1. Introduction
Private Service Connect for Google APIs (PSC) is a Google Cloud networking capability that allows users to configure private access via a private IP global endpoint within a VPC. For users that are running code or client side applications in a hybrid environment connected to Google Cloud by a VPN or Interconnect, PSC is used to resolve Google APIs over that private hybrid connection.
PSC for Google APIs can resolve many different domains, the full list of which can be found here. The domain that most Google APIs use is <API>.googleapis.com. Along with this domain, PSC also provides users a version of the googleapis.com that is <API>-<PSC-ENDPOINT-NAME>.**p.**googleapis.com. Using this domain, users can configure applications to use specific PSC endpoints. The most common use case allows users to choose which applications use the PSC endpoint to route Google API traffic over the hybrid connection, while allowing other applications to continue to route traffic to the public API endpoint.
Gemini falls under Google Cloud's Vertex AI product suite and is included in the list of Google APIs that can be resolved with PSC for Google APIs.
In this codelab, you will be building a simulated hybrid environment, hosting a Workbench Instance on prem and running Gemini Python code that accesses the Gemini API privately over an HA VPN, connecting to a PSC for Google APIs endpoint.
What you'll learn
- Create an NCC Hub.
- Configure VPC Spokes in an NCC Hub.
- Create a Cloud HA VPN.
- Configure Hybrid Spokes in an NCC Hub.
- Create a PSC for Google APIs endpoint.
- Configure a custom route over HA-VPN.
- Configure a DNS peering zone.
- Configure a Vertex Workbench Instance
- Configure Gemini Python code to use a PSC for Google APIs API Endpoint.
What you'll need
- A Google Cloud Project with "Owner" or full "Editor" permissions.
2. Codelab Topology
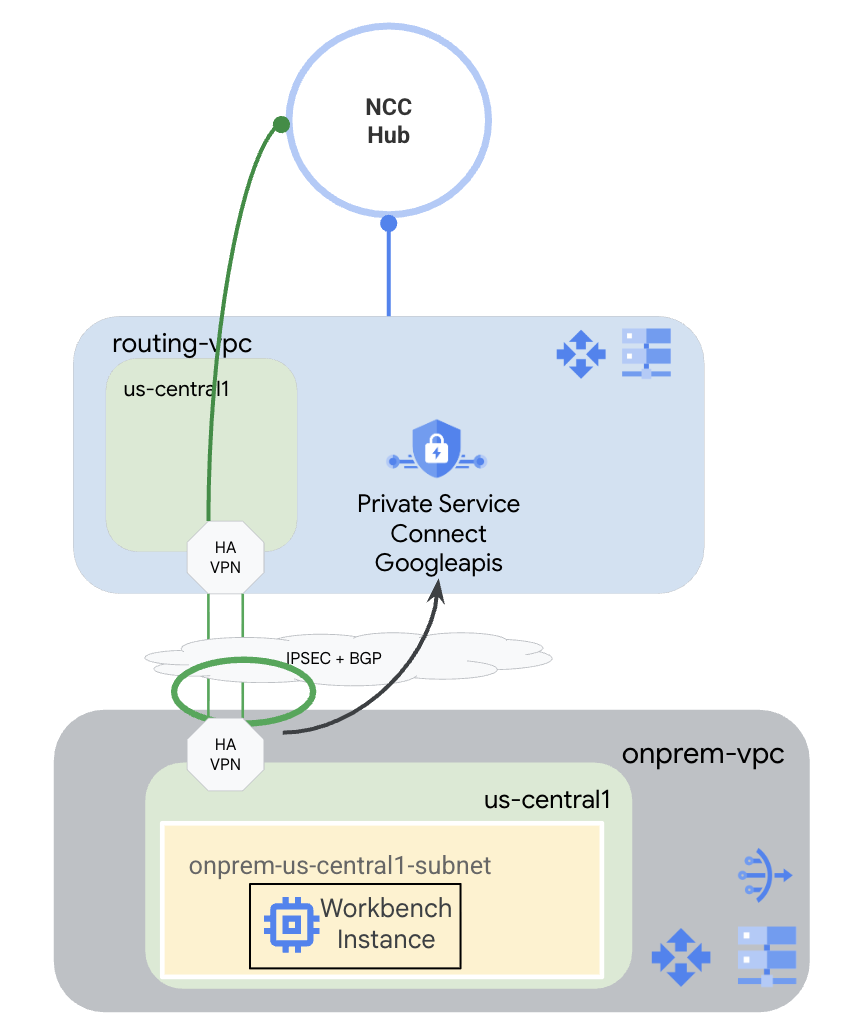
For this codelab, you will use Google Cloud to simulate a hybrid environment. There will be steps in this codelab that are specific to Google Cloud and would be different if configured from a true on-prem environment. Those steps will be called out.
You will create an NCC Hub that has a routing-vpc as a VPC Spoke. In that VPC, an HA-VPN will be configured to the on-prem VPC, which mimics an on-prem environment. The HA-VPN will be configured as a Hybrid Spoke in the NCC hub. In the on-prem VPC, you will create a subnet where a Workbench Instance will be hosted. You'll also create a Cloud NAT to be used for downloading packages on the Workbench instance.
Finally, you will create a DNS peering zone for the on-prem VPC to be able to use the Service Directory Private zone for p.googleapis.com that PSC for Google APIs automatically creates.
3. Setup and Requirements
Self-paced environment setup
- Sign-in to the Google Cloud Console and create a new project or reuse an existing one. If you don't already have a Gmail or Google Workspace account, you must create one.

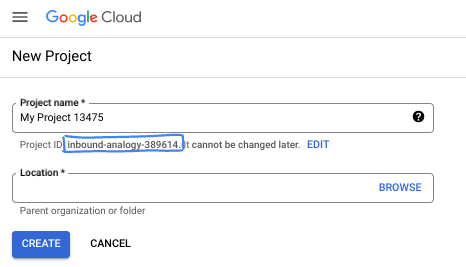
- The Project name is the display name for this project's participants. It is a character string not used by Google APIs. You can always update it.
- The Project ID is unique across all Google Cloud projects and is immutable (cannot be changed after it has been set). The Cloud Console auto-generates a unique string; usually you don't care what it is. In most codelabs, you'll need to reference your Project ID (typically identified as
PROJECT_ID). If you don't like the generated ID, you might generate another random one. Alternatively, you can try your own, and see if it's available. It can't be changed after this step and remains for the duration of the project. - For your information, there is a third value, a Project Number, which some APIs use. Learn more about all three of these values in the documentation.
- Next, you'll need to enable billing in the Cloud Console to use Cloud resources/APIs. Running through this codelab won't cost much, if anything at all. To shut down resources to avoid incurring billing beyond this tutorial, you can delete the resources you created or delete the project. New Google Cloud users are eligible for the $300 USD Free Trial program.
Start Cloud Shell
While Google Cloud can be operated remotely from your laptop, in this codelab you will be using Google Cloud Shell, a command line environment running in the Cloud.
From the Google Cloud Console, click the Cloud Shell icon on the top right toolbar:

It should only take a few moments to provision and connect to the environment. When it is finished, you should see something like this:
This virtual machine is loaded with all the development tools you'll need. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory, and runs on Google Cloud, greatly enhancing network performance and authentication. All of your work in this codelab can be done within a browser. You do not need to install anything.
4. Before you begin
Enable APIs
Inside Cloud Shell, make sure your project is configured correctly and set your environment variables.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud config list project gcloud config set project <project-id> export project=$(gcloud config get-value project) export region=us-central1 export zone=$region-a echo $project echo $region echo $zone
Enable all necessary Google APIs in the project.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud services enable compute.googleapis.com gcloud services enable networkconnectivity.googleapis.com gcloud services enable dns.googleapis.com gcloud services enable notebooks.googleapis.com gcloud services enable servicedirectory.googleapis.com gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com
5. Create VPCs and Subnets
Create Networks
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute networks create routing-vpc \
--subnet-mode=custom
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute networks create onprem-vpc \
--subnet-mode=custom
gcloud compute networks subnets create onprem-$region-subnet \
--network=onprem-vpc \
--range=10.0.0.0/24 \
--region=$region
--enable-private-ip-google-access
Create Cloud Routers and Cloud NAT
Create a Cloud Router that will be used in conjunction with the HA VPN in the routing-vpc.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute routers create routing-$region-cr \
--network=routing-vpc \
--region=$region \
--asn=64512
Create a Cloud Router that will be used in conjunction with the HA VPN in the onprem-vpc.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute routers create onprem-$region-cr \
--network=onprem-vpc \
--region=$region \
--asn=64513
Create a Cloud Router that will be used in conjunction with Cloud NAT in the onprem-vpc.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute routers create onprem-$region-cr-4nat \
--network=onprem-vpc \
--region=$region
The Cloud NAT in the onprem-vpc will be used for downloading packages to the Vertex AI Workbench Instance that will be configured in a later step.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute routers nats create onprem-$region-nat \
--router=onprem-$region-cr-4nat \
--region=$region \
--nat-all-subnet-ip-ranges \
--auto-allocate-nat-external-ips
6. Create Cloud HA-VPN
Create the VPN Gateways.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute vpn-gateways create routing-gateway \ --network=routing-vpc \ --region=$region \ --stack-type=IPV4_ONLY
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute vpn-gateways create onprem-gateway \ --network=onprem-vpc \ --region=$region \ --stack-type=IPV4_ONLY
Create the VPN tunnels originating from the routing-vpc.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute vpn-tunnels create routing-to-onprem-tunnel0 \
--peer-gcp-gateway=onprem-gateway \
--region=$region \
--ike-version=2 \
--shared-secret=mysecret \
--router=routing-$region-cr \
--vpn-gateway=routing-gateway \
--interface=0
gcloud compute vpn-tunnels create routing-to-onprem-tunnel1 \
--peer-gcp-gateway=onprem-gateway \
--region=$region \
--ike-version=2 \
--shared-secret=mysecret \
--router=routing-$region-cr \
--vpn-gateway=routing-gateway \
--interface=1
Create the VPN tunnels originating from the onprem-vpc.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute vpn-tunnels create onprem-to-routing-tunnel0 \
--peer-gcp-gateway=routing-gateway \
--region=$region \
--ike-version=2 \
--shared-secret=mysecret \
--router=onprem-$region-cr \
--vpn-gateway=onprem-gateway \
--interface=0
gcloud compute vpn-tunnels create onprem-to-routing-tunnel1 \
--peer-gcp-gateway=routing-gateway \
--region=$region \
--ike-version=2 \
--shared-secret=mysecret \
--router=onprem-$region-cr \
--vpn-gateway=onprem-gateway \
--interface=1
Set up BGP sessions for the two tunnels originating from the routing-vpc.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute routers add-interface routing-$region-cr \
--interface-name=routing-interface0 \
--ip-address=169.254.0.1 \
--mask-length=30 \
--vpn-tunnel=routing-to-onprem-tunnel0 \
--region=$region
gcloud compute routers add-bgp-peer routing-$region-cr \
--peer-name=routingtoonprem-bgp0 \
--interface=routing-interface0 \
--peer-ip-address=169.254.0.2 \
--peer-asn=64513 \
--region=$region
gcloud compute routers add-interface routing-$region-cr \
--interface-name=routing-interface1 \
--ip-address=169.254.1.1 \
--mask-length=30 \
--vpn-tunnel=routing-to-onprem-tunnel1 \
--region=$region
gcloud compute routers add-bgp-peer routing-$region-cr \
--peer-name=routingtoonprem-bgp1 \
--interface=routing-interface1 \
--peer-ip-address=169.254.1.2 \
--peer-asn=64513 \
--region=$region
Set up BGP sessions for the two tunnels originating from the onprem-vpc.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute routers add-interface onprem-$region-cr \
--interface-name=onprem-interface0 \
--ip-address=169.254.0.2 \
--mask-length=30 \
--vpn-tunnel=onprem-to-routing-tunnel0 \
--region=$region
gcloud compute routers add-bgp-peer onprem-$region-cr \
--peer-name=onpremtorouting-bgp0 \
--interface=onprem-interface0 \
--peer-ip-address=169.254.0.1 \
--peer-asn=64512 \
--region=$region
gcloud compute routers add-interface onprem-$region-cr \
--interface-name=onprem-interface1 \
--ip-address=169.254.1.2 \
--mask-length=30 \
--vpn-tunnel=onprem-to-routing-tunnel1 \
--region=$region
gcloud compute routers add-bgp-peer onprem-$region-cr \
--peer-name=onpremtorouting-bgp1 \
--interface=onprem-interface1 \
--peer-ip-address=169.254.1.1 \
--peer-asn=64512 \
--region=$region
Navigate to the Network Connectivity > VPN page in the console and make sure your HA-VPN tunnels and BGP sessions are configured properly.
7. Configure NCC Hub and Spokes
Create NCC Hub
From Cloud Shell
gcloud network-connectivity hubs create ncc-hub \
--project="$project" \
--preset-topology="mesh"
Create NCC Spokes
NCC gcloud requires that all spokes are configured with full path names, or URIs.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute networks describe routing-vpc
Note the full path (URI) of the routing-vpc for the following command.
Example Output
autoCreateSubnetworks: false creationTimestamp: '2025-08-20T11:13:42.233-07:00' id: 'xxx' kind: compute#network name: routing-vpc networkFirewallPolicyEnforcementOrder: AFTER_CLASSIC_FIREWALL routingConfig: bgpBestPathSelectionMode: LEGACY routingMode: REGIONAL selfLink: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/global/networks/routing-vpc selfLinkWithId: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/global/networks/355666541188722361 x_gcloud_bgp_routing_mode: REGIONAL x_gcloud_subnet_mode: CUSTOM
Configure Routing VPC Spoke
From Cloud Shell
gcloud network-connectivity spokes linked-vpc-network create routing-vpc \
--hub=ncc-hub \
--vpc-network=projects/$project/global/networks/routing-vpc \
--global
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute vpn-tunnels describe routing-to-onprem-tunnel0 --region=$region gcloud compute vpn-tunnels describe routing-to-onprem-tunnel1 --region=$region
Note the full paths (URIs) for the VPN tunnels originating from the routing-vpc.
Example Output
creationTimestamp: '2025-08-20T11:33:37.494-07:00' description: '' detailedStatus: Tunnel is up and running. id: 'xxx' ikeVersion: 2 kind: compute#vpnTunnel labelFingerprint: xxx localTrafficSelector: - 0.0.0.0/0 name: routing-to-onprem-tunnel0 peerGcpGateway: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/vpnGateways/onprem-gateway peerIp: 34.153.54.166 region: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1 remoteTrafficSelector: - 0.0.0.0/0 router: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/routers/routing-us-central1-cr selfLink: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/vpnTunnels/routing-to-onprem-tunnel0 sharedSecret: '*************' sharedSecretHash: xxx status: ESTABLISHED vpnGateway: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/vpnGateways/routing-gateway vpnGatewayInterface: 0 creationTimestamp: '2025-08-20T11:33:41.829-07:00' description: '' detailedStatus: Tunnel is up and running. id: 'xxx' ikeVersion: 2 kind: compute#vpnTunnel labelFingerprint: xxx localTrafficSelector: - 0.0.0.0/0 name: routing-to-onprem-tunnel1 peerGcpGateway: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/vpnGateways/onprem-gateway peerIp: 34.153.246.117 region: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1 remoteTrafficSelector: - 0.0.0.0/0 router: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/routers/routing-us-central1-cr selfLink: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/vpnTunnels/routing-to-onprem-tunnel1 sharedSecret: '*************' sharedSecretHash: xxx status: ESTABLISHED vpnGateway: https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/$project/regions/us-central1/vpnGateways/routing-gateway vpnGatewayInterface: 1
From Cloud Shell
gcloud network-connectivity spokes linked-vpn-tunnels create $region-vpn-spoke \
--hub=ncc-hub \
--vpn-tunnels=projects/$project/regions/$region/vpnTunnels/routing-to-onprem-tunnel0,projects/$project/regions/$region/vpnTunnels/routing-to-onprem-tunnel1 \
--region=$region
Check to make sure all your spokes are configured correctly before you move on.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud network-connectivity hubs list-spokes ncc-hub
Example Output
NAME: routing-vpc GROUP: default PROJECT: $project LOCATION: global TYPE: VPC_NETWORK STATE: ACTIVE STATE REASON: ETAG: 2 NAME: us-central1-vpn-spoke GROUP: default PROJECT: $project LOCATION: us-central1 TYPE: VPN_TUNNEL STATE: ACTIVE STATE REASON: ETAG:
8. Set Up Private Service Connect for Google APIs
PSC for Google APIs endpoints are created from global IP addresses that don't sit in a regional VPC subnet. The global IP address must be reserved specifically with the purpose of PRIVATE_SERVICE_CONNECT.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute addresses create psc-ip \ --global \ --purpose=PRIVATE_SERVICE_CONNECT \ --addresses=10.100.100.0 \ --network=routing-vpc
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute forwarding-rules create psc4googep \ --global \ --network=routing-vpc \ --address=psc-ip \ --target-google-apis-bundle=all-apis \ --service-directory-registration=projects/$project/locations/$region
From Cloud Shell
gcloud compute routers update routing-$region-cr \ --project=$project \ --region=$region \ --advertisement-mode custom \ --set-advertisement-groups=ALL_SUBNETS \ --set-advertisement-ranges=10.100.100.0/32
From Cloud Shell
gcloud dns managed-zones create peeringzone \
--description="dns peer onprem to routing" \
--dns-name=p.googleapis.com \
--networks=onprem-vpc \
--target-network=routing-vpc \
--target-project=$project \
--visibility=private
9. Set Up Vertex Workbench Instance
Create a Service Account to be used for the Workbench Instance identity.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud iam service-accounts create workbench-sa \
--display-name="workbench-sa"
Note the full name of your Service Account and give it the permission aiplatform.admin to execute calls to Vertex AI/Gemini.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud iam service-accounts list
Example Output
DISPLAY NAME: Compute Engine default service account EMAIL: xxx-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com DISABLED: False DISPLAY NAME: workbench-sa EMAIL: workbench-sa@$project.iam.gserviceaccount.com DISABLED: False
Make sure you replace <your-project-id> with your actual Project ID. We cannot use the variable $project here due to the required quotes.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $project --member='serviceAccount:workbench-sa@<your-project-id>.iam.gserviceaccount.com' --role='roles/aiplatform.admin' --condition=None
From Cloud Shell
gcloud workbench instances create workbench-$region --vm-image-project=cloud-notebooks-managed --vm-image-family=workbench-instances --location=$region-a --network=projects/$project/global/networks/onprem-vpc --subnet=projects/$project/regions/$region/subnetworks/onprem-$region-subnet --subnet-region=$region --disable-public-ip --service-account-email=workbench-sa@$project.iam.gserviceaccount.com
The provisioning of the Workbench Instance may take longer than the gcloud command runs.
10. Test Gemini Code
In the UI, click "Open JupyterLab".
Once in JupyterLab, open a new Python 3 Notebook.

Run the following code in the notebook. Make sure you update the code to include your specific project, and region information.
From JupyterLab Notebook
pip install --upgrade google-genai
Restart the notebook kernel.
Note the API endpoint. Here we are using the API endpoint <YOUR_REGION>-aiplatform.googleapis.com. This is the standard API endpoint for Vertex AI.
From JupyterLab Notebook
PROJECT_ID="YOUR_PROJECT_ID" # Google Cloud Project ID
LOCATION_ID="YOUR_REGION" # Enter Vertex AI Gemini region such a s us-central1
API_ENDPOINT="https://<YOUR_REGION>-aiplatform.googleapis.com" # API Endpoint
MODEL_ID="gemini-2.0-flash" # Gemini Model ID
from google import genai
from google.genai.types import (
GenerateContentConfig,
HarmBlockThreshold,
HarmCategory,
Part,
SafetySetting,
)
From JupyterLab Notebook
from google import genai
client= genai.Client(vertexai=True, project=PROJECT_ID, location=LOCATION_ID, http_options={'base_url': API_ENDPOINT})
prompt = "what weighs more, 1kg of feathers or 1kg of stones"
safety_settings = [
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HARASSMENT,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HATE_SPEECH,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
]
response = client.models.generate_content(
model=MODEL_ID,
contents=prompt,
config=GenerateContentConfig(
safety_settings=safety_settings,
),
)
# Response will be `None` if it is blocked.
print(response.text)
Sample Response
This is a classic trick question! They both weigh the same: 1 kilogram. The difference is in the volume they occupy and the density of the materials.
Note the API name that you used when you ran the code. YOUR_REGION-aiplatform.googleapis.com is the default API name for Vertex AI. We need to change the API name and run the code again. We can ensure that the code is using the PSC Endpoint by running a TCPdump in a terminal on the Workbench Instance.
Run a TCPdump in a Terminal
Open a Terminal on the Workbench by clicking File > New > Terminal.
If you have issues with seeing text output in the terminal you need to update your terminal theme. Do this in Settings > Terminal Theme > Light OR Dark.
From Terminal
sudo tcpdump host 10.100.100.0
Update Gemini Code
Switch back over to the notebook, update the API Endpoint and run the code again. Note that we changed the API endpoint to <YOUR_REGION>-aiplatform**-psc4googep.p**.googleapis.com. This aligns to the PSC specific API format <service>-<endpointname>.p.googleapis.com.
From JupyterLab Notebook
API_ENDPOINT="https://<YOUR_REGION>-aiplatform-psc4googep.p.googleapis.com" # API Endpoint
From JupyterLab Notebook
from google import genai
from google.genai.types import (
GenerateContentConfig,
HarmBlockThreshold,
HarmCategory,
Part,
SafetySetting,
)
From JupyterLab Notebook
from google import genai
client= genai.Client(vertexai=True, project=PROJECT_ID, location=LOCATION_ID, http_options={'base_url': API_ENDPOINT})
prompt = "what weighs more, 1kg of feathers or 1kg of stones"
safety_settings = [
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HARASSMENT,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HATE_SPEECH,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
SafetySetting(
category=HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT,
threshold=HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_LOW_AND_ABOVE,
),
]
response = client.models.generate_content(
model=MODEL_ID,
contents=prompt,
config=GenerateContentConfig(
safety_settings=safety_settings,
),
)
# Response will be `None` if it is blocked.
print(response.text)
Sample Response
They weigh the same. 1 kg is 1 kg, regardless of what it's made of.
Check TCPdump
Switch back over to the terminal and look for calls to the PSC endpoint (10.100.100.0). End the TCPdump (control+c)
Sample Output
listening on ens4, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes 19:12:01.473886 IP workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886 > 10.100.100.0.https: Flags [S], seq 3367930834, win 65320, options [mss 1420,sackOK,TS val 2933602967 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0 19:12:01.476561 IP 10.100.100.0.https > workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886: Flags [S.], seq 1863301110, ack 3367930835, win 65535, options [mss 1366,sackOK,TS val 3004118895 ecr 2933602967,nop,wscale 8], length 0 19:12:01.476602 IP workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886 > 10.100.100.0.https: Flags [.], ack 1, win 511, options [nop,nop,TS val 2933602969 ecr 3004118895], length 0 19:12:01.477283 IP workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886 > 10.100.100.0.https: Flags [P.], seq 1:1573, ack 1, win 511, options [nop,nop,TS val 2933602970 ecr 3004118895], length 1572 19:12:01.478836 IP 10.100.100.0.https > workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886: Flags [.], ack 1573, win 1045, options [nop,nop,TS val 3004118898 ecr 2933602970], length 0 19:12:01.480181 IP 10.100.100.0.https > workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886: Flags [P.], seq 1:6041, ack 1573, win 1045, options [nop,nop,TS val 3004118899 ecr 2933602970], length 6040 19:12:01.480183 IP 10.100.100.0.https > workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886: Flags [P.], seq 6041:8378, ack 1573, win 1045, options [nop,nop,TS val 3004118899 ecr 2933602970], length 2337 19:12:01.480215 IP workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886 > 10.100.100.0.https: Flags [.], ack 6041, win 485, options [nop,nop,TS val 2933602973 ecr 3004118899], length 0 19:12:01.480225 IP workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886 > 10.100.100.0.https: Flags [.], ack 8378, win 473, options [nop,nop,TS val 2933602973 ecr 3004118899], length 0 19:12:01.482580 IP workbench-us-central1.us-central1-a.c.xxx.internal.41886 > 10.100.100.0.https: Flags [P.], seq 1573:1653, ack 8378, win 501, options [nop,nop,TS val 2933602975 ecr 3004118899], length 80
SUCCESS!
11. Cleanup steps
Close the JupyterLab notebook and return to the Cloud Shell. Ensure your Cloud Shell hasn't timed out. If it has, reset your variables.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud config list project gcloud config set project <project-id> export project=$(gcloud config get-value project) export region=us-central1 export zone=$region-a echo $project echo $region echo $zone
Delete all resources.
From Cloud Shell
gcloud workbench instances delete workbench-$region --location=$zone -q gcloud iam service-accounts delete workbench-sa@$project.iam.gserviceaccount.com -q gcloud dns managed-zones delete peeringzone -q gcloud compute forwarding-rules delete psc4googep --global -q gcloud compute addresses delete psc-ip --global -q gcloud network-connectivity spokes delete $region-vpn-spoke --region=$region -q gcloud network-connectivity spokes delete routing-vpc --global -q gcloud network-connectivity hubs delete ncc-hub -q gcloud compute vpn-tunnels delete onprem-to-routing-tunnel1 --region=$region --project=$project -q gcloud compute vpn-tunnels delete onprem-to-routing-tunnel0 --region=$region --project=$project -q gcloud compute vpn-tunnels delete routing-to-onprem-tunnel1 --region=$region --project=$project -q gcloud compute vpn-tunnels delete routing-to-onprem-tunnel0 --region=$region --project=$project -q gcloud compute vpn-gateways delete onprem-gateway --region=$region --project=$project -q gcloud compute vpn-gateways delete routing-gateway --region=$region --project=$project -q gcloud compute routers nats delete onprem-$region-nat --router=onprem-$region-cr-4nat --region=$region -q gcloud compute routers delete onprem-$region-cr-4nat --region=$region -q gcloud compute routers delete onprem-$region-cr --region=$region -q gcloud compute routers delete routing-$region-cr --region=$region -q gcloud compute networks subnets delete onprem-$region-subnet --region=$region -q gcloud compute networks delete onprem-vpc -q gcloud compute networks delete routing-vpc -q
12. Congratulations!
Congratulations for completing the codelab.
What we've covered
- Create an NCC Hub.
- Configure VPC Spokes in an NCC Hub.
- Create a Cloud HA VPN.
- Configure Hybrid Spokes in an NCC Hub.
- Create a PSC for Google APIs endpoint.
- Configure a custom route over HA-VPN.
- Configure a DNS peering zone.
- Configure a Vertex Workbench Instance
- Configure Gemini Python code to use a PSC for Google APIs API Endpoint.
