1. Giới thiệu
Trong bối cảnh dữ liệu có tốc độ phát triển nhanh chóng như hiện nay, thông tin chi tiết theo thời gian thực là yếu tố quan trọng để đưa ra quyết định sáng suốt. Lớp học lập trình này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách tạo một quy trình đánh giá theo thời gian thực. Chúng ta sẽ bắt đầu bằng cách tận dụng khung Apache Beam. Khung này cung cấp một mô hình lập trình hợp nhất cho cả dữ liệu hàng loạt và dữ liệu phát trực tuyến. Điều này giúp đơn giản hoá đáng kể quá trình phát triển quy trình bằng cách trừu tượng hoá logic điện toán phân tán phức tạp mà bạn sẽ phải xây dựng từ đầu. Sau khi xác định quy trình bằng Beam, bạn sẽ chạy quy trình đó một cách liền mạch trên Google Cloud Dataflow, một dịch vụ được quản lý toàn diện, mang lại quy mô và hiệu suất vượt trội cho nhu cầu xử lý dữ liệu của bạn.
Trong lớp học lập trình này, bạn sẽ tìm hiểu cách thiết kế một quy trình Apache Beam có khả năng mở rộng để suy luận bằng học máy, phát triển một ModelHandler tuỳ chỉnh để tích hợp mô hình Gemini của Vertex AI, tận dụng kỹ thuật tạo câu lệnh để phân loại văn bản thông minh trong luồng dữ liệu, đồng thời triển khai và vận hành quy trình suy luận ML truyền trực tuyến này trên Google Cloud Dataflow. Đến cuối khoá học, bạn sẽ có được thông tin chi tiết có giá trị về việc áp dụng học máy để hiểu dữ liệu theo thời gian thực và đánh giá liên tục trong quy trình công việc kỹ thuật, đặc biệt là để duy trì AI đàm thoại mạnh mẽ và lấy người dùng làm trung tâm.
Trường hợp
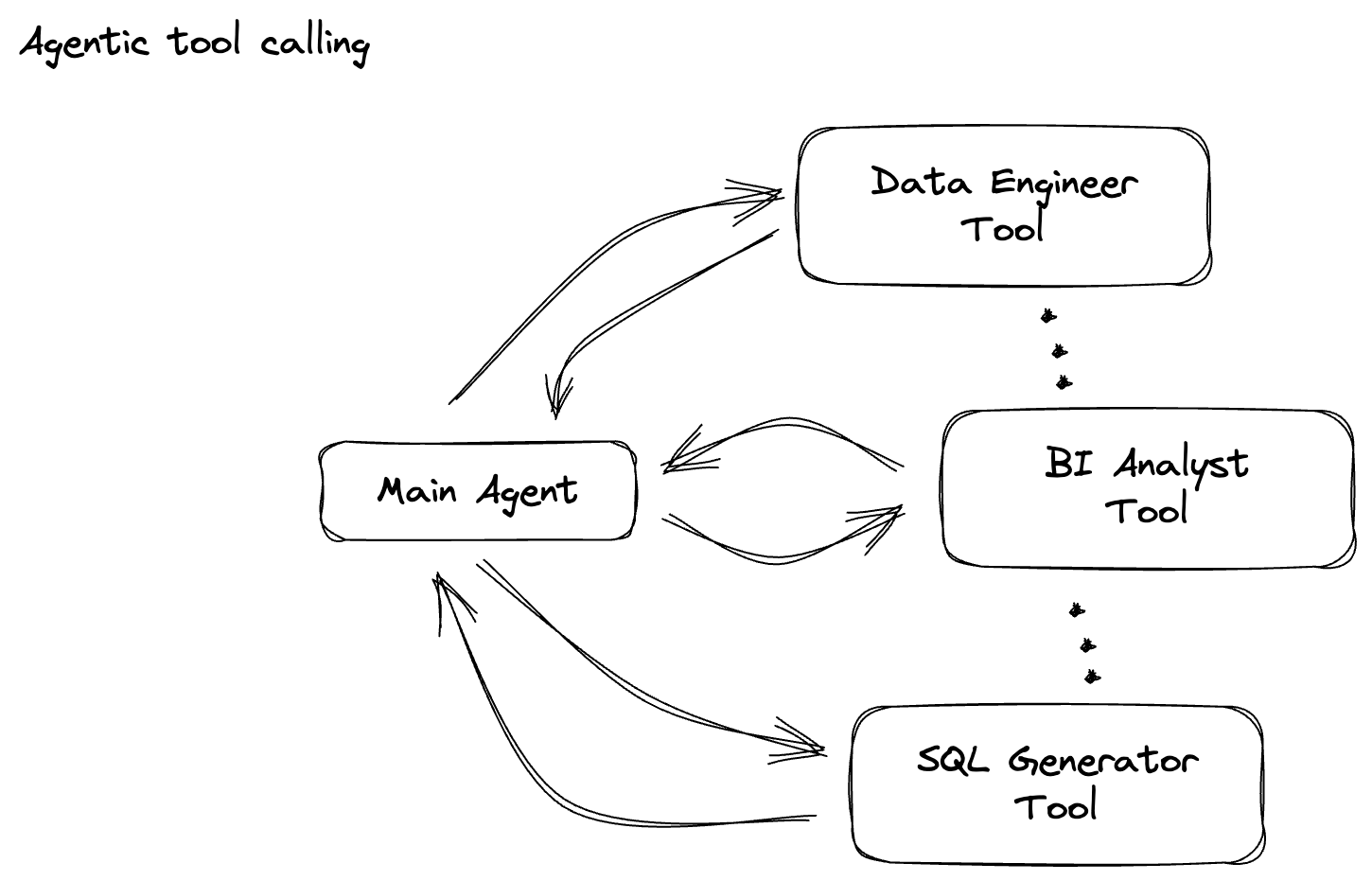
Công ty của bạn đã tạo một tác nhân dữ liệu. Được xây dựng bằng Agent Development Kit (ADK), trợ lý dữ liệu của bạn được trang bị nhiều chức năng chuyên biệt để hỗ trợ các tác vụ liên quan đến dữ liệu. Hãy tưởng tượng đây là một trợ lý dữ liệu đa năng, sẵn sàng xử lý nhiều yêu cầu, từ việc đóng vai trò là một Nhà phân tích thông tin doanh nghiệp để tạo báo cáo chi tiết, đến một Kỹ sư dữ liệu giúp bạn xây dựng các quy trình dữ liệu mạnh mẽ, hoặc một Trình tạo SQL tạo ra các câu lệnh SQL chính xác và nhiều yêu cầu khác. Mọi lượt tương tác mà tác nhân này có, mọi phản hồi mà tác nhân này tạo ra đều được tự động lưu trữ trong Firestore. Nhưng tại sao chúng ta cần một quy trình ở đây?
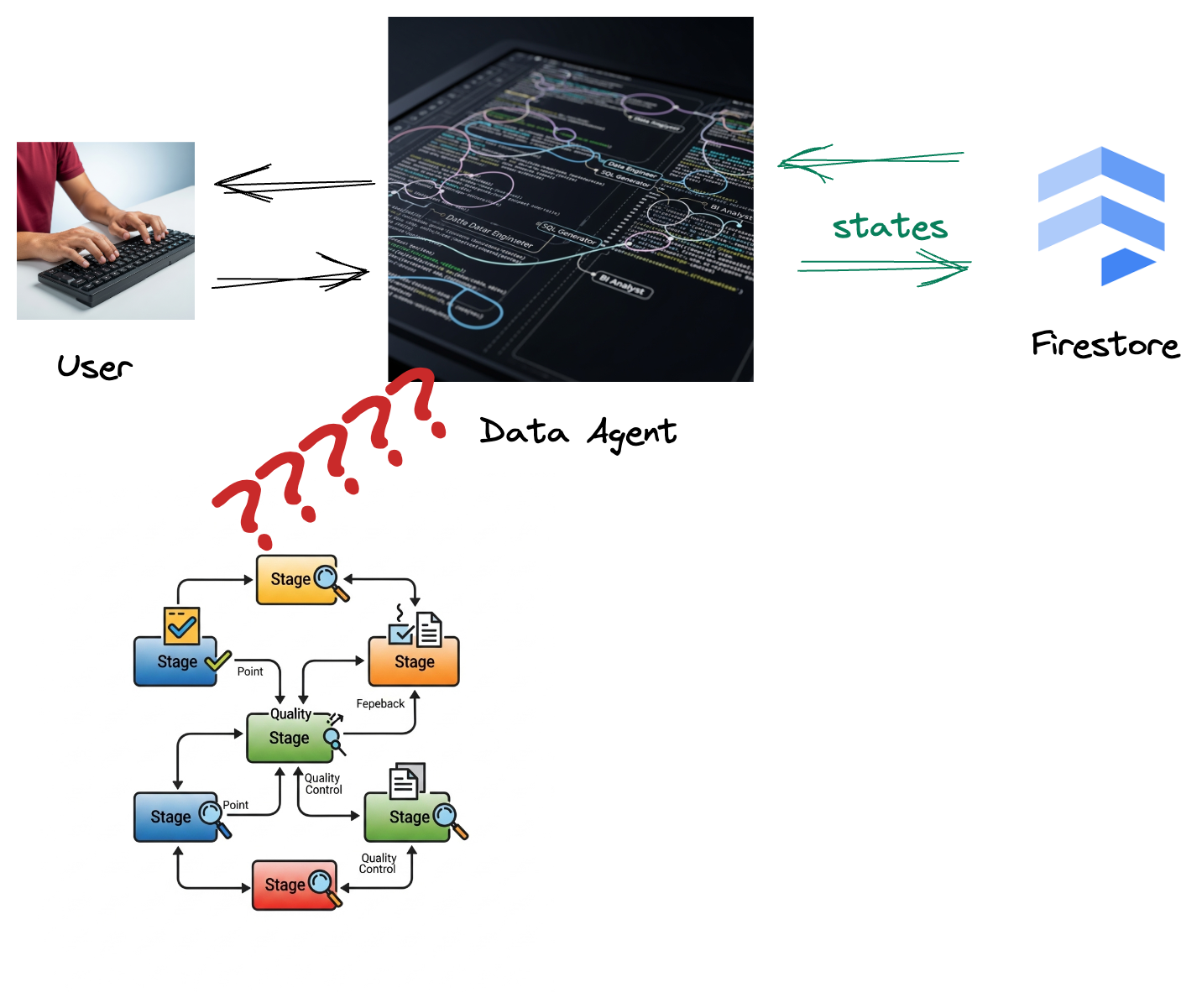
Vì từ Firestore, một trình kích hoạt sẽ gửi liền mạch dữ liệu tương tác này đến Pub/Sub, đảm bảo rằng chúng ta có thể xử lý và phân tích ngay những cuộc trò chuyện quan trọng này theo thời gian thực.
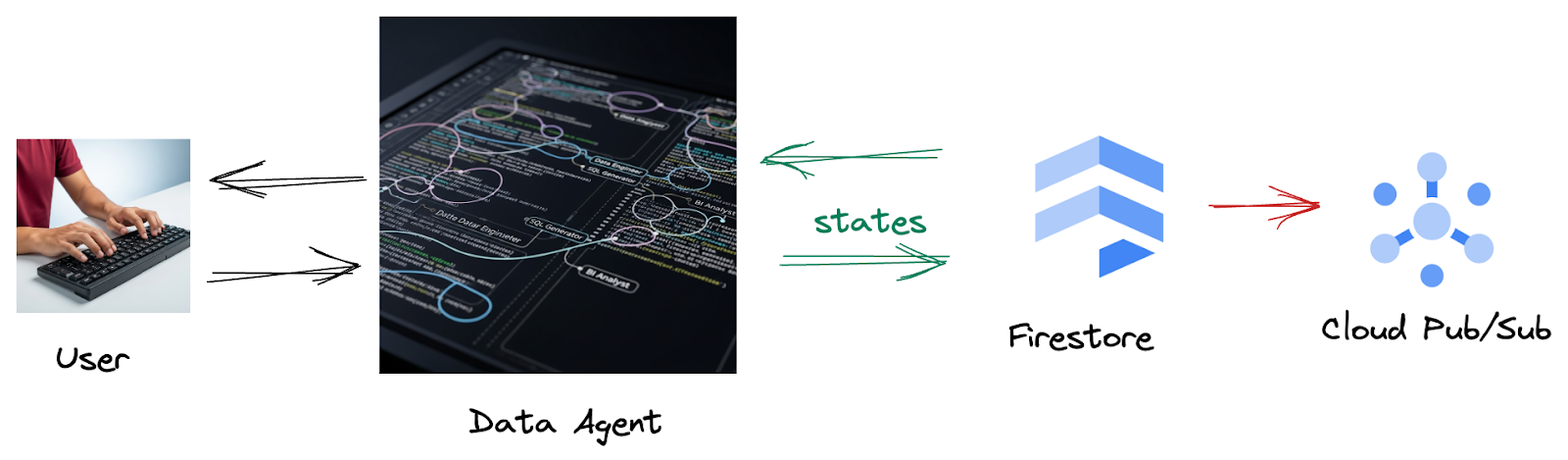
2. Trước khi bắt đầu
Tạo một dự án
- Trong Google Cloud Console, trên trang chọn dự án, hãy chọn hoặc tạo một dự án trên Google Cloud.
- Đảm bảo bạn đã bật tính năng thanh toán cho dự án trên Cloud. Tìm hiểu cách kiểm tra xem tính năng thanh toán có được bật trên một dự án hay không.
- Kích hoạt Cloud Shell bằng cách nhấp vào đường liên kết này. Bạn có thể chuyển đổi giữa Cloud Shell Terminal (để chạy các lệnh trên đám mây) và Trình chỉnh sửa (để tạo dự án) bằng cách nhấp vào nút tương ứng trong Cloud Shell.
- Sau khi kết nối với Cloud Shell, bạn có thể kiểm tra để đảm bảo rằng bạn đã được xác thực và dự án được đặt thành mã dự án của bạn bằng lệnh sau:
gcloud auth list
- Chạy lệnh sau trong Cloud Shell để xác nhận rằng lệnh gcloud biết về dự án của bạn.
gcloud config list project
- Nếu bạn chưa đặt dự án, hãy dùng lệnh sau để đặt:
export PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
- Bật các API bắt buộc thông qua lệnh bên dưới. Quá trình này có thể mất vài phút, vì vậy, vui lòng kiên nhẫn chờ đợi.
gcloud services enable \
dataflow.googleapis.com \
pubsub.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com
- Đảm bảo bạn có Python 3.10 trở lên
- Cài đặt gói Python
Cài đặt các thư viện Python bắt buộc cho Apache Beam, Google Cloud Vertex AI và Google Generative AI trong môi trường Cloud Shell.
pip install apache-beam[gcp] google-genai
- Sao chép kho lưu trữ github và chuyển sang thư mục minh hoạ.
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos
cd devrel-demos/data-analytics/beam_as_eval
Tham khảo tài liệu để biết các lệnh và cách sử dụng gcloud.
3. Cách sử dụng kho lưu trữ GitHub được cung cấp
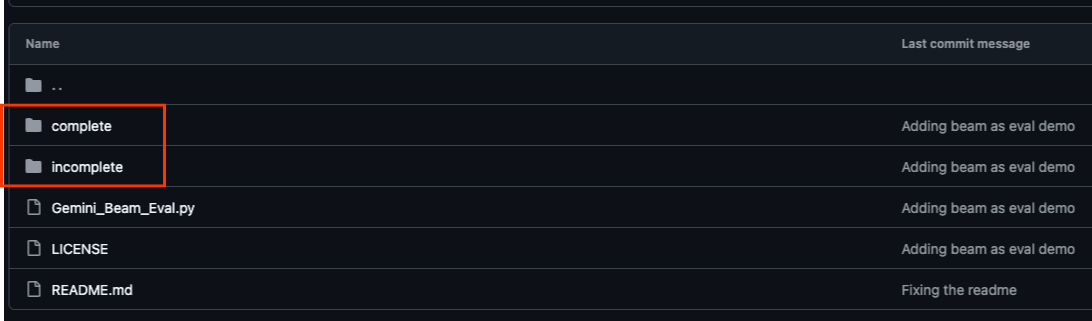
Kho lưu trữ GitHub liên kết với lớp học lập trình này (tại https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos/tree/main/data-analytics/beam_as_eval) được sắp xếp để tạo điều kiện cho trải nghiệm học tập có hướng dẫn. Nó chứa mã khung phù hợp với từng phần riêng biệt của lớp học lập trình, đảm bảo bạn có thể nắm bắt rõ ràng nội dung.
Trong kho lưu trữ, bạn sẽ thấy 2 thư mục chính: "complete" (đầy đủ) và "incomplete" (chưa đầy đủ). Thư mục "complete" (hoàn chỉnh) chứa mã có đầy đủ chức năng cho từng bước, cho phép bạn chạy và quan sát kết quả dự kiến. Ngược lại, thư mục "incomplete" cung cấp mã từ các bước trước đó, để lại các phần cụ thể được đánh dấu giữa ##### START STEP <NUMBER> ##### và ##### END STEP <NUMBER> ##### để bạn hoàn thành trong quá trình thực hiện bài tập. Cấu trúc này giúp bạn xây dựng kiến thức dựa trên những gì đã học trước đó trong khi tích cực tham gia các thử thách lập trình.
4. Tổng quan về kiến trúc
Quy trình của chúng tôi cung cấp một mẫu mạnh mẽ và có khả năng mở rộng để tích hợp suy luận bằng công nghệ học máy vào các luồng dữ liệu. Sau đây là cách các phần kết hợp với nhau:
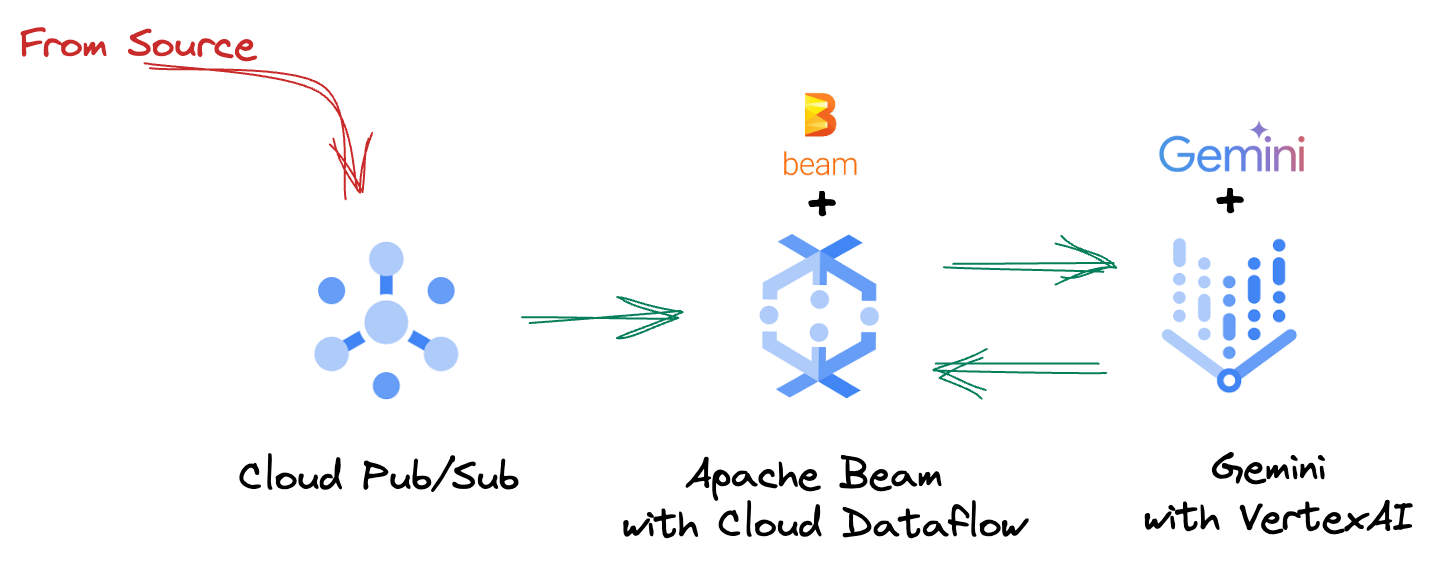
Trong quy trình Beam, bạn sẽ mã hoá nhiều đầu vào có điều kiện, sau đó tải các mô hình tuỳ chỉnh bằng biến đổi khép kín RunInference. Mặc dù bạn sử dụng Gemini với VertexAI trong ví dụ này, nhưng ví dụ này minh hoạ cách bạn sẽ tạo nhiều ModelHandler để phù hợp với số lượng mô hình mà bạn có. Cuối cùng, bạn sẽ sử dụng một DoFn có trạng thái để theo dõi các sự kiện và phát chúng theo cách có kiểm soát.
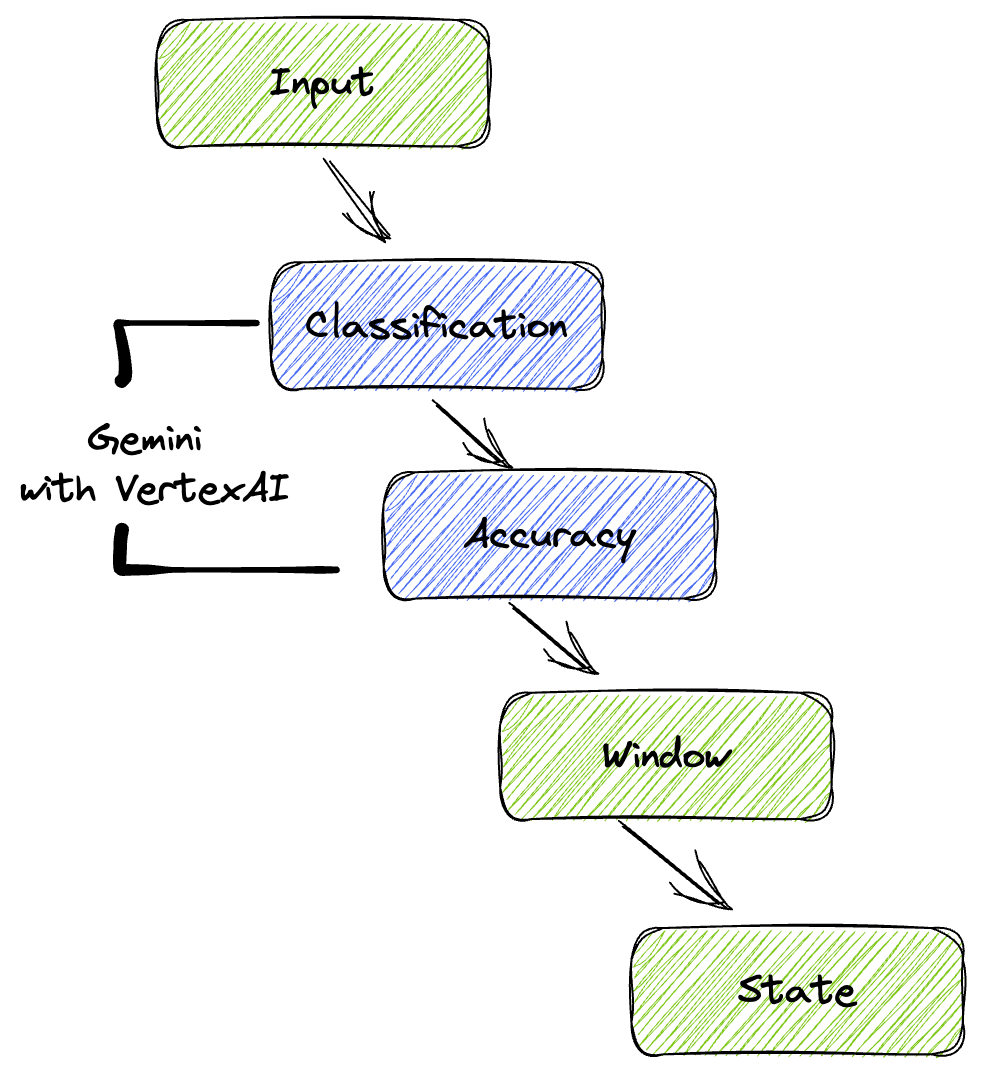
5. Nhập dữ liệu
Trước tiên, bạn sẽ thiết lập quy trình để nhập dữ liệu. Bạn sẽ sử dụng Pub/Sub để phát trực tuyến theo thời gian thực, nhưng để phát triển dễ dàng hơn, bạn cũng sẽ tạo một chế độ kiểm thử. test_mode này cho phép bạn chạy quy trình cục bộ bằng cách sử dụng dữ liệu mẫu được xác định trước, vì vậy, bạn không cần luồng Pub/Sub trực tiếp để xem quy trình của mình có hoạt động hay không.
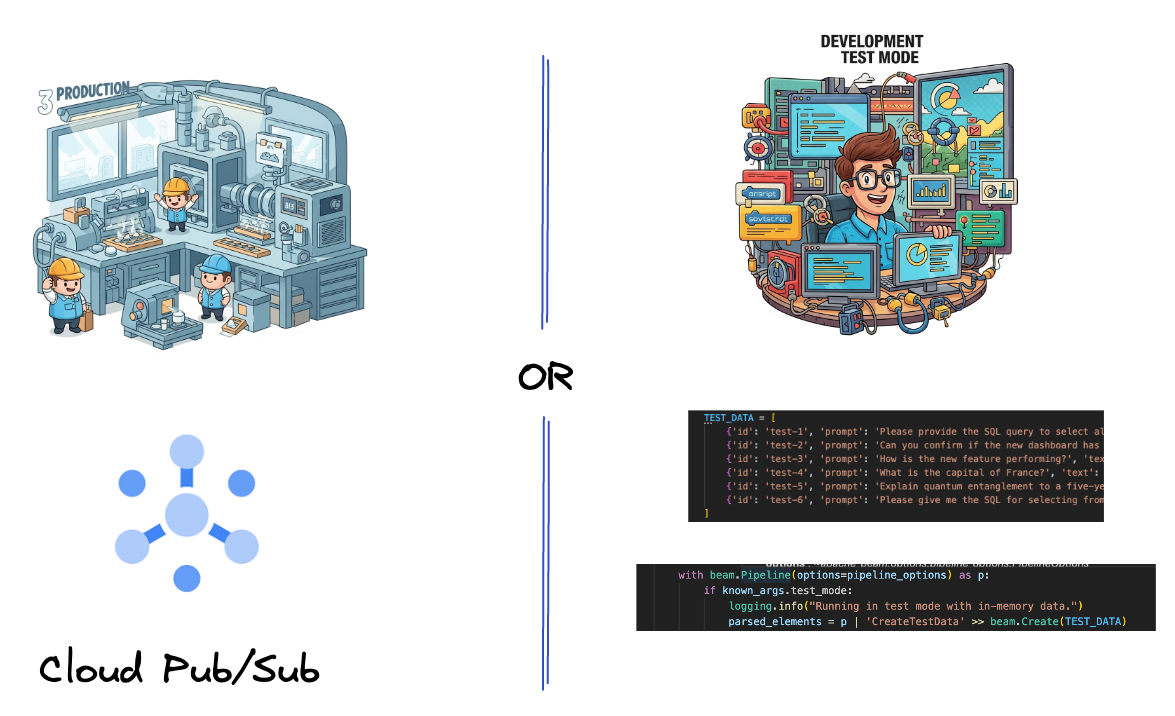
Đối với phần này, hãy sử dụng gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py.
- Sử dụng đối tượng quy trình p được cung cấp, mã hoá một đầu vào Pub/Sub và ghi đầu ra dưới dạng pCollection.
- Ngoài ra, hãy dùng một cờ để xác định xem TEST_MODE đã được đặt hay chưa.
- Nếu TEST_MODE được đặt, hãy chuyển sang phân tích cú pháp mảng TEST_DATA làm dữ liệu đầu vào.
Điều này không bắt buộc nhưng sẽ giúp rút ngắn quy trình để bạn không cần sử dụng Pub/Sub quá sớm.
Sau đây là ví dụ về mã bên dưới:
# Step 1
# Ingesting Data
# Write your data ingestion step here.
############## BEGIN STEP 1 ##############
if known_args.test_mode:
logging.info("Running in test mode with in-memory data.")
parsed_elements = p | 'CreateTestData' >> beam.Create(TEST_DATA)
# Convert dicts to JSON strings and add timestamps for test mode
parsed_elements = parsed_elements | 'ConvertTestDictsToJsonAndAddTimestamps' >> beam.Map(
lambda x: beam.window.TimestampedValue(json.dumps(x), x['timestamp'])
)
else:
logging.info(f"Reading from Pub/Sub topic: {known_args.input_topic}")
parsed_elements = (
p
| 'ReadFromPubSub' >> beam.io.ReadFromPubSub(
topic=known_args.input_topic
).with_output_types(bytes)
| 'DecodeBytes' >> beam.Map(lambda b: b.decode('utf-8')) # Output is JSON string
# Extract timestamp from JSON string for Pub/Sub messages
| 'AddTimestampsFromParsedJson' >> beam.Map(lambda s: beam.window.TimestampedValue(s, json.loads(s)['timestamp']))
)
############## END STEP 1 ##############
Kiểm thử mã này bằng cách thực thi:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Bước này sẽ phát ra tất cả các bản ghi, ghi nhật ký chúng vào stdout.
Bạn sẽ thấy kết quả như sau.
INFO:root:Running in test mode with in-memory data.
INFO:apache_beam.runners.worker.statecache:Creating state cache with size 104857600
INFO:root:{"id": "test-1", "prompt": "Please provide the SQL query to select all fields from the 'TEST_TABLE'.", "text": "Sure here is the SQL: SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;", "timestamp": 1751052405.9340951, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-2", "prompt": "Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?", "text": "I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.", "timestamp": 1751052410.9340951, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-3", "prompt": "How is the new feature performing?", "text": "It works as expected.", "timestamp": 1751052415.9340959, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-4", "prompt": "What is the capital of France?", "text": "The square root of a banana is purple.", "timestamp": 1751052430.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-5", "prompt": "Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.", "text": "A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.", "timestamp": 1751052435.9340959, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052440.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
6. Tạo PTransform để phân loại câu lệnh cho mô hình ngôn ngữ lớn
Tiếp theo, bạn sẽ tạo một PTransform để phân loại câu lệnh. Việc này liên quan đến việc sử dụng mô hình Gemini của Vertex AI để phân loại văn bản đến. Bạn sẽ xác định một GeminiModelHandler tuỳ chỉnh để tải mô hình Gemini, sau đó hướng dẫn mô hình cách phân loại văn bản thành các danh mục như "KỸ SƯ DỮ LIỆU", "NHÀ PHÂN TÍCH BI" hoặc "TRÌNH TẠO SQL".
Bạn sẽ sử dụng thông tin này bằng cách so sánh với các lệnh gọi công cụ thực tế trong nhật ký. Lớp học lập trình này không đề cập đến vấn đề này, nhưng bạn có thể gửi vấn đề này xuống luồng và so sánh. Có thể có một số câu hỏi không rõ ràng và đây là một điểm dữ liệu bổ sung hữu ích để đảm bảo trợ lý ảo của bạn đang gọi đúng công cụ.
Đối với phần này, hãy sử dụng gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py.
- Tạo ModelHandler tuỳ chỉnh; tuy nhiên, thay vì trả về một đối tượng mô hình trong load_model, hãy trả về genai.Client.
- Mã bạn sẽ cần để tạo hàm run_inference của ModelHandler tuỳ chỉnh. Dưới đây là một câu lệnh mẫu:
Câu lệnh có thể là một câu như sau:
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilities.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambiguous. Choose only one.
Finally, always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
- Tạo kết quả dưới dạng pCollection cho pTransform tiếp theo.
Sau đây là ví dụ về mã bên dưới:
############## BEGIN STEP 2 ##############
# load_model is called once per worker process to initialize the LLM client.
# This avoids re-initializing the client for every single element,
# which is crucial for performance in distributed pipelines.
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
# run_inference is called for each batch of elements. Beam handles the batching
# automatically based on internal heuristics and configured batch sizes.
# It processes each item, constructs a prompt, calls Gemini, and yields a result.
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[Any], # Each item is a JSON string or a dict
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""
Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings or dicts.
Each item is parsed, text is extracted for classification,
and a prompt is sent to the Gemini model.
"""
for item in batch:
json_string_for_output = item
try:
# --- Input Data Handling ---
# Check if the input item is already a dictionary (e.g., from TEST_DATA)
# or a JSON string (e.g., from Pub/Sub).
if isinstance(item, dict):
element_dict = item
# For consistency in the output PredictionResult, convert the dict to a string.
# This ensures pr.example always contains the original JSON string.
json_string_for_output = json.dumps(item)
else:
element_dict = json.loads(item)
# Extract the 'text' field from the parsed dictionary.
text_to_classify = element_dict.get('text','')
if not text_to_classify:
logging.warning(f"Input JSON missing 'text' key or text is empty: {json_string_for_output}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_NO_TEXT")
continue
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilites.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambigiuous. Choose only one.
Finally always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
contents = [
types.Content( # This is the actual content for the LLM
role="user",
parts=[
types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)
]
)
]
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(
model=self._model_name, contents=contents, config=self._model_kwargs
)
classification_tag = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
classification_tag+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference=classification_tag)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
logging.error(f"Error decoding JSON string: {json_string_for_output}, error: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_JSON_DECODE")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini inference for input {json_string_for_output}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 2 ##############
Kiểm thử mã này bằng cách thực thi:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Bước này sẽ trả về một suy luận từ Gemini. Công cụ này sẽ phân loại kết quả theo yêu cầu của câu lệnh.
Bạn sẽ thấy kết quả như sau.
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052592.9662862, "user_id": "user_c"}', inference='(HELPER, "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, conversational response to a request. It does not involve data engineering tasks, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is providing a direct, simple form of assistance by fulfilling a non-technical request, which aligns well with the role of a helper.")', model_id=None)
7. Xây dựng LLM dưới dạng một người đánh giá
Sau khi phân loại câu lệnh, bạn sẽ đánh giá độ chính xác của câu trả lời do mô hình đưa ra. Thao tác này liên quan đến một lệnh gọi khác đến mô hình Gemini, nhưng lần này, bạn sẽ nhắc mô hình này chấm điểm mức độ mà "văn bản" đáp ứng "câu lệnh" ban đầu theo thang điểm từ 0.0 đến 1.0. Điều này giúp bạn hiểu được chất lượng của kết quả do AI tạo ra. Bạn sẽ tạo một GeminiAccuracyModelHandler riêng cho nhiệm vụ này.

Đối với phần này, hãy sử dụng gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py.
- Tạo ModelHandler tuỳ chỉnh; tuy nhiên, thay vì trả về một đối tượng mô hình trong load_model, hãy trả về genai.Client giống như bạn đã làm ở trên.
- Mã bạn sẽ cần để tạo hàm run_inference của ModelHandler tuỳ chỉnh. Dưới đây là một câu lệnh mẫu:
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
Một điều cần lưu ý ở đây là bạn đã tạo hai mô hình khác nhau trong cùng một quy trình. Trong ví dụ cụ thể này, bạn cũng đang sử dụng một lệnh gọi Gemini với Vertex AI, nhưng theo cùng một khái niệm, bạn có thể chọn sử dụng và tải các mô hình khác. Điều này giúp đơn giản hoá việc quản lý mô hình và cho phép bạn sử dụng nhiều mô hình trong cùng một quy trình Beam.
- Tạo kết quả dưới dạng pCollection cho pTransform tiếp theo.
Sau đây là ví dụ về mã bên dưới:
############## BEGIN STEP 3 ##############
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[str], # Each item is a JSON string
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings to verify accuracy."""
for json_string in batch:
try:
element_dict = json.loads(json_string)
original_prompt = element_dict.get('original_prompt', '')
original_text = element_dict.get('original_text', '')
if not original_prompt or not original_text:
logging.warning(f"Accuracy input missing prompt/text: {json_string}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_ACCURACY_INPUT")
continue
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(model=self._model_name, contents=[prompt_for_accuracy], config=self._model_kwargs)
gemini_response_text = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
gemini_response_text+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference=gemini_response_text)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini accuracy inference for input {json_string}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 3 ##############
Kiểm thử mã này bằng cách thực thi:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Bước này cũng sẽ trả về một suy luận, đồng thời bình luận và trả về điểm số về độ chính xác mà Gemini cho là công cụ đã phản hồi.
Bạn sẽ thấy kết quả như sau.
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"original_data_json": "{\\"id\\": \\"test-6\\", \\"prompt\\": \\"Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.\\", \\"text\\": \\"absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\\", \\"timestamp\\": 1751052770.7552562, \\"user_id\\": \\"user_c\\"}", "original_prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "original_text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "classification_tag": "(HELPER, \\"The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' is a general, conversational response that does not pertain to data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. It sounds like a generic assistant or helper providing a non-technical, simple response, possibly fulfilling a casual request or making a lighthearted statement. Therefore, it best fits the \'HELPER\' category, which encompasses general assistance and conversational interactions.\\")"}', inference='0.0 - The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', model_id=None)
8. Phân tích và tạo cửa sổ kết quả
Giờ đây, bạn sẽ xem kết quả trong khoảng thời gian cụ thể để phân tích. Bạn sẽ sử dụng các khoảng thời gian cố định để nhóm dữ liệu, nhờ đó bạn có thể nhận được thông tin chi tiết tổng hợp. Sau khi phân chia thành các cửa sổ, bạn sẽ phân tích cú pháp đầu ra thô từ Gemini thành một định dạng có cấu trúc hơn, bao gồm dữ liệu gốc, thẻ phân loại, điểm số độ chính xác và nội dung giải thích.

Đối với phần này, hãy sử dụng gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py.
- Thêm một khoảng thời gian cố định là 60 giây để tất cả dữ liệu được đặt trong khoảng thời gian 60 giây.
Sau đây là ví dụ về mã bên dưới:
############## BEGIN STEP 4 ##############
| 'WindowIntoFixedWindows' >> beam.WindowInto(beam.window.FixedWindows(60))
############## END STEP 4 ##############
Kiểm thử mã này bằng cách thực thi:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Bước này mang tính chất cung cấp thông tin, bạn đang tìm kiếm cửa sổ của mình. Thông tin này sẽ xuất hiện dưới dạng dấu thời gian bắt đầu/kết thúc của cửa sổ.
Bạn sẽ thấy kết quả như sau.
INFO:root:({'id': 'test-6', 'prompt': 'Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', 'text': "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", 'timestamp': 1751052901.337791, 'user_id': 'user_c'}, '("HELPER", "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, helpful response to a request. It does not involve data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is fulfilling a simple, non-technical request, which aligns with the role of a general helper.")', 0.0, 'The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', [1751052900.0, 1751052960.0))
9. Đếm kết quả tốt và kết quả xấu bằng tính năng xử lý có trạng thái
Cuối cùng, bạn sẽ sử dụng một DoFn có trạng thái để đếm số kết quả "tốt" và "xấu" trong mỗi cửa sổ. Kết quả "tốt" có thể là một lượt tương tác có điểm chính xác cao, trong khi kết quả "xấu" cho biết điểm số thấp. Quy trình xử lý có trạng thái này cho phép bạn duy trì số lượng và thậm chí thu thập các ví dụ về những lượt tương tác "không tốt" theo thời gian. Đây là điều quan trọng để theo dõi tình trạng và hiệu suất của chatbot theo thời gian thực.
Đối với phần này, hãy sử dụng gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py.
- Tạo một hàm có trạng thái. Bạn sẽ cần 2 trạng thái: (1) để theo dõi số lượng lượt đếm không hợp lệ và (2) giữ lại các bản ghi không hợp lệ để hiển thị. Sử dụng bộ mã hoá thích hợp để đảm bảo hệ thống có thể hoạt động hiệu quả.
- Mỗi khi thấy các giá trị cho một suy luận không chính xác, bạn nên theo dõi cả hai và phát chúng vào cuối khoảng thời gian. Hãy nhớ đặt lại các trạng thái sau khi phát. Phần sau chỉ mang tính minh hoạ, đừng cố gắng lưu giữ tất cả những thông tin này trong bộ nhớ trong môi trường thực.
Sau đây là ví dụ về mã bên dưới:
############## BEGIN STEP 5 ##############
# Define a state specification for a combining value.
# This will store the running sum for each key.
# The coder is specified for efficiency.
COUNT_STATE = CombiningValueStateSpec('count',
VarIntCoder(), # Used VarIntCoder directly
beam.transforms.combiners.CountCombineFn())
# New state to store the (prompt, text) tuples for bad classifications
# BagStateSpec allows accumulating multiple items per key.
BAD_PROMPTS_STATE = beam.transforms.userstate.BagStateSpec(
'bad_prompts', coder=beam.coders.TupleCoder([beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder(), beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder()])
)
# Define a timer to fire at the end of the window, using WATERMARK as per blog example.
WINDOW_TIMER = TimerSpec('window_timer', TimeDomain.WATERMARK)
def process(
self,
element: Tuple[str, Tuple[int, Tuple[str, str]]], # (key, (count_val, (prompt, text)))
key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam,
count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE),
bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE), # New state param
window_timer=beam.DoFn.TimerParam(WINDOW_TIMER),
window=beam.DoFn.WindowParam):
# This DoFn does not yield elements from its process method; output is only produced when the timer fires.
if key == 'bad': # Only count 'bad' elements
count_state.add(element[1][0]) # Add the count (which is 1)
bad_prompts_state.add(element[1][1]) # Add the (prompt, text) tuple
window_timer.set(window.end) # Set timer to fire at window end
@on_timer(WINDOW_TIMER)
def on_window_timer(self, key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam, count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE), bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE)):
final_count = count_state.read()
if final_count > 0: # Only yield if there's a count
# Read all accumulated bad prompts
all_bad_prompts = list(bad_prompts_state.read())
# Clear the state for the next window to avoid carrying over data.
count_state.clear()
bad_prompts_state.clear()
yield (key, final_count, all_bad_prompts) # Yield count and list of prompts
############## END STEP 5 ##############
Kiểm thử mã này bằng cách thực thi:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
Bước này sẽ xuất ra tất cả các số lượng, hãy thử thay đổi kích thước cửa sổ và bạn sẽ thấy các lô sẽ khác nhau. Khoảng thời gian mặc định sẽ nằm trong vòng một phút, vì vậy, hãy thử sử dụng 30 giây hoặc một khung thời gian khác để thấy các lô và số lượng khác nhau.
Bạn sẽ thấy kết quả như sau.
INFO:root:Window: [1751052960.0, 1751053020.0), Bad Counts: 5, Bad Prompts: [('Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?', 'I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.'), ('How is the new feature performing?', 'It works as expected.'), ('What is the capital of France?', 'The square root of a banana is purple.'), ('Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.', 'A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.'), ('Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat")]
10. Dọn dẹp
- Xoá dự án trên Google Cloud (Không bắt buộc nhưng nên thực hiện đối với các lớp học lập trình): Nếu dự án này chỉ được tạo cho lớp học lập trình này và bạn không cần đến dự án nữa, thì việc xoá toàn bộ dự án là cách triệt để nhất để đảm bảo tất cả tài nguyên đều bị xoá.
- Chuyển đến trang Quản lý tài nguyên trong Google Cloud Console.
- Chọn dự án của bạn.
- Nhấp vào Xoá dự án rồi làm theo hướng dẫn trên màn hình.
11. Xin chúc mừng!
Chúc mừng bạn đã hoàn thành lớp học lập trình này! Bạn đã tạo thành công một quy trình suy luận ML theo thời gian thực bằng Apache Beam và Gemini trên Dataflow. Bạn đã tìm hiểu cách khai thác sức mạnh của AI tạo sinh cho các luồng dữ liệu, trích xuất thông tin chi tiết có giá trị để có được kỹ thuật dữ liệu thông minh và tự động hơn.

