1. 簡介
在當今快速變化的資料環境中,即時洞察資料對於做出明智決策至關重要。本程式碼研究室會引導您建構即時評估管道。首先,我們會運用 Apache Beam 架構,為批次和串流資料提供整合式程式設計模型。這項功能會將您原本必須從頭建構的複雜分散式運算邏輯抽象化,大幅簡化管道開發作業。使用 Beam 定義管道後,您就能在 Google Cloud Dataflow 上順暢執行管道。這項全代管服務可提供無與倫比的規模和效能,滿足您的資料處理需求。
在本程式碼研究室中,您將瞭解如何為機器學習推論設計可擴充的 Apache Beam 管道、開發自訂 ModelHandler 來整合 Vertex AI 的 Gemini 模型、運用提示工程技術在資料串流中進行智慧文字分類,以及在 Google Cloud Dataflow 上部署及運作這個串流 ML 推論管道。課程結束後,您將深入瞭解如何運用機器學習技術,在工程工作流程中即時解讀資料及持續評估,特別是維護穩定且以使用者為中心的對話式 AI。
情境
貴公司已建構資料代理程式。使用 Agent Development Kit (ADK) 建構的資料代理具備各種專業功能,可協助處理資料相關工作。這項工具就像是多功能的資料助理,可處理各種要求,例如擔任 BI 分析師來產生深入的報表、擔任資料工程師來協助您建構穩健的資料管道,或是擔任 SQL 產生器來製作精確的 SQL 陳述式等等。這個代理程式的每次互動和生成的回應,都會自動儲存到 Firestore。但為什麼這裡需要管道?
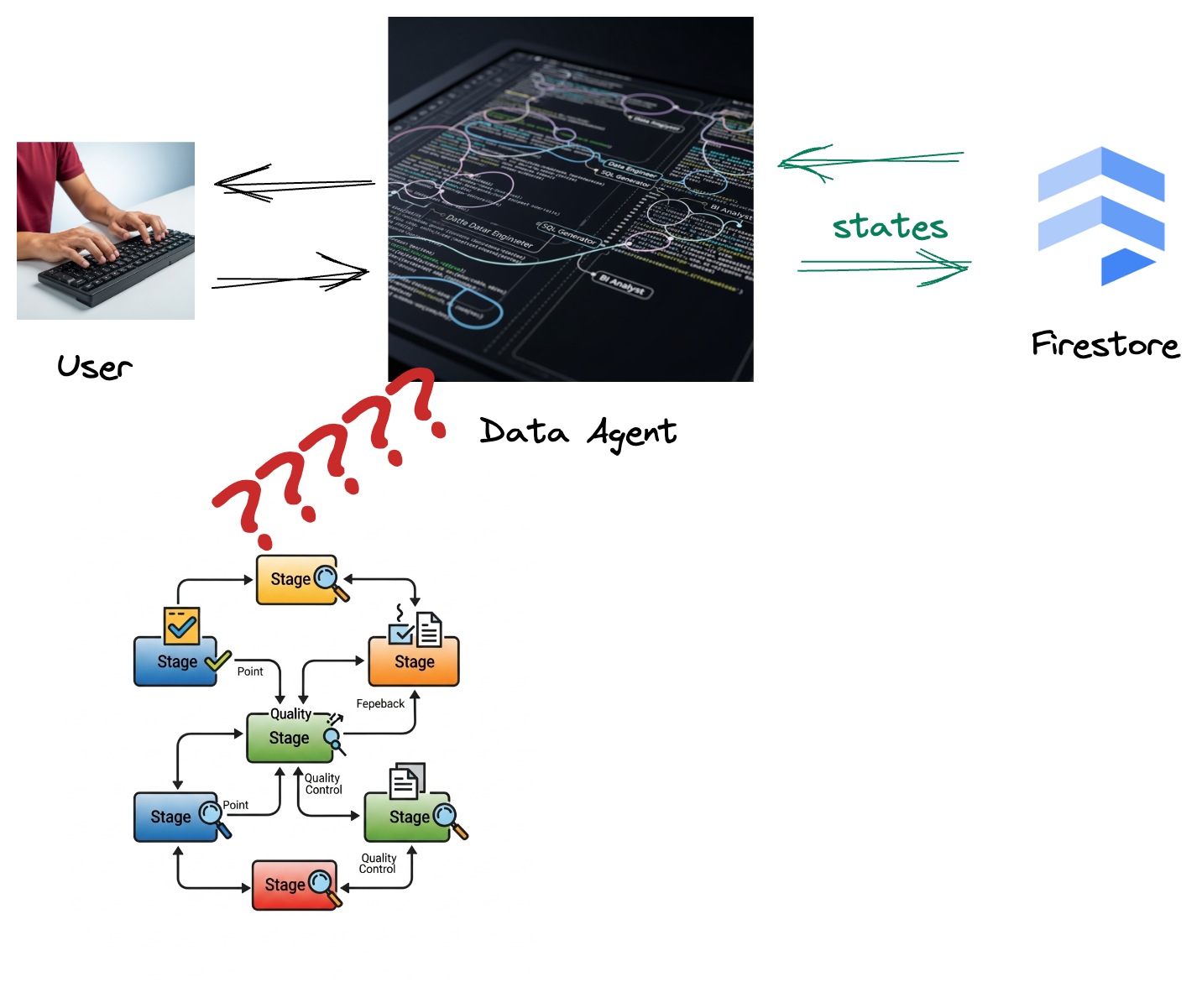
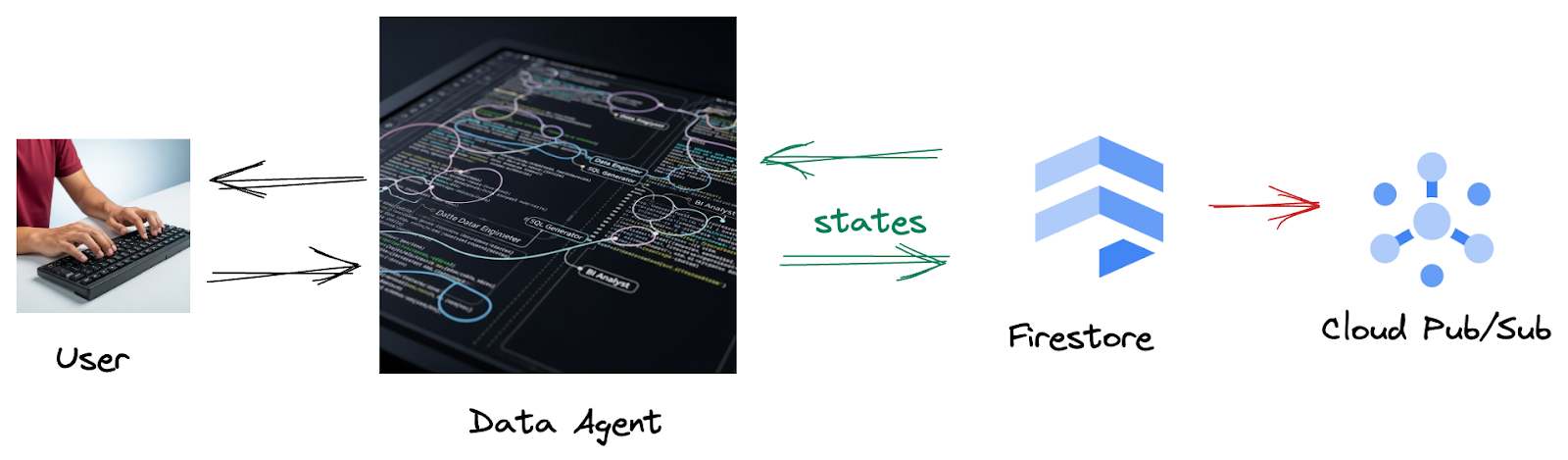
因為 Firestore 的觸發程序會將互動資料順暢地傳送至 Pub/Sub,確保我們能立即處理及分析這些重要對話。
2. 事前準備
建立專案
- 在 Google Cloud 控制台的專案選取器頁面中,選取或建立 Google Cloud 專案。
- 確認 Cloud 專案已啟用計費功能。瞭解如何檢查專案是否已啟用計費功能。
- 按一下這個連結,啟動 Cloud Shell。如要在 Cloud Shell 終端機 (用於執行雲端指令) 和編輯器 (用於建構專案) 之間切換,請點選 Cloud Shell 中的對應按鈕。
- 連線至 Cloud Shell 後,請使用下列指令檢查您是否已通過驗證,且專案已設為您的專案 ID:
gcloud auth list
- 在 Cloud Shell 中執行下列指令,確認 gcloud 指令已瞭解您的專案。
gcloud config list project
- 如果未設定專案,請使用下列指令來設定:
export PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
- 透過下列指令啟用必要的 API。這可能需要幾分鐘的時間,請耐心等候。
gcloud services enable \
dataflow.googleapis.com \
pubsub.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com
- 請務必使用 Python 3.10 以上版本
- 安裝 Python 套件
在 Cloud Shell 環境中,安裝 Apache Beam、Google Cloud Vertex AI 和 Google Generative AI 必要的 Python 程式庫。
pip install apache-beam[gcp] google-genai
- 複製 GitHub 存放區,然後切換至示範目錄。
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos
cd devrel-demos/data-analytics/beam_as_eval
如要瞭解 gcloud 指令和用法,請參閱說明文件。
3. 如何使用提供的 GitHub 存放區
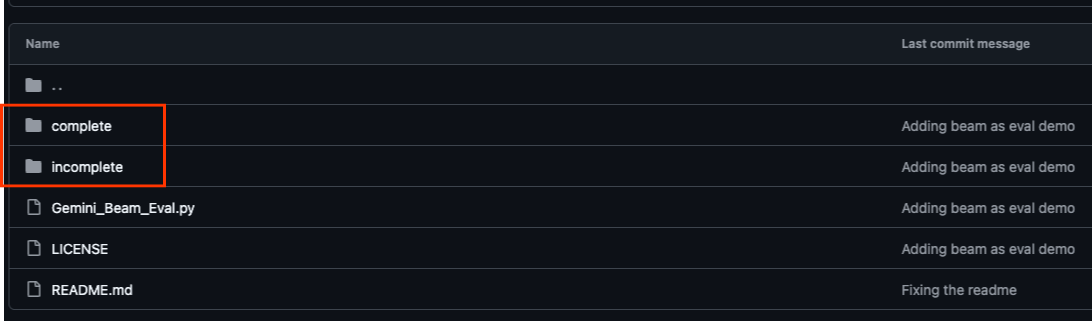
本程式碼研究室的相關 GitHub 存放區 (位於 https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos/tree/main/data-analytics/beam_as_eval) 經過整理,可提供引導式學習體驗。其中包含與程式碼研究室各個不同部分相符的架構程式碼,確保您能清楚瞭解教材內容。
在存放區中,您會看到兩個主要資料夾:「complete」和「incomplete」。「complete」資料夾包含每個步驟的完整程式碼,方便您執行並觀察預期輸出內容。相反地,「incomplete」資料夾提供先前步驟的程式碼,並在 ##### START STEP <NUMBER> ##### 和 ##### END STEP <NUMBER> ##### 之間標示特定區段,供您在練習中完成。這個結構可讓您在積極參與程式設計挑戰的同時,運用先前的知識。
4. 架構總覽
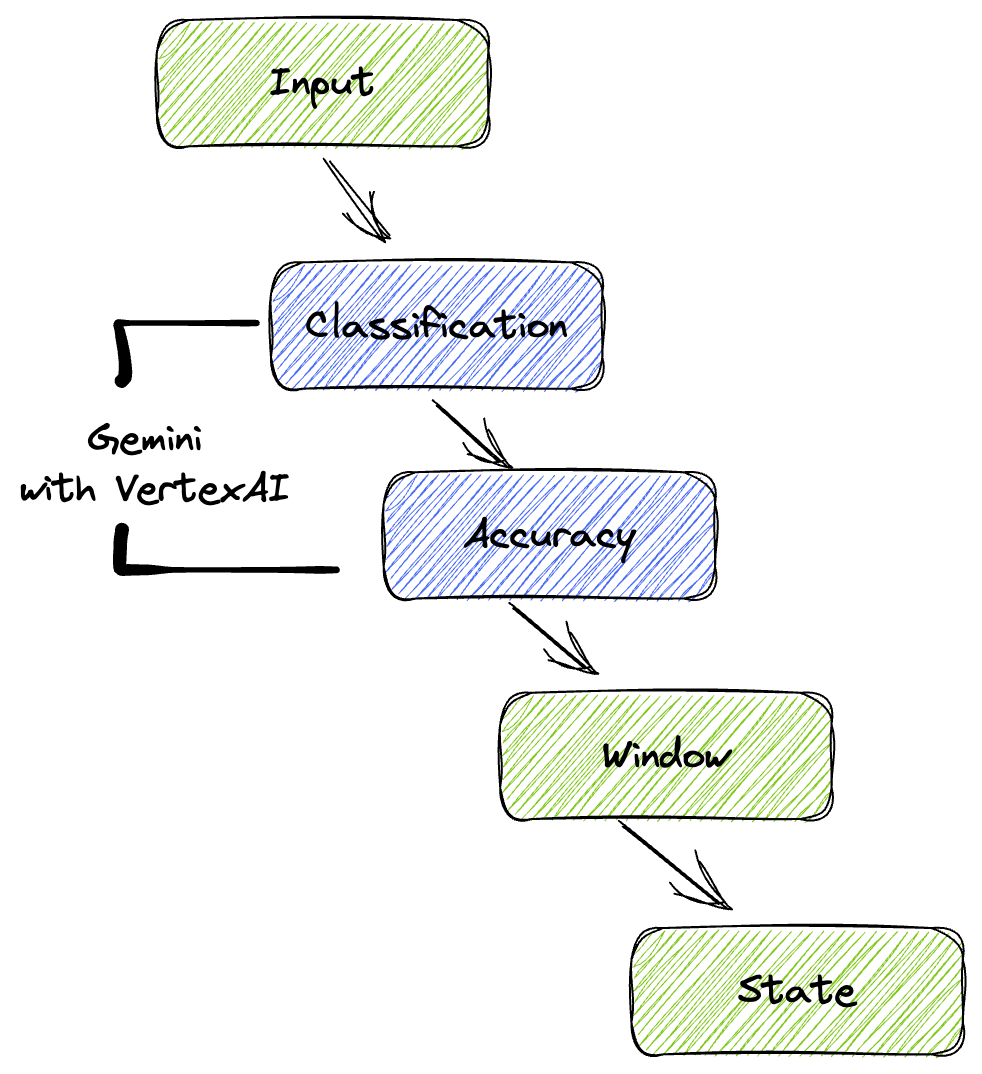
我們的管道提供強大且可擴充的模式,可將機器學習推論整合至資料串流。以下說明各部分如何整合運作:
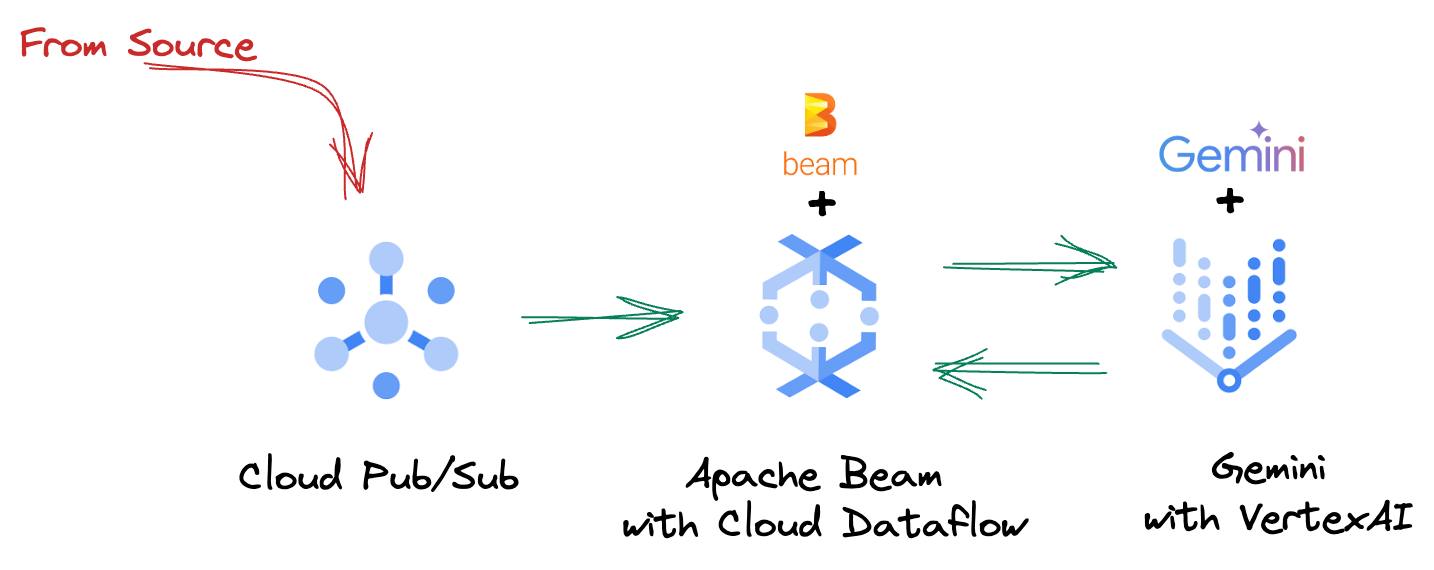
在 Beam 管道中,您會以條件方式編寫多個輸入內容,然後使用 RunInference 簡易轉換載入自訂模型。雖然範例中您是搭配 Vertex AI 使用 Gemini,但這項範例會示範如何建立多個 ModelHandler,以配合您擁有的模型數量。最後,您將使用具狀態的 DoFn 追蹤事件,並以受控方式發出事件。
5. 擷取資料
首先,您要設定管道來擷取資料。您將使用 Pub/Sub 進行即時串流,但為了簡化開發作業,您也會建立測試模式。這個 test_mode 可讓您使用預先定義的範例資料在本機執行管道,因此不需要即時 Pub/Sub 串流,即可查看管道是否正常運作。
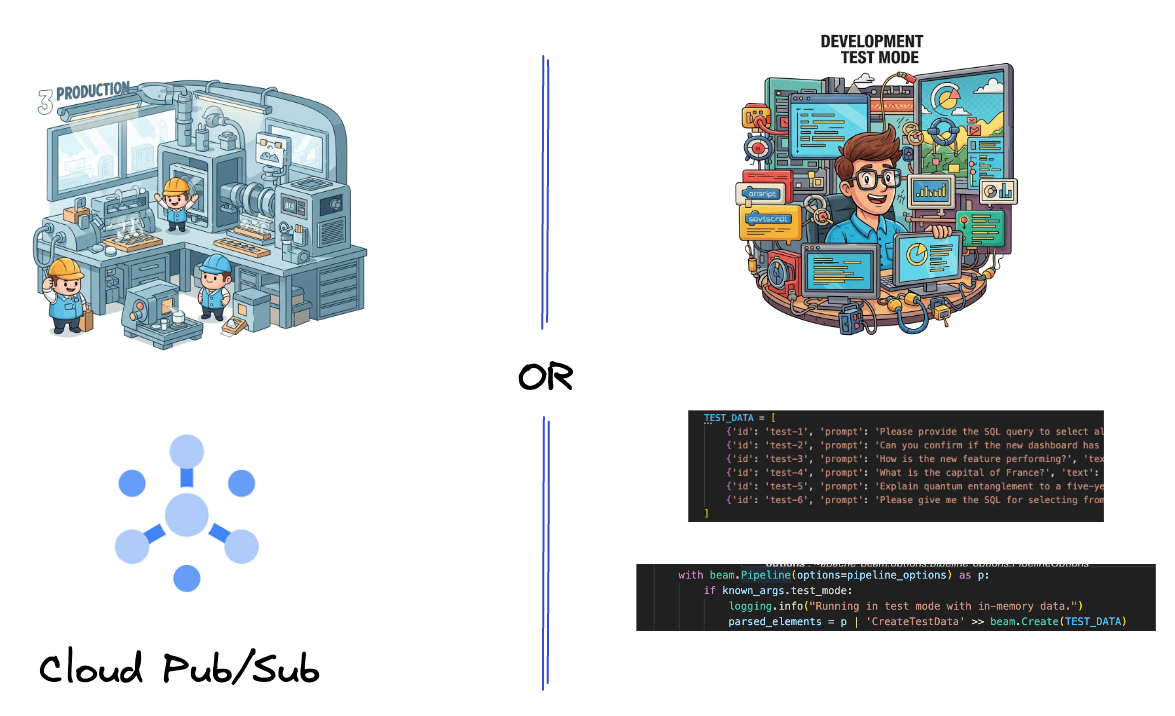
本節請使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py。
- 使用提供的管道物件 p,編寫 Pub/Sub 輸入內容,並將輸出內容寫為 pCollection。
- 此外,請使用旗標判斷是否已設定 TEST_MODE。
- 如果已設定 TEST_MODE,請改為將 TEST_DATA 陣列剖析為輸入內容。
這並非必要步驟,但有助於縮短程序,因此您不需要這麼早加入 Pub/Sub。
以下是程式碼範例:
# Step 1
# Ingesting Data
# Write your data ingestion step here.
############## BEGIN STEP 1 ##############
if known_args.test_mode:
logging.info("Running in test mode with in-memory data.")
parsed_elements = p | 'CreateTestData' >> beam.Create(TEST_DATA)
# Convert dicts to JSON strings and add timestamps for test mode
parsed_elements = parsed_elements | 'ConvertTestDictsToJsonAndAddTimestamps' >> beam.Map(
lambda x: beam.window.TimestampedValue(json.dumps(x), x['timestamp'])
)
else:
logging.info(f"Reading from Pub/Sub topic: {known_args.input_topic}")
parsed_elements = (
p
| 'ReadFromPubSub' >> beam.io.ReadFromPubSub(
topic=known_args.input_topic
).with_output_types(bytes)
| 'DecodeBytes' >> beam.Map(lambda b: b.decode('utf-8')) # Output is JSON string
# Extract timestamp from JSON string for Pub/Sub messages
| 'AddTimestampsFromParsedJson' >> beam.Map(lambda s: beam.window.TimestampedValue(s, json.loads(s)['timestamp']))
)
############## END STEP 1 ##############
執行下列指令來測試這段程式碼:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step1.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
這個步驟應會發出所有記錄,並將記錄寫入 stdout。
您應該會看到類似以下的輸出內容。
INFO:root:Running in test mode with in-memory data.
INFO:apache_beam.runners.worker.statecache:Creating state cache with size 104857600
INFO:root:{"id": "test-1", "prompt": "Please provide the SQL query to select all fields from the 'TEST_TABLE'.", "text": "Sure here is the SQL: SELECT * FROM TEST_TABLE;", "timestamp": 1751052405.9340951, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-2", "prompt": "Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?", "text": "I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.", "timestamp": 1751052410.9340951, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-3", "prompt": "How is the new feature performing?", "text": "It works as expected.", "timestamp": 1751052415.9340959, "user_id": "user_a"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-4", "prompt": "What is the capital of France?", "text": "The square root of a banana is purple.", "timestamp": 1751052430.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-5", "prompt": "Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.", "text": "A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.", "timestamp": 1751052435.9340959, "user_id": "user_b"}
INFO:root:{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052440.9340959, "user_id": "user_c"}
6. 為 LLM 提示分類建構 PTransform
接下來,您將建構 PTransform 來分類提示。這包括使用 Vertex AI 的 Gemini 模型,將傳入的文字分類。您將定義自訂 GeminiModelHandler,載入 Gemini 模型,然後指示模型如何將文字分類為「資料工程師」、「商業智慧分析師」或「SQL 產生器」等類別。
您可以與記錄中的實際工具呼叫進行比較,藉此使用這項功能。本程式碼研究室不會介紹這項功能,但您可以將其傳送至下游並進行比較。有些意圖可能模稜兩可,這時意圖是確保代理程式呼叫正確工具的絕佳額外資料點。
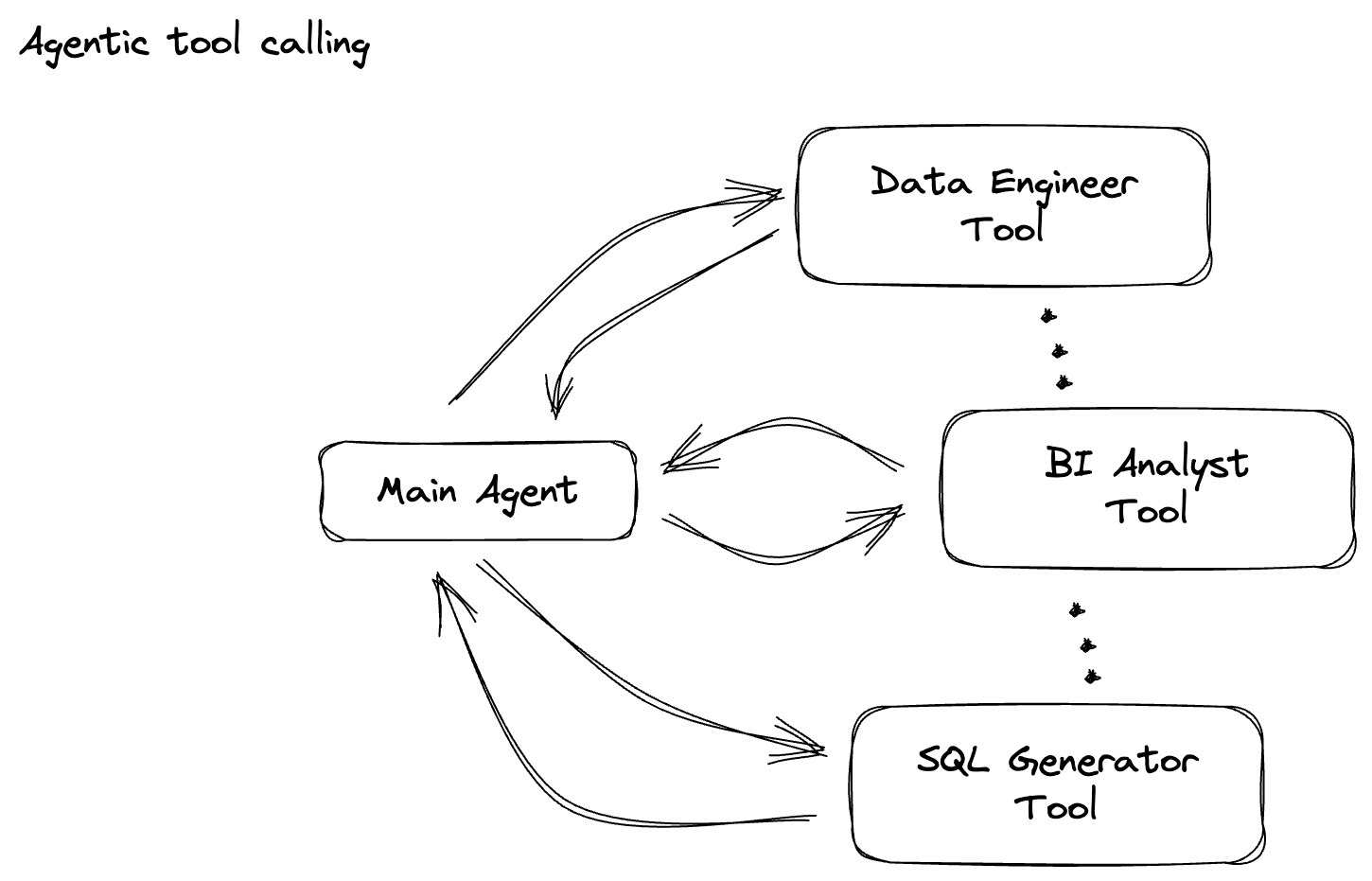
本節請使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py。
- 建立自訂 ModelHandler,但不要在 load_model 中傳回模型物件,而是傳回 genai.Client。
- 您需要建立自訂 ModelHandler 的 run_inference 函式。我們提供了一個範例提示:
提示可以如下所示:
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilities.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambiguous. Choose only one.
Finally, always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
- 將結果做為下一個 pTransform 的 pCollection。
以下是程式碼範例:
############## BEGIN STEP 2 ##############
# load_model is called once per worker process to initialize the LLM client.
# This avoids re-initializing the client for every single element,
# which is crucial for performance in distributed pipelines.
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
# run_inference is called for each batch of elements. Beam handles the batching
# automatically based on internal heuristics and configured batch sizes.
# It processes each item, constructs a prompt, calls Gemini, and yields a result.
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[Any], # Each item is a JSON string or a dict
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""
Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings or dicts.
Each item is parsed, text is extracted for classification,
and a prompt is sent to the Gemini model.
"""
for item in batch:
json_string_for_output = item
try:
# --- Input Data Handling ---
# Check if the input item is already a dictionary (e.g., from TEST_DATA)
# or a JSON string (e.g., from Pub/Sub).
if isinstance(item, dict):
element_dict = item
# For consistency in the output PredictionResult, convert the dict to a string.
# This ensures pr.example always contains the original JSON string.
json_string_for_output = json.dumps(item)
else:
element_dict = json.loads(item)
# Extract the 'text' field from the parsed dictionary.
text_to_classify = element_dict.get('text','')
if not text_to_classify:
logging.warning(f"Input JSON missing 'text' key or text is empty: {json_string_for_output}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_NO_TEXT")
continue
prompt =f"""
The input is a response from another agent.
The agent has multiple tools, each having their own responsibilites.
You are to analyze the input and then classify it into one and only one.
Use the best one if it seems like it is ambigiuous. Choose only one.
Finally always provide a paragraph on why you think it is in one of the categories.
Classify the text into one of these categories:
DATA ENGINEER
BI ANALYST
SQL GENERATOR
HELPER
OTHER
Respond with only the one single classification tag.
Your response should be in a tuple (classification_tag, reason)
Text: "{text_to_classify}"
"""
contents = [
types.Content( # This is the actual content for the LLM
role="user",
parts=[
types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)
]
)
]
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(
model=self._model_name, contents=contents, config=self._model_kwargs
)
classification_tag = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
classification_tag+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference=classification_tag)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
logging.error(f"Error decoding JSON string: {json_string_for_output}, error: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_JSON_DECODE")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini inference for input {json_string_for_output}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string_for_output, inference="ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 2 ##############
執行下列指令來測試這段程式碼:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step2.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
這個步驟應會傳回 Gemini 的推論結果。並按照提示要求分類結果。
您應該會看到類似以下的輸出內容。
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"id": "test-6", "prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "timestamp": 1751052592.9662862, "user_id": "user_c"}', inference='(HELPER, "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, conversational response to a request. It does not involve data engineering tasks, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is providing a direct, simple form of assistance by fulfilling a non-technical request, which aligns well with the role of a helper.")', model_id=None)
7. 建構 LLM 做為評估者
分類提示後,請評估模型回覆的準確度。這會涉及對 Gemini 模型進行另一次呼叫,但這次您會提示模型,根據 0.0 到 1.0 的評分標準,評估「text」是否符合原始「prompt」。這有助於瞭解 AI 輸出內容的品質。您將為這項工作建立個別的 GeminiAccuracyModelHandler。

本節請使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py。
- 建構自訂 ModelHandler,但不要在 load_model 中傳回模型物件,而是傳回 genai.Client,就像您在上方所做的一樣。
- 您需要建立自訂 ModelHandler 的 run_inference 函式。我們提供了一個範例提示:
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
請注意,您基本上是在同一個管道中建立兩個不同的模型。在這個特定範例中,您也使用 Vertex AI 呼叫 Gemini,但根據相同概念,您可以選擇使用及載入其他模型。這項功能可簡化模型管理作業,並讓您在同一個 Beam 管線中使用多個模型。
- 將結果做為下一個 pTransform 的 pCollection。
以下是程式碼範例:
############## BEGIN STEP 3 ##############
def load_model(self) -> genai.Client:
"""Loads and initializes a model for processing."""
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=self._project,
location=self._location,
)
return client
def run_inference(
self,
batch: Sequence[str], # Each item is a JSON string
model: genai.Client,
inference_args: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None
) -> Iterable[PredictionResult]:
"""Runs inference on a batch of JSON strings to verify accuracy."""
for json_string in batch:
try:
element_dict = json.loads(json_string)
original_prompt = element_dict.get('original_prompt', '')
original_text = element_dict.get('original_text', '')
if not original_prompt or not original_text:
logging.warning(f"Accuracy input missing prompt/text: {json_string}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_ACCURACY_INPUT")
continue
prompt_for_accuracy = f"""
You are an AI assistant evaluating the accuracy of another AI agent's response to a given prompt.
Score the accuracy of the 'text' in fulfilling the 'prompt' from 0.0 to 1.0 (float).
0.0 is very bad, 1.0 is excellent.
Example of very bad, score of 0:
prompt: Give me the SQL for test_Table
text: SUre, here's a picture of a dog
Example of very good score of 1:
prompt: generate a sql statement to select all fields from test_table
text: SELECT * from test_table;
Your response should be ONLY the float score, followed by a brief explanation of why.
For example: "0.8 - The response was mostly accurate but missed a minor detail."
Prompt: "{original_prompt}"
Text: "{original_text}"
Score and Explanation:
"""
gemini_response = model.models.generate_content_stream(model=self._model_name, contents=[prompt_for_accuracy], config=self._model_kwargs)
gemini_response_text = ""
for chunk in gemini_response:
if chunk.text is not None:
gemini_response_text+=chunk.text
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference=gemini_response_text)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error during Gemini accuracy inference for input {json_string}: {e}")
yield PredictionResult(example=json_string, inference="0.0 - ERROR_INFERENCE")
############## END STEP 3 ##############
執行下列指令來測試這段程式碼:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step3.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
這個步驟也應傳回推論結果,並根據 Gemini 認為工具回覆的準確度,加上註解並傳回分數。
您應該會看到類似以下的輸出內容。
INFO:root:PredictionResult(example='{"original_data_json": "{\\"id\\": \\"test-6\\", \\"prompt\\": \\"Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.\\", \\"text\\": \\"absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\\", \\"timestamp\\": 1751052770.7552562, \\"user_id\\": \\"user_c\\"}", "original_prompt": "Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.", "original_text": "absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat", "classification_tag": "(HELPER, \\"The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' is a general, conversational response that does not pertain to data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. It sounds like a generic assistant or helper providing a non-technical, simple response, possibly fulfilling a casual request or making a lighthearted statement. Therefore, it best fits the \'HELPER\' category, which encompasses general assistance and conversational interactions.\\")"}', inference='0.0 - The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', model_id=None)
8. 時間區間和分析結果
現在,您可以設定結果的時間範圍,以便分析特定時間間隔的結果。您將使用固定時間區間分組資料,以便取得匯總洞察資料。完成視窗化後,您會將 Gemini 的原始輸出內容剖析為更結構化的格式,包括原始資料、分類標記、準確度分數和說明。

本節請使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py。
- 加入 60 秒的固定時間範圍,將所有資料放在 60 秒的範圍內。
以下是程式碼範例:
############## BEGIN STEP 4 ##############
| 'WindowIntoFixedWindows' >> beam.WindowInto(beam.window.FixedWindows(60))
############## END STEP 4 ##############
執行下列指令來測試這段程式碼:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step4.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
這個步驟是為了提供資訊,您要尋找的是視窗。系統會顯示為視窗停止/開始時間戳記。
您應該會看到類似以下的輸出內容。
INFO:root:({'id': 'test-6', 'prompt': 'Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', 'text': "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat", 'timestamp': 1751052901.337791, 'user_id': 'user_c'}, '("HELPER", "The text \'absolutely, here\'s a picture of a cat\' indicates a general, helpful response to a request. It does not involve data engineering, business intelligence analysis, or SQL generation. Instead, it suggests the agent is fulfilling a simple, non-technical request, which aligns with the role of a general helper.")', 0.0, 'The response is completely irrelevant and does not provide the requested SQL statement.', [1751052900.0, 1751052960.0))
9. 使用有狀態處理程序計算良好和不良結果
最後,您將使用有狀態的 DoFn,計算每個視窗中的「良好」和「不良」結果。「良好」結果可能代表互動的準確度分數較高,「不良」結果則代表分數較低。這種有狀態的處理方式可讓您維持計數,甚至長期收集「不良」互動的範例,這對於即時監控聊天機器人的健康狀態和成效至關重要。
本節請使用 gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py。
- 建立有狀態函式。您需要兩種狀態:(1) 追蹤錯誤計數,以及 (2) 保留要顯示的錯誤記錄。請使用適當的編碼器,確保系統效能良好。
- 每次看到錯誤推論的值時,您都想追蹤這兩者,並在視窗結尾發出。發出狀態後,請記得重設狀態。後者僅供說明用途,請勿嘗試在實際環境中將所有這些項目保留在記憶體中。
以下是程式碼範例:
############## BEGIN STEP 5 ##############
# Define a state specification for a combining value.
# This will store the running sum for each key.
# The coder is specified for efficiency.
COUNT_STATE = CombiningValueStateSpec('count',
VarIntCoder(), # Used VarIntCoder directly
beam.transforms.combiners.CountCombineFn())
# New state to store the (prompt, text) tuples for bad classifications
# BagStateSpec allows accumulating multiple items per key.
BAD_PROMPTS_STATE = beam.transforms.userstate.BagStateSpec(
'bad_prompts', coder=beam.coders.TupleCoder([beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder(), beam.coders.StrUtf8Coder()])
)
# Define a timer to fire at the end of the window, using WATERMARK as per blog example.
WINDOW_TIMER = TimerSpec('window_timer', TimeDomain.WATERMARK)
def process(
self,
element: Tuple[str, Tuple[int, Tuple[str, str]]], # (key, (count_val, (prompt, text)))
key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam,
count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE),
bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE), # New state param
window_timer=beam.DoFn.TimerParam(WINDOW_TIMER),
window=beam.DoFn.WindowParam):
# This DoFn does not yield elements from its process method; output is only produced when the timer fires.
if key == 'bad': # Only count 'bad' elements
count_state.add(element[1][0]) # Add the count (which is 1)
bad_prompts_state.add(element[1][1]) # Add the (prompt, text) tuple
window_timer.set(window.end) # Set timer to fire at window end
@on_timer(WINDOW_TIMER)
def on_window_timer(self, key=beam.DoFn.KeyParam, count_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(COUNT_STATE), bad_prompts_state=beam.DoFn.StateParam(BAD_PROMPTS_STATE)):
final_count = count_state.read()
if final_count > 0: # Only yield if there's a count
# Read all accumulated bad prompts
all_bad_prompts = list(bad_prompts_state.read())
# Clear the state for the next window to avoid carrying over data.
count_state.clear()
bad_prompts_state.clear()
yield (key, final_count, all_bad_prompts) # Yield count and list of prompts
############## END STEP 5 ##############
執行下列指令來測試這段程式碼:
python gemini_beam_pipeline_step5.py --project $PROJECT_ID --runner DirectRunner --test_mode
這個步驟應會輸出所有計數,請調整視窗大小,您會發現批次大小不同。預設視窗會在一分鐘內完成,因此請嘗試使用 30 秒或其他時間範圍,您應該會看到批次和計數有所不同。
您應該會看到類似以下的輸出內容。
INFO:root:Window: [1751052960.0, 1751053020.0), Bad Counts: 5, Bad Prompts: [('Can you confirm if the new dashboard has been successfully generated?', 'I have gone ahead and generated a new dashboard for you.'), ('How is the new feature performing?', 'It works as expected.'), ('What is the capital of France?', 'The square root of a banana is purple.'), ('Explain quantum entanglement to a five-year-old.', 'A flock of geese wearing tiny hats danced the tango on the moon.'), ('Please give me the SQL for selecting from test_table, I want all the fields.', "absolutely, here's a picture of a cat")]
10. 清除
- 刪除 Google Cloud 專案 (選用,但建議用於程式碼研究室):如果這個專案是專為本程式碼研究室建立,且您不再需要,刪除整個專案是確保移除所有資源最徹底的方式。
11. 恭喜!
恭喜您完成本程式碼研究室!您已成功使用 Apache Beam 和 Gemini on Dataflow,建構即時機器學習推論管道。您已瞭解如何運用生成式 AI 的強大功能處理資料串流,從中擷取寶貴洞察資訊,進一步實現智慧化和自動化資料工程。

