1. Introduction
Overview
In this lab, you'll explore a multimodal data science workflow in BigQuery, framed around a real estate scenario. You will start with a raw dataset of house listings and their images, enrich this data with AI to extract visual features, build a clustering model to discover distinct market segments, and finally, create a powerful visual search tool using vector embeddings.
You'll compare this SQL-native workflow with a modern, generative AI approach by using the Data Science Agent to automatically generate a Python-based clustering model from a simple text prompt.
What you'll learn
- Prepare a raw dataset of real estate listings for analysis through feature engineering.
- Enrich listings by using BigQuery's AI functions to analyze house photos for key visual features.
- Build and evaluate a K-means model with BigQuery Machine Learning (BQML) to segment properties into distinct clusters.
- Automate model creation by using the Data Science Agent to generate a clustering model with Python.
- Generate embeddings for house images to power a visual search tool, finding similar homes with text or image queries.
Prerequisites
Before starting this lab, you should be familiar with:
- Basic SQL and Python programming.
- Running Python code in a Jupyter notebook.
2. Before you begin
Create a Google Cloud Project
- In the Google Cloud Console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
- Make sure that billing is enabled for your Cloud project. Learn how to check if billing is enabled on a project.
Enable APIs with Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell is a command-line environment running in Google Cloud that comes preloaded with necessary tools.
- Click Activate Cloud Shell at the top of the Google Cloud console:

- Once connected to Cloud Shell, run this command to verify your authentication in Cloud Shell:
gcloud auth list
- Run the following command to confirm that your project is configured for use with gcloud:
gcloud config list project
- If your project is not set, use the following command to set it:
export PROJECT_ID=<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
Enable APIs
- Run this command to enable all the required APIs and services:
gcloud services enable bigquery.googleapis.com \
bigqueryunified.googleapis.com \
cloudaicompanion.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com
- On successful execution of the command, you should see a message similar to the one shown below:
Operation "operations/..." finished successfully.
- Exit Cloud Shell.
3. Open Lab Notebook in BigQuery Studio
Navigating the UI:
- In the Google Cloud Console, go to Navigation menu > BigQuery.
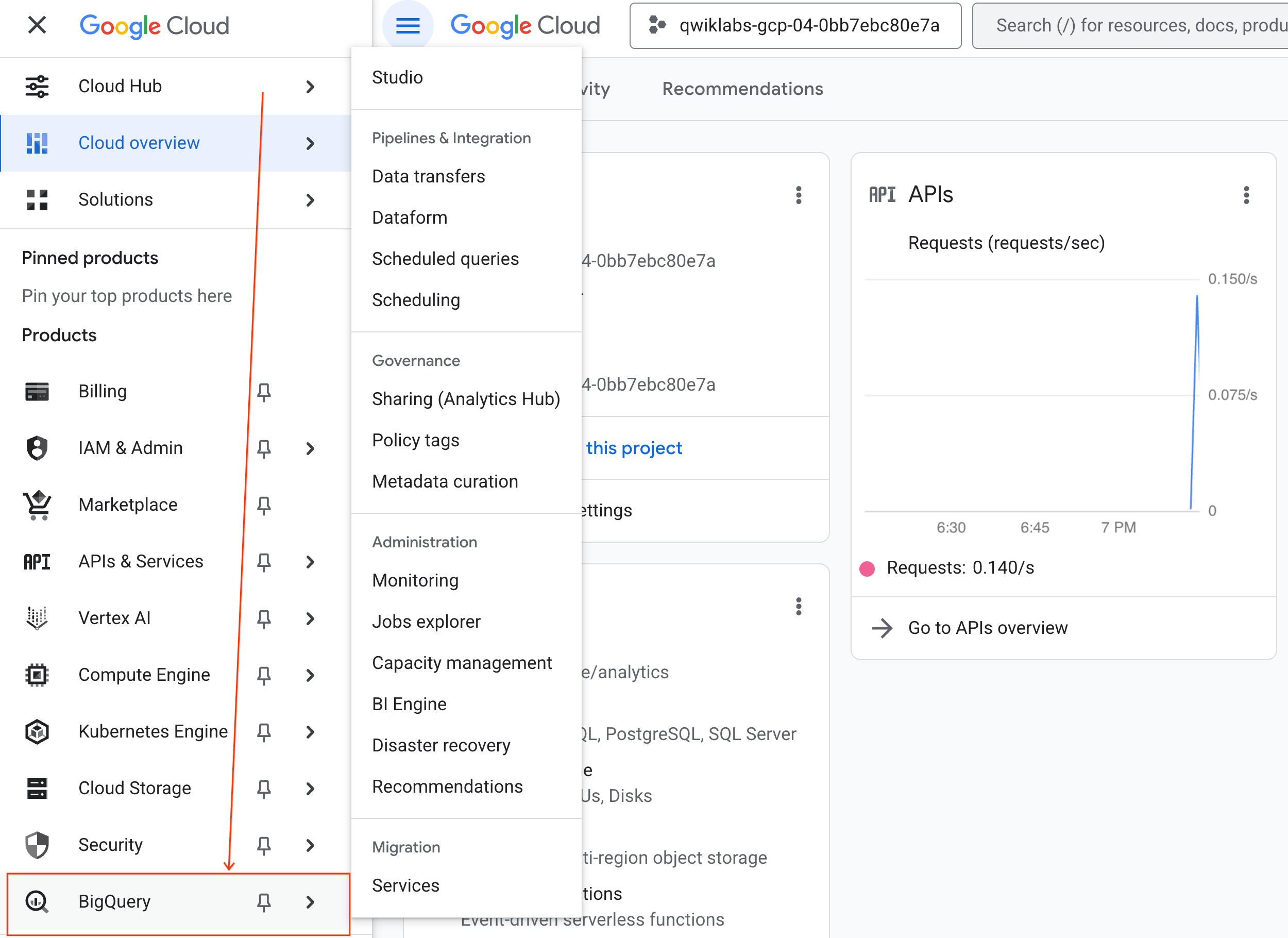
- In the BigQuery Studio pane, click the dropdown arrow button, hover over Notebook, and then select Upload.
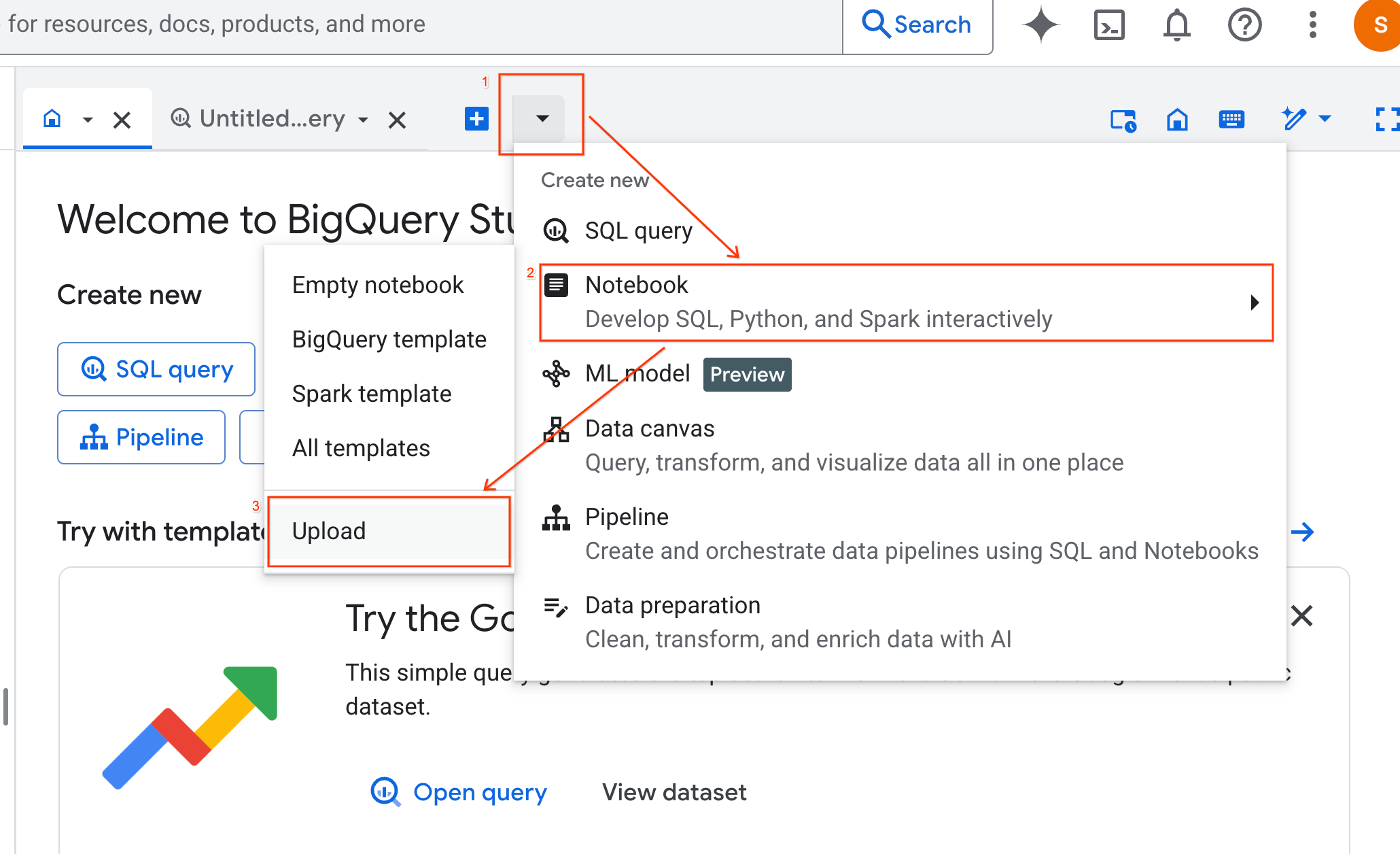
- Select the URL radio button, and input the following URL:
https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/generative-ai/blob/main/gemini/use-cases/applying-llms-to-data/ai-assisted-data-science/ai-assisted-data-science.ipynb
- Set the region to
us-central1and click Upload.
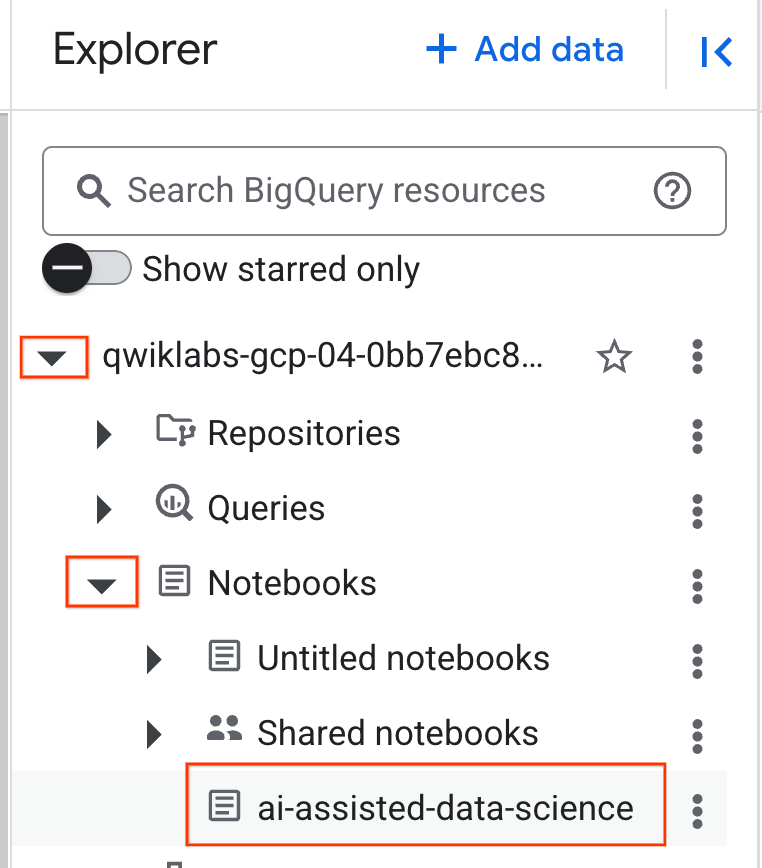
- To open the notebook, click the dropdown arrow in the Explorer pane that contains your project ID. Then click the dropdown for Notebooks. Click the notebook
ai-assisted-data-science.
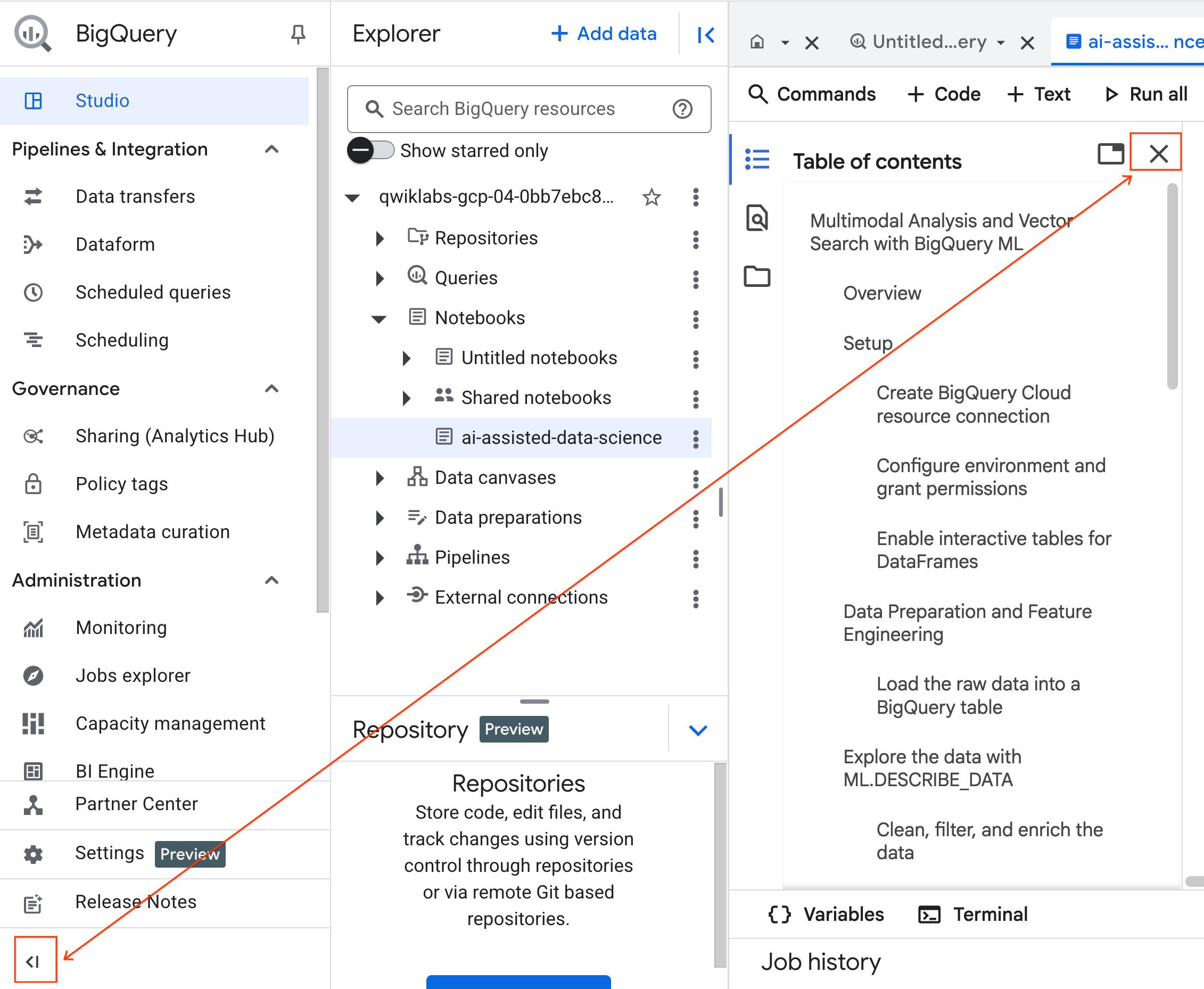
- (Optional) Collapse the BigQuery navigation menu and the Notebook's Table of Contents for more space.
4. Connect to a Runtime and Run Setup Code
- Click Connect. If a pop-up appears, authorize Colab Enterprise with your user. Your notebook will automatically connect to a runtime. This may take a couple of minutes to complete.
- Once the runtime is established, you will see the following:
- Within the notebook, scroll to the Setup section. Click the "Run" button next to the hidden cells. This creates a few resources necessary for the lab in your project. This process may take a minute to complete. Feel free to check the cells under Setup in the meantime.
5. Data Preparation and Feature Engineering
In this section, you will run through the first important step in any data science project: preparing your data. You start by creating a BigQuery dataset to organize your work and then load the raw real estate / housing data from a CSV file in Cloud Storage into a new table.
Then, you will transform this raw data into a cleaned table with new features. This involves filtering the listings, creating a new property_age feature, and preparing the image data for multimodal analysis.
6. Multimodal Enrichment with AI Functions
Now you will enrich your data using the power of generative AI. In this section, you use BigQuery's built-in AI functions to analyze the images for each house listing.
By connecting BigQuery to a Gemini model, you extract new, valuable features from images (such as whether a property is near water and a brief description of the home) directly with SQL.
7. Model Training with K-Means Clustering
With your newly enriched dataset, you are ready to build a machine learning model. Your goal is to segment the house listings into distinct groups, and you do this by training a K-means clustering model directly in BigQuery using BigQuery Machine Learning (BQML). As part of this single step, you also register the model in the Vertex AI Model Registry, making it instantly available within the broader MLOps ecosystem on Google Cloud.
To confirm your model was successfully registered, you can find it in the Vertex AI Model Registry by following these steps:
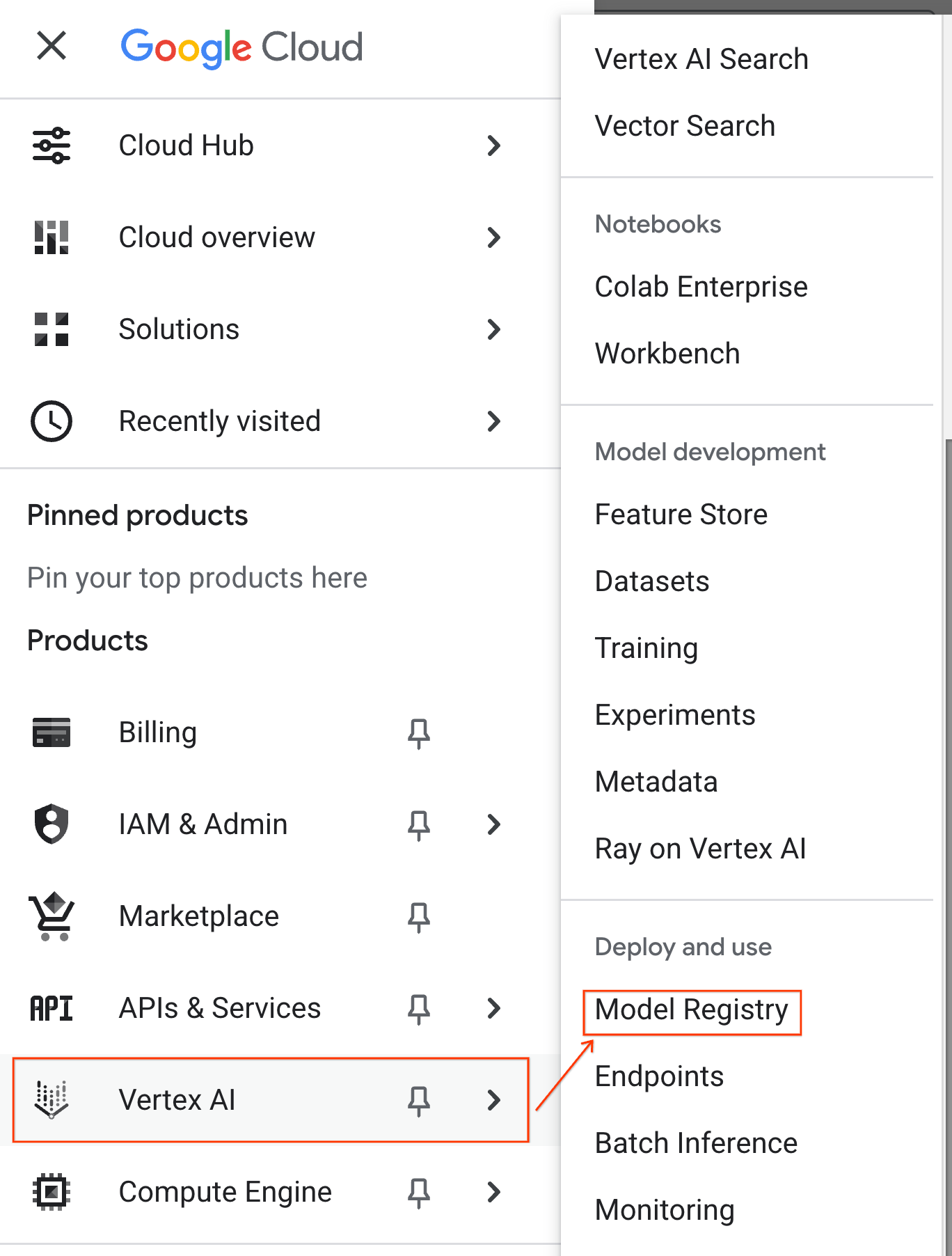
- In the Google Cloud Console, click the Navigation menu (☰) in the top-left corner.
- Scroll to the Vertex AI section and click on Model Registry. You will now see your BQML model listed alongside all your other custom models.
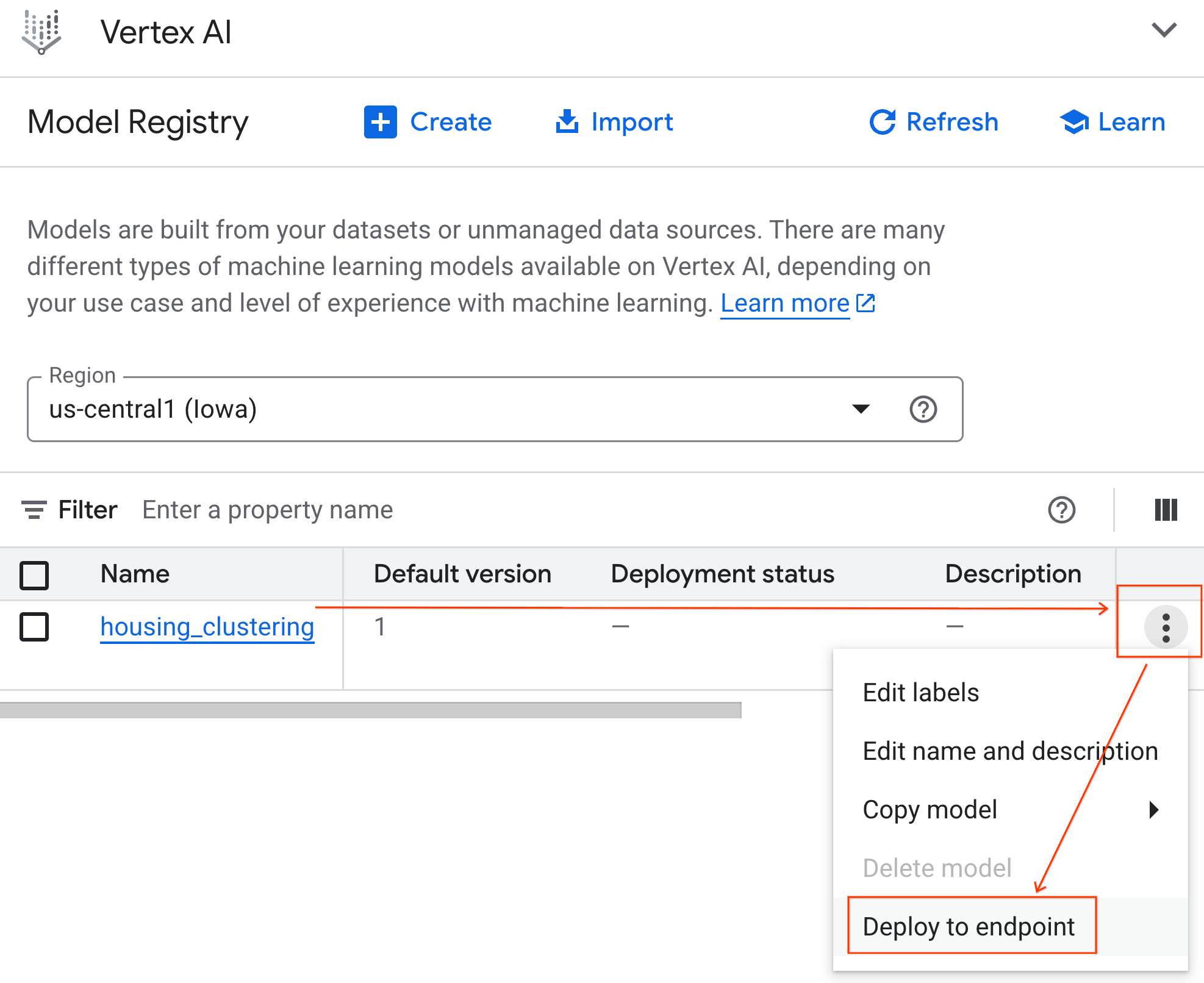
- In the list of models, find the model named housing_clustering. You could take the next step to Deploy to an endpoint, which would make your model available for real-time, online predictions outside of the BigQuery environment.
After exploring the Model Registry, you can return to your Colab notebook in BigQuery with these steps:
- In the Navigation menu (☰), navigate to BigQuery > Studio.
- Expand the menus in the Explore pane to find your notebook and open it.
8. Model Evaluation and Prediction
After training your model, the next step is to understand the clusters it created. Here, you use BigQuery Machine Learning functions like ML.EVALUATE and ML.CENTROIDS to analyze the model's quality and the defining characteristics of each segment.
You then use ML.PREDICT to assign each house to a cluster. By running this query with the %%bigquery df magic command, you store the results in a pandas DataFrame named df. This makes the data immediately available for the subsequent Python steps. This highlights the interoperability between SQL and Python in Colab Enterprise.
9. Visualize and Interpret Clusters
With your predictions now loaded into a DataFrame, you can create visualizations to bring the data to life. In this section, you will use popular Python libraries like Matplotlib to explore the differences between the housing segments.
You will create box plots and bar charts to visually compare key features like price and property age, making it easy to build an intuitive understanding of each cluster.
10. Generate Cluster Descriptions with Gemini Models
While numerical centroids and charts are powerful, generative AI allows you to go a step further and create rich, qualitative personas for each housing segment. This helps you understand not just what the clusters are, but who they represent.
In this section, you will first aggregate the average statistics for each cluster, like price and square footage. Then, you will pass this data into a prompt for the Gemini model. You then instruct the model to act as a real estate professional and generate a detailed summary, including key characteristics and a target buyer for each segment. The result is a set of clear, human-readable descriptions that make the clusters immediately understandable and actionable for a marketing team.
Feel free to alter the prompt as you see fit and experiment with the results!
11. Automate Modeling with the Data Science Agent
Now, you will explore a powerful, alternative workflow. Instead of writing code manually, you will use the integrated Data Science Agent to automatically generate a complete clustering model workflow from a single, natural language prompt.
Follow these steps to generate and run the model using the agent:
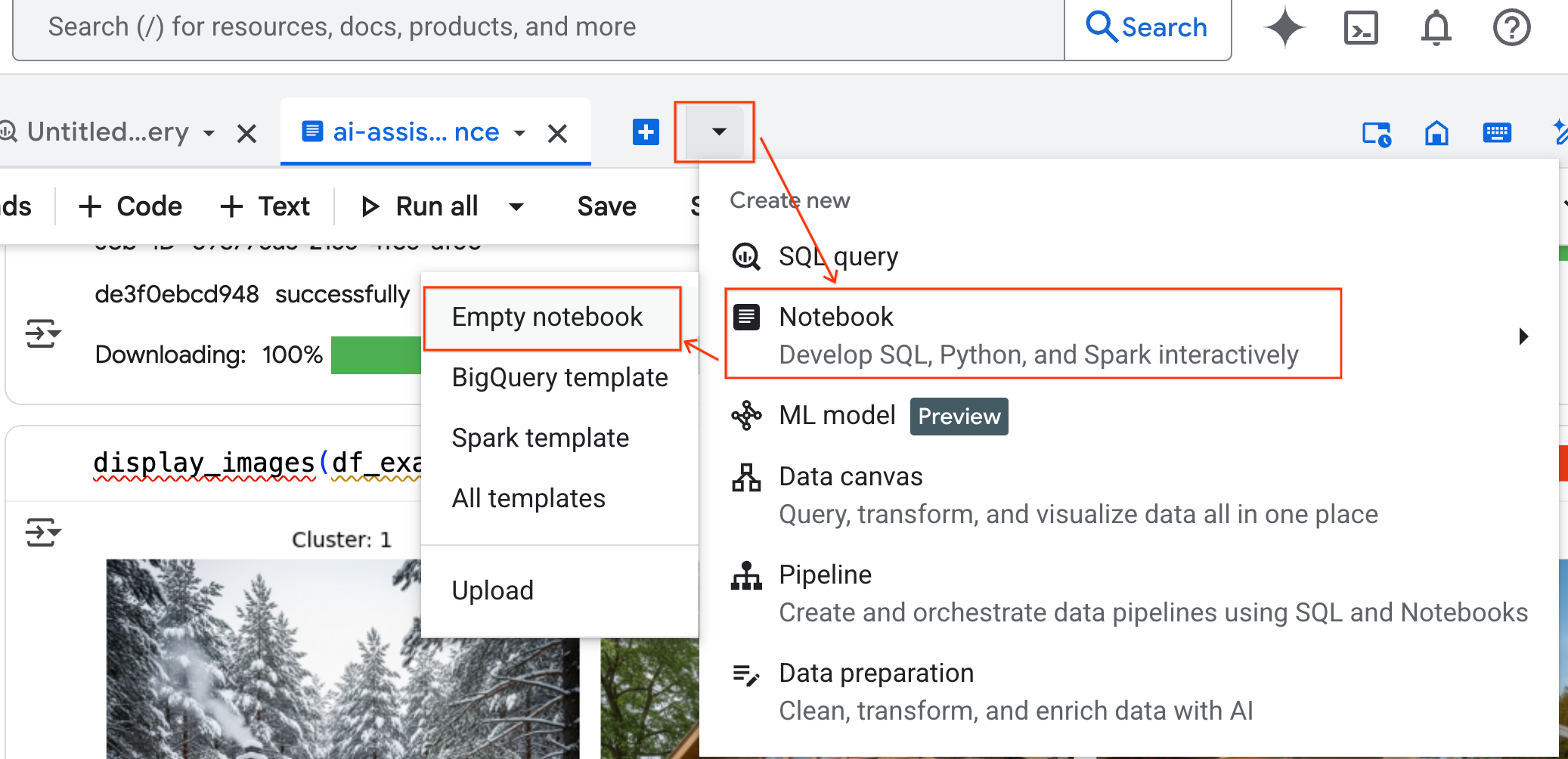
- In the BigQuery Studio pane, click the dropdown arrow button, hover over Notebook, and then select Empty Notebook. This ensures the agent's code doesn't interfere with your original lab notebook.
- The Data Science Agent chat interface opens at the bottom of the notebook. Click the Move to panel button to pin the chat to the right side.
- Begin to type
@listing_multimodalin the chat pane and Click the table. This explicitly sets thelistings_multimodaltable as context.
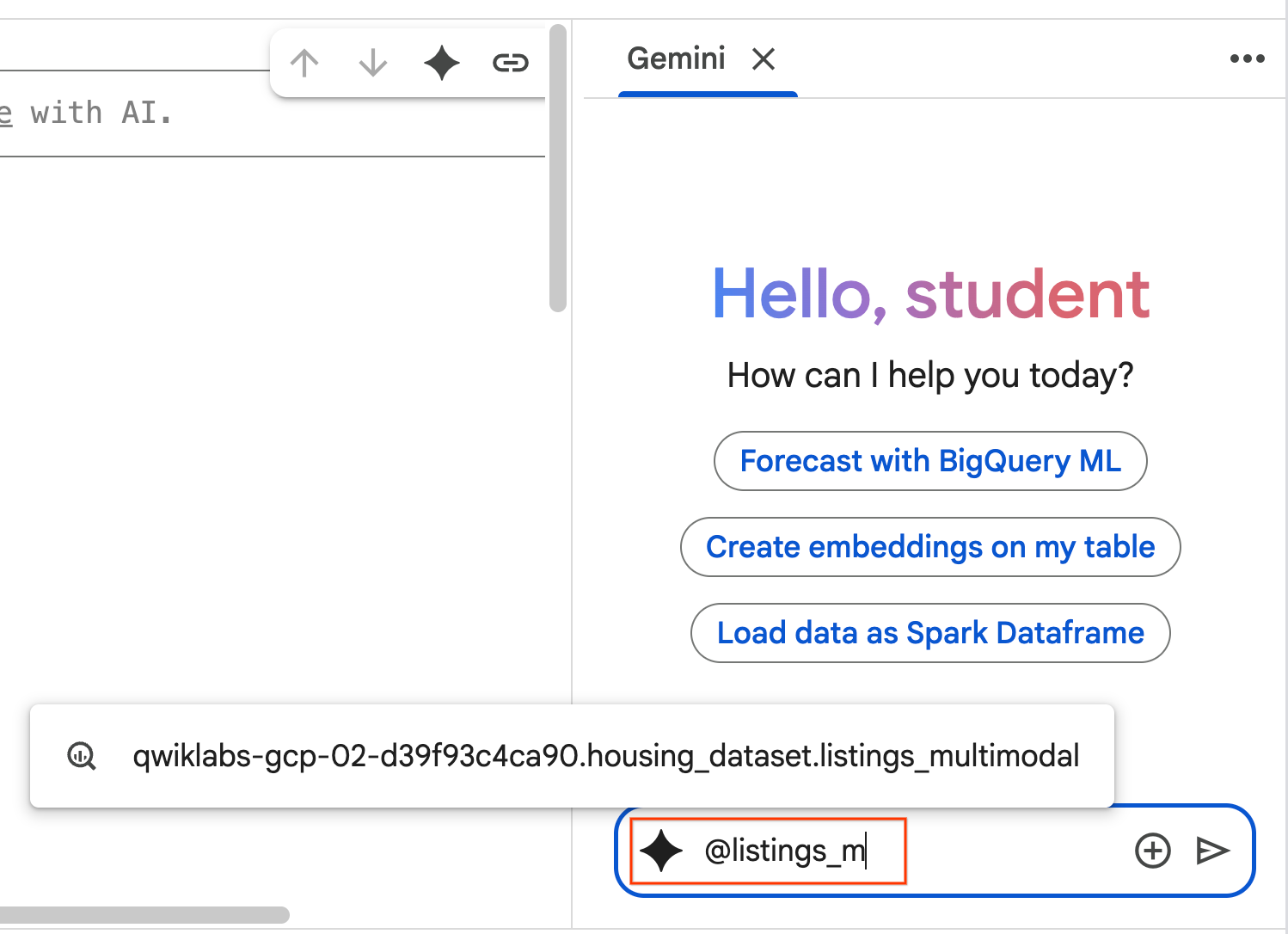
- Copy the prompt below and enter it into the Agent Chat box. Afterward, click Send to submit the prompt to the Agent.
Use the selected table to generate a k-means clustering model with 3 clusters for housing listings. Then, help me understand the characteristics of each cluster so I can market to them as a real estate professional. Use Python.
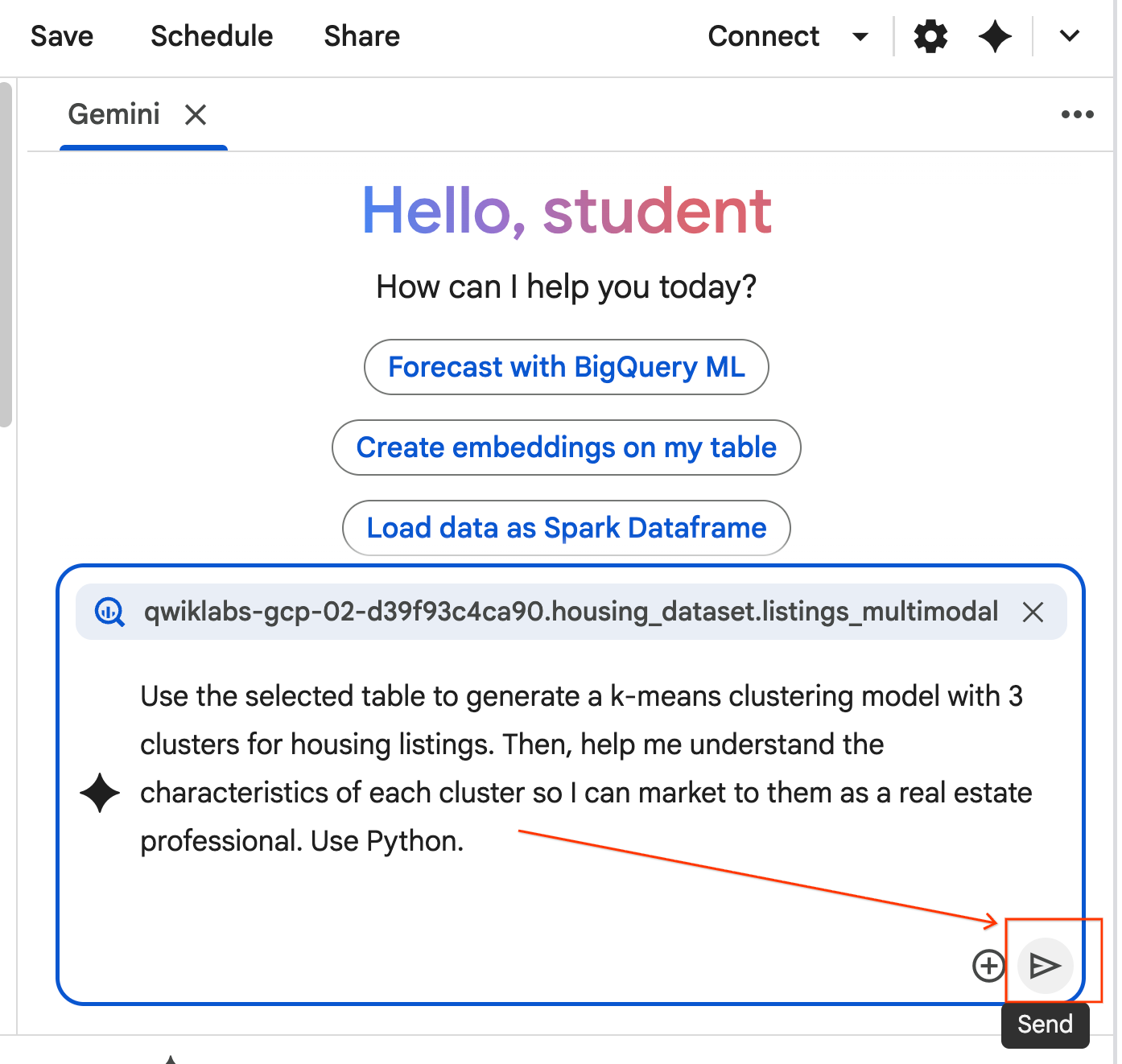
- The agent will think and formulate a plan. If you are okay with this plan, click Accept & Run. The Agent will generate Python code in one or more new cells.
- The Agent asks you to Accept & Run each block of code it generates. This keeps a human-in-the-loop. Feel free to review or edit the code and continue through each of the steps until you finish.
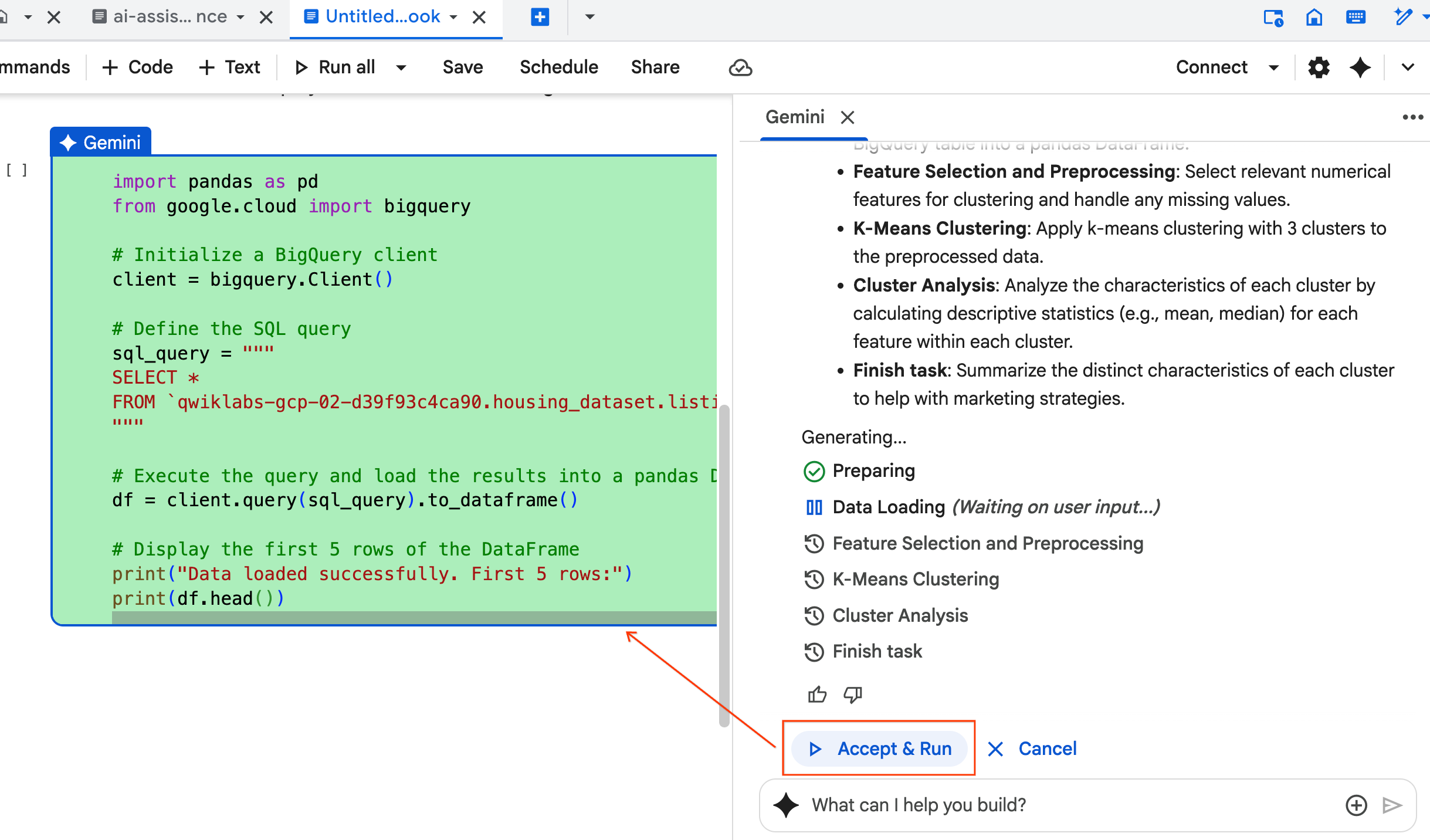
- Once you finish, simply close this new notebook tab and return to the original
ai-assisted-data-science.ipynbtab to continue with the final section of the lab.
12. Multimodal Search with Embeddings and Vector Search
In this final section, you implement multimodal search directly within BigQuery. This allows for intuitive searches, like finding houses based on a text description or finding homes that look similar to a sample picture.
The process works by first converting each house image into a numerical representation called an embedding. An embedding captures the semantic meaning of an image, allowing you to find similar items by comparing their numerical vectors.
You will use the multimodalembedding model to generate these vectors for all your listings. After creating a vector index to accelerate lookups, you then perform two types of similarity search: text-to-image (finding houses that match a description) and image-to-image (finding houses that look like a sample image).
You will complete all of this in BigQuery, using functions like ML.GENERATE_EMBEDDING to generate embeddings or VECTOR_SEARCH for similarity search.
13. Cleaning Up
To clean up all Google Cloud resources used in this project, you can delete the Google Cloud project.
Alternatively, you can delete the individual resources you created by running the following code in a new cell in your notebook:
# Delete the BigQuery tables
!bq rm --table -f housing_dataset.listings
!bq rm --table -f housing_dataset.listings_multimodal
!bq rm --table -f housing_dataset.home_embeddings
# Delete the remote model
!bq rm --model -f housing_dataset.gemini
!bq rm --model -f housing_dataset.kmeans_clustering_model
!bq rm --model -f housing_dataset.multimodal_embedding_model
# Delete the remote connection
!bq rm --connection --project_id=$PROJECT_ID --location=us ai_connection
# Delete the BigQuery dataset
!bq rm -r -f $PROJECT_ID:housing_dataset
Finally, you can delete the notebook itself:
- In the Explorer pane of BigQuery Studio, expand your project and the Notebooks node.
- Click the three vertical dots next to the
ai-assisted-data-sciencenotebook. - Select Delete.
14. Congratulations!
Congratulations for completing the Codelab!
What we've covered
- Prepare a raw dataset of real estate listings for analysis through feature engineering.
- Enrich listings by using BigQuery's AI functions to analyze house photos for key visual features.
- Build and evaluate a K-means model with BigQuery Machine Learning (BQML) to segment properties into distinct clusters.
- Automate model creation by using the Data Science Agent to generate a clustering model with Python.
- Generate embeddings for house images to power a visual search tool, finding similar homes with text or image queries.
