Beam, Anda dapat menjalankannya dengan lancar di Google Cloud Dataflow, layanan terkelola sepenuhnya yang memberikan skala dan performa yang tak tertandingi untuk kebutuhan pemrosesan data Anda.
Dalam codelab ini, Anda akan mempelajari cara merancang pipeline Apache Beam yang skalabel untuk inferensi machine learning, mengembangkan ModelHandler kustom untuk mengintegrasikan model Gemini Vertex AI, memanfaatkan teknik pembuatan perintah untuk klasifikasi teks cerdas dalam aliran data, serta men-deploy dan mengoperasikan pipeline inferensi ML streaming ini di Google Cloud Dataflow. Pada akhirnya, Anda akan mendapatkan insight berharga tentang penerapan machine learning untuk pemahaman data real-time dan evaluasi berkelanjutan dalam alur kerja engineering, terutama untuk mempertahankan AI percakapan yang andal dan berfokus pada pengguna.
Skenario
Perusahaan Anda telah membuat agen data. Agen data Anda, yang dibuat dengan Agent Development Kit (ADK), dilengkapi dengan berbagai kemampuan khusus untuk membantu tugas terkait data. Bayangkan Gemini sebagai asisten data serbaguna, yang siap menangani berbagai permintaan, mulai dari bertindak sebagai Analis BI untuk membuat laporan yang berwawasan, hingga sebagai Engineer Data yang membantu Anda membangun pipeline data yang andal, atau sebagai Pembuat SQL yang membuat pernyataan SQL yang presisi, dan banyak lagi. Setiap interaksi yang dilakukan agen ini, setiap respons yang dihasilkannya, akan otomatis disimpan di Firestore. Namun, mengapa kita memerlukan pipeline di sini?
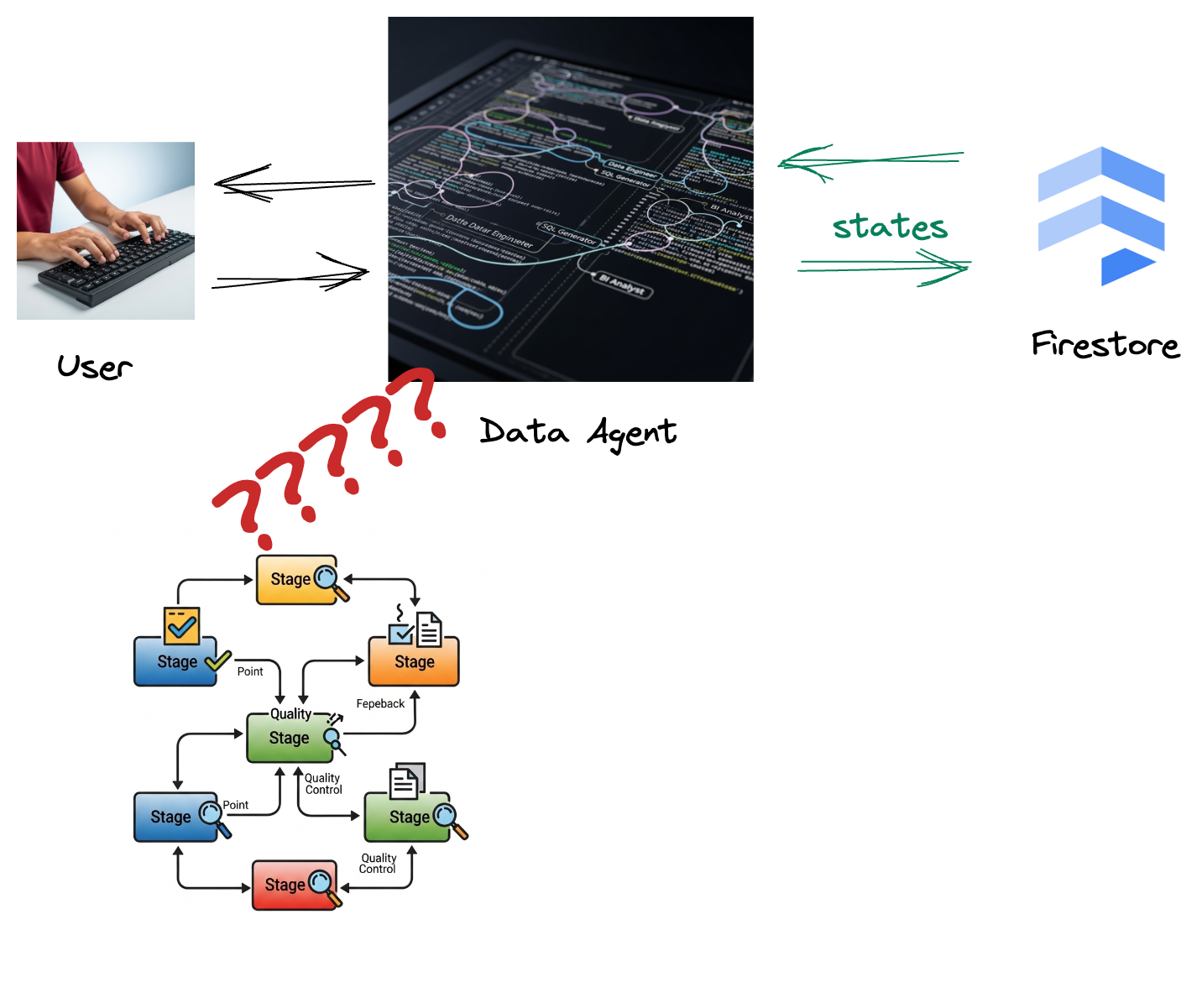
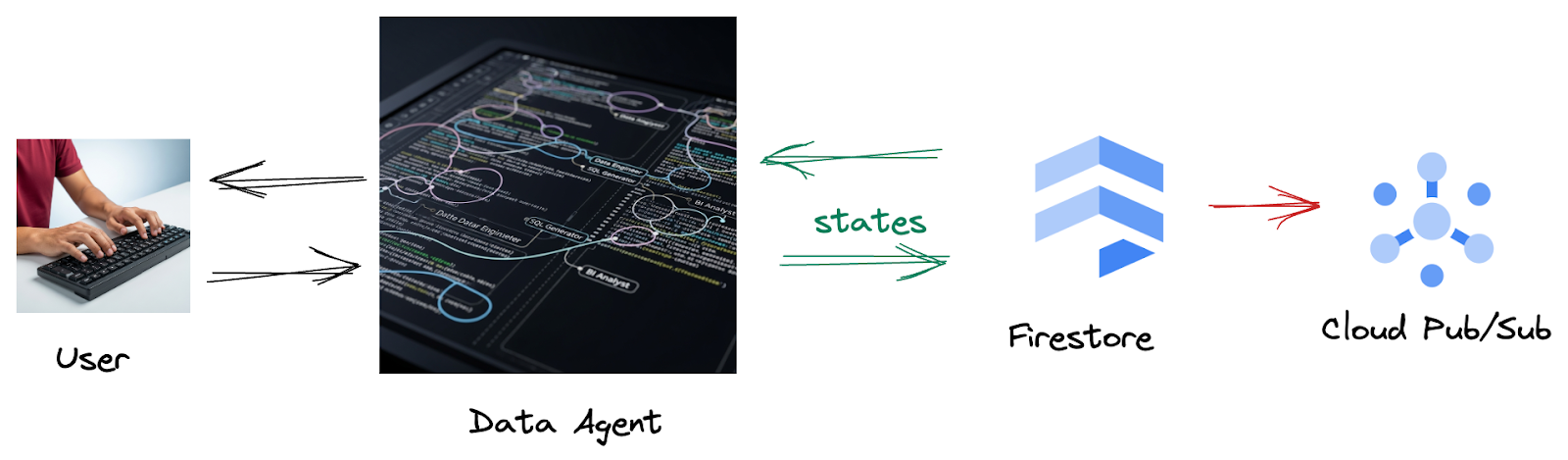
Karena dari Firestore, pemicu mengirimkan data interaksi ini dengan lancar ke Pub/Sub, sehingga kami dapat segera memproses dan menganalisis percakapan penting ini secara real-time.
2. Sebelum memulai
Membuat project
- Di Konsol Google Cloud, di halaman pemilih project, pilih atau buat project Google Cloud.
- Pastikan penagihan diaktifkan untuk project Cloud Anda. Pelajari cara memeriksa apakah penagihan telah diaktifkan pada suatu project.
- Aktifkan Cloud Shell dengan mengklik link ini. Anda dapat beralih antara Terminal Cloud Shell (untuk menjalankan perintah cloud) dan Editor (untuk membangun project) dengan mengklik tombol yang sesuai dari Cloud Shell.
- Setelah terhubung ke Cloud Shell, Anda dapat memeriksa bahwa Anda sudah diautentikasi dan project sudah ditetapkan ke project ID Anda menggunakan perintah berikut:
gcloud auth list
- Jalankan perintah berikut di Cloud Shell untuk mengonfirmasi bahwa perintah gcloud mengetahui project Anda.
gcloud config list project
- Jika project Anda belum ditetapkan, gunakan perintah berikut untuk menetapkannya:
export PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
- Aktifkan API yang diperlukan melalui perintah yang ditampilkan di bawah. Proses ini mungkin memerlukan waktu beberapa menit, jadi harap bersabar.
gcloud services enable \
dataflow.googleapis.com \
pubsub.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com
- Pastikan Anda memiliki Python 3.10+
- Menginstal Paket Python
Instal library Python yang diperlukan untuk Apache Beam, Google Cloud Vertex AI, dan Google Generative AI di lingkungan Cloud Shell Anda.
pip install apache-beam[gcp] google-genai
- Clone repositori github dan beralih ke direktori demo.
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos
cd devrel-demos/data-analytics/beam_as_eval
Baca dokumentasi untuk mempelajari perintah gcloud dan penggunaannya.
3. Cara menggunakan repositori GitHub yang disediakan
Repositori GitHub yang terkait dengan codelab ini, yang dapat ditemukan di https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos/tree/main/data-analytics/beam_as_eval , disusun untuk memfasilitasi pengalaman belajar yang terpandu. File ini berisi kode kerangka yang selaras dengan setiap bagian codelab yang berbeda, sehingga memastikan progres yang jelas dalam mempelajari materi.
Di dalam repositori, Anda akan menemukan dua folder utama: "complete" dan "incomplete". Folder "complete" berisi kode yang berfungsi penuh untuk setiap langkah, sehingga Anda dapat menjalankan dan mengamati output yang diinginkan. Sebaliknya, folder "incomplete" menyediakan kode dari langkah-langkah sebelumnya, sehingga bagian tertentu yang ditandai antara ##### START STEP <NUMBER> ##### dan ##### END STEP <NUMBER> ##### dapat Anda selesaikan sebagai bagian dari latihan. Struktur ini memungkinkan Anda membangun pengetahuan sebelumnya sambil berpartisipasi aktif dalam tantangan pengodean.
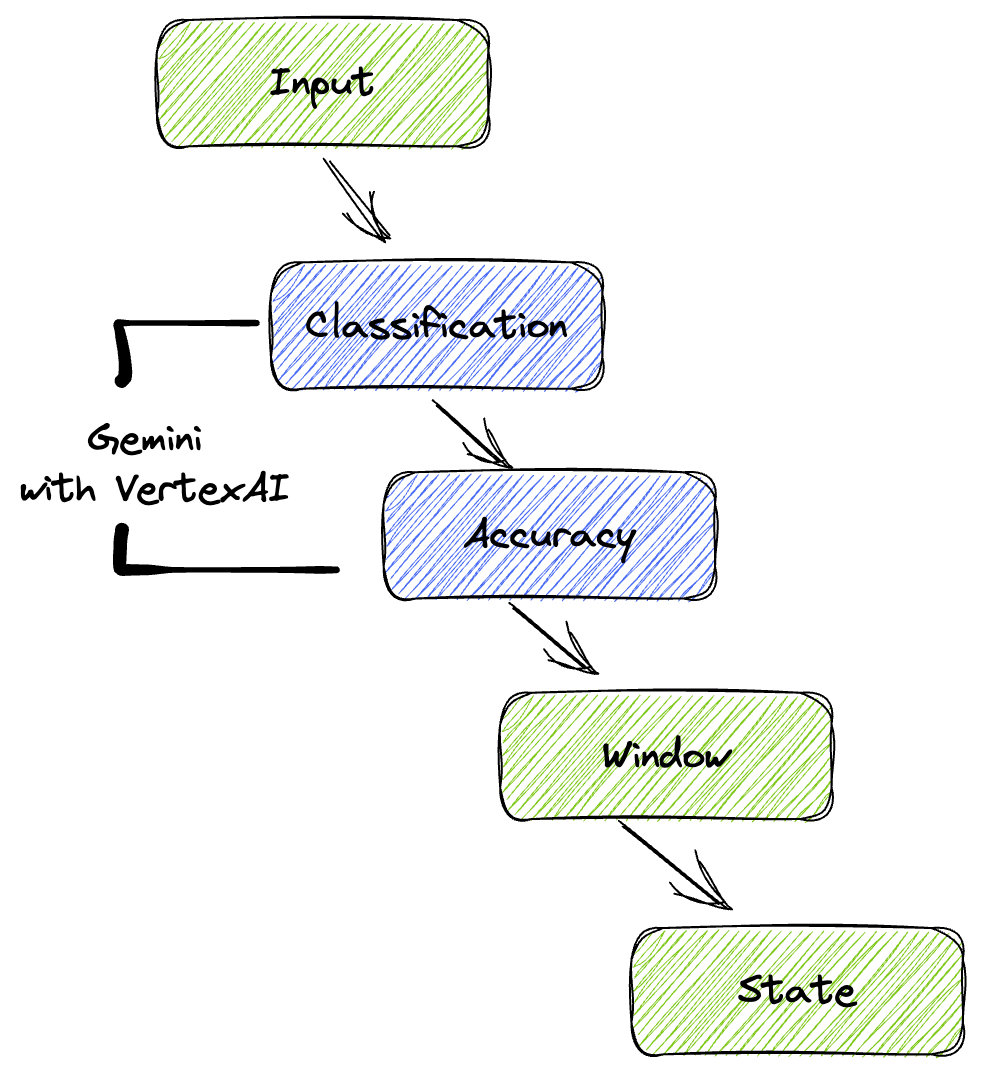
4. Ringkasan Arsitektur
Pipeline kami menyediakan pola yang andal dan skalabel untuk mengintegrasikan inferensi ML ke dalam aliran data. Berikut cara kerja komponen-komponen tersebut:
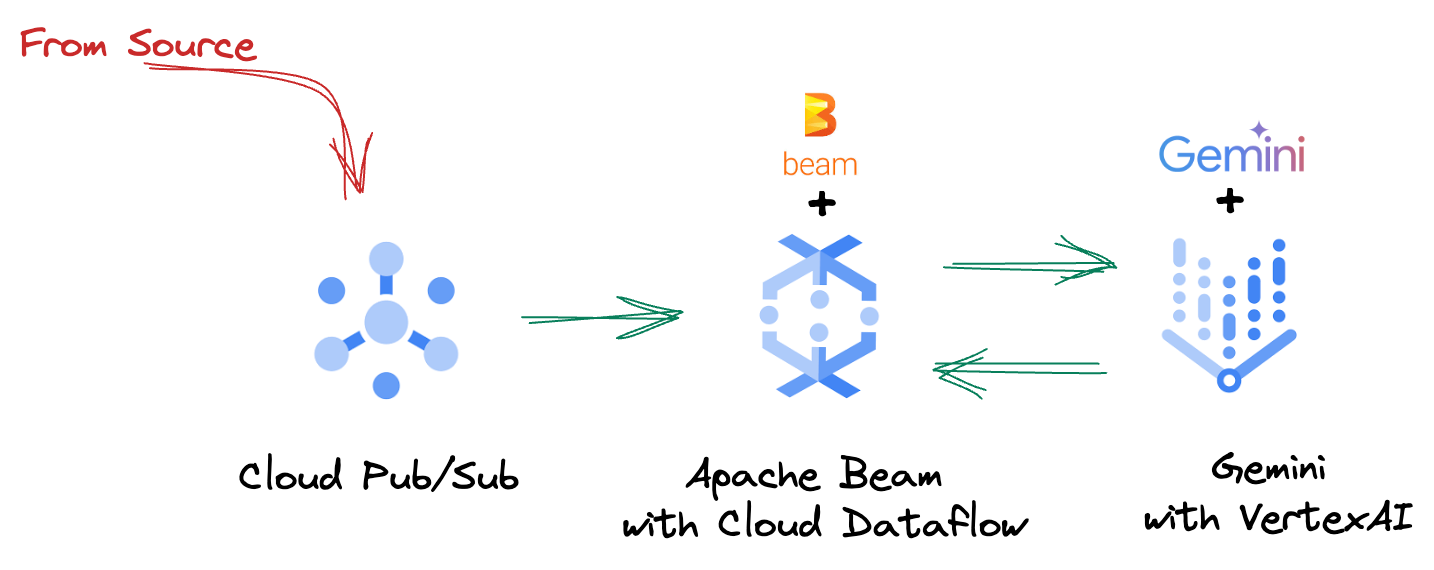
Di pipeline Beam, Anda akan mengodekan beberapa input secara kondisional, lalu memuat model kustom dengan transformasi siap pakai RunInference. Meskipun Anda menggunakan Gemini dengan Vertex AI dalam contoh, hal ini menunjukkan cara Anda pada dasarnya membuat beberapa ModelHandler agar sesuai dengan jumlah model yang Anda miliki. Terakhir, Anda akan menggunakan DoFn stateful untuk melacak peristiwa dan memancarkannya secara terkontrol.
5. Menyerap Data
Pertama, Anda akan menyiapkan pipeline untuk menyerap data. Anda akan menggunakan Pub/Sub untuk streaming real-time, tetapi untuk mempermudah pengembangan, Anda juga akan membuat mode pengujian. test_mode ini memungkinkan Anda menjalankan pipeline secara lokal menggunakan data sampel yang telah ditentukan sebelumnya, sehingga Anda tidak memerlukan streaming Pub/Sub langsung untuk melihat apakah pipeline Anda berfungsi.
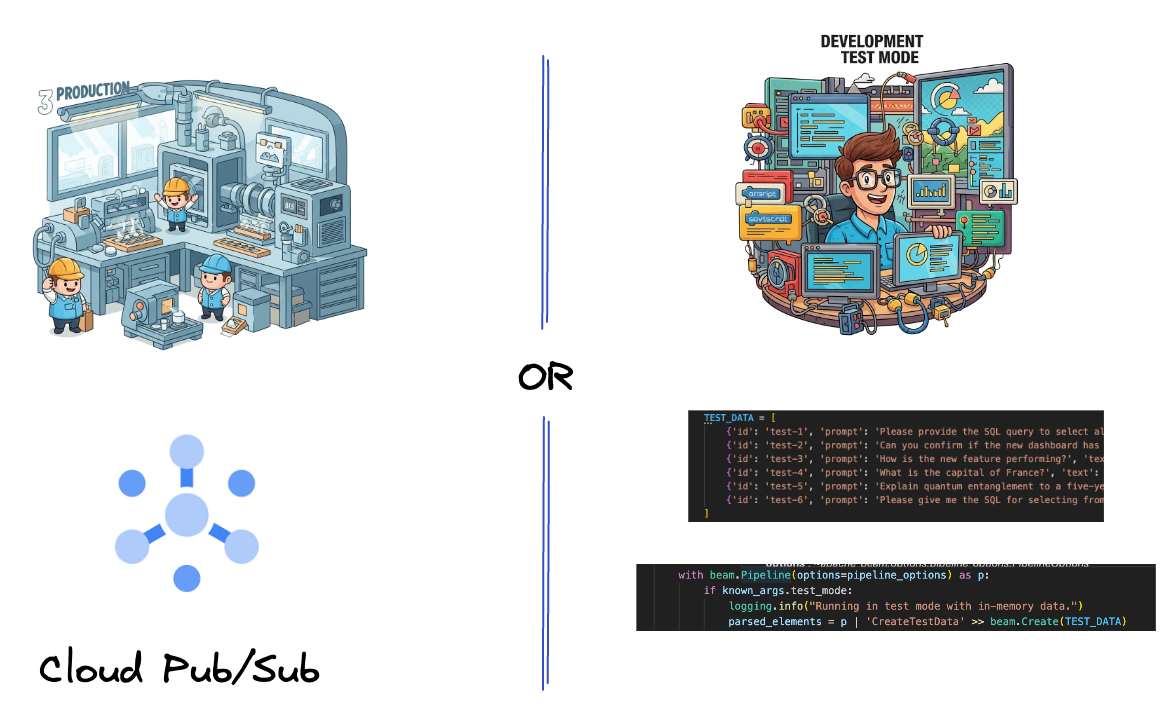
Untuk bagian ini, gunakan gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py.
- Dengan menggunakan objek pipeline p yang disediakan, kodekan input Pub/Sub dan tulis output sebagai pCollection.
- Selain itu, gunakan tanda untuk menentukan apakah TEST_MODE telah ditetapkan.
- Jika TEST_MODE disetel, beralihlah ke penguraian array TEST_DATA sebagai input.
Hal ini tidak diperlukan, tetapi akan membantu mempersingkat proses sehingga Anda tidak perlu melibatkan Pub/Sub di tahap awal ini.
Berikut adalah contoh kode di bawah:
# Step 1
# Ingesting Data
# Write your data ingestion step here.
############## BEGIN STEP 1 ##############
if known_args.test_mode:
logging.info("Running in test mode with in-memory data.")
parsed_elements = p | 'CreateTestData' >> beam.Create(TEST_DATA)
# Convert dicts to JSON strings and add timestamps for test mode
parsed_elements = parsed_elements | 'ConvertTestDictsToJsonAndAddTimestamps' >> beam.Map(
lambda x: beam.window.TimestampedValue(json.dumps(x), x['timestamp'])
)
else:
logging.info(f"Reading from Pub/Sub topic: {known_args.input_topic}")
parsed_elements = (
p
| 'ReadFromPubSub' >> beam.io.ReadFromPubSub(
topic=known_args.input_topic
).with_output_types(bytes)
| 'DecodeBytes' >> beam.Map(lambda b: b.decode('utf-8')) # Output is JSON string
# Extract timestamp from JSON string for Pub/Sub messages
| 'AddTimestampsFromParsedJson' >> beam.Map(lambda s: beam.window.TimestampedValue(s, json.loads(s)['timestamp']))
)
############## END STEP 1 ##############
Uji kode ini dengan menjalankan:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Langkah ini akan memancarkan semua data, mencatatnya ke stdout.
Anda akan mendapatkan output seperti berikut.
INFO:root:Running in test mode with in-memory data.
INFO:apache_beam.runners.worker.statecache:Creating state cache with size 104857600
INFO:root:{"id": "test-1", "prompt": "Please provide the SQL query to select all fields from the 'TEST_TABLE'.", "text": "Sure here is the SQL: SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;", "timestamp": 1751052405.9340951, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-2", "prompt": "Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?", "text": "I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.", "timestamp": 1751052410.9340951, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-3", "prompt": "How is the new feature performing?", "text": "It works as expected.", "timestamp": 1751052415.9340959, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-4", "prompt": "What is the capital of France?", "text": "The square root of a banana is purple.", "timestamp": 1751052430.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-5", "prompt": "Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.", "text": "A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.", "timestamp": 1751052435.9340959, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052440.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
6. Membangun PTransform untuk Klasifikasi Perintah LLM
Selanjutnya, Anda akan membuat PTransform untuk mengklasifikasikan perintah. Hal ini melibatkan penggunaan model Gemini Vertex AI untuk mengategorikan teks yang masuk. Anda akan menentukan GeminiModelHandler kustom yang memuat model Gemini, lalu menginstruksikan model tentang cara mengklasifikasikan teks ke dalam kategori seperti "DATA ENGINEER", "BI ANALYST", atau "SQL GENERATOR".
Anda akan menggunakannya dengan membandingkan panggilan alat sebenarnya dalam log. Hal ini tidak dibahas dalam codelab ini, tetapi Anda dapat mengirimkannya ke hilir dan membandingkannya. Mungkin ada beberapa yang ambigu dan hal ini berfungsi sebagai titik data tambahan yang bagus untuk memastikan agen Anda memanggil alat yang tepat.
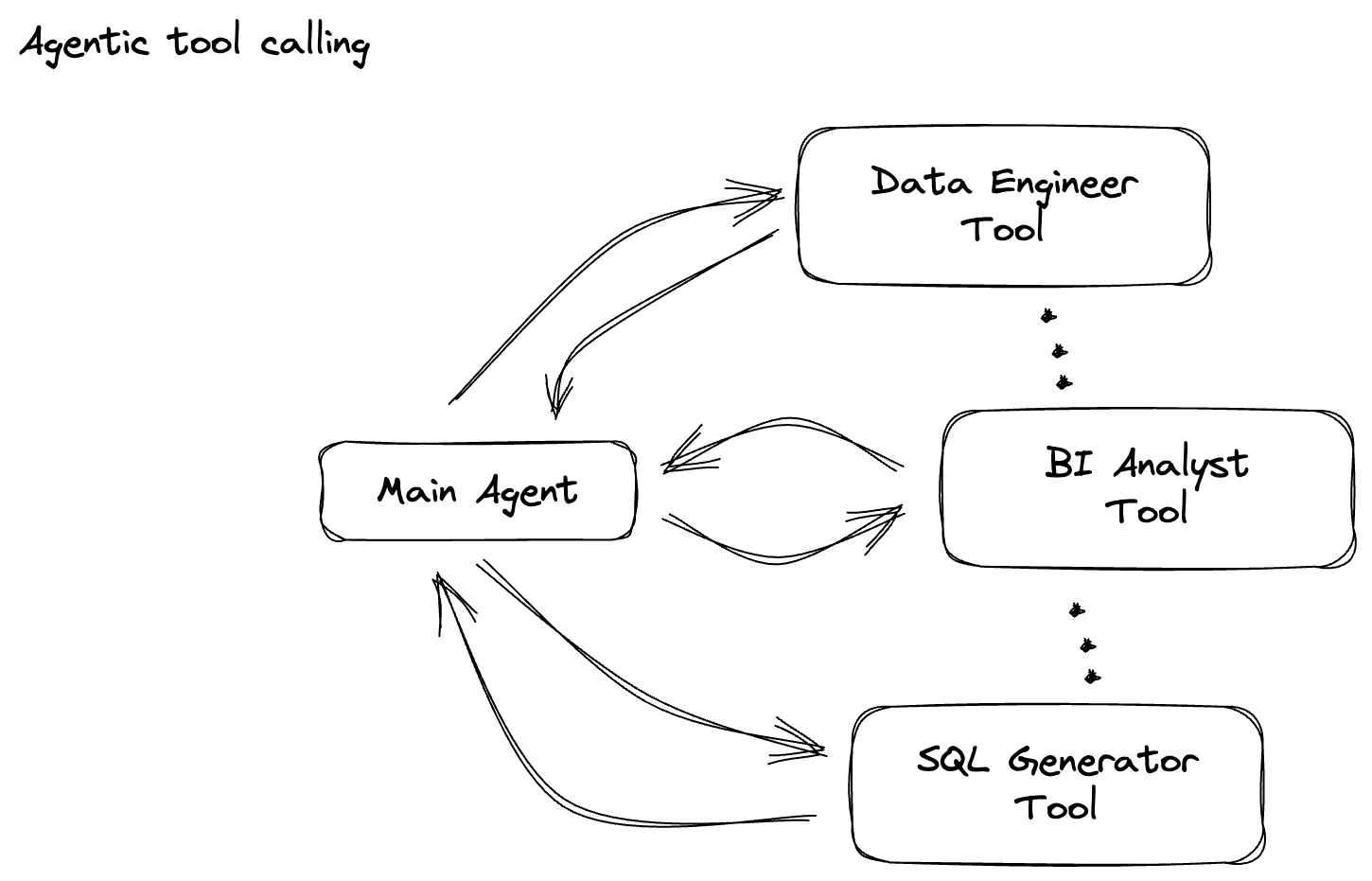
Untuk bagian ini, gunakan gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py.
- Buat ModelHandler kustom Anda; namun, alih-alih menampilkan objek model di load_model, tampilkan genai.Client.
- Kode yang akan Anda perlukan untuk membuat fungsi run_inference ModelHandler kustom. Contoh perintah telah diberikan:
Perintahnya dapat berupa seperti berikut:
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilities.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambiguous. Choose only one.
Finally, always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
- Menghasilkan hasil sebagai pCollection untuk pTransform berikutnya.
Berikut adalah contoh kode di bawah:
############## BEGIN STEP 2 ##############
# load_model is called once per worker process to initialize the LLM client.
# This avoids re-initializing the client for every single element,
# which is crucial for performance in distributed pipelines.
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
# run_inference is called for each batch of elements. Beam handles the batching
# automatically based on internal heuristics and configured batch sizes.
# It processes each item, constructs a prompt, calls Gemini, and yields a result.
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[Any], # Each item is a JSON string or a dict
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""
Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings or dicts.
Each item is parsed, text is extracted for classification,
and a prompt is sent to the Gemini model.
"""
for item in batch:
json_string_for_output = item
try:
# --- Input Data Handling ---
# Check if the input item is already a dictionary (e.g., from TEST_DATA)
# or a JSON string (e.g., from Pub/Sub).
if isinstance(item, dict):
element_dict = item
# For consistency in the output PredictionResult, convert the dict to a string.
# This ensures pr.example always contains the original JSON string.
json_string_for_output = json.dumps(item)
else:
element_dict = json.loads(item)
# Extract the 'text' field from the parsed dictionary.
text_to_classify = element_dict.get('text','')
if not text_to_classify:
logging.warning(f"Input JSON missing 'text' key or text is empty: {json_string_for_output}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_NO_TEXT")
continue
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilites.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambigiuous. Choose only one.
Finally always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
contents = [
types.Content( # This is the actual content for the LLM
role="user",
parts=[
types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)
]
)
]
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(
model=self._model_name, contents=contents, config=self._model_kwargs
)
classification_tag = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
classification_tag+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference=classification_tag)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
logging.error(f"Error decoding JSON string: {json_string_for_output}, error: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_JSON_DECODE")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini inference for input {json_string_for_output}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 2 ##############
Uji kode ini dengan menjalankan:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Langkah ini akan menampilkan inferensi dari Gemini. Model ini akan mengklasifikasikan hasil sesuai permintaan perintah Anda.
Anda akan mendapatkan output seperti berikut.
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052592.9662862, "user_id": "user_c"}', inference='(HELPER, "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, conversational response to a request. It does not involve data engineering tasks, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is providing a direct, simple form of assistance by fulfilling a non-technical request, which aligns well with the role of a helper.")', model_id=None)
7. Membangun LLM sebagai Penilai
Setelah mengklasifikasikan perintah, Anda akan mengevaluasi akurasi respons model. Hal ini melibatkan panggilan lain ke model Gemini, tetapi kali ini, Anda akan meminta model tersebut untuk menilai seberapa baik "teks" memenuhi "perintah" asli dalam skala 0,0 hingga 1,0. Hal ini membantu Anda memahami kualitas output AI. Anda akan membuat GeminiAccuracyModelHandler terpisah untuk tugas ini.

Untuk bagian ini, gunakan gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py.
- Buat ModelHandler kustom Anda; namun, alih-alih menampilkan objek model di load_model, tampilkan genai.Client seperti yang Anda lakukan di atas.
- Kode yang akan Anda perlukan untuk membuat fungsi run_inference ModelHandler kustom. Contoh perintah telah diberikan:
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
Satu hal yang perlu diperhatikan di sini adalah Anda pada dasarnya telah membuat dua model berbeda dalam pipeline yang sama. Dalam contoh khusus ini, Anda juga menggunakan panggilan Gemini dengan VertexAI, tetapi dengan konsep yang sama, Anda dapat memilih untuk menggunakan dan memuat model lain. Hal ini menyederhanakan pengelolaan model dan memungkinkan Anda menggunakan beberapa model dalam pipeline Beam yang sama.
- Menghasilkan hasil sebagai pCollection untuk pTransform berikutnya.
Berikut adalah contoh kode di bawah:
############## BEGIN STEP 3 ##############
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[str], # Each item is a JSON string
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings to verify accuracy."""
for json_string in batch:
try:
element_dict = json.loads(json_string)
original_prompt = element_dict.get('original_prompt', '')
original_text = element_dict.get('original_text', '')
if not original_prompt or not original_text:
logging.warning(f"Accuracy input missing prompt/text: {json_string}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_ACCURACY_INPUT")
continue
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(model=self._model_name, contents=[prompt_for_accuracy], config=self._model_kwargs)
gemini_response_text = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
gemini_response_text+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference=gemini_response_text)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini accuracy inference for input {json_string}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 3 ##############
Uji kode ini dengan menjalankan:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Langkah ini juga harus menampilkan inferensi, memberikan komentar, dan menampilkan skor tentang seberapa akurat respons alat menurut Gemini.
Anda akan mendapatkan output seperti berikut.
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"original_data_json": "{\\"id\\": \\"test-6\\", \\"prompt\\": \\"Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.\\", \\"text\\": \\"absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\\", \\"timestamp\\": 1751052770.7552562, \\"user_id\\": \\"user_c\\"}", "original_prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "original_text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "classification_tag": "(HELPER, \\"The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' is a general, conversational response that does not pertain to data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. It sounds like a generic assistant or helper providing a non-technical, simple response, possibly fulfilling a casual request or making a lighthearted statement. Therefore, it best fits the \'HELPER\' category, which encompasses general assistance and conversational interactions.\\")"}', inference='0.0 - The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', model_id=None)
8. Membuat Jendela dan Menganalisis Hasil
Sekarang, Anda akan melihat hasil untuk menganalisisnya selama interval waktu tertentu. Anda akan menggunakan jendela tetap untuk mengelompokkan data, sehingga Anda bisa mendapatkan insight gabungan. Setelah melakukan windowing, Anda akan mengurai output mentah dari Gemini ke dalam format yang lebih terstruktur, termasuk data asli, tag klasifikasi, skor akurasi, dan penjelasan.

Untuk bagian ini, gunakan gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py.
- Tambahkan dalam jangka waktu tetap 60 detik sehingga semua data ditempatkan dalam jangka waktu 60 detik.
Berikut adalah contoh kode di bawah:
############## BEGIN STEP 4 ##############
| 'WindowIntoFixedWindows' >> beam.WindowInto(beam.window.FixedWindows(60))
############## END STEP 4 ##############
Uji kode ini dengan menjalankan:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Langkah ini bersifat informatif, Anda mencari jendela Anda. Ini akan ditampilkan sebagai stempel waktu mulai/berhenti jendela.
Anda akan mendapatkan output seperti berikut.
INFO:root:({'id': 'test-6', 'prompt': 'Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', 'text': "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", 'timestamp': 1751052901.337791, 'user_id': 'user_c'}, '("HELPER", "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, helpful response to a request. It does not involve data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is fulfilling a simple, non-technical request, which aligns with the role of a general helper.")', 0.0, 'The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', [1751052900.0, 1751052960.0))
9. Menghitung Hasil Baik dan Buruk dengan Pemrosesan Stateful
Terakhir, Anda akan menggunakan DoFn stateful untuk menghitung hasil "baik" dan "buruk" dalam setiap jendela. Hasil "baik" mungkin berupa interaksi dengan skor akurasi tinggi, sedangkan hasil "buruk" menunjukkan skor rendah. Pemrosesan stateful ini memungkinkan Anda mempertahankan jumlah dan bahkan mengumpulkan contoh interaksi "buruk" dari waktu ke waktu, yang sangat penting untuk memantau kondisi dan performa chatbot Anda secara real time.
Untuk bagian ini, gunakan gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py.
- Buat fungsi stateful. Anda akan memerlukan dua status: (1) untuk melacak jumlah hitungan buruk dan (2) menyimpan catatan buruk untuk ditampilkan. Gunakan coder yang tepat untuk memastikan sistem dapat berfungsi dengan baik.
- Setiap kali Anda melihat nilai untuk inferensi yang buruk, Anda ingin melacak keduanya dan memancarkannya di akhir jendela. Jangan lupa mereset status setelah memancarkan. Yang terakhir hanya untuk tujuan ilustrasi, jangan mencoba menyimpan semuanya dalam memori di lingkungan yang sebenarnya.
Berikut adalah contoh kode di bawah:
############## BEGIN STEP 5 ##############
# Define a state specification for a combining value.
# This will store the running sum for each key.
# The coder is specified for efficiency.
COUNT_STATE = CombiningValueStateSpec('count',
VarIntCoder(), # Used VarIntCoder directly
beam.transforms.combiners.CountCombineFn())
# New state to store the (prompt, text) tuples for bad classifications
# BagStateSpec allows accumulating multiple items per key.
BAD_PROMPTS_STATE = beam.transforms.userstate.BagStateSpec(
'bad_prompts', coder=beam.coders.TupleCoder([beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder(), beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder()])
)
# Define a timer to fire at the end of the window, using WATERMARK as per blog example.
WINDOW_TIMER = TimerSpec('window_timer', TimeDomain.WATERMARK)
def process(
self,
element: Tuple[str, Tuple[int, Tuple[str, str]]], # (key, (count_val, (prompt, text)))
key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam,
count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE),
bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE), # New state param
window_timer=beam.DoFn.TimerParam(WINDOW_TIMER),
window=beam.DoFn.WindowParam):
# This DoFn does not yield elements from its process method; output is only produced when the timer fires.
if key == 'bad': # Only count 'bad' elements
count_state.add(element[1][0]) # Add the count (which is 1)
bad_prompts_state.add(element[1][1]) # Add the (prompt, text) tuple
window_timer.set(window.end) # Set timer to fire at window end
@on_timer(WINDOW_TIMER)
def on_window_timer(self, key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam, count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE), bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE)):
final_count = count_state.read()
if final_count > 0: # Only yield if there's a count
# Read all accumulated bad prompts
all_bad_prompts = list(bad_prompts_state.read())
# Clear the state for the next window to avoid carrying over data.
count_state.clear()
bad_prompts_state.clear()
yield (key, final_count, all_bad_prompts) # Yield count and list of prompts
############## END STEP 5 ##############
Uji kode ini dengan menjalankan:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Langkah ini akan menghasilkan semua jumlah, bereksperimenlah dengan ukuran jendela dan Anda akan melihat bahwa batchnya akan berbeda. Rentang waktu default akan sesuai dalam satu menit, jadi coba gunakan 30 detik atau jangka waktu lain dan Anda akan melihat batch dan jumlah yang berbeda.
Anda akan mendapatkan output seperti berikut.
INFO:root:Window: [1751052960.0, 1751053020.0), Bad Counts: 5, Bad Prompts: [('Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?', 'I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.'), ('How is the new feature performing?', 'It works as expected.'), ('What is the capital of France?', 'The square root of a banana is purple.'), ('Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.', 'A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.'), ('Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat")]
10. Pembersihan
- Hapus Project Google Cloud (Opsional, tetapi Direkomendasikan untuk Codelab): Jika project ini dibuat hanya untuk codelab ini dan Anda tidak lagi membutuhkannya, menghapus seluruh project adalah cara paling menyeluruh untuk memastikan semua resource dihapus.
- Buka halaman Manage Resources di Konsol Google Cloud.
- Pilih project Anda.
- Klik Hapus Project dan ikuti petunjuk di layar.
11. Selamat!
Selamat, Anda telah menyelesaikan codelab. Anda telah berhasil membangun pipeline inferensi ML real-time menggunakan Apache Beam dan Gemini di Dataflow. Anda telah mempelajari cara menghadirkan kecanggihan AI generatif ke aliran data Anda, mengekstrak insight berharga untuk rekayasa data yang lebih cerdas dan otomatis.

