1. 简介
在当今快节奏的数据环境中,实时数据洞见对于做出明智的决策至关重要。此 Codelab 将引导您构建实时评估流水线。我们将首先利用 Apache Beam 框架,该框架为批量数据和流式数据提供统一的编程模型。这样一来,您无需从头开始构建复杂的分布式计算逻辑,从而显著简化了流水线开发。使用 Beam 定义流水线后,您就可以在 Google Cloud Dataflow 上无缝运行该流水线。这是一种全托管式服务,可为您的数据处理需求提供无与伦比的规模和性能。
在此 Codelab 中,您将学习如何设计可扩缩的 Apache Beam 流水线以进行机器学习推理,开发自定义 ModelHandler 以集成 Vertex AI 的 Gemini 模型,利用提示工程在数据流中实现智能文本分类,以及在 Google Cloud Dataflow 上部署和运行此流处理 ML 推理流水线。完成本课程后,您将深入了解如何在工程工作流中应用机器学习技术来实时了解数据并进行持续评估,尤其是在维护稳健且以用户为中心的对话式 AI 方面。
场景
贵公司已构建数据代理。使用智能体开发套件 (ADK) 构建的数据智能体具备各种专业功能,可协助您完成与数据相关的任务。您可以将其视为多功能数据助理,它能够处理各种请求,例如充当 BI 分析师来生成富有洞察力的报告,充当数据工程师来帮助您构建强大的数据流水线,充当 SQL 生成器来精心编写精确的 SQL 语句,等等。此代理的每次互动、生成的每个回答都会自动存储在 Firestore 中。但为什么我们需要在此处使用流水线?
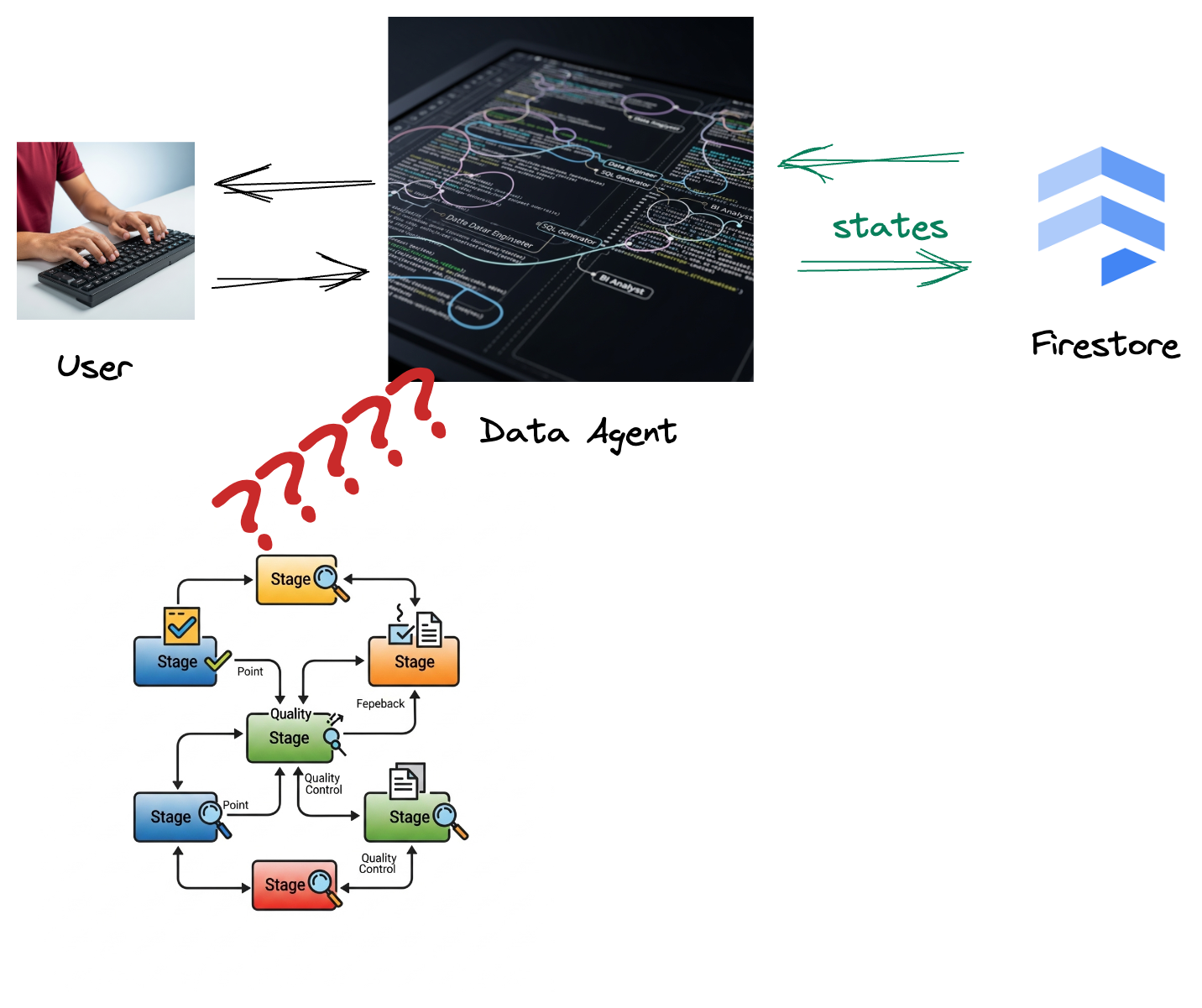
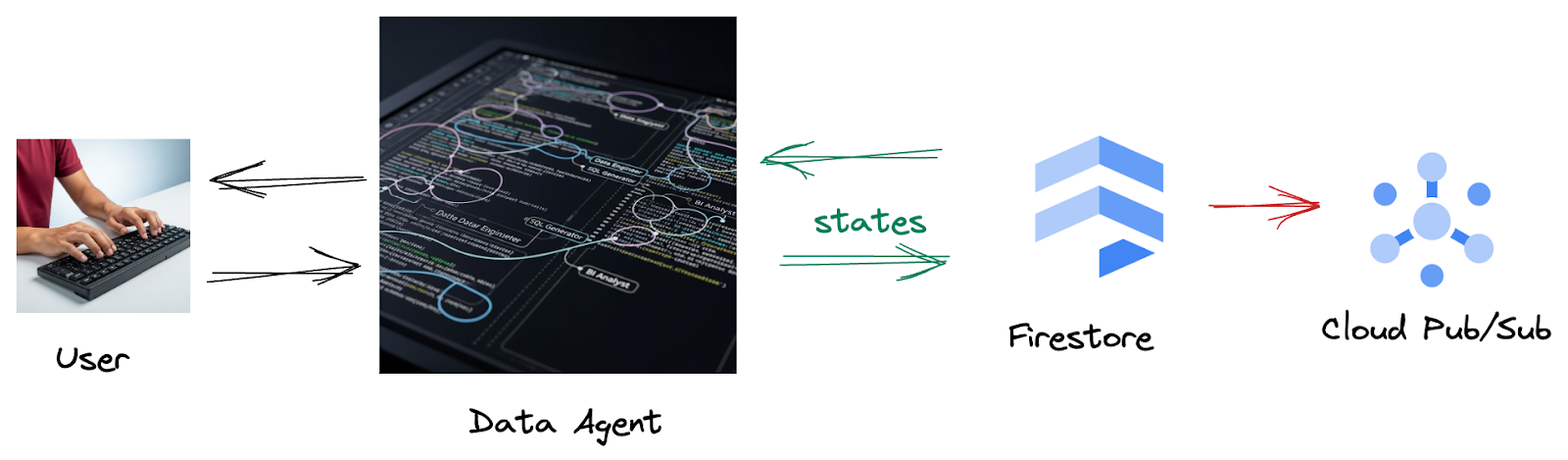
这是因为,Firestore 中的触发器可将这些互动数据无缝发送到 Pub/Sub,确保我们可以立即实时处理和分析这些关键对话。
2. 准备工作
创建项目
- 在 Google Cloud Console 的项目选择器页面上,选择或创建一个 Google Cloud 项目。
- 确保您的 Cloud 项目已启用结算功能。了解如何检查项目是否已启用结算功能。
- 点击此链接以激活 Cloud Shell。您可以在 Cloud Shell 中点击相应按钮,在 Cloud Shell 终端(用于运行云命令)和编辑器(用于构建项目)之间切换。
- 连接到 Cloud Shell 后,您可以使用以下命令检查自己是否已通过身份验证,以及项目是否已设置为您的项目 ID:
gcloud auth list
- 在 Cloud Shell 中运行以下命令,以确认 gcloud 命令了解您的项目。
gcloud config list project
- 如果项目未设置,请使用以下命令进行设置:
export PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
- 通过以下命令启用必需的 API。这可能需要几分钟的时间,请耐心等待。
gcloud services enable \
dataflow.googleapis.com \
pubsub.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com
- 确保已安装 Python 3.10 及更高版本
- 安装 Python 软件包
在 Cloud Shell 环境中安装 Apache Beam、Google Cloud Vertex AI 和 Google Generative AI 所需的 Python 库。
pip install apache-beam[gcp] google-genai
- 克隆 GitHub 代码库并切换到演示目录。
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos
cd devrel-demos/data-analytics/beam_as_eval
如需了解 gcloud 命令和用法,请参阅文档。
3. 如何使用提供的 GitHub 代码库
与本 Codelab 关联的 GitHub 代码库(网址为 https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos/tree/main/data-analytics/beam_as_eval)经过精心整理,可帮助您获得引导式学习体验。它包含与 Codelab 的每个不同部分相对应的框架代码,确保您能清晰地了解相关内容。
在该代码库中,您会发现两个主要文件夹:“complete”和“incomplete”。“complete”文件夹包含每个步骤的完整功能代码,可让您运行并观察预期输出。相反,“incomplete”文件夹提供了之前步骤中的代码,但留下了介于 ##### START STEP <NUMBER> ##### 和 ##### END STEP <NUMBER> ##### 之间的特定部分,供您在练习中完成。这种结构可让您在积极参与编码挑战的同时,在已有知识的基础上不断进步。
4. 架构概览
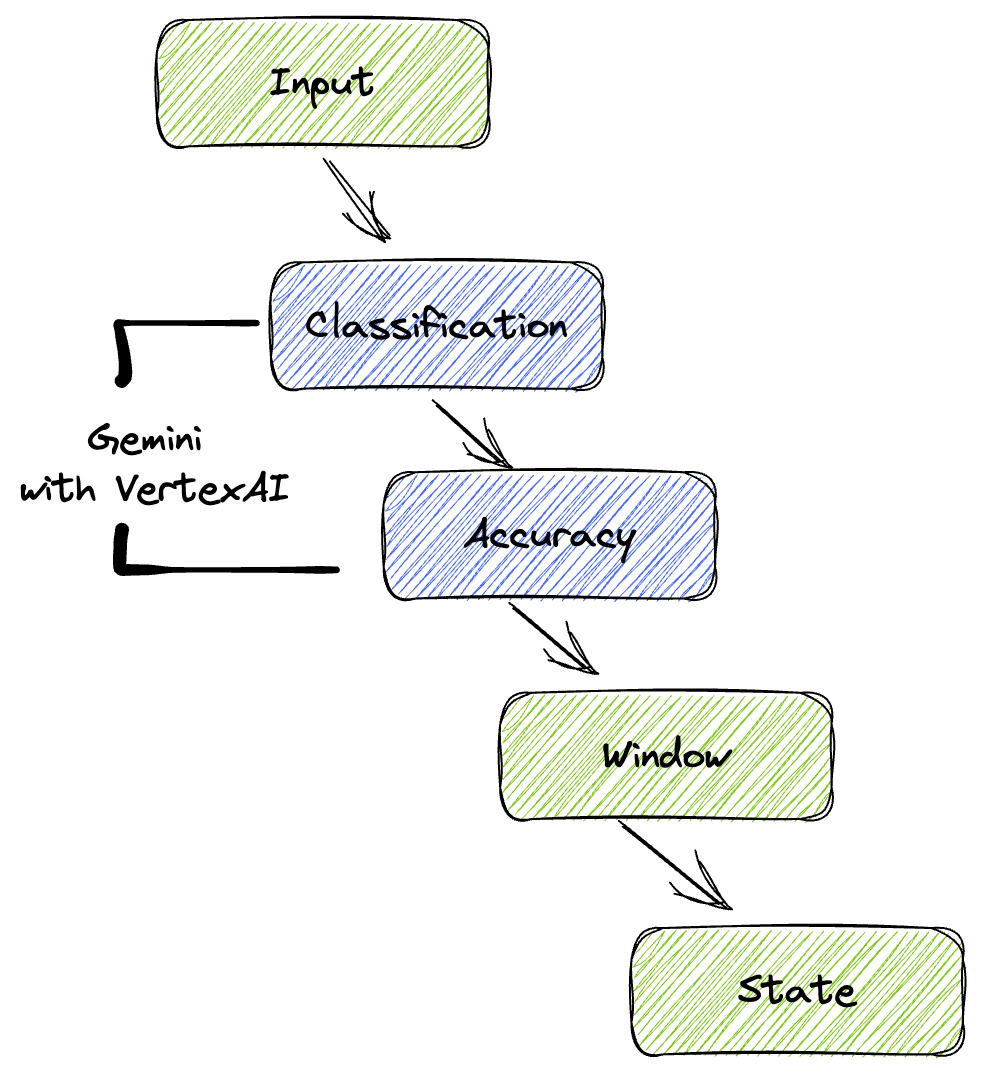
我们的流水线提供了一种强大且可扩缩的模式,用于将机器学习推理集成到数据流中。以下是各个部分如何组合在一起的:
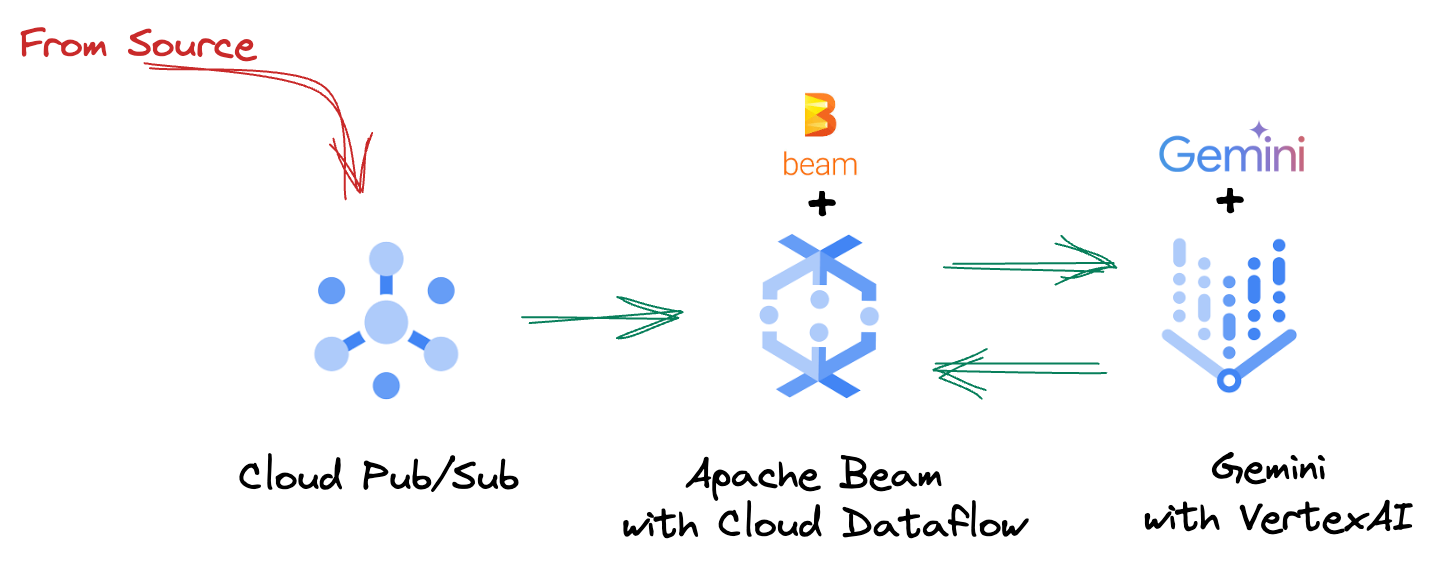
在 Beam 流水线中,您将有条件地编码多个输入,然后使用 RunInference 一站式转换作业加载自定义模型。虽然此示例中使用了 Gemini with VertexAI,但它演示了如何创建多个 ModelHandler 来适应您拥有的模型数量。最后,您将使用有状态的 DoFn 来跟踪事件并以受控方式发出这些事件。
5. 提取数据
首先,您需要设置流水线以提取数据。您将使用 Pub/Sub 进行实时流式传输,但为了简化开发,您还将创建一个测试模式。借助此 test_mode,您可以使用预定义的示例数据在本地运行流水线,因此无需实时 Pub/Sub 流即可查看流水线是否正常运行。
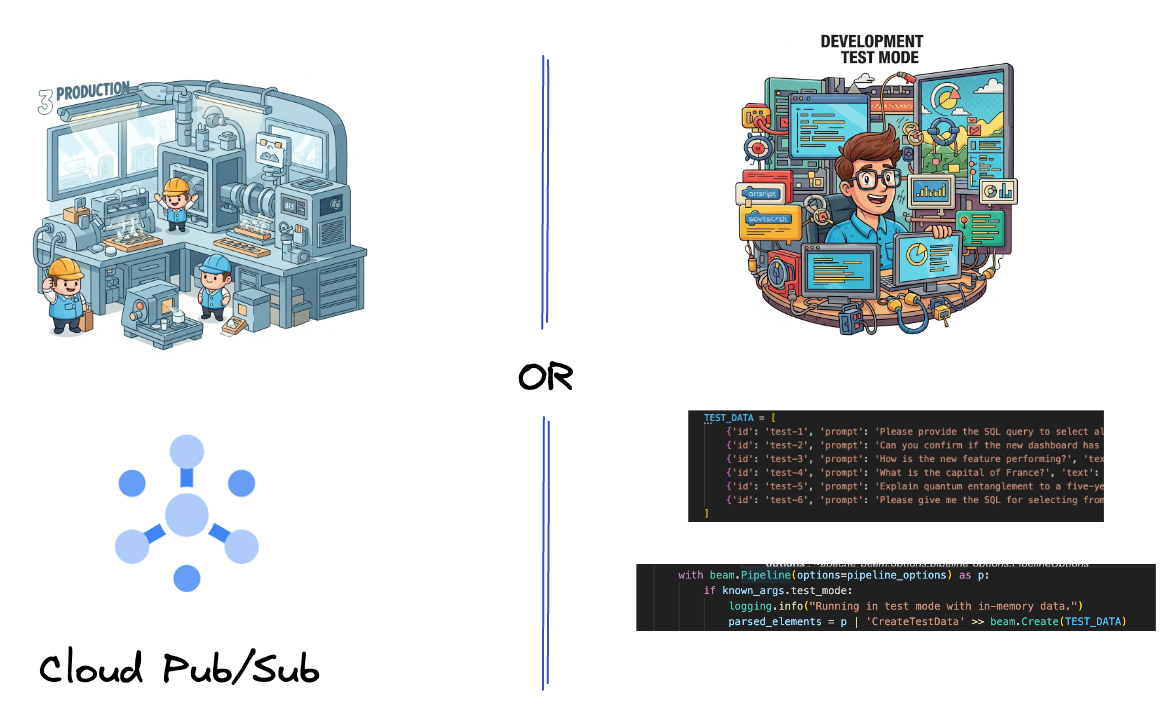
对于本部分,请使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py。
- 使用提供的流水线对象 p,对 Pub/Sub 输入进行编码,并将输出写为 pCollection。
- 此外,还使用一个标志来确定是否已设置 TEST_MODE。
- 如果设置了 TEST_MODE,则切换为将 TEST_DATA 数组解析为输入。
这不是必需的,但有助于缩短流程,这样您就不需要在这么早的时候就涉及 Pub/Sub。
以下是一个代码示例:
# Step 1
# Ingesting Data
# Write your data ingestion step here.
############## BEGIN STEP 1 ##############
if known_args.test_mode:
logging.info("Running in test mode with in-memory data.")
parsed_elements = p | 'CreateTestData' >> beam.Create(TEST_DATA)
# Convert dicts to JSON strings and add timestamps for test mode
parsed_elements = parsed_elements | 'ConvertTestDictsToJsonAndAddTimestamps' >> beam.Map(
lambda x: beam.window.TimestampedValue(json.dumps(x), x['timestamp'])
)
else:
logging.info(f"Reading from Pub/Sub topic: {known_args.input_topic}")
parsed_elements = (
p
| 'ReadFromPubSub' >> beam.io.ReadFromPubSub(
topic=known_args.input_topic
).with_output_types(bytes)
| 'DecodeBytes' >> beam.Map(lambda b: b.decode('utf-8')) # Output is JSON string
# Extract timestamp from JSON string for Pub/Sub messages
| 'AddTimestampsFromParsedJson' >> beam.Map(lambda s: beam.window.TimestampedValue(s, json.loads(s)['timestamp']))
)
############## END STEP 1 ##############
通过执行以下命令来测试此代码:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
此步骤应输出所有记录,并将其记录到标准输出中。
您应该会看到如下所示的输出。
INFO:root:Running in test mode with in-memory data.
INFO:apache_beam.runners.worker.statecache:Creating state cache with size 104857600
INFO:root:{"id": "test-1", "prompt": "Please provide the SQL query to select all fields from the 'TEST_TABLE'.", "text": "Sure here is the SQL: SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;", "timestamp": 1751052405.9340951, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-2", "prompt": "Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?", "text": "I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.", "timestamp": 1751052410.9340951, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-3", "prompt": "How is the new feature performing?", "text": "It works as expected.", "timestamp": 1751052415.9340959, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-4", "prompt": "What is the capital of France?", "text": "The square root of a banana is purple.", "timestamp": 1751052430.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-5", "prompt": "Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.", "text": "A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.", "timestamp": 1751052435.9340959, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052440.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
6. 为 LLM 提示分类构建 PTransform
接下来,您将构建一个用于对提示进行分类的 PTransform。这包括使用 Vertex AI 的 Gemini 模型对传入的文本进行分类。您将定义一个自定义 GeminiModelHandler,用于加载 Gemini 模型,然后指示该模型如何将文本分类为“数据工程师”“BI 分析师”或“SQL 生成器”等类别。
您可以通过与日志中的实际工具调用进行比较来使用此功能。此 Codelab 中未涵盖此内容,但您可以将其发送到下游并进行比较。有些可能比较模糊,这可以作为重要的额外数据点,确保代理调用正确的工具。
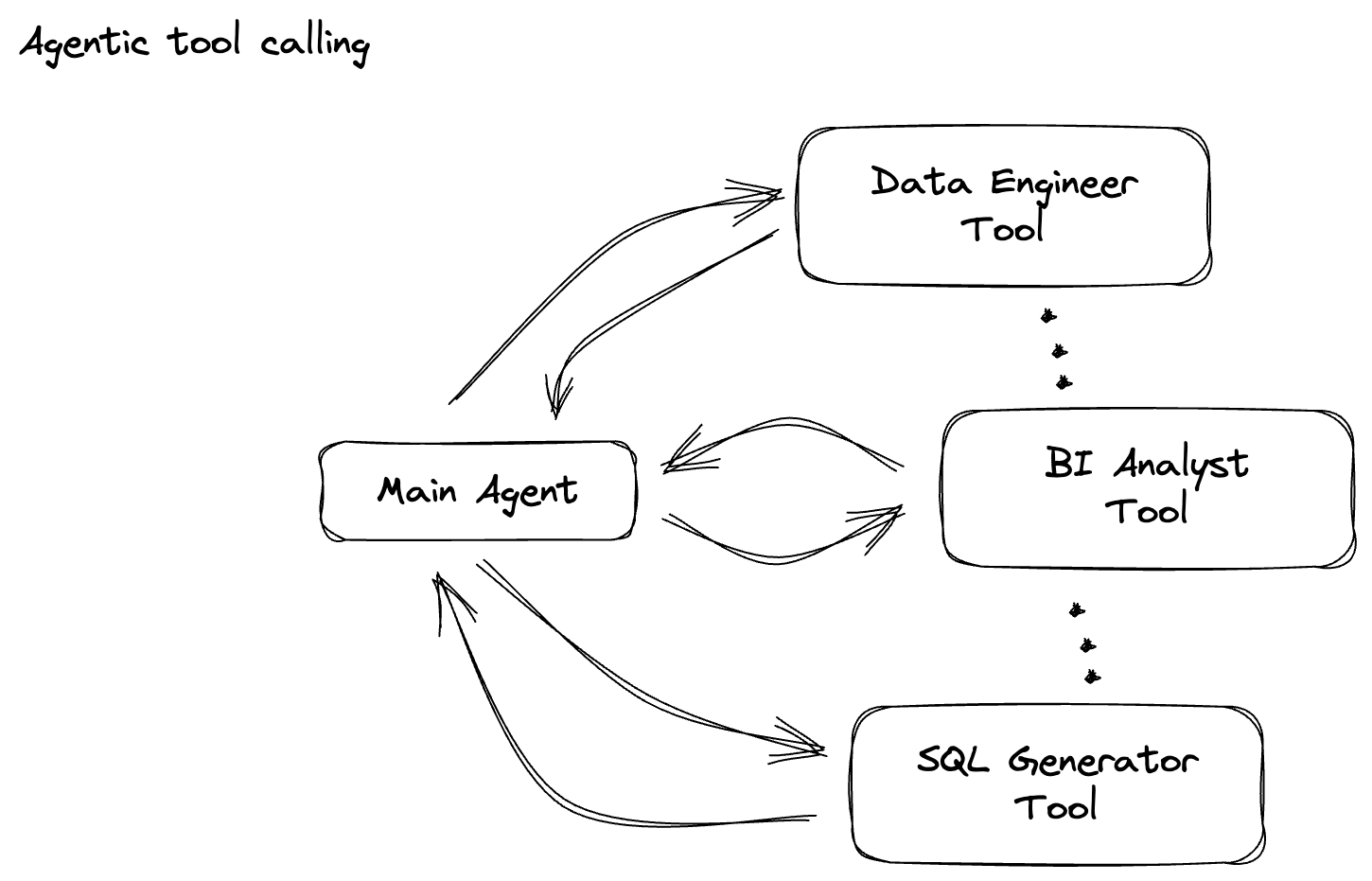
对于本部分,请使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py。
- 构建自定义 ModelHandler;不过,请在 load_model 中返回 genai.Client,而不是返回模型对象。
- 创建自定义 ModelHandler 的 run_inference 函数所需的代码。以下是提示示例:
提示可以如下所示:
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilities.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambiguous. Choose only one.
Finally, always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
- 以 pCollection 的形式生成结果,供下一个 pTransform 使用。
以下是一个代码示例:
############## BEGIN STEP 2 ##############
# load_model is called once per worker process to initialize the LLM client.
# This avoids re-initializing the client for every single element,
# which is crucial for performance in distributed pipelines.
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
# run_inference is called for each batch of elements. Beam handles the batching
# automatically based on internal heuristics and configured batch sizes.
# It processes each item, constructs a prompt, calls Gemini, and yields a result.
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[Any], # Each item is a JSON string or a dict
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""
Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings or dicts.
Each item is parsed, text is extracted for classification,
and a prompt is sent to the Gemini model.
"""
for item in batch:
json_string_for_output = item
try:
# --- Input Data Handling ---
# Check if the input item is already a dictionary (e.g., from TEST_DATA)
# or a JSON string (e.g., from Pub/Sub).
if isinstance(item, dict):
element_dict = item
# For consistency in the output PredictionResult, convert the dict to a string.
# This ensures pr.example always contains the original JSON string.
json_string_for_output = json.dumps(item)
else:
element_dict = json.loads(item)
# Extract the 'text' field from the parsed dictionary.
text_to_classify = element_dict.get('text','')
if not text_to_classify:
logging.warning(f"Input JSON missing 'text' key or text is empty: {json_string_for_output}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_NO_TEXT")
continue
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilites.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambigiuous. Choose only one.
Finally always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
contents = [
types.Content( # This is the actual content for the LLM
role="user",
parts=[
types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)
]
)
]
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(
model=self._model_name, contents=contents, config=self._model_kwargs
)
classification_tag = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
classification_tag+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference=classification_tag)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
logging.error(f"Error decoding JSON string: {json_string_for_output}, error: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_JSON_DECODE")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini inference for input {json_string_for_output}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 2 ##############
通过执行以下命令来测试此代码:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
此步骤应返回来自 Gemini 的推理结果。它会按照提示中的要求对结果进行分类。
您应该会看到如下所示的输出。
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052592.9662862, "user_id": "user_c"}', inference='(HELPER, "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, conversational response to a request. It does not involve data engineering tasks, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is providing a direct, simple form of assistance by fulfilling a non-technical request, which aligns well with the role of a helper.")', model_id=None)
7. 构建 LLM 作为评判者
对提示进行分类后,您将评估模型回答的准确率。这需要再次调用 Gemini 模型,但这次,您将提示模型根据 0.0 到 1.0 的评分标准,评估“文本”满足原始“提示”的程度。这有助于您了解 AI 输出的质量。您将为此任务创建一个单独的 GeminiAccuracyModelHandler。

对于本部分,请使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py。
- 构建自定义 ModelHandler;不过,在 load_model 中返回 genai.Client,就像您在上面所做的那样,而不是返回模型对象。
- 创建自定义 ModelHandler 的 run_inference 函数所需的代码。以下是提示示例:
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
这里需要注意的一点是,您实际上在同一流水线中创建了两个不同的模型。在此特定示例中,您还使用 VertexAI 调用了 Gemini,但根据相同的概念,您可以选择使用和加载其他模型。这简化了模型管理,并允许您在同一 Beam 流水线中使用多个模型。
- 以 pCollection 的形式生成结果,供下一个 pTransform 使用。
以下是一个代码示例:
############## BEGIN STEP 3 ##############
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[str], # Each item is a JSON string
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings to verify accuracy."""
for json_string in batch:
try:
element_dict = json.loads(json_string)
original_prompt = element_dict.get('original_prompt', '')
original_text = element_dict.get('original_text', '')
if not original_prompt or not original_text:
logging.warning(f"Accuracy input missing prompt/text: {json_string}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_ACCURACY_INPUT")
continue
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(model=self._model_name, contents=[prompt_for_accuracy], config=self._model_kwargs)
gemini_response_text = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
gemini_response_text+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference=gemini_response_text)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini accuracy inference for input {json_string}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 3 ##############
通过执行以下命令来测试此代码:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
此步骤还应返回推理结果,并应针对 Gemini 认为工具回答的准确程度添加注释并返回得分。
您应该会看到如下所示的输出。
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"original_data_json": "{\\"id\\": \\"test-6\\", \\"prompt\\": \\"Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.\\", \\"text\\": \\"absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\\", \\"timestamp\\": 1751052770.7552562, \\"user_id\\": \\"user_c\\"}", "original_prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "original_text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "classification_tag": "(HELPER, \\"The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' is a general, conversational response that does not pertain to data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. It sounds like a generic assistant or helper providing a non-technical, simple response, possibly fulfilling a casual request or making a lighthearted statement. Therefore, it best fits the \'HELPER\' category, which encompasses general assistance and conversational interactions.\\")"}', inference='0.0 - The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', model_id=None)
8. 窗口化和分析结果
现在,您将对结果进行窗口化处理,以便在特定时间间隔内进行分析。您将使用固定窗口来对数据进行分组,以便获得汇总的分析洞见。完成窗口化后,您需要将 Gemini 的原始输出解析为更结构化的格式,包括原始数据、分类标记、准确度得分和说明。

在本部分中,请使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py。
- 添加 60 秒的固定时间窗口,以便将所有数据都放置在 60 秒的窗口内。
以下是一个代码示例:
############## BEGIN STEP 4 ##############
| 'WindowIntoFixedWindows' >> beam.WindowInto(beam.window.FixedWindows(60))
############## END STEP 4 ##############
通过执行以下命令来测试此代码:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
此步骤仅供参考,您需要找到自己的窗口。系统会将其显示为窗口停止/启动时间戳。
您应该会看到如下所示的输出。
INFO:root:({'id': 'test-6', 'prompt': 'Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', 'text': "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", 'timestamp': 1751052901.337791, 'user_id': 'user_c'}, '("HELPER", "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, helpful response to a request. It does not involve data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is fulfilling a simple, non-technical request, which aligns with the role of a general helper.")', 0.0, 'The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', [1751052900.0, 1751052960.0))
9. 通过有状态处理来统计好结果和坏结果
最后,您将使用有状态的 DoFn 来统计每个窗口中的“好”结果和“坏”结果。“好”结果可能表示互动具有较高的准确度得分,而“差”结果则表示得分较低。这种有状态处理方式可让您随着时间的推移保持计数,甚至收集“不良”互动的示例,这对于实时监控聊天机器人的健康状况和性能至关重要。
在本部分中,请使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py。
- 创建有状态函数。您需要两种状态:(1) 用于跟踪错误计数,(2) 用于保存要显示的错误记录。使用合适的编码器,确保系统能够高效运行。
- 每次看到不良推理的值时,您都需要跟踪这两个值,并在窗口结束时发出它们。请记得在发出后重置状态。后者仅用于说明,请勿尝试在实际环境中将所有这些内容都保留在内存中。
以下是一个代码示例:
############## BEGIN STEP 5 ##############
# Define a state specification for a combining value.
# This will store the running sum for each key.
# The coder is specified for efficiency.
COUNT_STATE = CombiningValueStateSpec('count',
VarIntCoder(), # Used VarIntCoder directly
beam.transforms.combiners.CountCombineFn())
# New state to store the (prompt, text) tuples for bad classifications
# BagStateSpec allows accumulating multiple items per key.
BAD_PROMPTS_STATE = beam.transforms.userstate.BagStateSpec(
'bad_prompts', coder=beam.coders.TupleCoder([beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder(), beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder()])
)
# Define a timer to fire at the end of the window, using WATERMARK as per blog example.
WINDOW_TIMER = TimerSpec('window_timer', TimeDomain.WATERMARK)
def process(
self,
element: Tuple[str, Tuple[int, Tuple[str, str]]], # (key, (count_val, (prompt, text)))
key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam,
count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE),
bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE), # New state param
window_timer=beam.DoFn.TimerParam(WINDOW_TIMER),
window=beam.DoFn.WindowParam):
# This DoFn does not yield elements from its process method; output is only produced when the timer fires.
if key == 'bad': # Only count 'bad' elements
count_state.add(element[1][0]) # Add the count (which is 1)
bad_prompts_state.add(element[1][1]) # Add the (prompt, text) tuple
window_timer.set(window.end) # Set timer to fire at window end
@on_timer(WINDOW_TIMER)
def on_window_timer(self, key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam, count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE), bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE)):
final_count = count_state.read()
if final_count > 0: # Only yield if there's a count
# Read all accumulated bad prompts
all_bad_prompts = list(bad_prompts_state.read())
# Clear the state for the next window to avoid carrying over data.
count_state.clear()
bad_prompts_state.clear()
yield (key, final_count, all_bad_prompts) # Yield count and list of prompts
############## END STEP 5 ##############
通过执行以下命令来测试此代码:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
此步骤应输出所有计数,您可以尝试调整窗口大小,然后会发现批次有所不同。默认窗口将在一分钟内完成,因此请尝试使用 30 秒或其他时间范围,您应该会看到批次和数量有所不同。
您应该会看到如下所示的输出。
INFO:root:Window: [1751052960.0, 1751053020.0), Bad Counts: 5, Bad Prompts: [('Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?', 'I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.'), ('How is the new feature performing?', 'It works as expected.'), ('What is the capital of France?', 'The square root of a banana is purple.'), ('Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.', 'A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.'), ('Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat")]
10. 清理
- 删除 Google Cloud 项目(可选,但建议用于 Codelab):如果此项目仅为此 Codelab 而创建,并且您不再需要它,那么删除整个项目是确保移除所有资源的最彻底方法。
- 前往 Google Cloud 控制台中的 “管理资源”页面。
- 选择您的项目。
- 点击删除项目,然后按照屏幕上的说明操作。
11. 恭喜!
恭喜您完成此 Codelab!您已成功使用 Apache Beam 和 Gemini 在 Dataflow 上构建了实时机器学习推理流水线。您已了解如何将生成式 AI 的强大功能应用于数据流,从而提取有价值的分析洞见,实现更智能、更自动化的数据工程。

