1. Before you begin
What are Google Chat apps with AI?
Google Chat apps with AI do the following:
- Bring your services and resources into Google Chat, which lets users get information and take action without leaving the conversation.
- Integrate with generative AI models to create, search, and edit data like text or images.
- Support an agentic experience by applying conversational AI concepts for more practical, natural, sophisticated and helpful interactions.
Why integrate Google Chat apps with AI?
The typical use cases fall in the following categories:
- Content creation and edition. Generate marketing copy, craft social media posts, create realistic images, compose music, or aid in the creation of video content.
- Data search and analysis. Extract key insights from an unstructured knowledge base, summarize lengthy texts, classify contents, or translate languages with enhanced accuracy and speed.
- Conversation. Engage in natural, informative, and efficient conversations like you would with an assistant.
- Task automation. Take actions on behalf of the user, such as creating a new calendar event, sending a document, or managing a ticket in an external system.
The ability to integrate these capabilities directly within the familiar interface of Google Chat is a huge opportunity for anyone who wants to improve the experience and productivity of their users.
Prerequisites
- Basic knowledge of Google Cloud and Node.js.
- Basic knowledge of Google Chat apps, including messages, cards, authentication, APIs, and HTTP endpoints.
What you will build
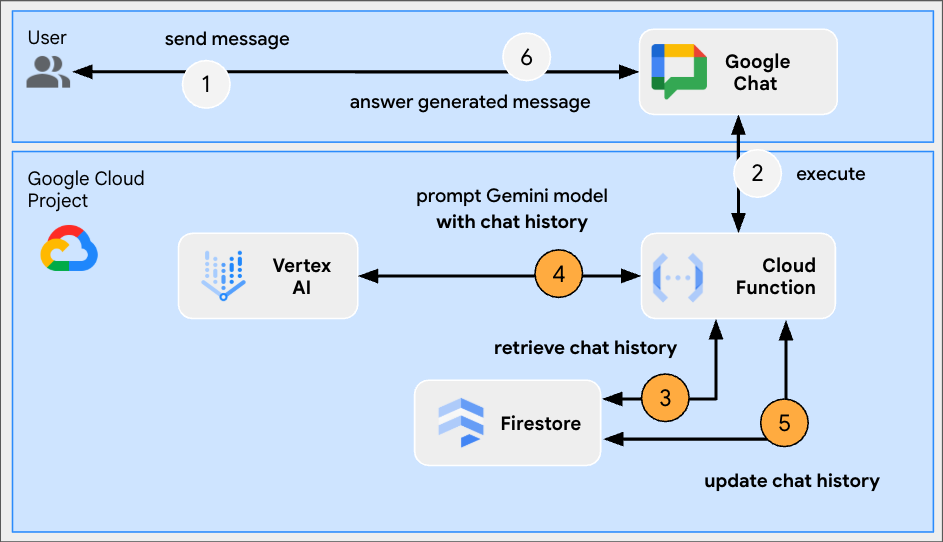
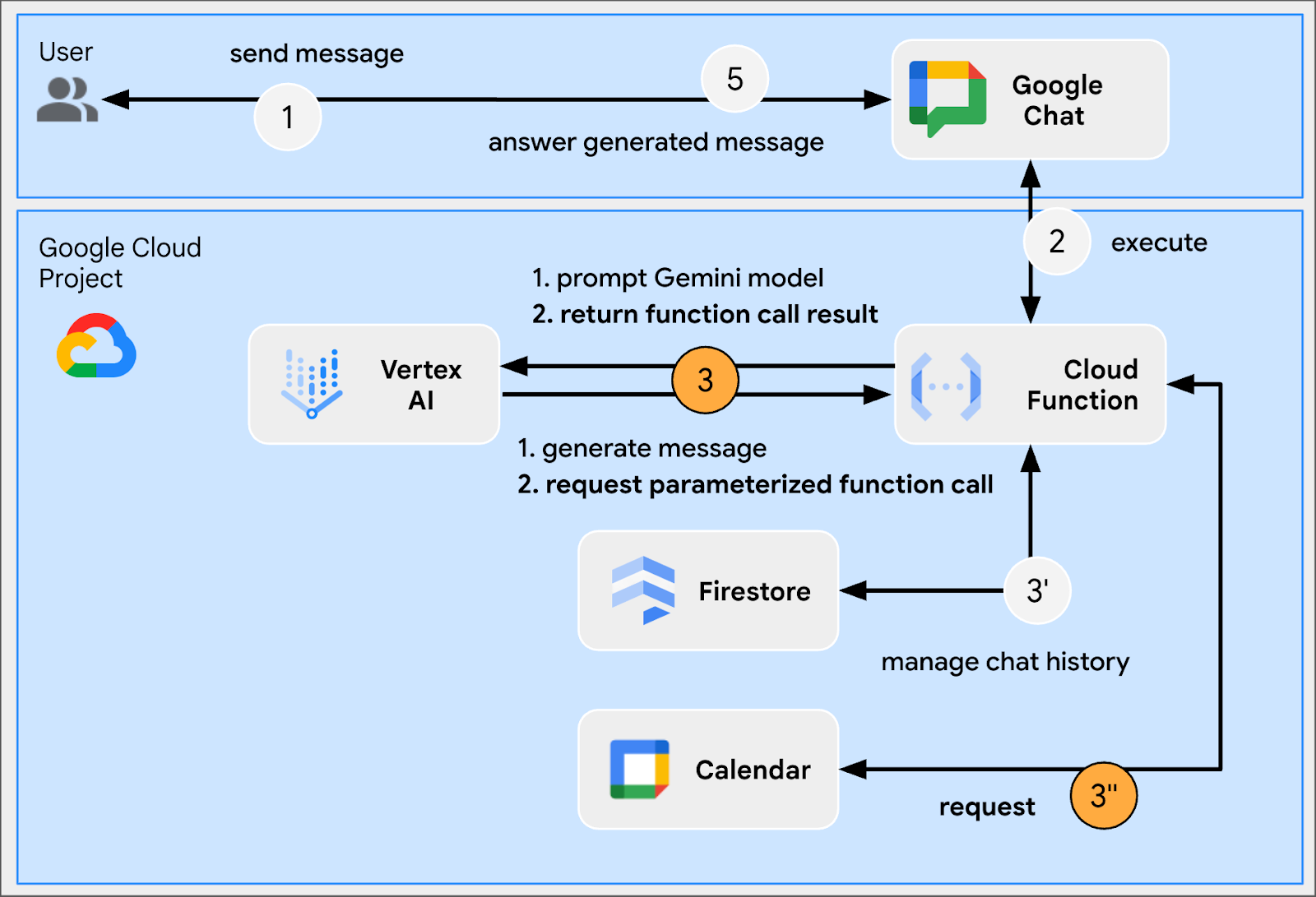
In this codelab, you will build eight minimalist Google Chat apps that integrate fundamental AI concepts to show how they can be applied in real-world applications. They are all built as Google Workspace add ons and rely on the HTTP architecture:
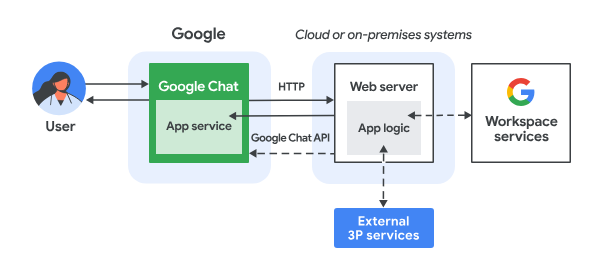
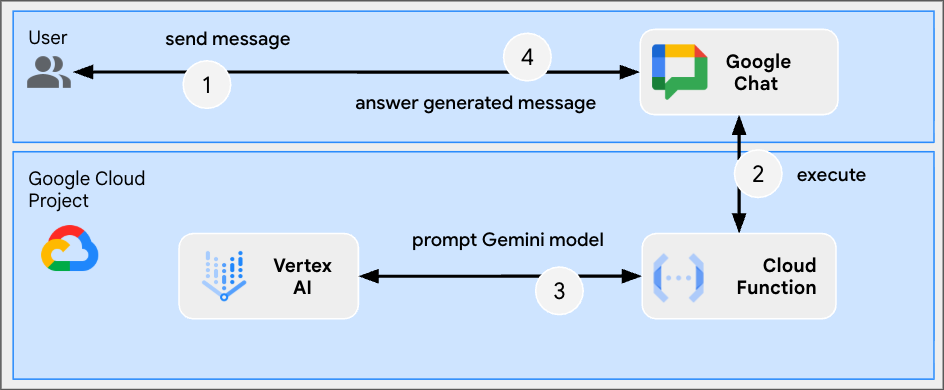
It works as follows:
- A user sends a message in Google Chat to a Chat app, either as a direct message or in a Chat space.
- An HTTP request is sent to the web server running as a Node.js Google Cloud Run function that contains the Chat app logic.
- Optionally, the Chat app logic can integrate with Google Workspace services (like Calendar and Sheets), other Google services (like Maps, YouTube, and Vertex AI), or other web services (like a project management system or ticketing tool).
- The web server sends an HTTP response back to the Chat app service in Chat.
- The response is delivered to the user.
- Optionally, the Chat app can call the Chat API to asynchronously post messages or perform other operations.
Each Google Chat app's Node.js Google Cloud Run function contains their own version of the following source files to take the necessary actions in steps #3 and #6 above:
package.json: A central manifest that acts as a blueprint for the Node.js project. It's used to define the metadata, dependencies, and scripts.env.js: A script that sets constants required for execution. It should be edited based on the environment and configuration.index.js:The main script that handles the logic for the Google Chat interaction events. Only the message event type is implemented in this codelab but it would typically include other types such as card click, slash command, and dialog in real-life applications.
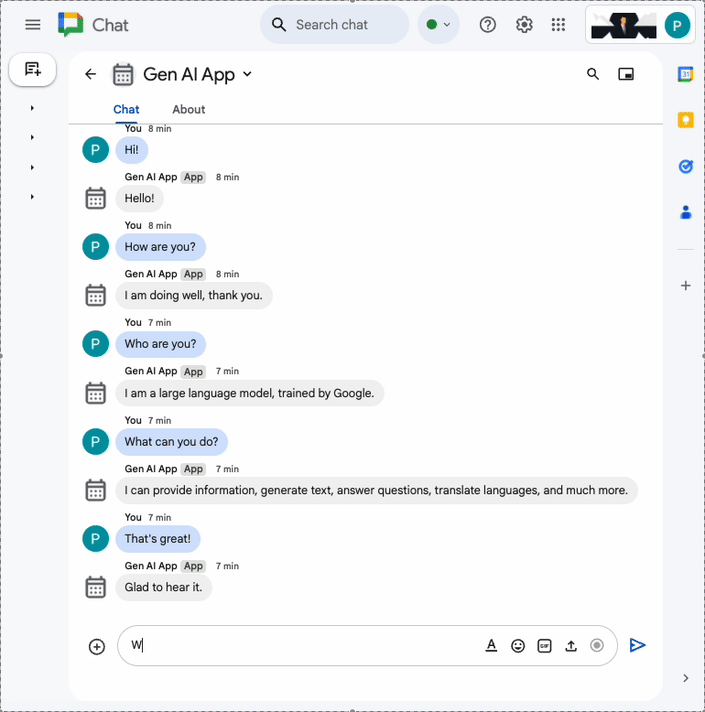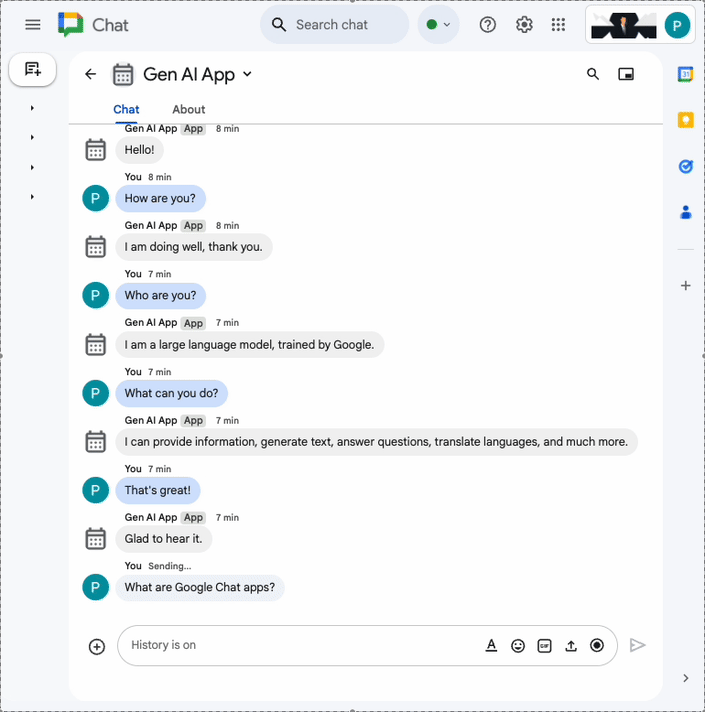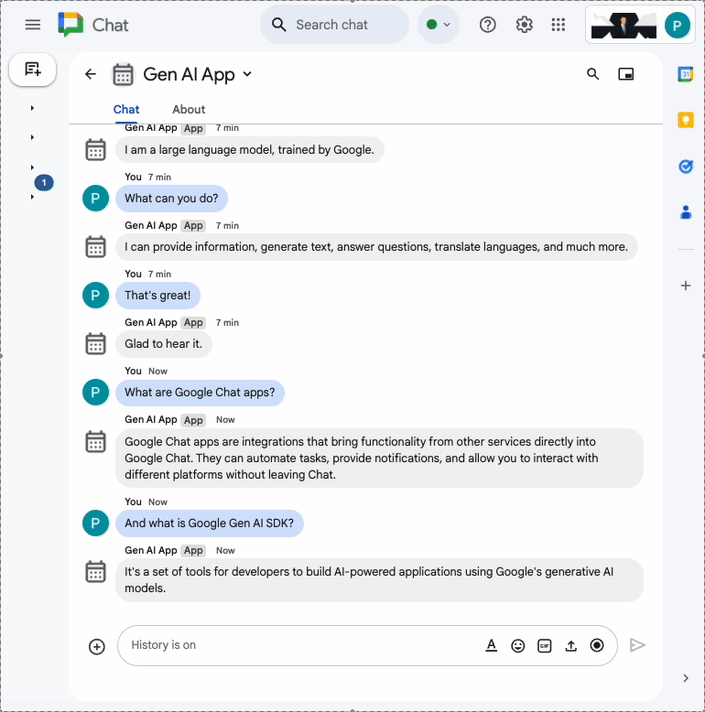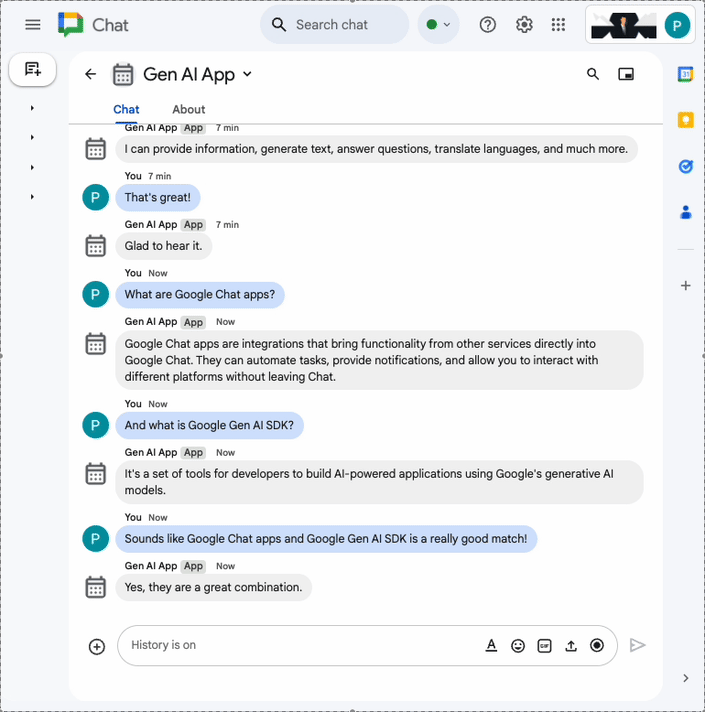
Prompt app
This app relies on a Gemini model to converse with users in their natural languages using concise and plain text answers.
Format app
This app builds on the Prompt app by adding support for rich text answers compliant with the specific text format of Google Chat messages.
Ground app
This app builds on the Format app by adding support for the Google Search tool and returning sources in answer messages with cards.
MCP app
This app builds on the Format app by adding support for the Google Workspace Developer Assist Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Multi-turn app
This app builds on the Format app by adding support for conversational memory with a Google Cloud Firestore database.
Custom tool app
This app builds on the Multi-turn app by adding support for a function calling custom tool that calls the Google Workspace Calendar API based on information provided by the user.
Stream app
This app relies on a Gemini model to generate short stories based on themes provided by users. The Google Chat API is used to send results and statuses in messages as progress is made.
Multimodal app
This app relies on a Gemini model to edit images based on textual instructions from users. Google Chat APIs are used to download and upload the images as message attachments.
What you will learn
- The fundamental AI concepts are relevant to Google Chat apps and how to apply them.
- To access Vertex AI using the Google Gen AI SDK.
- To use Google Workspace APIs to develop delightful and powerful features.
- To leverage Cloud Run to build scalable Google Chat apps.
What you will need
- Completion of the Build an HTTP Google Chat app quickstart with Node.js. This codelab builds on the resulting Google Cloud project, Google Chat app, and Google Cloud Run function.
2. Get set up
Initialize and access resources
In this section, you access and configure the following resources from your preferred web browser.
Google Chat API configuration
Open the Google Cloud console in a new tab, then follow these steps:
- Select your project.
- In the Google Cloud search field, search for "Google Chat API", then click Google Chat API, click Manage, and click Configuration.
- Set the App name and Description to
Gen AI App. - Click Save.
Google Chat space
Open Google Chat in a new tab, then follow these steps:
- If not already done, open a direct message space with the Chat app.
- Type
Helloand pressenter, the Chat app should reply with your name and avatar image.
Google Cloud Run function service
Open the Google Cloud console in a new tab, then follow these steps:
- Select your project.
- Click Menu ☰ > Cloud Run > Services.
- In the list of services, click addonchatapp, then open the Source tab.
Download source code and resources locally
- Download this GitHub repository.
- In your preferred local development environment, open the
node/chat/gen-ai-appsdirectory.
3. Prompt app
This app prompts Gemini on Vertex AI to converse with users in their natural languages using concise and plain text answers. The implementation relies on the Google Gen AI SDK for Node.js.
Review concepts
Natural language
Any language spoken or written by humans for everyday communication, in contrast to artificial or computer-based languages.
Cloud Run functions
Cloud Run functions are great for building serverless backends, doing real-time data processing, and creating intelligent apps. There are no servers to provision, manage, patch, or update. They automatically scale, and are highly available and fault-tolerant.
Prompting
Prompting refers to the technique of crafting input (prompts) to guide a generative AI model to produce a desired output. It usually involves carefully phrasing questions, providing context, giving instructions, or giving examples to obtain specific and relevant responses from the model.
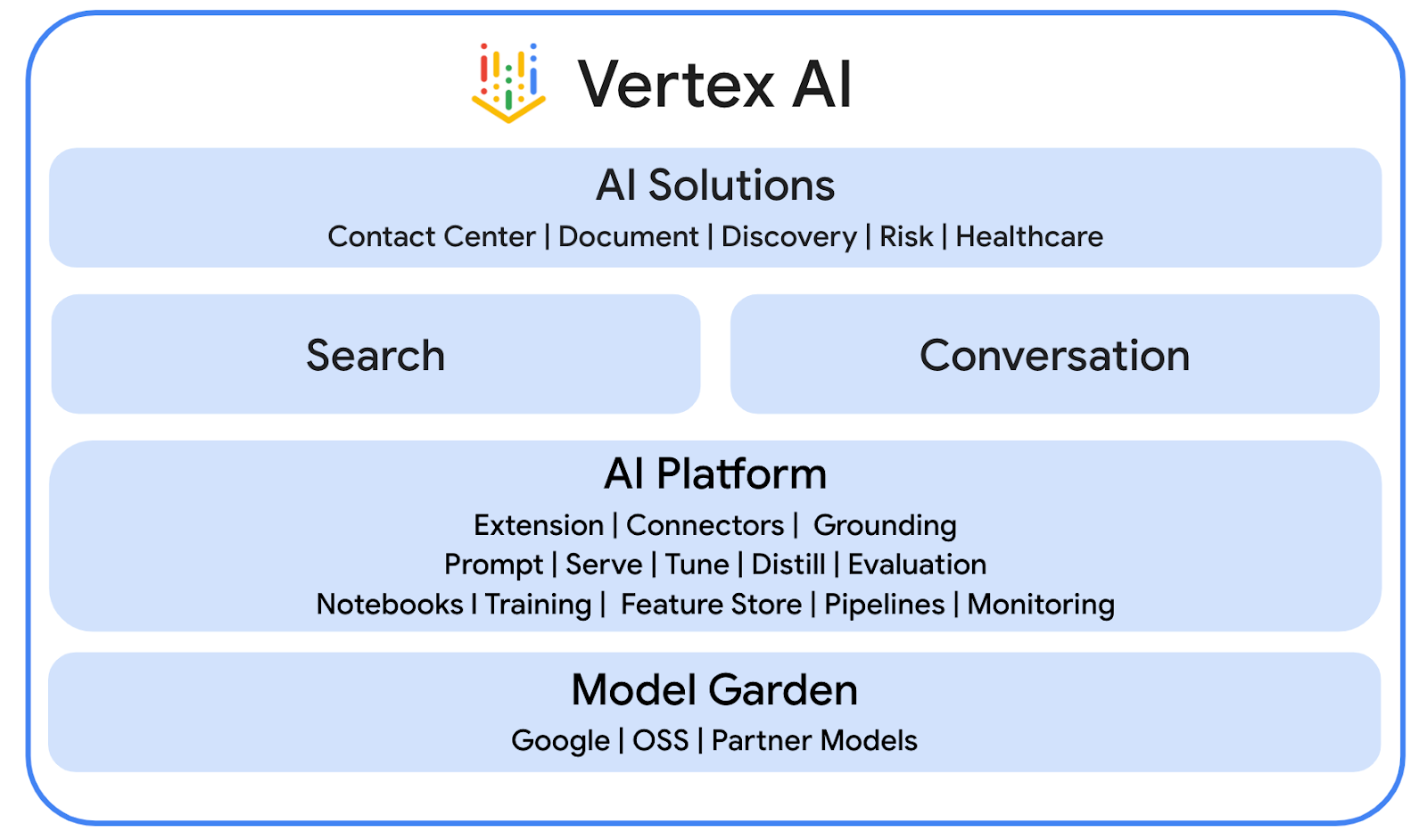
Vertex AI
Vertex AI offers everything you need to build and use generative AI, including AI solutions, search and conversation, more than 130 foundation models, and a unified AI platform.
Gemini
Gemini is a multimodal LLM from Google accessible through Vertex AI. It helps people unlock their human potential so that they can augment their imagination, expand their curiosity, and enhance their productivity.
Google Gen AI SDK
The Google Gen AI SDK is designed for developers to build applications powered by Gemini, it provides a unified interface compatible with both the Gemini Developer API and Vertex AI. It comes with client libraries in Python, Go, Node.js, and Java.
Review flow
Review source code
env.js
...
// Replace with your GCP project ID.
projectID: process.env.PROJECT_ID || 'your-google-cloud-project-id',
// Replace with your GCP project location.
location: process.env.LOCATION || 'your-google-cloud-project-location',
// Replace with the Gemini model to use.
model: process.env.MODEL || 'gemini-2.5-flash-lite',
...
index.js
// Import the Google Gen AI SDK.
import { GoogleGenAI } from '@google/genai';
...
// Use Vertex AI.
const genAI = new GoogleGenAI({vertexai: true, project: env.projectID, location: env.location});
http('gen-ai-app', async (req, res) => {
// Send a new Chat message with the generated answer
return res.send({ hostAppDataAction: { chatDataAction: { createMessageAction: { message: {
text: await generateAnswer(req.body.chat.messagePayload.message.text)
}}}}});
});
async function generateAnswer(message) {
// The prompt is made of the user's message and specific instructions for the model.
const prompt = 'In a consice and with plain text only (no formatting), '
+ 'answer the following message in the same language: ' + message;
const aiResponse = await genAI.models.generateContent({model: env.model, contents: prompt});
return aiResponse.candidates[0].content.parts[0].text;
};
...
package.json
...
"main": "index.js",
"type": "module",
"scripts": {
"start": "node index.js"
},
"dependencies": {
"@google-cloud/functions-framework": "^4.0.0",
"@google/genai": "1.15.0"
},
...
Enable Vertex AI API
- In the Google Cloud console, enable the Vertex AI API:
- Click Menu ☰ > APIs & Services > Enabled APIs & Services and then confirm that Vertex AI API is in the list.
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
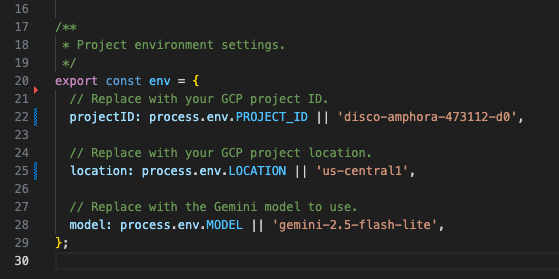
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/1-prompt. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Open
env.jsin an editor and set the following: - projectID: The ID of your Google Cloud project. It can be retrieved from the Google Cloud console welcome page.
- location: The region of your Google Cloud Run function service. It can be retrieved from the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- model: The model to use. You can find all available models from the Vertex AI documentation. The model set by default is Flash for a fast and cheap execution.
- Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Set Function entry point to
gen-ai-app. - Click ➕, type
env.js, and click ✔️to create the missing source file. - Replace the entire contents of the
index.js,env.js, andpackage.jsonfiles with those in your local development environment. - Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.
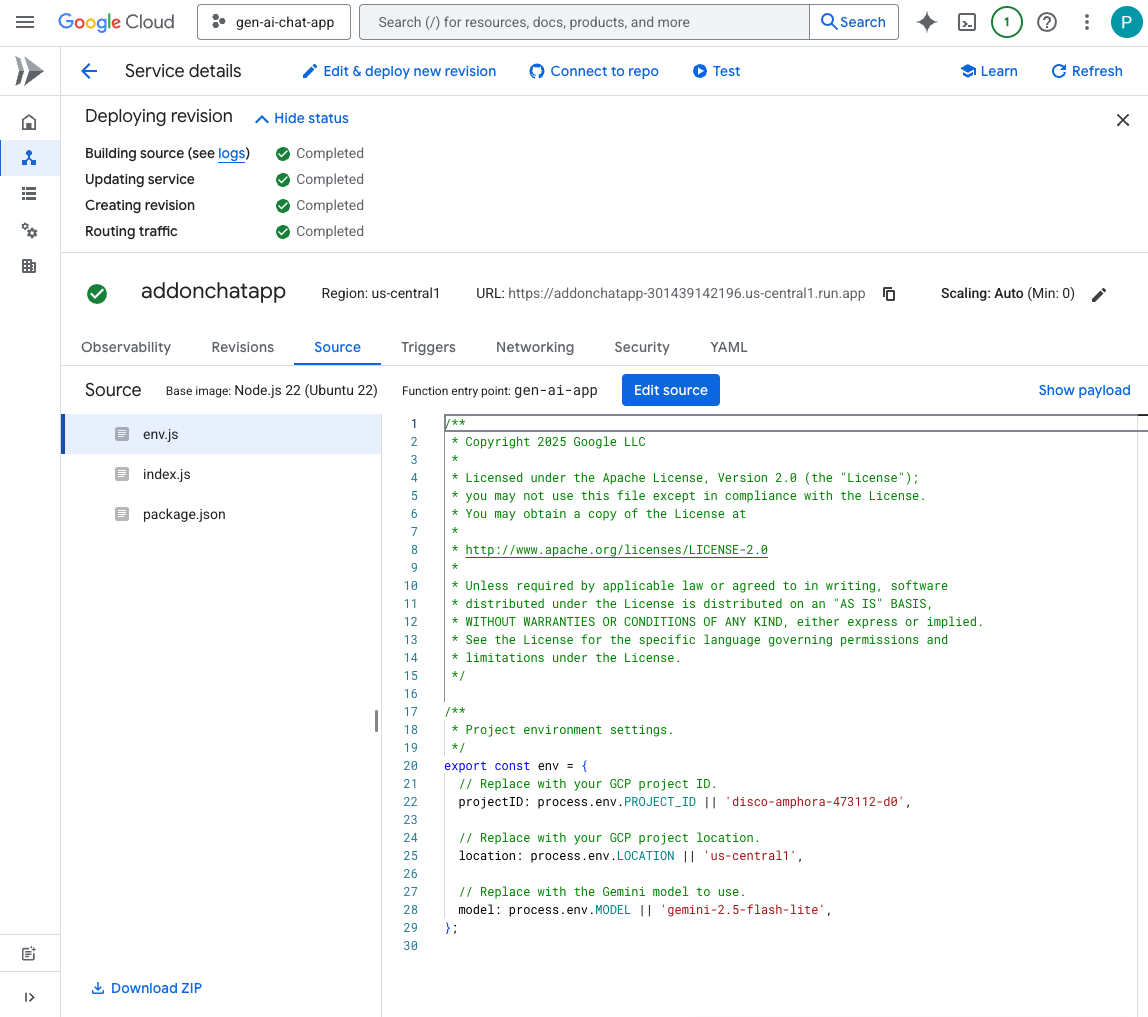
Try it
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
Hello, how are you?and pressenter. The app should answer concisely in plain text as per our instructions in the prompt.
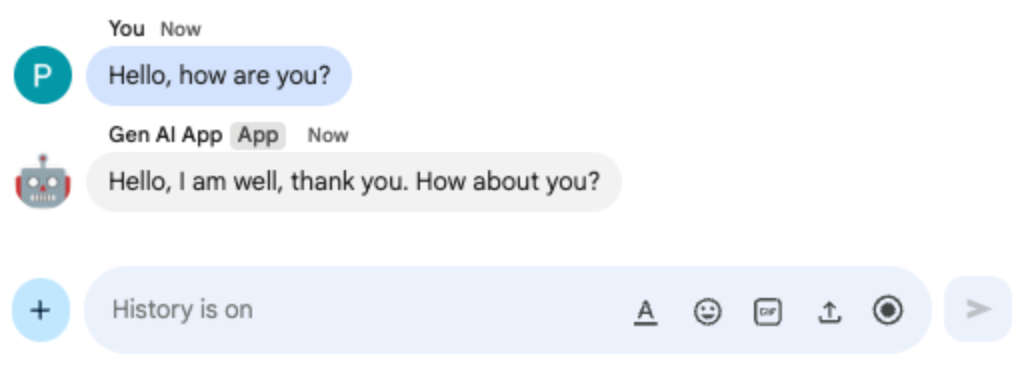
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
Bonjour comment allez-vous?and pressenter. The app should answer in French as per our instructions in the prompt.
4. Format app
This app builds on the Prompt app by adding support for rich text answers compliant with Google Chat text message format. Instructions in the prompt are updated with an exhaustive description of the different options that the model can use.
Review concepts
Google Chat text messages
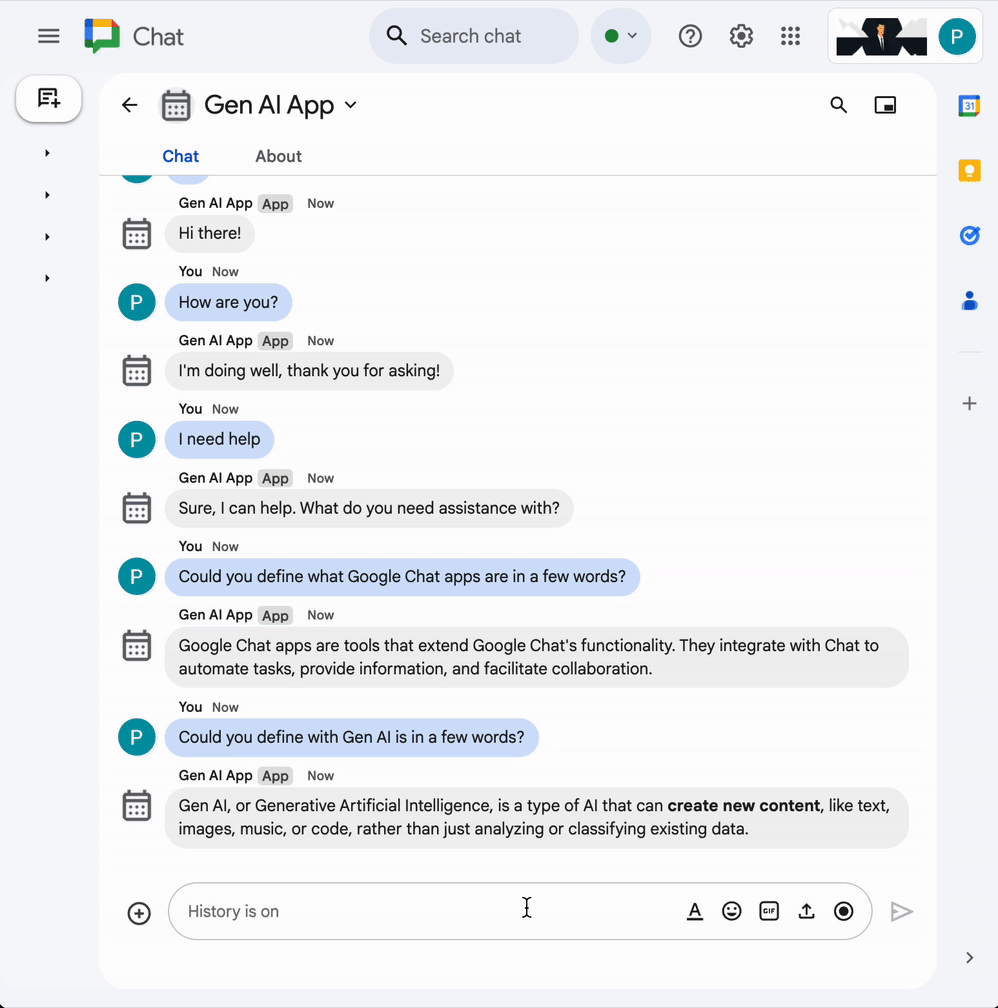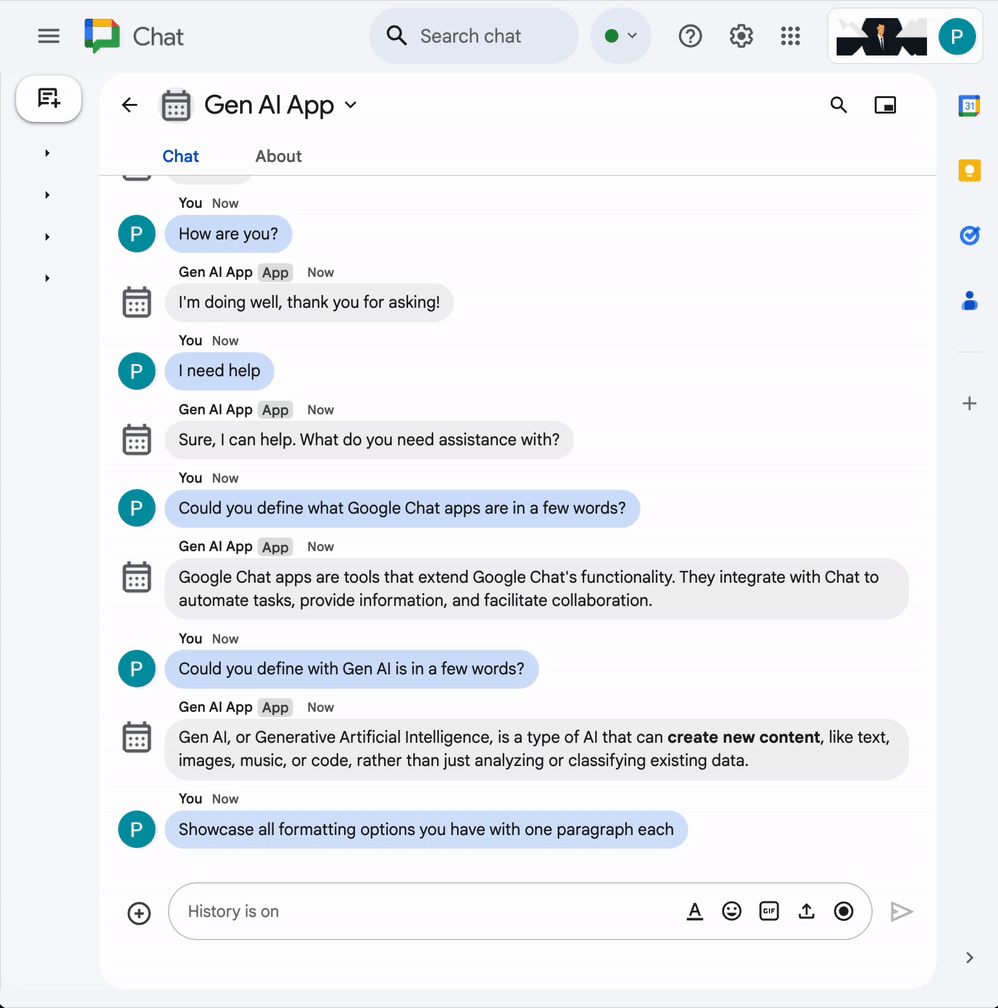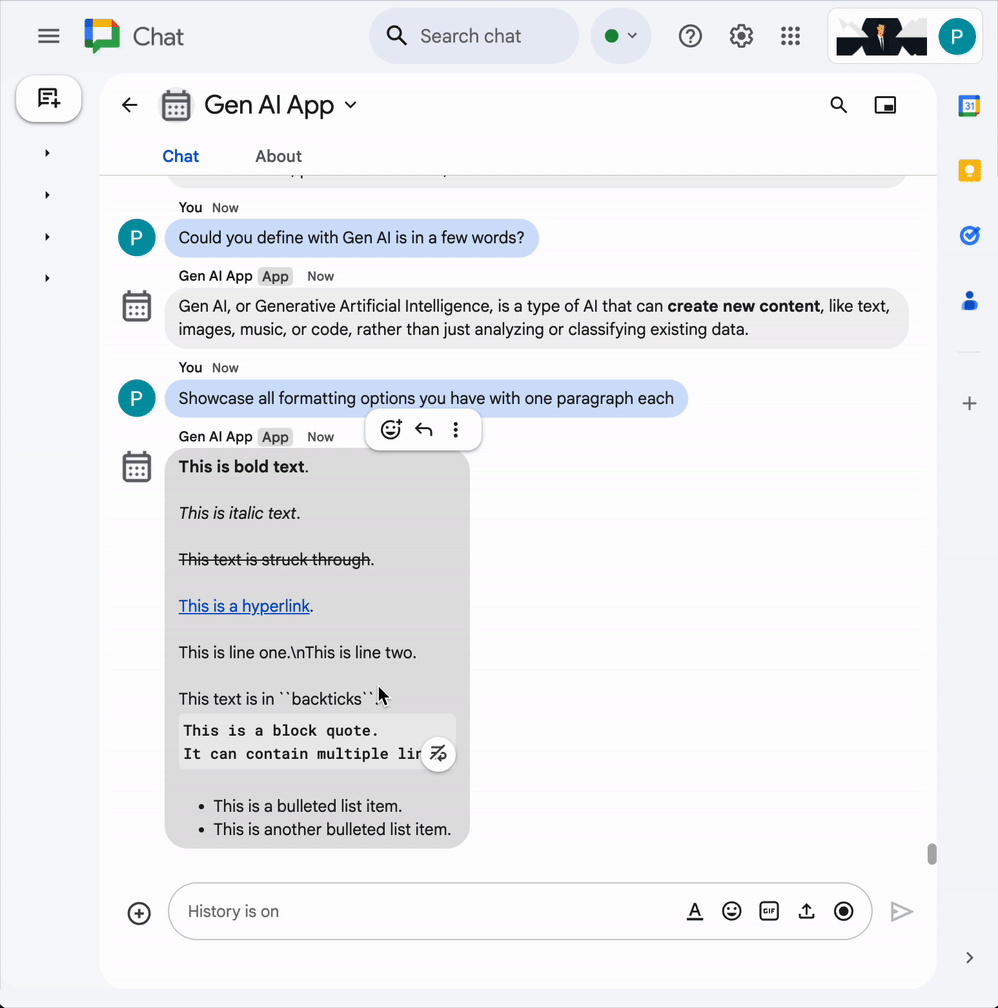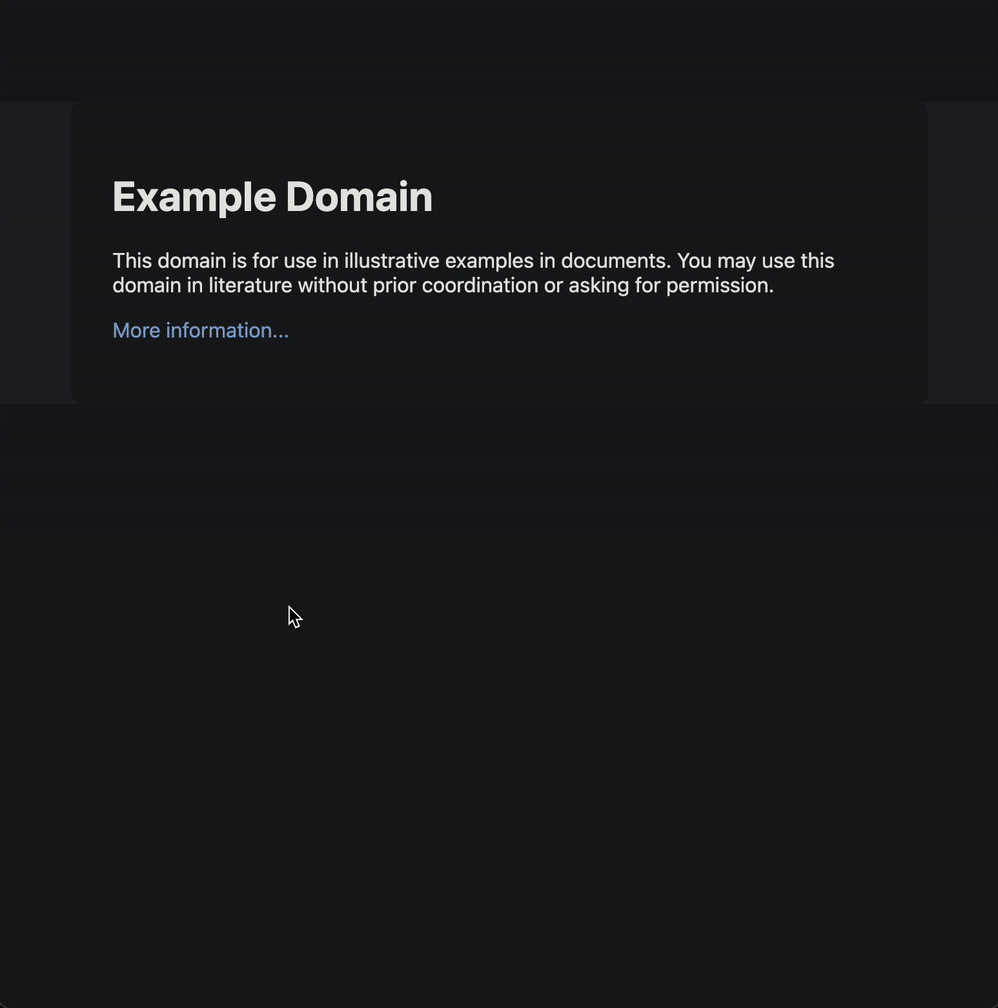
Google Chat text messages support various formatting options to allow for clearer, more expressive messages directly within the Google Chat interface. They are based on specific markdown rules to apply bold, italics, strikethrough, create hyperlinks, etc.
Review flow

Review source code
index.js
...
async function generateAnswer(message) {
// Specify formatting options that are compatible with Google Chat messages
// https://developers.google.com/workspace/chat/format-messages#format-texts
const prompt = `Use simple text for concise answers. The only formatting options you can use is to
(1) surround some text with a single star for bold such as *text* for strong emphasis
(2) surround some text with a single underscore for italic such as _text_ for gentle emphasis
(3) surround some text with a single tild for strikethrough such as ~text~ for removal
(4) use a less than before followed by a URL followed by a pipe followed by a link text followed
by a more than for a hyperlink such as <https://example.com|link text> for resource referencing
(5) use a backslash followed by the letter n for a new line such as \n for readibility
(6) surround some text with a single backquote such as \`text\` for quoting code
(7) surround an entire paragraph with three backquotes in dedicated lines such as
\`\`\`\nparagraph\n\`\`\` for quoting code
(8) prepend lines with list items with a single star or hyphen followed by a single space
such as * list item or - list item for bulleting ;
DO NOT USE ANY OTHER FORMATTING OTHER THAN THOSE.
Answer the following message in the same language: ${message}`;
...
};
...
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/2-format. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Replace the entire content of the
index.jsfile with the one in your local development environment. - Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.

Try it
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
Showcase all formatting options you have with one paragraph eachand pressenter. The app should answer with formatting samples based on our instructions in the prompt.
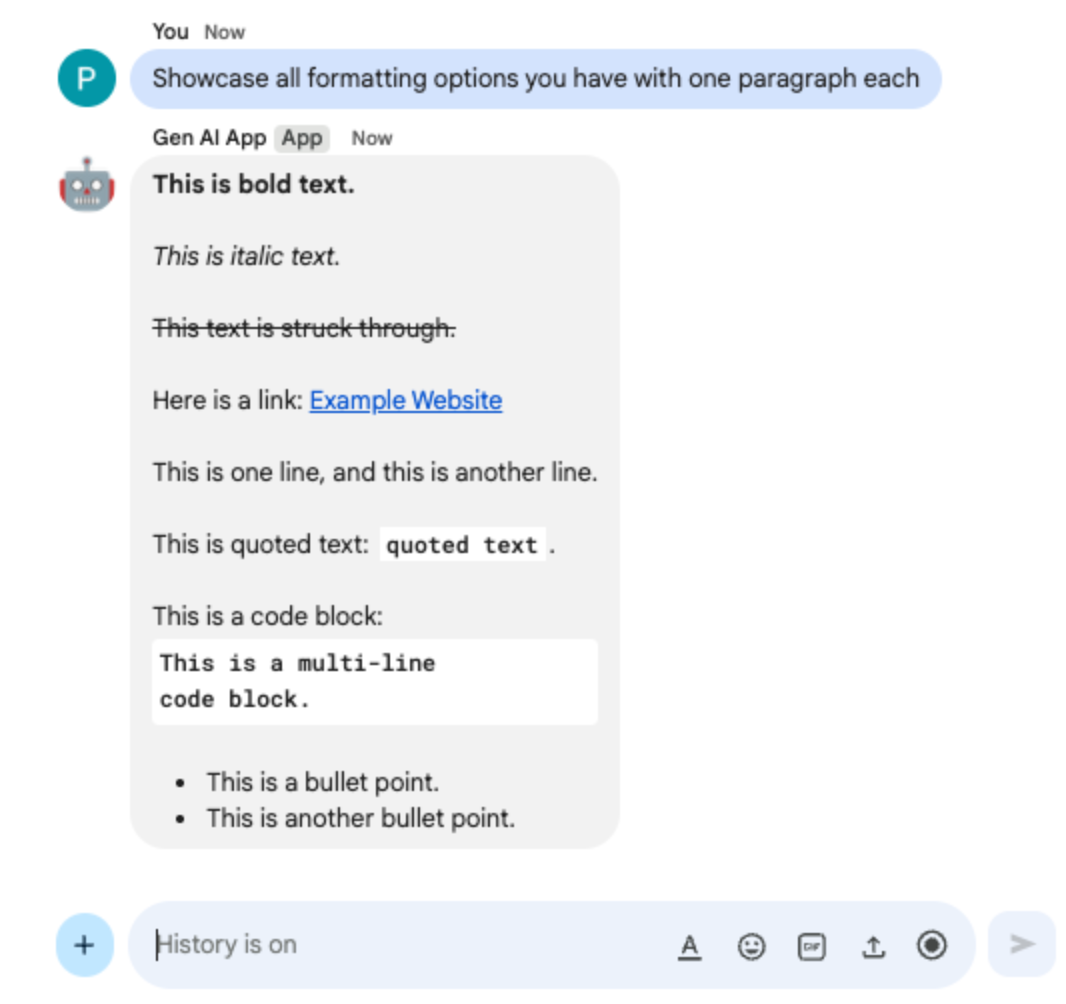
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
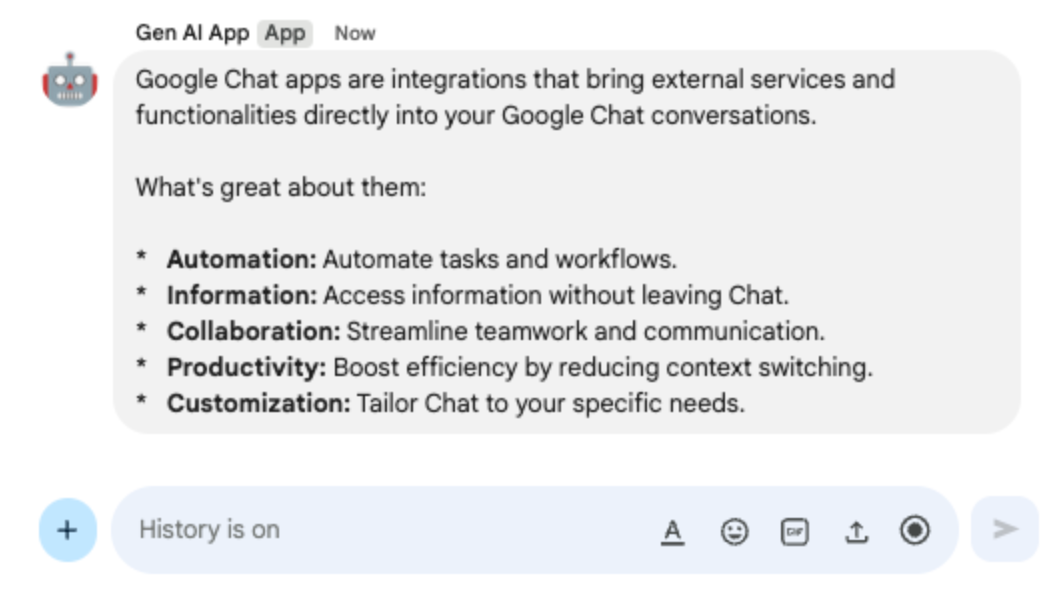
What are Google Chat apps? What's great about them?and pressenter. The app should answer with formatting when useful.
5. Ground app
This app builds on the Format app by adding support for grounding and returning sources. It runs the Google Search tool and attaches cards with links to answers.
Review concepts
Grounding
Grounding is the technique of connecting models to sources of information. It's often used in practical applications to improve the accuracy and relevance of the generated content by referencing real-world data, thereby preventing the model from hallucinating or producing factually incorrect information.
Google Search tool
The Google Search tool enhances grounding by allowing models to search the web for real-time information, ensuring responses are accurate and current.
Google Workspace Card framework
The Card framework in Google Workspace enables developers to create rich, interactive user interfaces. It allows for the construction of organized and visually appealing cards that can include text, images, buttons, and other widgets. These cards enhance user experience by providing structured information and enabling quick actions directly within the conversation.
Review flow
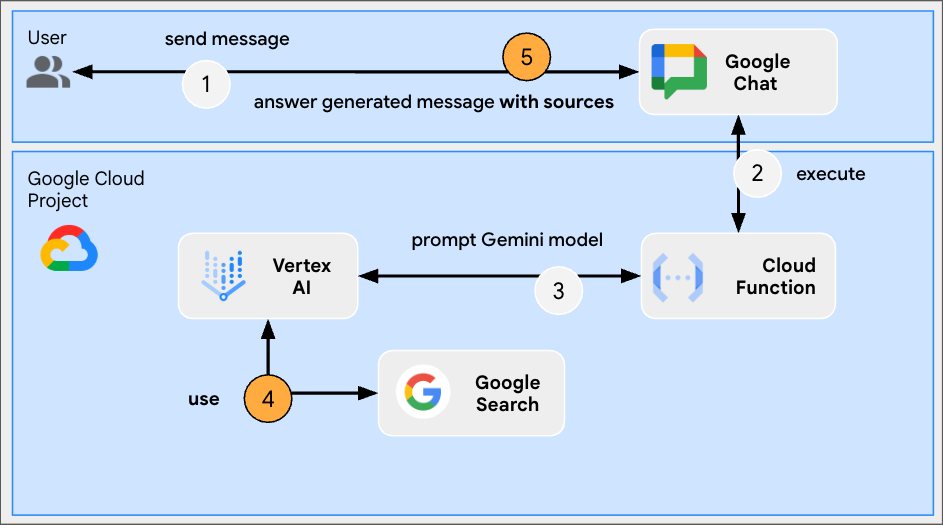
Review source code
index.js
...
const aiResponse = await genAI.models.generateContent({
model: env.model,
contents: prompt,
// Google Search tool is enabled
config: { tools: [{ googleSearch: {}}]}
});
let groundingCardsV2 = undefined;
const grounding = aiResponse.candidates[0].groundingMetadata;
// Go through the grounding metadata if any
if (grounding && grounding.groundingChunks && grounding.groundingChunks.length > 0) {
let linkButtons = [];
grounding.groundingChunks.forEach(groundingChunk => {
if (groundingChunk.web) {
// Create one link button per web URL returned
linkButtons.push({
text: groundingChunk.web.domain,
onClick: { openLink: { url: groundingChunk.web.uri}}
});
}
});
// Create a card with link buttons
groundingCardsV2 = [{
cardId: "sourcesCard",
card: { sections: [{
header: "Sources",
widgets: [{ buttonList: { buttons: linkButtons}}]
}]}
}];
}
// Send a Chat message with the generated answer
return res.send({ hostAppDataAction: { chatDataAction: { createMessageAction: { message: {
text: aiResponse.candidates[0].content.parts[0].text,
// The sources are referenced in the card
cardsV2: groundingCardsV2
}}}}});
...
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/3-ground. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Replace the entire content of the
index.jsfile with the one in your local development environment. - Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.

Try it
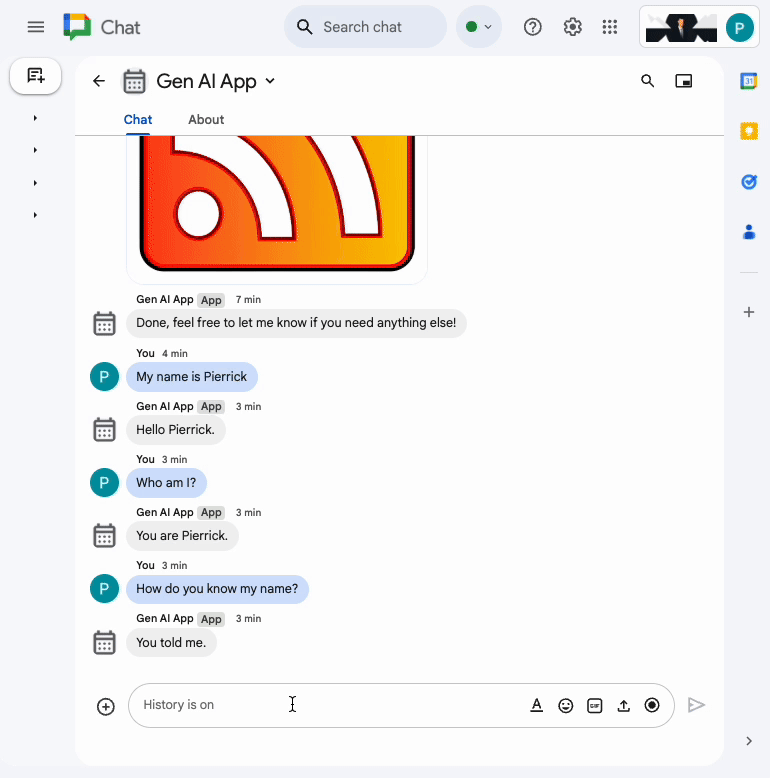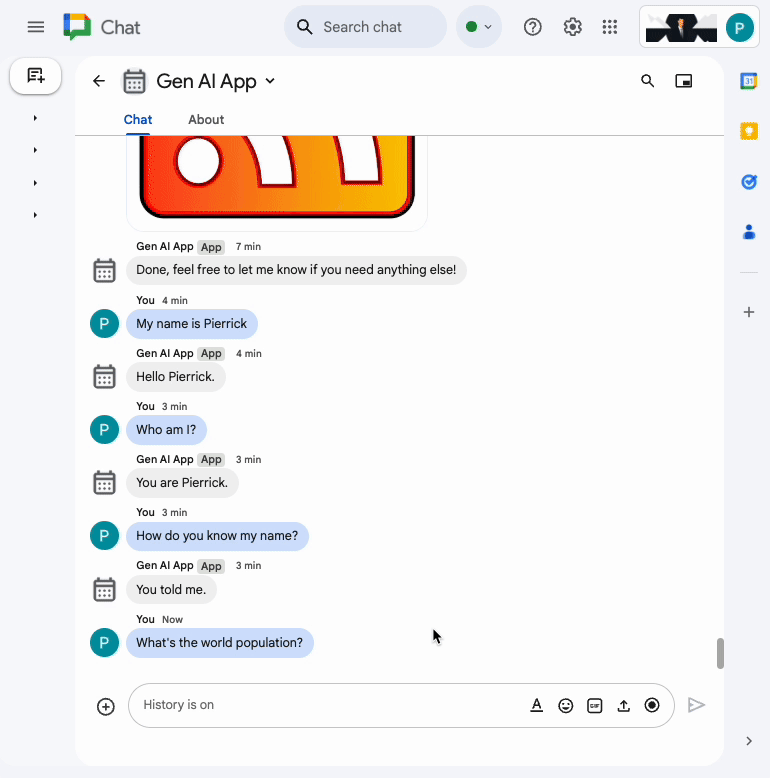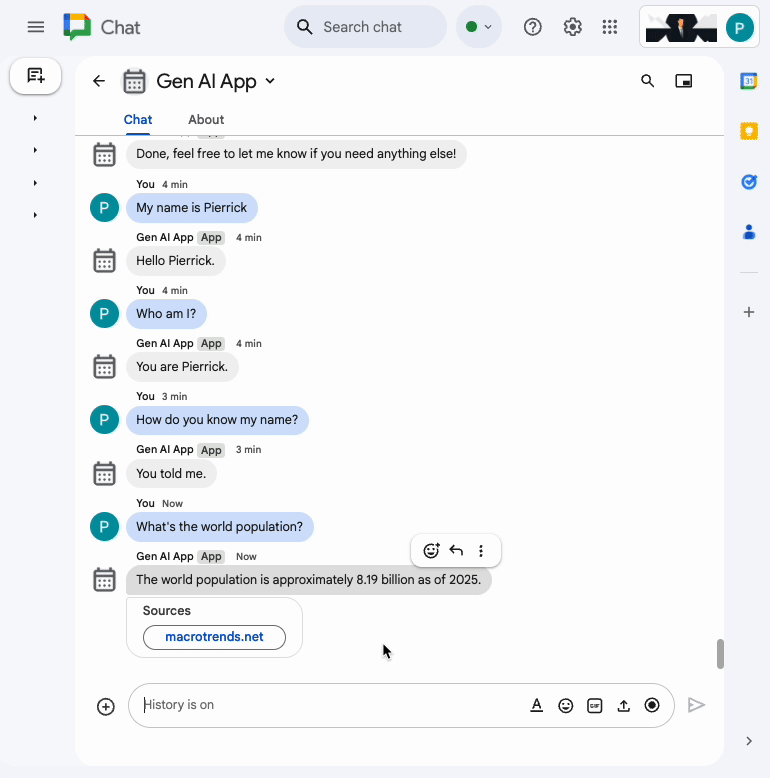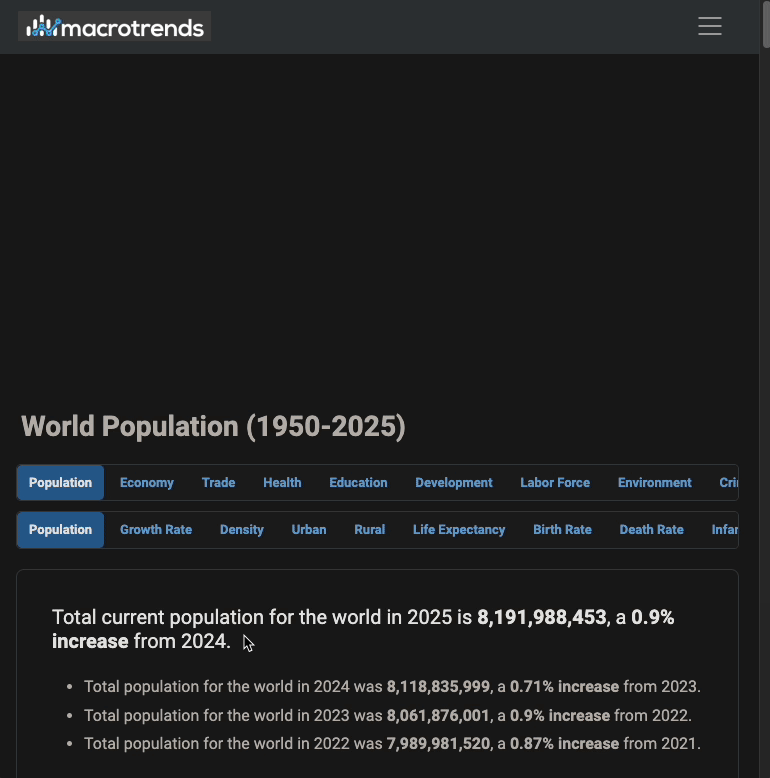
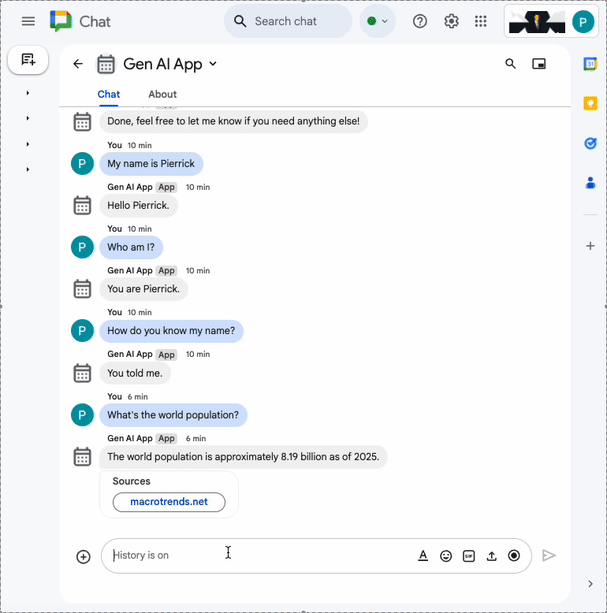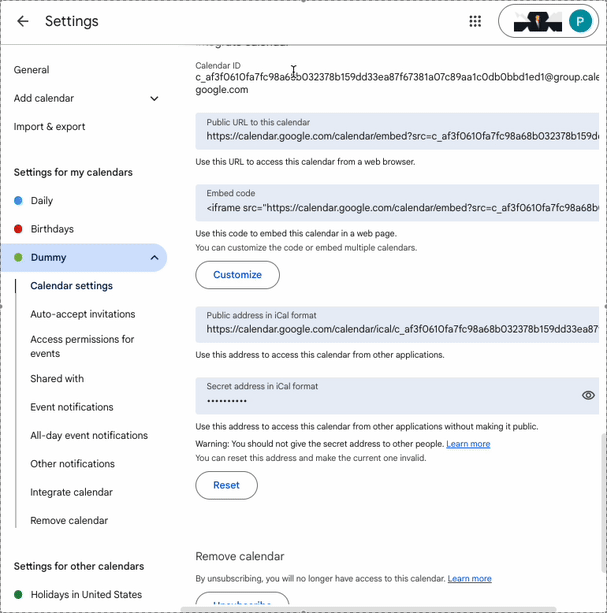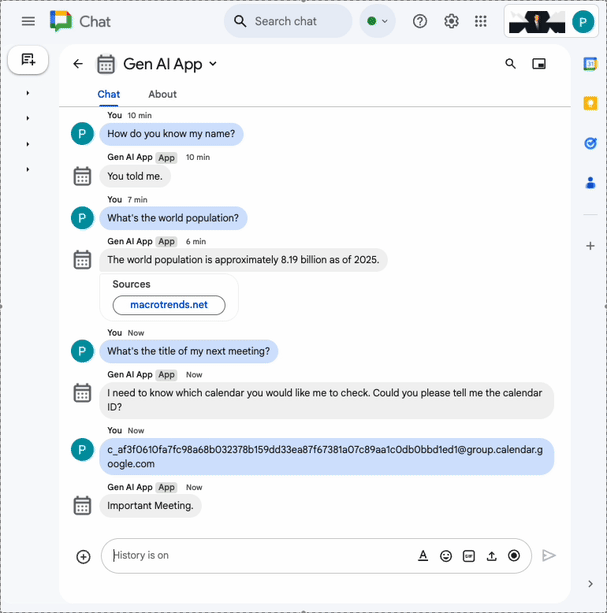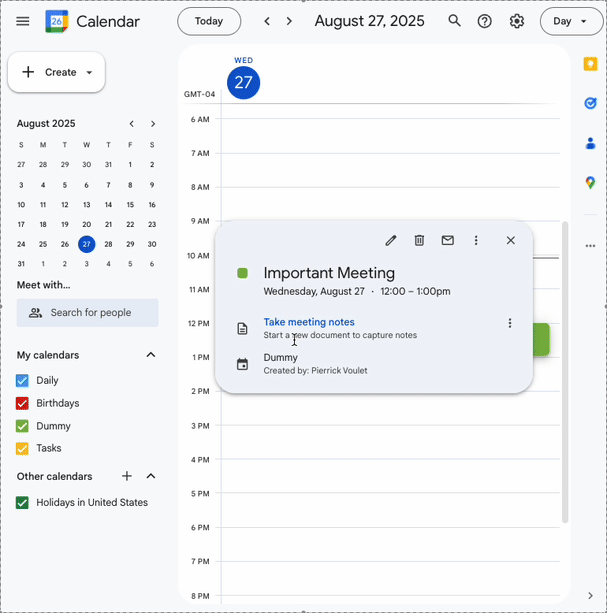
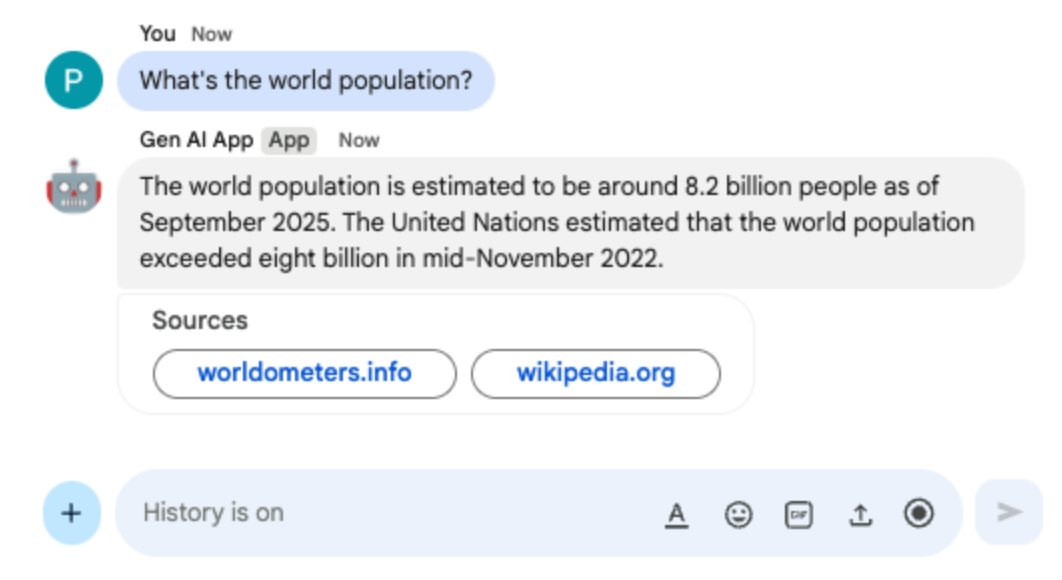
In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type What's the world population? and press enter. The app should answer by attaching source links in a card.
6. MCP app
This app builds on the Format app by adding support for tools provided by an Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that is hosted remotely. It connects to the Google Workspace Developer Assist MCP that provides tools for accessing and searching Google Workspace Developers documentation.
Review concepts
Model Context Protocol (MCP)
Model Context Protocol is an open-source framework integrating models with external services in a standardized way. Models can programmatically discover, understand, and interact with various tools, expanding their capabilities, performing real-world actions, and accessing updated information.
MCP TypeScript SDK
The TypeScript SDK implements the full MCP specification, simplifying the creation of MCP clients that connect to any MCP server. It also enables the development of MCP servers that provide access to resources, prompts, and tools.
Review flow
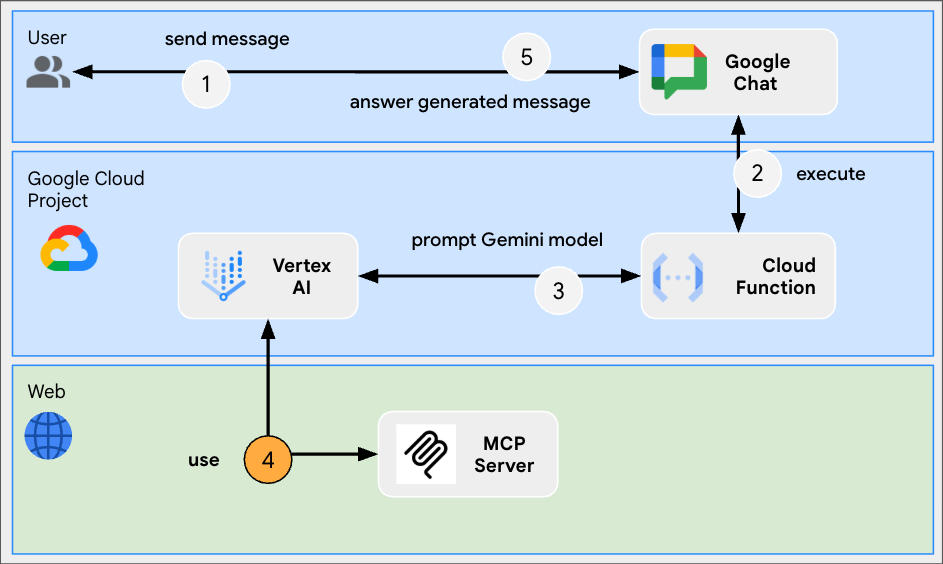
Review source code
index.js
// Import the MCP TypeScript SDK.
import { Client } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/index.js";
import { StreamableHTTPClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/streamableHttp.js";
import { SSEClientTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/client/sse.js";
...
// Create and connect the MCP client from the URL.
const mcpServerUrl = new URL("https://workspace-developer.goog/mcp");
const client = new Client({ name: "gen-ai-app-mcp", version: "1.0.0" });
// Try Streamable HTTP first (new) and SSE (old) as fallback for transport
try {
await client.connect(new StreamableHTTPClientTransport(mcpServerUrl));
} catch (error) {
await client.connect(new SSEClientTransport(mcpServerUrl));
}
http('gen-ai-app', async (req, res) => {
...
const aiResponse = await genAI.models.generateContent({
model: env.model,
contents: prompt,
// MCP tools are enabled
config: { tools: [mcpToTool(client)]}
});
...
}
...
package.json
...
"dependencies": {
...
"@modelcontextprotocol/sdk": "^1.18.1"
},
...
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/4-mcp. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Replace the entire contents of the
index.jsandpackage.jsonfiles with the ones in your local development environment. - Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.

Try it
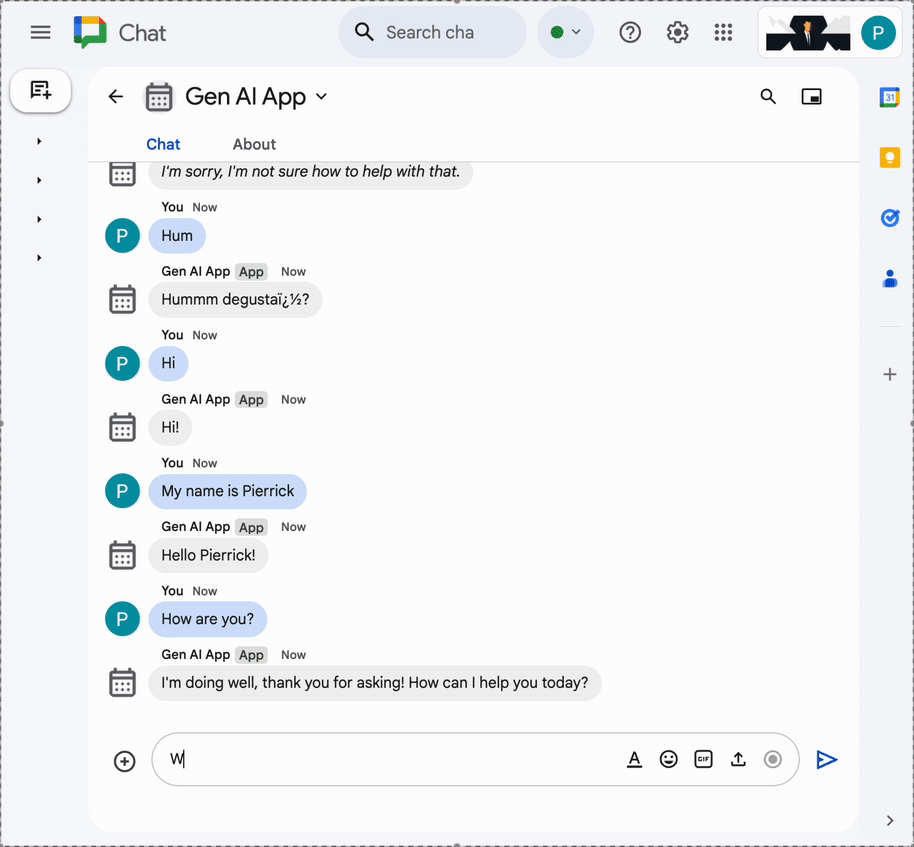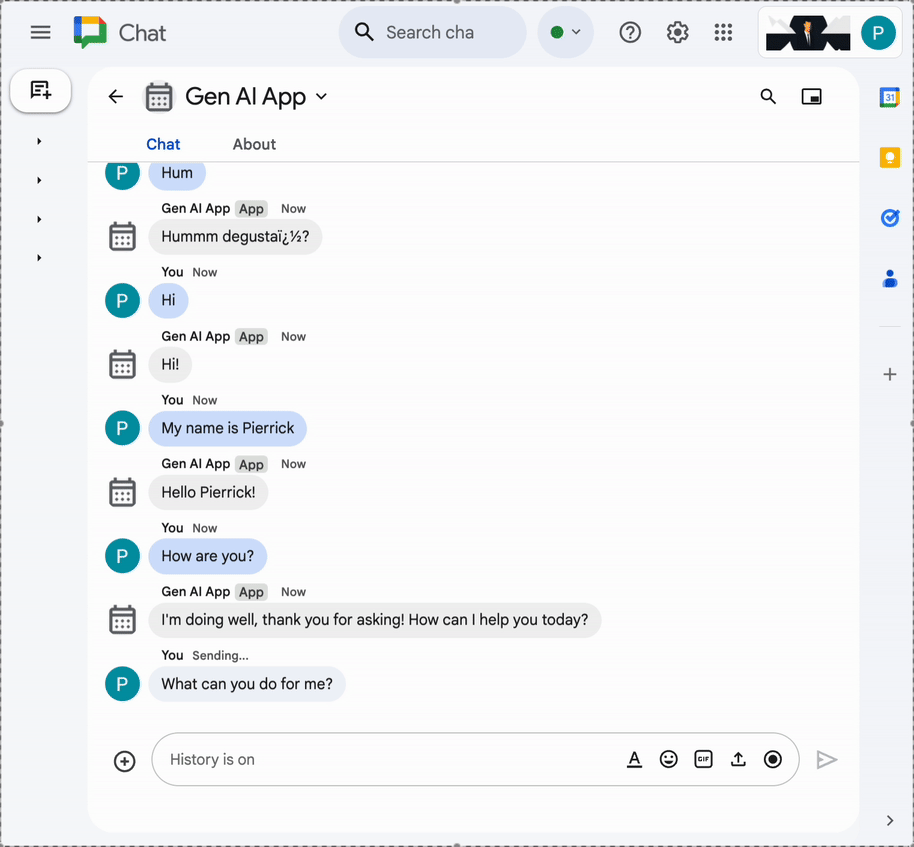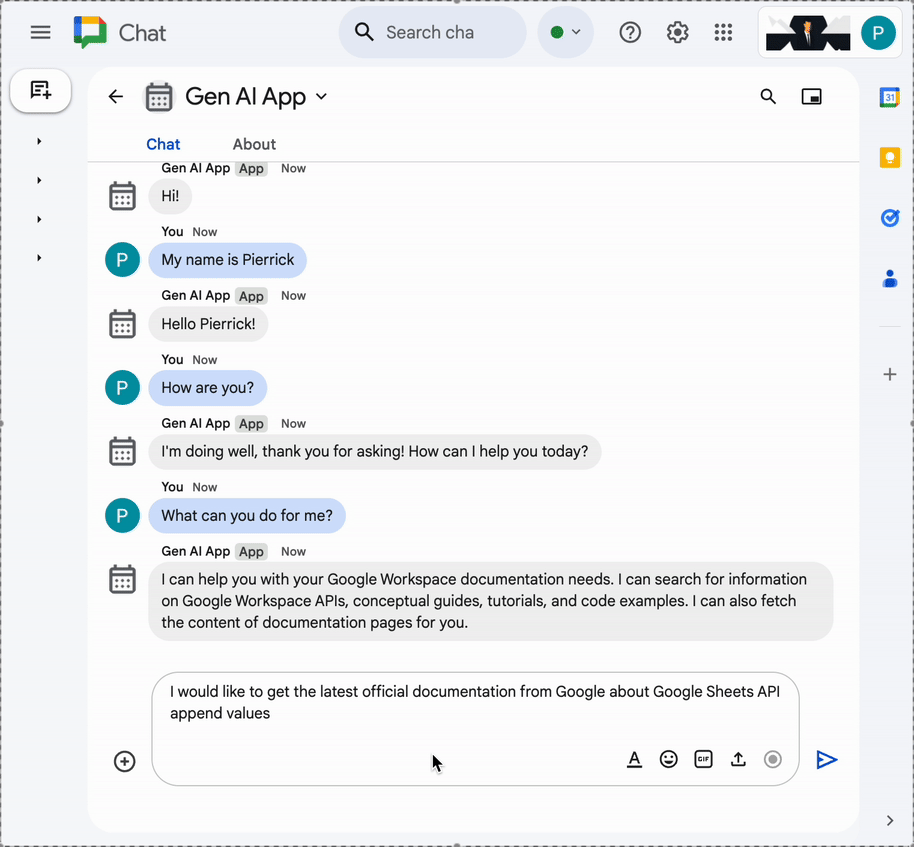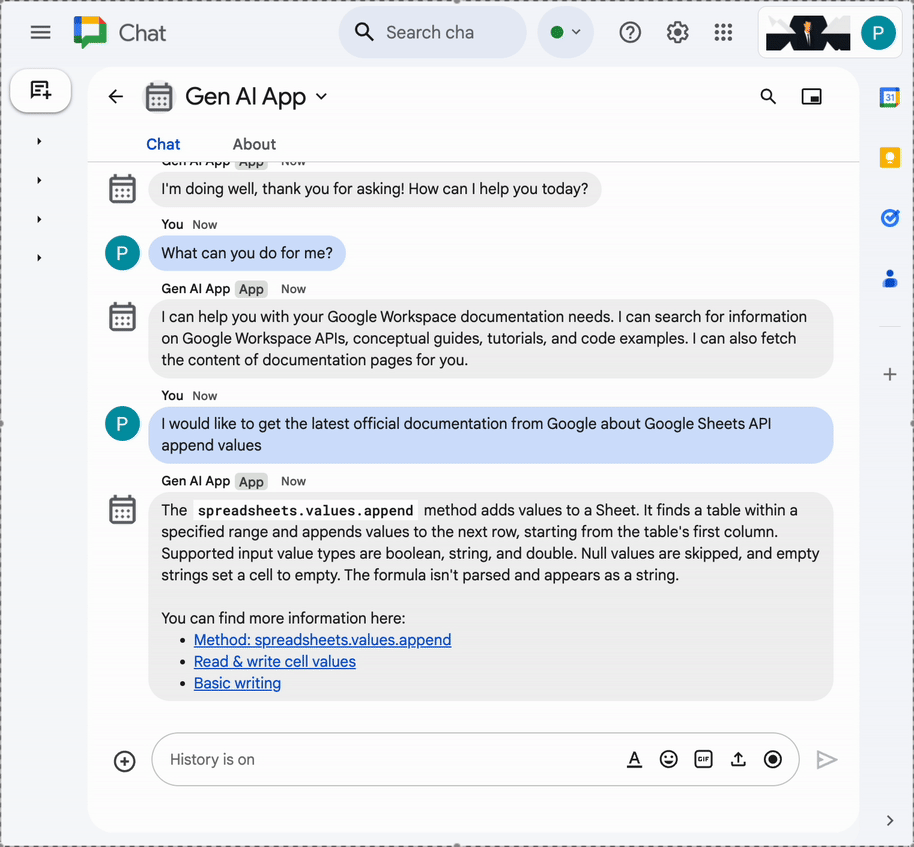
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
What can you do for me?and pressenter. The app should describe what it's capable of doing (MCP tools).
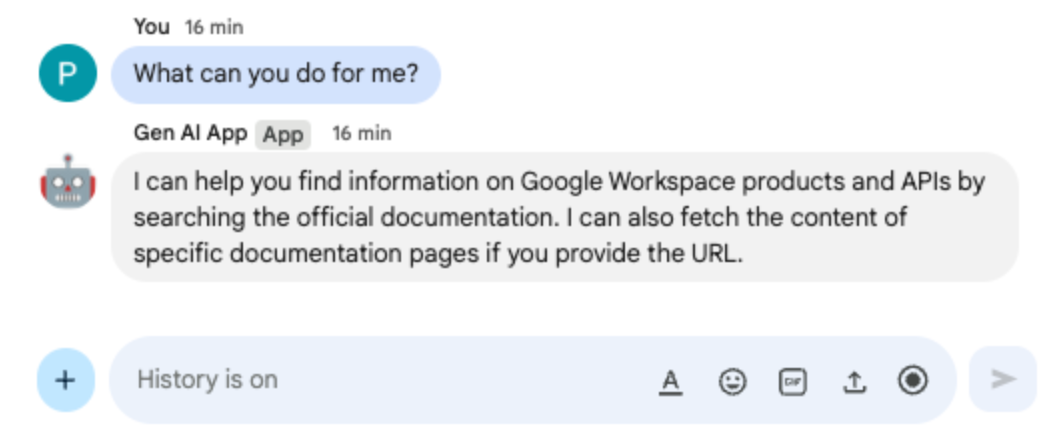
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
I would like to get the latest official documentation for the Google Sheets API append valuesand pressenter. The app should answer with the requested documentation (using MCP tools).
7. Multi-turn app
This app builds on the Format app by adding support for conversational memory by tracking the history of chat interactions. It enables a more natural, intelligent, and personalized experience. The app uses the default Google Cloud Firestore database associated with their Google Cloud project for storage.
Review concepts
Multi-turn
The multi-turn concept refers to the ability of a model to maintain contexts and continuity across multiple exchanges and conversations. It is a must-have feature to support complex conversations, sophisticated AI-driven functionalities, and natural user experience.
Google Cloud Firestore
Google Cloud Firestore is a flexible, scalable NoSQL cloud database for mobile, web, and server development. It stores data in documents, organized into collections, and allows for real-time synchronization and offline support.
Review flow
Review source code
index.js
// Import the Google Cloud Firestore client library.
import { Firestore } from '@google-cloud/firestore';
...
// Configure DB
const USERS_PREFIX = 'users/';
const CHATS_COLLECTION = 'chats';
const db = new Firestore();
...
// Create or update data for a given user
async function createOrUpdateChatHistory(userId, data) {
await db.collection(CHATS_COLLECTION).doc(userId.replace(USERS_PREFIX, '')).set(data);
};
// Retrieve data snapshot for a given user
async function getChatHistory(userId) {
return await db.collection(CHATS_COLLECTION).doc(userId.replace(USERS_PREFIX, '')).get();
};
...
...
http('gen-ai-app', async (req, res) => {
// Retrieve the chat history of the user
const chatHistory = await getChatHistory(userId);
const chat = genAI.chats.create({
model: env.model,
// Initiate the model with chat history for context
history: chatHistory.exists ? chatHistory.data().contents : []
});
// If no history, send a first message to the model with instructions on how to behave
if(!chatHistory.exists) {
const preambule = 'The only formatting options you can use is to '
+ ...
+ 'DO NOT USE ANY OTHER FORMATTING OTHER THAN THOSE. '
+ 'Answer in the same language that I use.';
// The answer to this message is ignored
await chat.sendMessage({message: preambule});
}
// Send the user's message to the model to generate the answer
const aiResponse = await chat.sendMessage({message: userMessage});
// Persist the updated chat history of the user
await createOrUpdateChatHistory(userId, {contents: chat.getHistory({curated: true})});
// Send a Chat message with the generated answer
return res.send({ hostAppDataAction: { chatDataAction: { createMessageAction: { message: {
text: aiResponse.candidates[0].content.parts[0].text
}}}}});
});
...
package.json
...
"dependencies": {
...
"@google-cloud/firestore": "^7.11.5"
},
...
Enable Google Cloud Firestore API
- In the Google Cloud console, enable the Google Cloud Firestore API:
- Click Menu ☰ > APIs & Services > Enabled APIs & Services and then confirm that Cloud Firestore API is in the list.
Create Cloud Firestore database
- In the Google Cloud console, click Menu ☰ > Firestore
- Click Create a Firestore database
- Leave the default configuration and click Create Database
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/5-multi-turn. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Replace the entire contents of the
index.jsandpackage.jsonfiles with the ones in your local development environment. - Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.

Try it
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
Can you speak with the English from the 80's for now on?and pressenter. The app should respond positively.
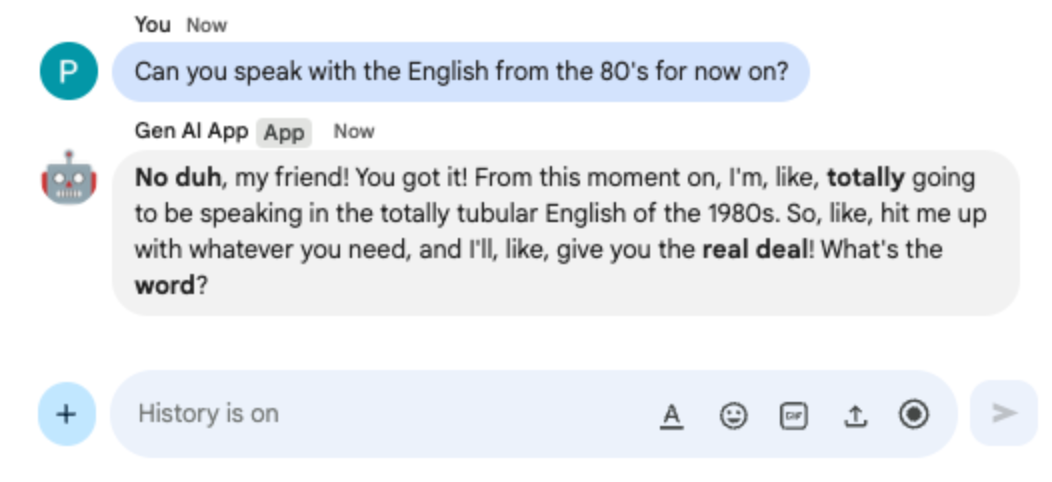
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
Define what Google Chat apps are in one sentenceand pressenter. The app should continue responding with the English from the 80's.
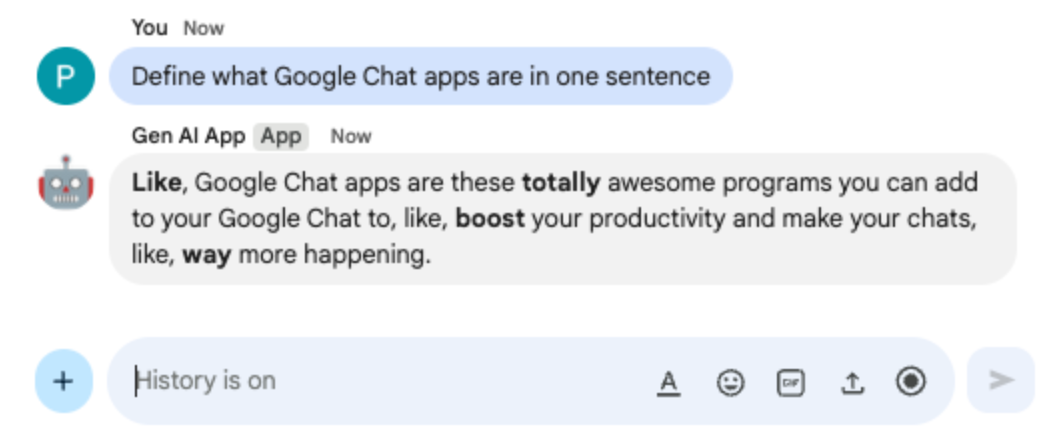
8. Custom tool app
This app builds on the Multi-turn app by adding support for a function calling custom tool that relies on the Google Workspace Calendar API to retrieve the next event from a public calendar. The model manages all user interactions, including receiving input and delivering output from the tool. The application is, however, still responsible for executing the necessary API calls and providing results to the model upon request. The app uses a Google API Key because there is no need for user credentials to fetch public calendar data.
Review concepts
Function calling
Function calling enables a model to detect when a user's request can be fulfilled by an external tool or API. The model then provides the parameters needed to call that tool, integrating external functionalities into its responses.
Google Workspace APIs
Google Workspace APIs enable developers to integrate their applications with various Google Workspace services. These APIs provide programmatic access to functionalities across products like Gmail, Chat, Calendar, Drive, Docs, Sheets, and more, allowing for automation, data synchronization, and the creation of custom workflows.
Review flow
Review source code
env.js
...
// Replace with your Google API key.
googleApiKey: process.env.GOOGLE_API_KEY || 'your-google-api-key',
...
index.js
// Import parameter type definitions from Google Gen AI SDK.
import { GoogleGenAI, Type } from '@google/genai';
// Import Google APIs that include the Google Calendar API.
import { google } from 'googleapis';
...
// Create a Google Calendar API client using a Google API key.
const calendar = google.calendar({version: 'v3', auth: env.googleApiKey});
...
// Define the tool used for function calling
const getNextPublicCalendarEventTitleFunctionDeclaration = {
name: 'getNextPublicCalendarEventTitle',
parameters: {
type: Type.OBJECT,
description: 'Get the title of the next event of a public calendar.',
properties: {
calendarId: {
type: Type.STRING,
description: 'ID of the public calendar to get the next event title.',
}
},
required: ['calendarId']
}
};
// The function referenced in the tool definition
async function getNextPublicCalendarEventTitle(calendarId) {
// Use Calendar API to retrieve the next event in the given calendar
const response = await calendar.events.list({
calendarId: calendarId,
timeMin: new Date().toISOString(),
maxResults: 1,
singleEvents: true,
orderBy: 'startTime',
});
const events = response.data.items;
if (!events || events.length === 0) {
return null;
}
return `${events[0].summary}`;
};
...
...
http('gen-ai-app', async (req, res) => {
...
// Send the user's message to the model to generate the answer
let aiResponse = await chat.sendMessage({
message: userMessage,
// The tool used for function calling is enabled
config: { tools: [{ functionDeclarations: [getNextPublicCalendarEventTitleFunctionDeclaration]}]}
});
// Handle the function calling turn with the model if any
const functionCall = aiResponse.candidates[0].content.parts[0].functionCall;
if (functionCall) {
let functionResult = null;
switch(functionCall.name) {
case 'getNextPublicCalendarEventTitle':
// Make the function call as per model request
functionResult = await getNextPublicCalendarEventTitle(functionCall.args['calendarId']);
break;
default:
}
// Finish the function calling turn by sending the execution result to the model
aiResponse = await chat.sendMessage({ message: { functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name,
response: { output: functionResult }
}}});
}
...
// Send a Chat message with the generated answer
return res.send({ hostAppDataAction: { chatDataAction: { createMessageAction: { message: {
text: aiResponse.candidates[0].content.parts[0].text
}}}}});
});
...
package.json
...
"dependencies": {
...
"googleapis": "^160.0.0"
},
...
Enable Calendar API
- In the Google Cloud console, enable the Google Calendar API:
- Click Menu ☰ > APIs & Services > Enabled APIs & Services and then confirm that Google Calendar API is in the list.
Create Google API Key
In the Google Cloud console, follow these steps:
- Click Menu ☰ > APIs & Services > Credentials.
- Click + Create credentials and then select API key.
- Wait for the completion of the operation.
- In the confirmation dialog, locate the text field Your API Key, and click Copy to clipboard.
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/6-custom-tool. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Replace the entire contents of the
index.jsandpackage.jsonfiles with the ones in your local development environment. - Open the
env.jsfile and do the following - Add googleApiKey to the exported fields
export const env = {
...
googleApiKey: 'your-google-api-key',
};
- Replace
your-google-api-keywith the Google API Key copied in the previous step. It can be retrieved from the Google Cloud credentials page by clicking Show key.
- Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.

Try it
- In Google Calendar, follow these steps:
- Under Other calendars, click +, then click Create new calendar.
- Set Name to
My Public Calendar - Click Create calendar
- Wait for the completion of the operation.
- Under Settings for my calendars, select the newly created calendar My Public Calendar
- Under Access permissions for events, select Make available to public, and then click OK in the Warning dialog.
- Under Access permissions for events, select See all event details from the dropdown menu next to the option Make available to public
- Under Integrate calendar, copy the value of the field Calendar ID to clipboard
- Click the left arrow in the top left corner to leave Settings.
- Click on the calendar to create a new event for tomorrow, type
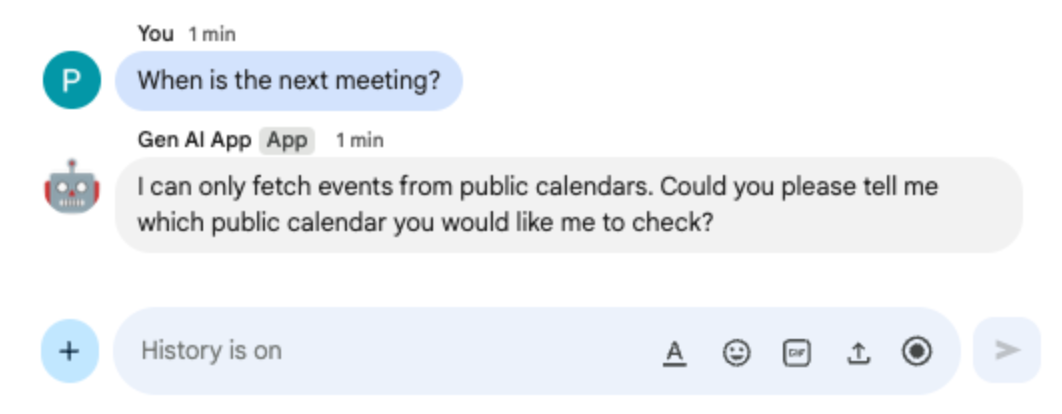
Important meeting, select My Public Calendar from the dropdown, then click Save - In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type
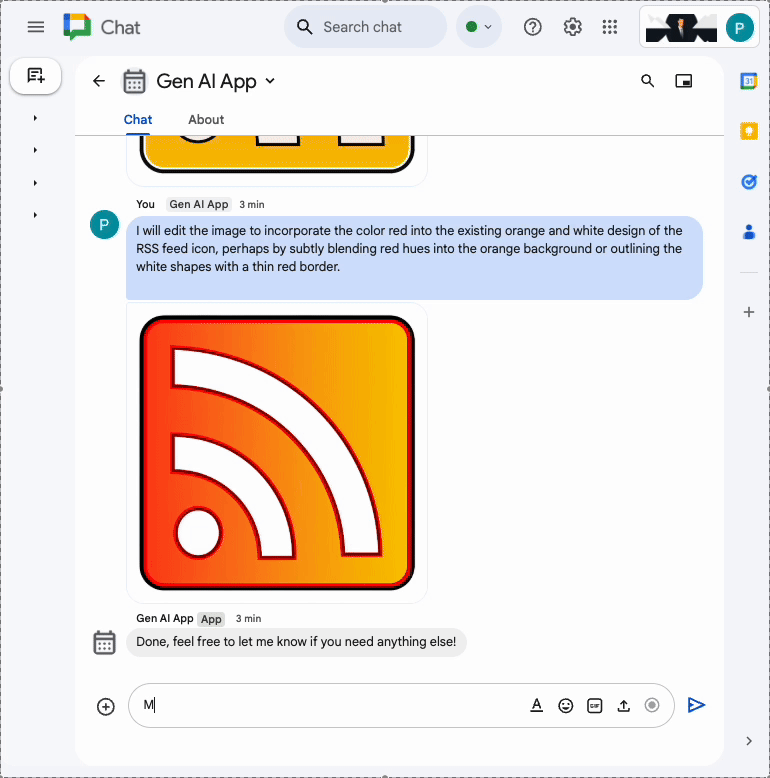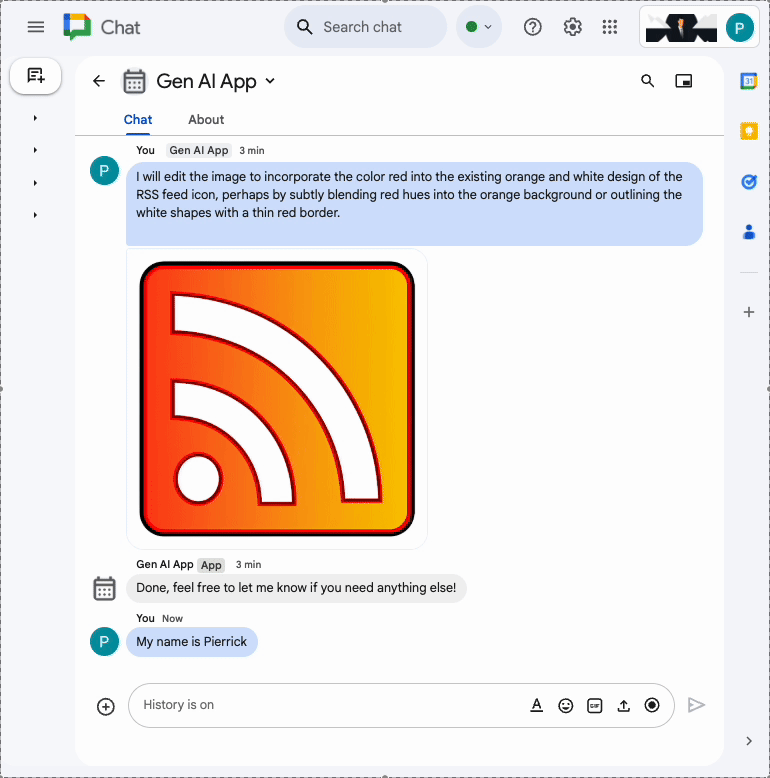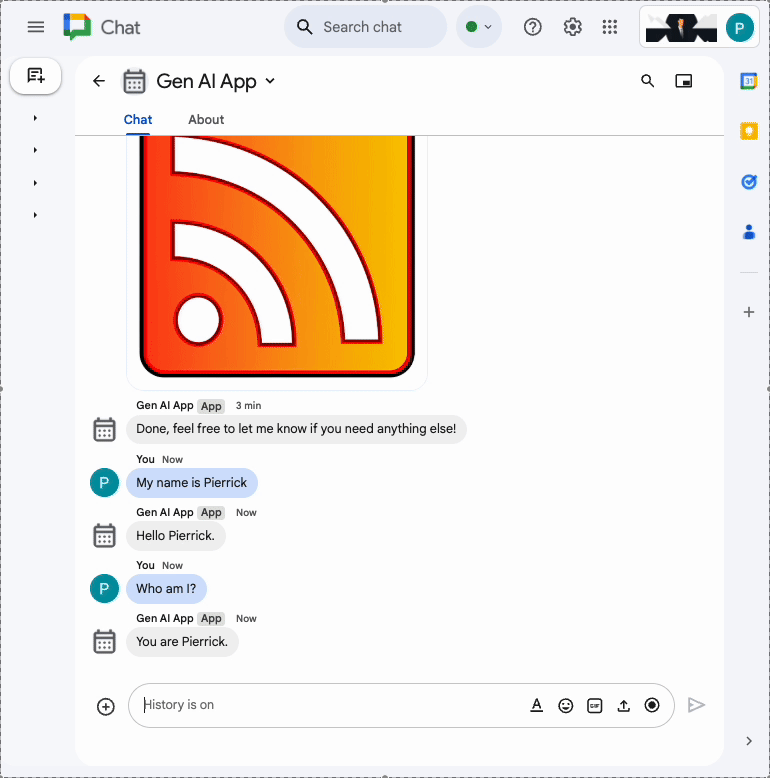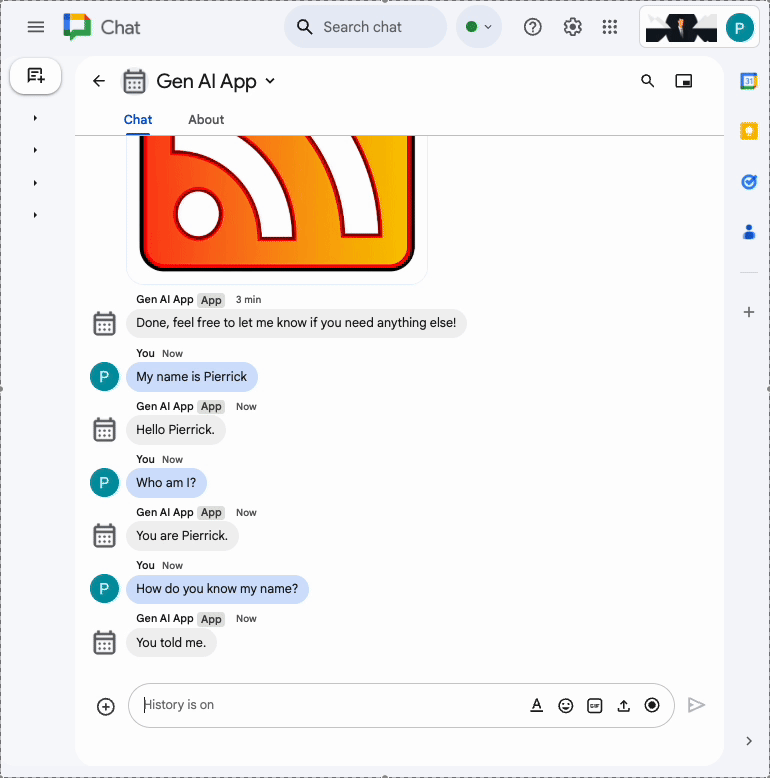
When is the next meeting?and pressenter. The app should request a precision because it's unclear what calendar is being referred to.
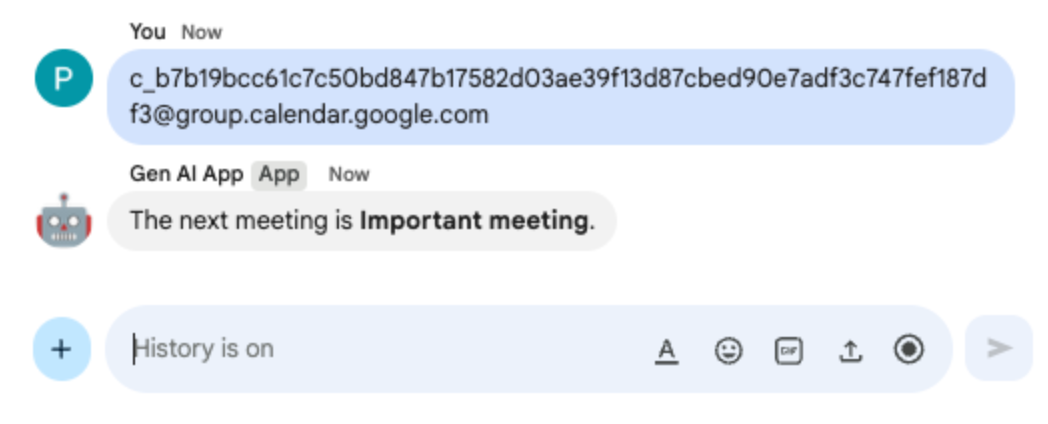
- In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, paste the calendar ID you previously copied to clipboard and press
enter. The app should answer with details about the event created previously.
9. Stream app
This app relies on a Gemini model to generate 2-minute stories based on themes provided by users. Because it takes time to generate full answers, the app makes calls to the model in streaming mode and relies on the Google Chat API to send contents and statuses in messages as progress is made.
Review concepts
Google Chat API
The Google Chat API allows developers to programmatically interact with Google Chat, enabling them to send messages, create spaces, manage members, and more, to build custom integrations and bots.
Streaming
Streaming refers to the process of receiving data in a continuous flow rather than waiting for the entire response to be generated. When it comes to AI model calls, streaming allows applications to display partial results to users as soon as they become available, improving perceived performance and user experience, especially for longer generation tasks. This is particularly relevant for generative AI models that might take a significant amount of time to produce a complete output.
Review flow
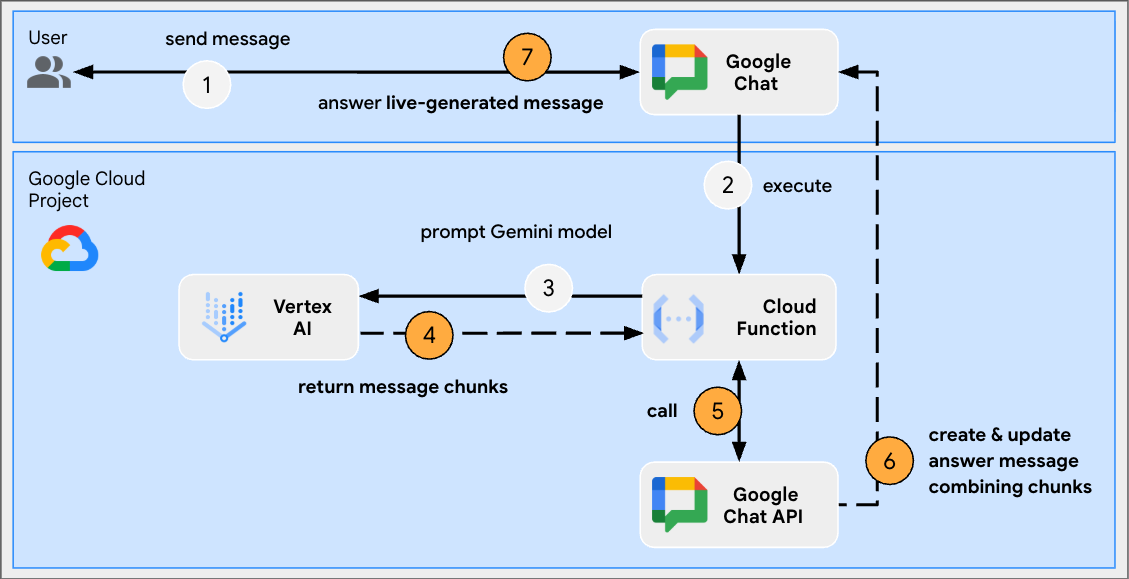
Review source code
index.js
// Import Google Auth library used to create Google Chat API client
import { GoogleAuth } from 'google-auth-library';
...
http('gen-ai-app', async (req, res) => {
// Use app authentication.
// Application Default Credentials (ADC) will use the Cloud Run function's
// default service account, we just need to specify the Chat API app auth scopes.
const auth = new GoogleAuth({
// Chat API app authentication scopes
scopes: ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.bot']
});
// Create Chat service client with application credentials
const chatClient = google.chat({
version: 'v1',
auth: await auth.getClient()
});
// Send a server streaming request to generate the answer
const aiResponse = await genAI.models.generateContentStream({
model: env.model,
contents: `Generate a story about a ${userMessage}. `
+ `It should take 2 minutes to read it out loud.`
});
// Send a first Chat message to summarize what will be done
await chatClient.spaces.messages.create({
parent: spaceName,
requestBody: { text: `Sure, let me work on generating a short story `
+ `about a ${userMessage} like you requested.`}
});
// Go through the response chunks received from the stream
let messageName = undefined;
let answer = "";
for await (const chunk of aiResponse) {
const text = chunk.text;
if (text) {
// Update the answer by concatenating the response chunks
answer += text;
// The Chat message request body is the same for message creation and update
const responseBody = {
text: answer,
accessoryWidgets: [getStatusAccessoryWidget('Generating story...', 'progress_activity')]
}
if (!messageName) {
// Create a Chat message dedicated to the generated content
const messageResponse = await chatClient.spaces.messages.create({
parent: spaceName,
requestBody: responseBody
});
messageName = messageResponse.data.name;
} else {
// Update the Chat message dedicated to the generated content
await chatClient.spaces.messages.patch({
name: messageName,
updateMask: 'text,accessory_widgets',
requestBody: responseBody
});
}
}
}
// Update the accessory widget with final progress status
await chatClient.spaces.messages.patch({
name: messageName,
updateMask: 'accessory_widgets',
requestBody: {
accessoryWidgets: [getStatusAccessoryWidget('Story is fully generated', 'check')]
}
});
// Send a last Chat message to confirm it's done
return res.send({ hostAppDataAction: { chatDataAction: { createMessageAction: { message: {
text: 'All done, I hope you like it!'
}}}}});
});
// Create an accessory widget with progress status
function getStatusAccessoryWidget(text, icon) {
return { buttonList: { buttons: [{
text: text,
icon: { materialIcon: { name: icon}},
// This is a workaround to have the icon shown, it's not clickable
onClick: { openLink: { url: "https://google.com"}},
disabled: true
}]}};
}
package.json
...
"dependencies": {
...
"google-auth-library": "^10.3.0"
},
...
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/7-stream. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Replace the entire contents of the
index.jsandpackage.jsonfiles with the ones in your local development environment. - Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.

Try it
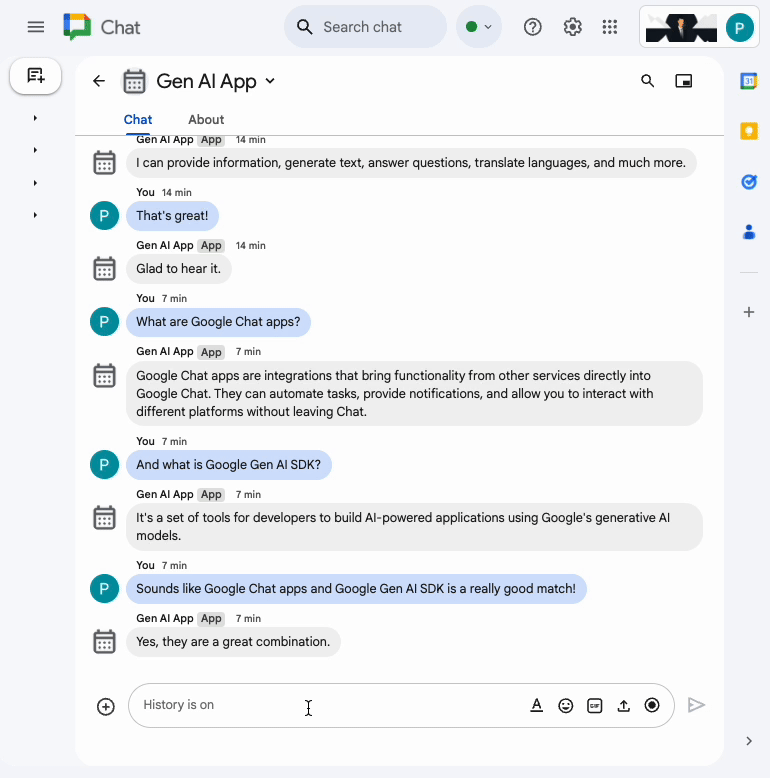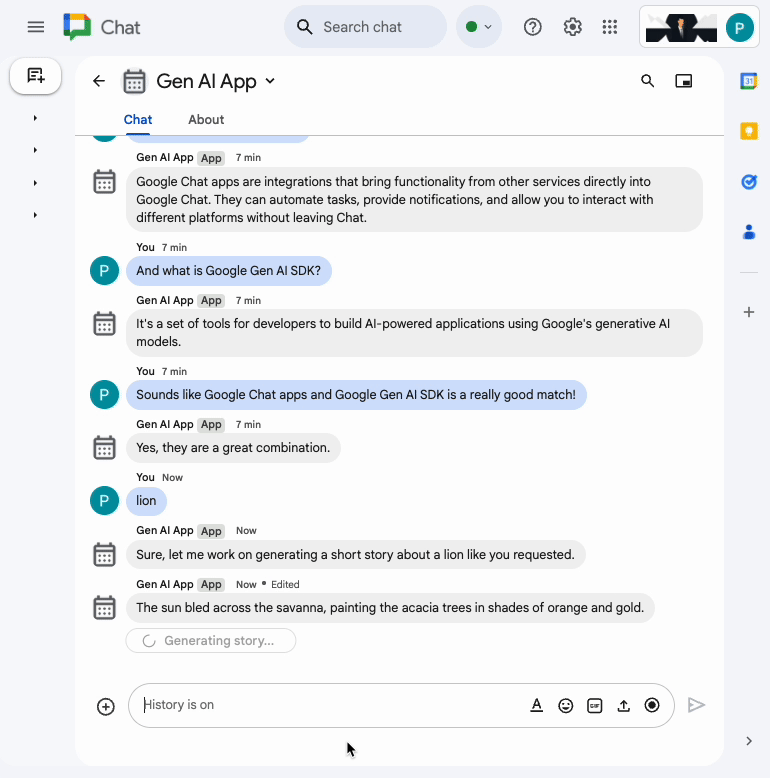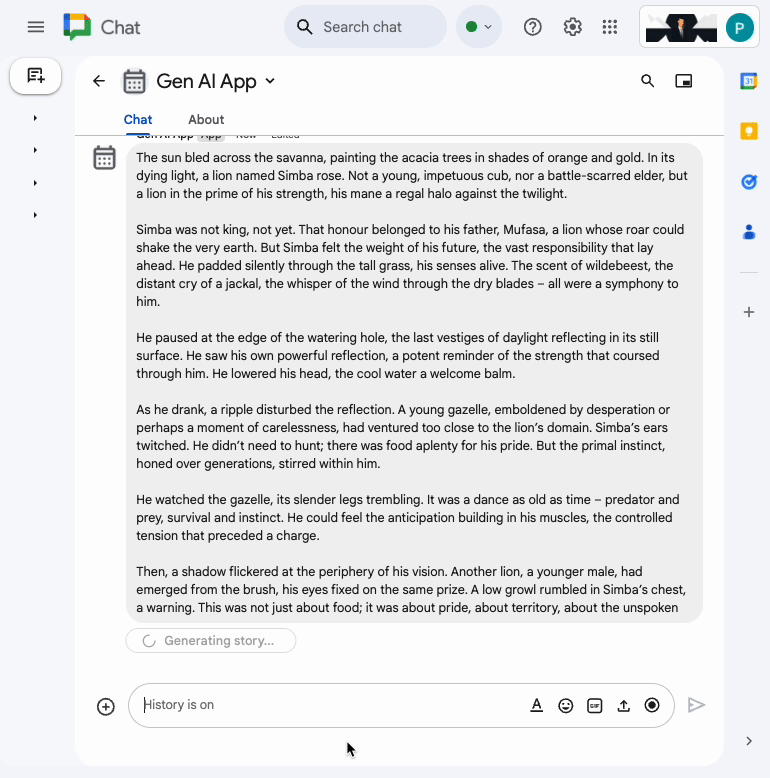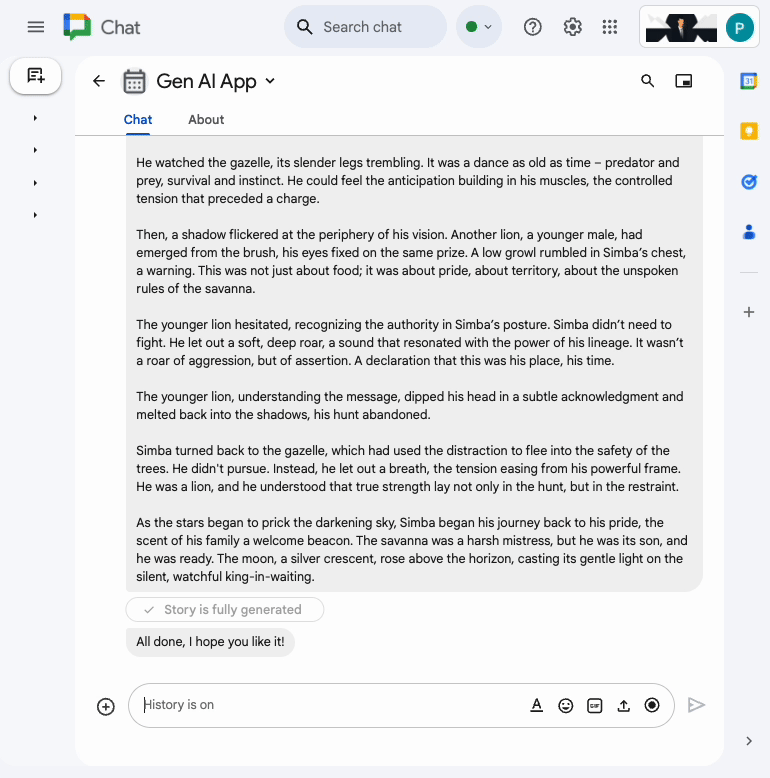
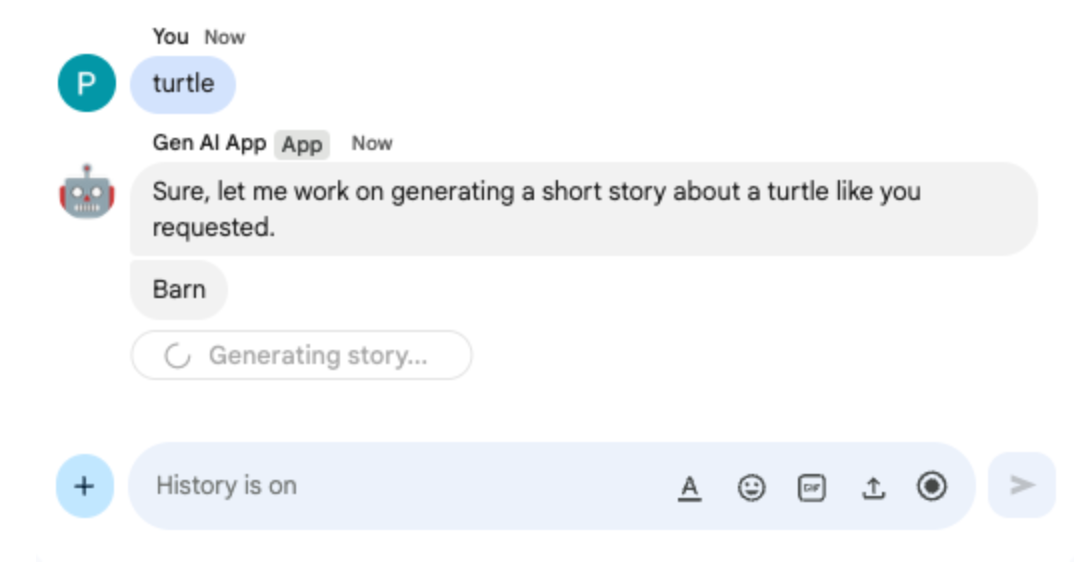
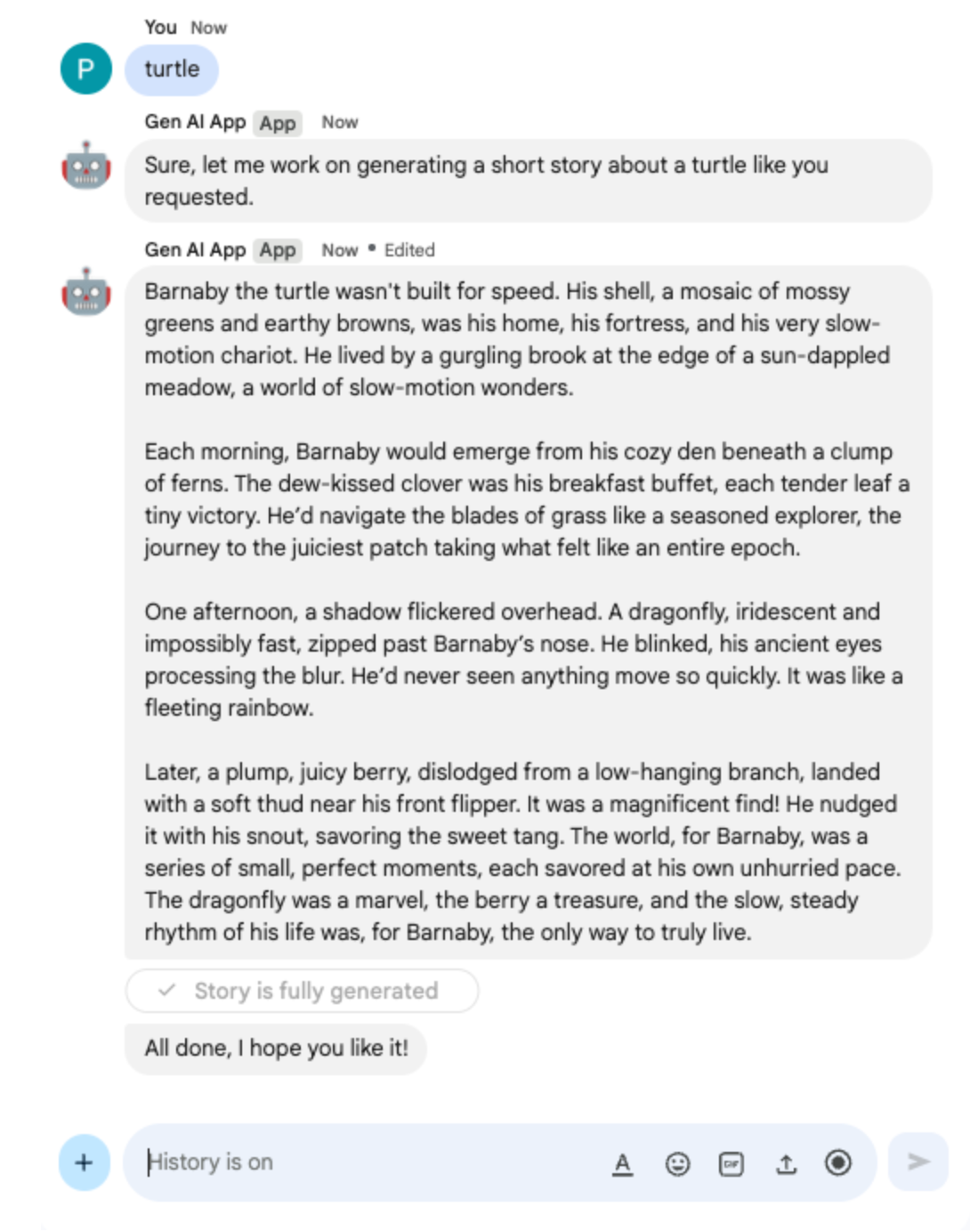
In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, type turtle and press enter. The app should answer with an acknowledgment message, the story generated with status as progress is made, and a completion confirmation message.
10. Multimodal app
This app relies on a model to edit images based on textual instructions from users. Both the users and the app add their images as Google Chat message attachments to exchange. The app relies on Google Chat APIs to programmatically download and upload images.
Review concepts
Google Chat message attachment
Google Chat message attachments are files, such as images or videos, that are uploaded to a Google Chat message. These attachments can be managed programmatically, enabling applications to interact with rich media directly within conversations.
Domain-Wide Delegation (DWD)
Domain-Wide Delegation (DWD) allows a service account to impersonate users in a Google Workspace domain, enabling applications to take actions on behalf of those users without direct authorization. This is useful for apps that need to access user data or perform actions (like uploading attachments to Google Chat) in the user's context, even when the user is not actively present, by granting the service account broad access across the domain.
Review flow
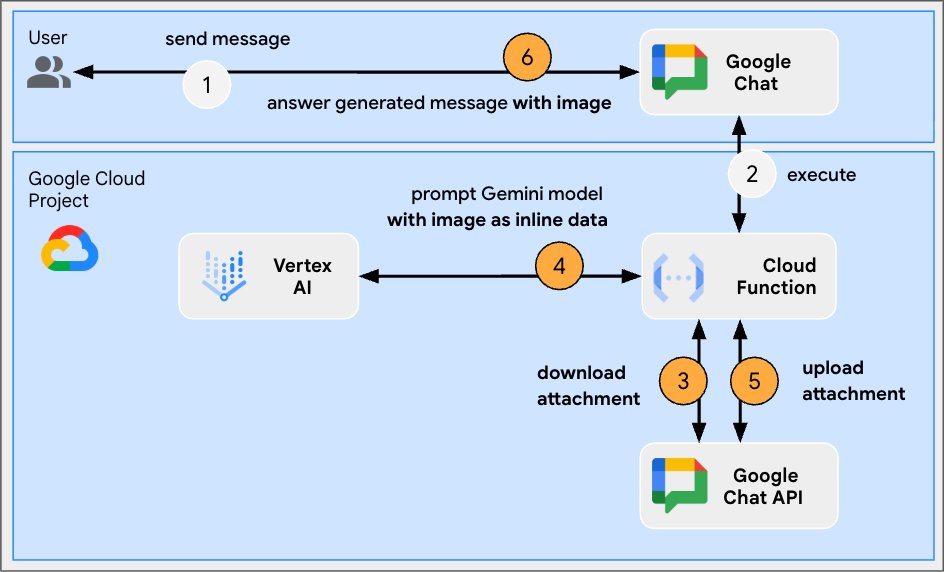
Review source code
env.js
...
// Replace with the Gemini model to use.
model: process.env.MODEL || 'gemini-2.0-flash-preview-image-generation',
...
index.js
...
// Import byte stream management libraries.
import { Buffer } from 'buffer';
import { Readable } from 'stream';
...
// Download a Google Chat attachment as base 64 string.
async function downloadFile(appChatClient, attachmentName) {
const response = await appChatClient.media.download({
resourceName: attachmentName,
alt: 'media'
}, {
responseType: 'stream'
});
const chunks = [];
return new Promise((resolve) => {
response.data.on('data', (chunk) => {
chunks.push(chunk);
});
response.data.on('end', () => {
const fileBuffer = Buffer.concat(chunks);
const base64String = fileBuffer.toString('base64');
resolve(base64String);
});
});
}
// Upload a base 64 string as Google Chat attachment of a space.
async function uploadFile(useChatClient, spaceName, data) {
const filename = 'generated_image.png';
return await userChatClient.media.upload({
parent: spaceName,
requestBody: { filename: filename },
media: {
mimeType: 'image/png',
body: Readable.from(Buffer.from(data, 'base64'))
}
});
}
...
...
http('gen-ai-app', async (req, res) => {
const userEmail = req.body.chat.user.email;
const spaceName = req.body.chat.messagePayload.space.name;
const userMessage = req.body.chat.messagePayload.message.text;
const attachmentName = req.body.chat.messagePayload.message.attachment[0].attachmentDataRef.resourceName;
const attachmentContentType = req.body.chat.messagePayload.message.attachment[0].contentType;
// Set up app authentication used to download the attachment input
// Application Default Credentials (ADC) will use the Cloud Run function's
// default service account.
const appAuth = new GoogleAuth({
// Specify the Chat API app authentication scopes
scopes: ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.bot']
});
// Create Chat service client with application credentials
const appChatClient = google.chat({
version: 'v1',
auth: await appAuth.getClient()
});
// Send a request to generate the answer with both text and image contents
const aiResponse = await genAI.models.generateContent({
model: env.model,
contents: [{
role: 'USER',
parts: [
// The text content of the message
{ text: userMessage },
// The attachment of the message is downloaded and added inline
{ inlineData: {
data: await downloadFile(appChatClient, attachmentName),
mimeType: attachmentContentType
}}
]
}],
config: { responseModalities: ['TEXT', 'IMAGE']}
});
// Set up user impersonation authentication used to upload the attachment output
// and send the response.
const impersonatedUserAuth = new GoogleAuth({
// Specify the Chat API user authentication scopes
scopes: ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages'],
keyFile: './credentials.json',
clientOptions: {
// Impersonate the user who sent the original message
subject: userEmail
}
});
// Create Chat service client with impersonated user credentials
const userChatClient = google.chat({
version: 'v1',
auth: await impersonatedUserAuth.getClient()
});
let responseText = undefined;
let responseAttachment = undefined;
// Go through the response parts received
for (const part of aiResponse.candidates[0].content.parts) {
if (part.inlineData) {
// The resulting image is retrieved inline and uploaded
const mediaResponse = await uploadFile(userChatClient, spaceName, part.inlineData.data);
responseAttachment = mediaResponse.data;
} else {
responseText = part.text;
}
}
// Create a Chat message dedicated to the generated content
await userChatClient.spaces.messages.create({
parent: spaceName,
requestBody: {
text: responseText ? responseText : 'Here it is!',
// The uploaded image is referenced as attachment
attachment: responseAttachment ? [responseAttachment] : undefined
}
});
// Send a last Chat message to confirm it's done
return res.send({ hostAppDataAction: { chatDataAction: { createMessageAction: { message: {
text: 'Done, feel free to let me know if you need anything else!'
}}}}});
});
...
Configure service account and export private key
- Delegate the Cloud Run default service account to manage Google Chat messages for users. Follow the instructions with the scope https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages. To retrieve the Cloud Run default service account Client ID, follow these steps:
- Click Menu ☰ > IAM & Admin > Service Accounts
- Click the service account with name Default compute service account.
- Expand section Advanced settings
- Copy Client ID to clipboard.
- Create and download a new private key for the Cloud Run default service account
- Click Menu ☰ > IAM & Admin > Service Accounts
- Click the service account with name Default compute service account.
- Select the Keys tab, click Add key, then Create new key.
- Select JSON, then click Create.
- Your new public/private key pair is generated and downloaded to your machine as a new file. Save the downloaded JSON file and copy its content to clipboard. This file is the only copy of this key. For information about how to store your key securely, see Managing service account keys.
Update Google Cloud Run Node.js function
- In your local development environment, change the current directory to
node/chat/gen-ai-apps/8-multimodal. It contains the entire source code and resources. - Go to the Source tab of the Google Cloud Run function service details page.
- Click Edit source.
- Click ➕, type
credentials.json, and click ✔️to create the missing resource file. - Paste contents of the JSON file downloaded in the previous step in the newly created
credentials.jsonfile. - Replace the entire contents of the
index.jsfile with the one in your local development environment. - Open the
env.jsfile and set the value of model togemini-2.0-flash-preview-image-generation.
...
model: 'gemini-2.0-flash-preview-image-generation',
...
- Click Save and redeploy.
- Wait for the successful completion of the revision deployment.

Try it
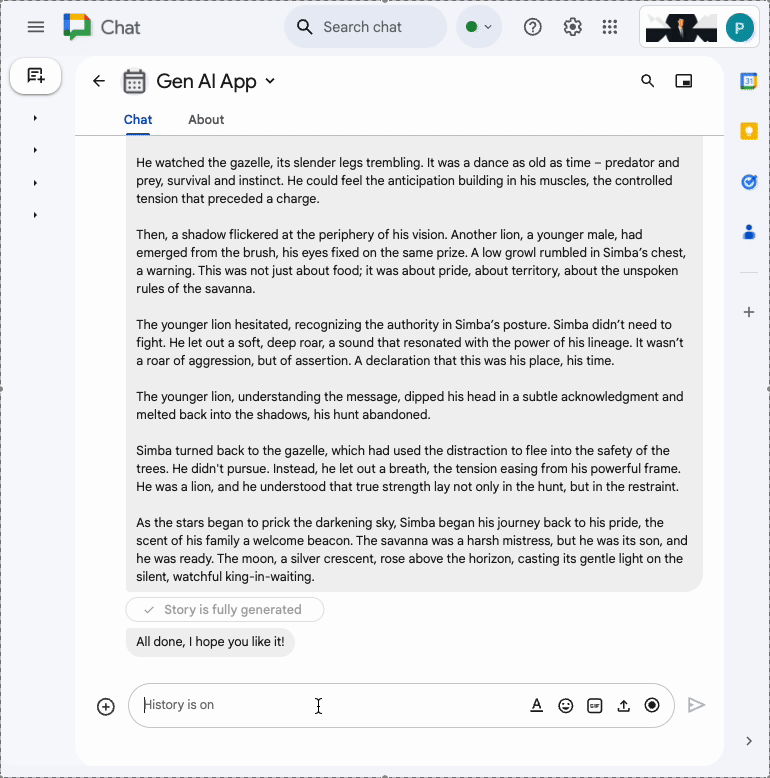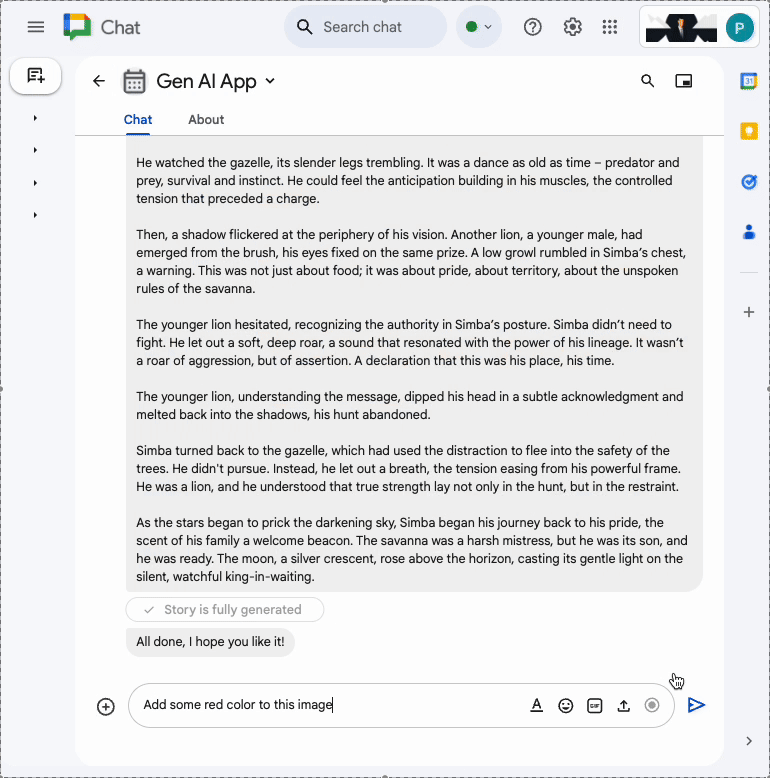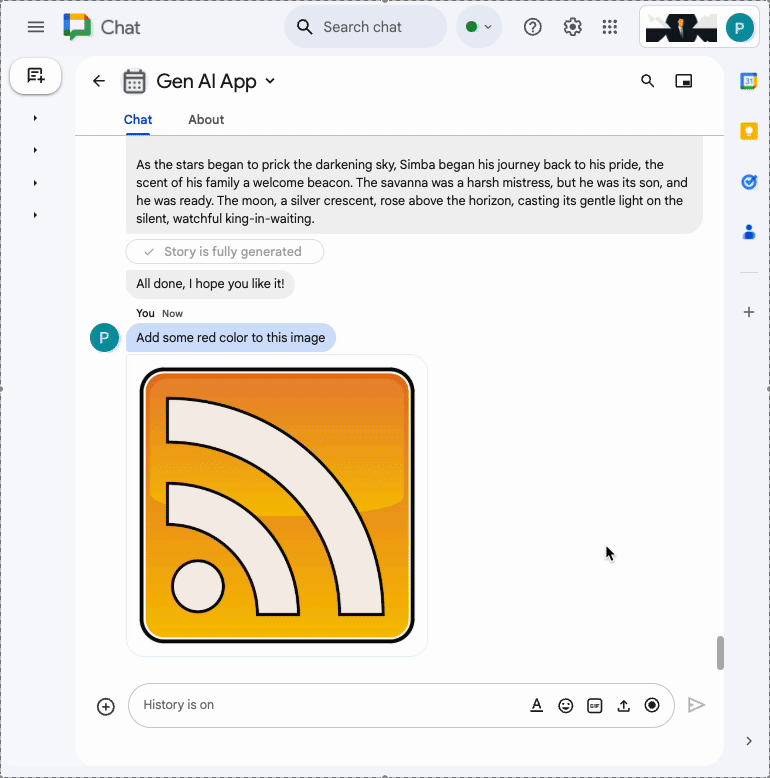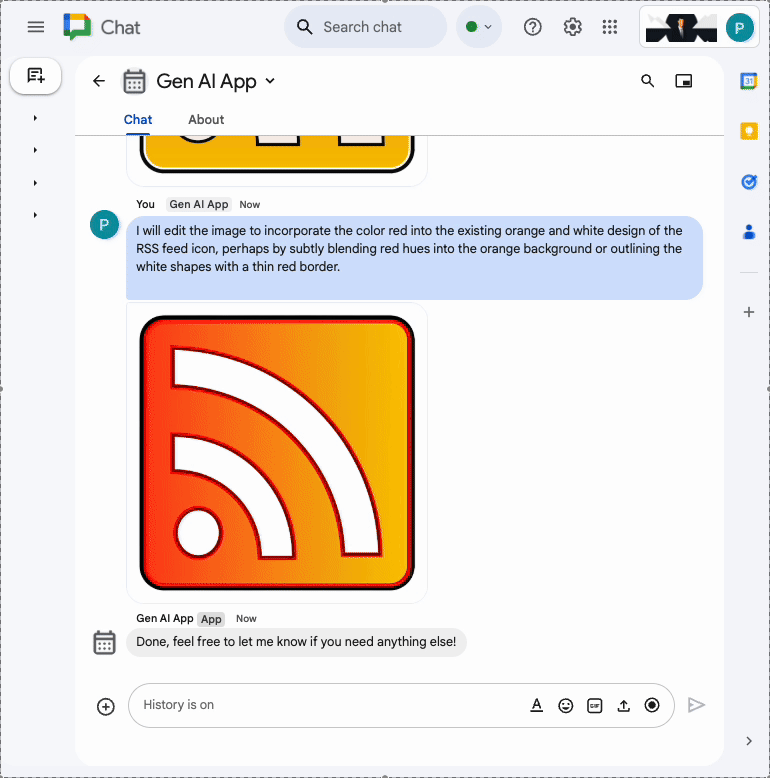
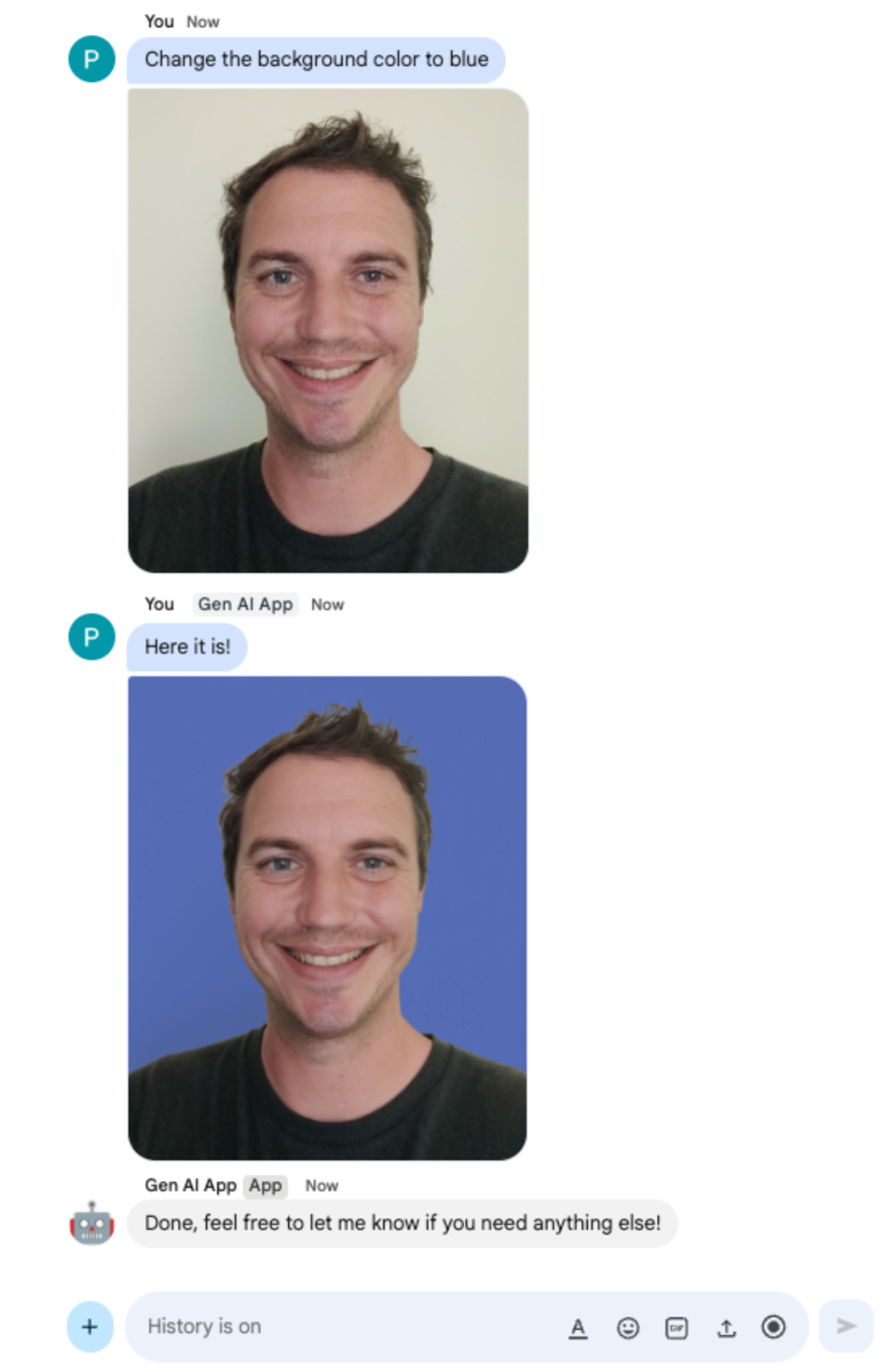
In the direct message space with the Chat app in Google Chat, upload a portrait picture of yourself in PNG format, type Change the background color to blue and press enter. The app should answer with a version of the picture with a blue background and a completion confirmation message.
11. Clean up
Delete Google Cloud project
To avoid incurring charges to your Google Cloud Account for the resources used in this codelab, we recommend that you delete the Google Cloud project.
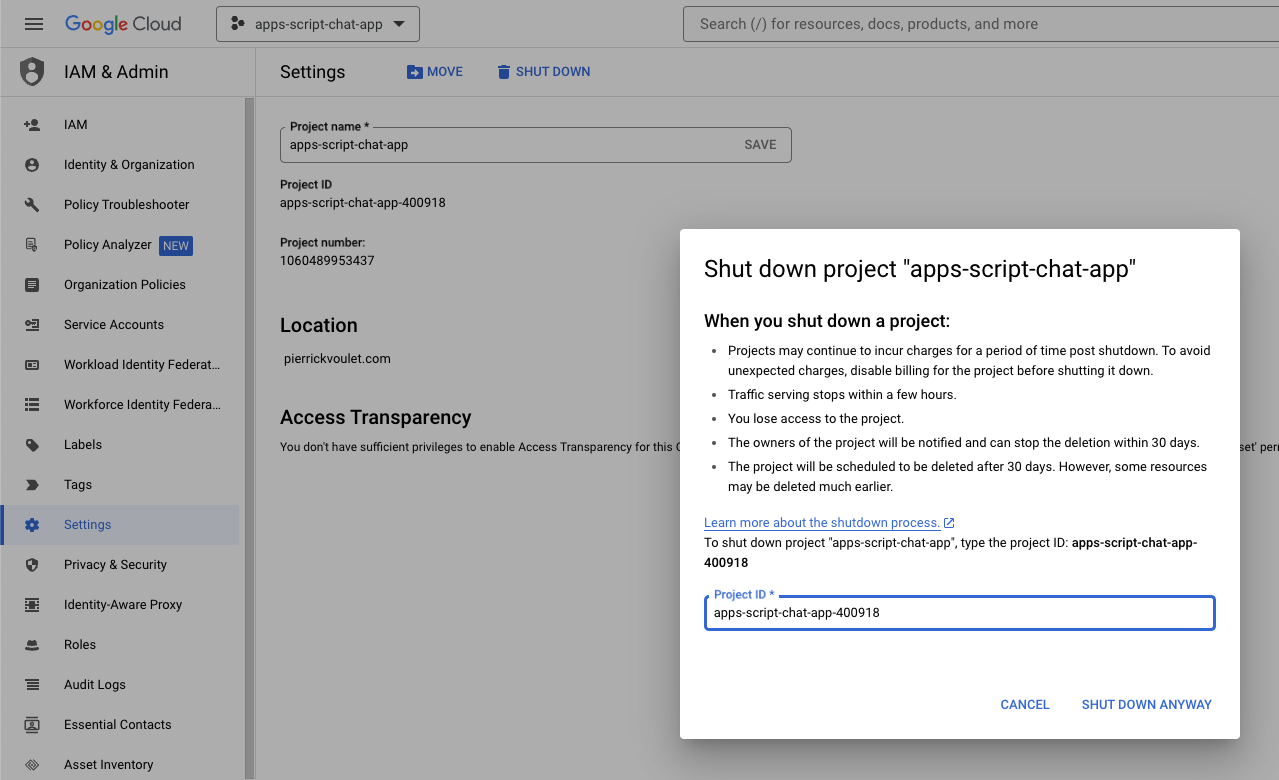
In the Google Cloud console, follow these steps:
- Click Menu ☰ > IAM & Admin > Settings.
- Click Shut down.
- Enter the project ID.
- Click Shut down anyway.
12. Congratulations
Congratulations! You built Google Chat apps as Google Workspace add ons that integrate fundamental AI concepts!
What's next?
We only showcase minimalist use cases in this codelab, but there are plenty of expansion areas that you might want to consider in your Google Chat apps, such as the following:
- Support other types of media such as audio, and video.
- Integrate with other AI models, including customs, hosted in dedicated platforms such as Vertex AI.
- Integrate with agents, including customs, hosted in dedicated platforms such as Agentspace and Dialogflow CX.
- Rely on feedback loops and classifications to monitor and improve performance.
- Publish on the marketplace to empower teams, organizations or public users.
Learn more
There are plenty of resources available for developers such as YouTube videos, documentation websites, code samples, and tutorials:
