1. はじめに
概要
このラボでは、Model Context Protocol(MCP)サーバーを構築してデプロイします。MCP サーバーは、LLM に外部のツールやサービスへのアクセス権を付与する場合に便利です。このサービスは、複数のクライアントからアクセスできる安全な本番環境対応のサービスとして Cloud Run に構成します。次に、Gemini CLI からリモート MCP サーバーに接続します。
演習内容
ここでは、FastMCP を使用して、get_animals_by_species と get_animal_details という 2 つのツールを持つ zoo MCP サーバーを作成します。FastMCP は、MCP サーバーとクライアントを Python で迅速に構築するためのツールです。

学習内容
- MCP サーバーを Cloud Run にデプロイします。
- すべてのリクエストに認証を要求してサーバーのエンドポイントを保護し、承認されたクライアントとエージェントのみが通信できるようにします。
- Gemini CLI からセキュアな MCP サーバー エンドポイントに接続する
2. プロジェクトの設定
- Google アカウントをまだお持ちでない場合は、Google アカウントを作成する必要があります。
- 仕事用または学校用アカウントではなく、個人アカウントを使用します。職場用アカウントと学校用アカウントには、このラボに必要な API を有効にできない制限が設定されている場合があります。
- Google Cloud コンソールにログインします。
- Cloud コンソールで課金を有効にします。
- このラボを完了するのにかかる Cloud リソースの費用は 1 米ドル未満です。
- このラボの最後の手順に沿ってリソースを削除すると、それ以上の料金は発生しません。
- 新規ユーザーは、300 米ドル分の無料トライアルをご利用いただけます。
- 新しいプロジェクトを作成するか、既存のプロジェクトを再利用します。
- プロジェクトの割り当てに関するエラーが表示された場合は、既存のプロジェクトを再利用するか、既存のプロジェクトを削除して新しいプロジェクトを作成します。
3. Cloud Shell エディタを開く
- このリンクをクリックすると、Cloud Shell エディタに直接移動します。
- 本日、承認を求めるメッセージがどこかの時点で表示された場合は、[承認] をクリックして続行します。
- ターミナルが画面の下部に表示されない場合は、ターミナルを開きます。
- [表示] をクリックします。
- [ターミナル] をクリックします。
- ターミナルで、次のコマンドを使用してプロジェクトを設定します。
- 形式:
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID] - 例:
gcloud config set project lab-project-id-example - プロジェクト ID を忘れた場合:
- 次のコマンドを使用すると、すべてのプロジェクト ID を一覧表示できます。
gcloud projects list | awk '/PROJECT_ID/{print $2}'
- 次のコマンドを使用すると、すべてのプロジェクト ID を一覧表示できます。
- 形式:
- 次のようなメッセージが表示されます。
Updated property [core/project].
WARNINGが表示され、Do you want to continue (Y/n)?と表示された場合は、プロジェクト ID が正しく入力されていない可能性があります。nを押してEnterを押し、gcloud config set projectコマンドを再実行します。
4. API を有効にする
ターミナルで API を有効にします。
gcloud services enable \
run.googleapis.com \
artifactregistry.googleapis.com \
cloudbuild.googleapis.com
承認を求められたら、[承認] をクリックして続行します。
このコマンドが完了するまで数分かかる場合がありますが、最終的には次のような成功メッセージが表示されます。
Operation "operations/acf.p2-73d90d00-47ee-447a-b600" finished successfully.
5. Python プロジェクトを準備する
- デプロイ用のソースコードを保存する、
mcp-on-cloudrunという名前のフォルダを作成します。mkdir mcp-on-cloudrun && cd mcp-on-cloudrun uvツールを使用して Python プロジェクトを作成し、pyproject.tomlファイルを生成します。uv init --description "Example of deploying an MCP server on Cloud Run" --bare --python 3.13uv initコマンドは、プロジェクトのpyproject.tomlファイルを作成します。ファイルの内容を表示するには、次のコマンドを実行します。cat pyproject.toml[project] name = "mcp-on-cloudrun" version = "0.1.0" description = "Example of deploying an MCP server on Cloud Run" requires-python = ">=3.13" dependencies = []
6. zoo MCP サーバーを作成する
LLM の使用を改善するための重要なコンテキストを MCP によって提供するには、FastMCP(Model Context Protocol を使用するための標準フレームワーク)を使用して動物園 MCP サーバーを設定します。FastMCP は、Python で MCP のサーバーとクライアントを迅速に構築するためのツールです。この MCP サーバーは、架空の動物園に登場する動物に関するデータを提供します。わかりやすくするため、データをメモリに保存します。本番環境の MCP サーバーでは、データベースや API などのソースからデータを提供することをおすすめします。
- 次のコマンドを実行して、
pyproject.tomlファイルに FastMCP を依存関係として追加します。uv add fastmcp==2.12.4 --no-syncuv.lockファイルがプロジェクトに追加されます。 - MCP サーバーのソースコード用の新しい
server.pyファイルを作成して開きます。cloudshell edit ~/mcp-on-cloudrun/server.pycloudshell editコマンドを実行すると、ターミナルの上にエディタでserver.pyファイルが開きます。 server.pyファイルに次の動物園 MCP サーバーのソースコードを追加します。import asyncio import logging import os from typing import List, Dict, Any from fastmcp import FastMCP logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) logging.basicConfig(format="[%(levelname)s]: %(message)s", level=logging.INFO) mcp = FastMCP("Zoo Animal MCP Server 🦁🐧🐻") # Dictionary of animals at the zoo ZOO_ANIMALS = [ { "species": "lion", "name": "Leo", "age": 7, "enclosure": "The Big Cat Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "lion", "name": "Nala", "age": 6, "enclosure": "The Big Cat Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "lion", "name": "Simba", "age": 3, "enclosure": "The Big Cat Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "lion", "name": "King", "age": 8, "enclosure": "The Big Cat Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "penguin", "name": "Waddles", "age": 2, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "penguin", "name": "Pip", "age": 4, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "penguin", "name": "Skipper", "age": 5, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "penguin", "name": "Chilly", "age": 3, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "penguin", "name": "Pingu", "age": 6, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "penguin", "name": "Noot", "age": 1, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "elephant", "name": "Ellie", "age": 15, "enclosure": "The Pachyderm Sanctuary", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "elephant", "name": "Peanut", "age": 12, "enclosure": "The Pachyderm Sanctuary", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "elephant", "name": "Dumbo", "age": 5, "enclosure": "The Pachyderm Sanctuary", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "elephant", "name": "Trunkers", "age": 10, "enclosure": "The Pachyderm Sanctuary", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "bear", "name": "Smokey", "age": 10, "enclosure": "The Grizzly Gulch", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "bear", "name": "Grizzly", "age": 8, "enclosure": "The Grizzly Gulch", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "bear", "name": "Barnaby", "age": 6, "enclosure": "The Grizzly Gulch", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "bear", "name": "Bruin", "age": 12, "enclosure": "The Grizzly Gulch", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "giraffe", "name": "Gerald", "age": 4, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "giraffe", "name": "Longneck", "age": 5, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "giraffe", "name": "Patches", "age": 3, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "giraffe", "name": "Stretch", "age": 6, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "antelope", "name": "Speedy", "age": 2, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "antelope", "name": "Dash", "age": 3, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "antelope", "name": "Gazelle", "age": 4, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "antelope", "name": "Swift", "age": 5, "enclosure": "The Tall Grass Plains", "trail": "Savannah Heights" }, { "species": "polar bear", "name": "Snowflake", "age": 7, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "polar bear", "name": "Blizzard", "age": 5, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "polar bear", "name": "Iceberg", "age": 9, "enclosure": "The Arctic Exhibit", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "walrus", "name": "Wally", "age": 10, "enclosure": "The Walrus Cove", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "walrus", "name": "Tusker", "age": 12, "enclosure": "The Walrus Cove", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "walrus", "name": "Moby", "age": 8, "enclosure": "The Walrus Cove", "trail": "Polar Path" }, { "species": "walrus", "name": "Flippers", "age": 9, "enclosure": "The Walrus Cove", "trail": "Polar Path" } ] @mcp.tool() def get_animals_by_species(species: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]: """ Retrieves all animals of a specific species from the zoo. Can also be used to collect the base data for aggregate queries of animals of a specific species - like counting the number of penguins or finding the oldest lion. Args: species: The species of the animal (e.g., 'lion', 'penguin'). Returns: A list of dictionaries, where each dictionary represents an animal and contains details like name, age, enclosure, and trail. """ logger.info(f">>> 🛠️ Tool: 'get_animals_by_species' called for '{species}'") return [animal for animal in ZOO_ANIMALS if animal["species"].lower() == species.lower()] @mcp.tool() def get_animal_details(name: str) -> Dict[str, Any]: """ Retrieves the details of a specific animal by its name. Args: name: The name of the animal. Returns: A dictionary with the animal's details (species, name, age, enclosure, trail) or an empty dictionary if the animal is not found. """ logger.info(f">>> 🛠️ Tool: 'get_animal_details' called for '{name}'") for animal in ZOO_ANIMALS: if animal["name"].lower() == name.lower(): return animal return {} if __name__ == "__main__": port = int(os.getenv("PORT", 8080)) logger.info(f"🚀 MCP server started on port {port}") asyncio.run( mcp.run_async( transport="http", host="0.0.0.0", port=port, ) )
コードが完成しました。MCP サーバーを Cloud Run にデプロイします。
7. Cloud Run へのデプロイ
次に、ソースコードから直接 Cloud Run に MCP サーバーをデプロイします。
- Cloud Run にデプロイするための新しい
Dockerfileを作成して開きます。cloudshell edit ~/mcp-on-cloudrun/Dockerfile uvツールを使用してserver.pyファイルを実行するため、Dockerfile に次のコードを追加します。# Use the official Python image FROM python:3.13-slim # Install uv COPY --from=ghcr.io/astral-sh/uv:latest /uv /uvx /bin/ # Install the project into /app COPY . /app WORKDIR /app # Allow statements and log messages to immediately appear in the logs ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1 # Install dependencies RUN uv sync EXPOSE $PORT # Run the FastMCP server CMD ["uv", "run", "server.py"]mcp-server-saという名前のサービス アカウントを作成します。gcloud iam service-accounts create mcp-server-sa --display-name="MCP Server Service Account"gcloudコマンドを実行して、アプリケーションを Cloud Run にデプロイするcd ~/mcp-on-cloudrun gcloud run deploy zoo-mcp-server \ --service-account=mcp-server-sa@$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT.iam.gserviceaccount.com \ --no-allow-unauthenticated \ --region=europe-west1 \ --source=. \ --labels=dev-tutorial=codelab-mcp--no-allow-unauthenticatedフラグを使用します。これはセキュリティ上の理由から重要です。認証を必須にしない場合、誰でも MCP サーバーを呼び出すことができ、システムに損害を与える可能性があります。- 新しい Artifact Registry リポジトリの作成を確認します。ソースコードから Cloud Run に初めてデプロイする場合は、次のメッセージが表示されます。
Deploying from source requires an Artifact Registry Docker repository to store built containers. A repository named [cloud-run-source-deploy] in region [europe-west1] will be created. Do you want to continue (Y/n)?
Yと入力してEnterを押すと、デプロイ用の Artifact Registry リポジトリが作成されます。これは、Cloud Run サービスの MCP サーバー Docker コンテナを保存するために必要です。 - 数分後、次のようなメッセージが表示されます。
Service [zoo-mcp-server] revision [zoo-mcp-server-12345-abc] has been deployed and is serving 100 percent of traffic.
MCP サーバーをデプロイしている。これで、この機能を使用できるようになりました。
8. Gemini CLI にリモート MCP サーバーを追加する
リモート MCP サーバーのデプロイが完了したので、Google Code Assist や Gemini CLI などのさまざまなアプリケーションを使用して接続できます。このセクションでは、Gemini CLI を使用して、新しいリモート MCP サーバーへの接続を確立します。
- リモート MCP サーバーを呼び出す権限をユーザー アカウントに付与する
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \ --member=user:$(gcloud config get-value account) \ --role='roles/run.invoker' - Gemini 設定ファイルで使用するために、Google Cloud 認証情報とプロジェクト番号を、次のように環境変数に保存します。
export PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects describe $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT --format="value(projectNumber)") export ID_TOKEN=$(gcloud auth print-identity-token) .geminiフォルダがまだ作成されていない場合は作成しますmkdir -p ~/.gemini- Gemini CLI の設定ファイルを開く
cloudshell edit ~/.gemini/settings.json - Gemini CLI 設定ファイルを置き換えて Cloud Run MCP サーバーを追加する
{ "ide": { "hasSeenNudge": true }, "mcpServers": { "zoo-remote": { "httpUrl": "https://zoo-mcp-server-$PROJECT_NUMBER.europe-west1.run.app/mcp", "headers": { "Authorization": "Bearer $ID_TOKEN" } } }, "security": { "auth": { "selectedType": "cloud-shell" } } } - Cloud Shell で Gemini CLI を起動する
geminiEnterキーを押す必要がある場合があります。
- Gemini がコンテキスト内で利用可能な MCP ツールを一覧表示する
/mcp - 動物園で何かを探すよう、Gemini に依頼する
Where can I find penguins?zoo-remoteMCP サーバーを使用することを認識し、MCP の実行を許可するかどうかを尋ねます。 - 下矢印キーを使用して
Enterを押して選択します。Yes, always allow all tools from server "zoo-remote"
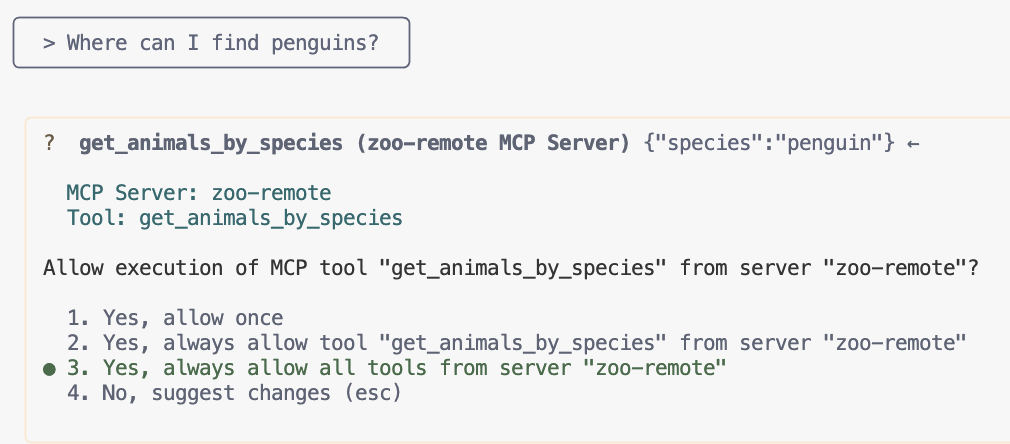
出力には正しい回答と、MCP サーバーが使用されたことを示すディスプレイ ボックスが表示されます。

これで完了です。リモート MCP サーバーを Cloud Run にデプロイし、Gemini CLI を使用してテストしました。
セッションを終了する準備ができたら、「/quit」と入力して Enter を押して Gemini CLI を終了します。
デバッグ
次のようなエラーが表示された場合:
🔍 Attempting OAuth discovery for 'zoo-remote'... ❌ 'zoo-remote' requires authentication but no OAuth configuration found Error connecting to MCP server 'zoo-remote': MCP server 'zoo-remote' requires authentication. Please configure OAuth or check server settings.
ID トークンがタイムアウトしたため、ID_TOKEN を再度設定する必要がある可能性があります。
- 「
/quit」と入力し、Enterキーを押して Gemini CLI を終了します。 - ターミナルでプロジェクトを設定する
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID] - 上記のステップ 2 から再開します
9. (省略可)サーバーログでツール呼び出しを確認する
Cloud Run MCP サーバーが呼び出されたことを確認するには、サービスログを確認します。
gcloud run services logs read zoo-mcp-server --region europe-west1 --limit=5
ツール呼び出しが行われたことを示す出力ログが表示されます。🛠️
2025-08-05 19:50:31 INFO: 169.254.169.126:39444 - "POST /mcp HTTP/1.1" 200 OK 2025-08-05 19:50:31 [INFO]: Processing request of type CallToolRequest 2025-08-05 19:50:31 [INFO]: >>> 🛠️ Tool: 'get_animals_by_species' called for 'penguin'
10. (省略可)サーバーに MCP プロンプトを追加する
MCP プロンプトを使用すると、長いプロンプトの短縮形を作成して、頻繁に実行するプロンプトのワークフローを高速化できます。
Gemini CLI は、MCP プロンプトをカスタム スラッシュ コマンドに自動的に変換します。これにより、/prompt_name と入力して MCP プロンプトを呼び出すことができます。ここで、prompt_name は MCP プロンプトの名前です。
Gemini CLI に /find animal と入力して動物園の動物をすばやく見つけられるように、MCP プロンプトを作成します。
server.pyファイルで、メインガード(if __name__ == "__main__":)の前に次のコードを追加します。@mcp.prompt() def find(animal: str) -> str: """ Find which exhibit and trail a specific animal might be located. """ return ( f"Please find the exhibit and trail information for {animal} in the zoo. " f"Respond with '[animal] can be found in the [exhibit] on the [trail].'" f"Example: Penguins can be found in The Arctic Exhibit on the Polar Path." )- アプリケーションを Cloud Run に再デプロイする
gcloud run deploy zoo-mcp-server \ --region=europe-west1 \ --source=. \ --labels=dev-tutorial=codelab-mcp - リモート MCP サーバーの ID_TOKEN を更新する
export ID_TOKEN=$(gcloud auth print-identity-token) - アプリケーションの新しいバージョンをデプロイしたら、Gemini CLI を起動します。
gemini - プロンプトで、作成した新しいカスタム コマンドを使用します。
/find --animal="lions"/find lions
Gemini CLI が get_animals_by_species ツールを呼び出し、MCP プロンプトの指示に従ってレスポンスをフォーマットしていることがわかります。
╭───────────────────────────╮
│ > /find --animal="lion" │
╰───────────────────────────╯
╭───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ ✔ get_animals_by_species (zoo-remote MCP Server) get_animals_by_species (zoo-remote MCP Server) │
│ │
│ [{"species":"lion","name":"Leo","age":7,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah │
│ Heights"},{"species":"lion","name":"Nala","age":6,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah │
│ Heights"},{"species":"lion","name":"Simba","age":3,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah │
│ Heights"},{"species":"lion","name":"King","age":8,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah Heights"}] │
╰───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
✦ Lions can be found in The Big Cat Plains on the Savannah Heights.
11. (省略可)Gemini Flash Lite を使用して回答を高速化する
Gemini CLI では、使用するモデルを選択できます。
- Gemini 2.5 Pro は、Google の最先端の思考モデルです。コード、数学、STEM の複雑な問題を推論できるほか、長いコンテキストを使用して大規模なデータセット、コードベース、ドキュメントを分析できます。
- Gemini 2.5 Flash は、価格とパフォーマンスの面で最適な Google のモデルであり、バランスの取れた機能を提供します。2.5 Flash は、大規模な処理、低レイテンシ、思考を必要とする大量のタスク、エージェントのユースケースに最適です。
- Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite は、費用対効果と高スループットを重視して最適化された、Google の最も高速な Flash モデルです。
動物園の動物を見つけるリクエストには思考や推論が必要ないため、より高速なモデルを使用して処理を高速化してみます。
Gemini CLI に /find animal と入力して動物園の動物をすばやく見つけられるように、MCP プロンプトを作成します。
- アプリケーションの新しいバージョンをデプロイしたら、Gemini CLI を起動します。
gemini --model=gemini-2.5-flash-lite - プロンプトで、作成した新しいカスタム コマンドを使用します。
/find lions
Gemini CLI が get_animals_by_species ツールを呼び出し、MCP プロンプトの指示に従ってレスポンスをフォーマットしていることがわかります。ただし、回答ははるかに速く表示されます。
╭───────────────────────────╮
│ > /find --animal="lion" │
╰───────────────────────────╯
╭───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╮
│ ✔ get_animals_by_species (zoo-remote MCP Server) get_animals_by_species (zoo-remote MCP Server) │
│ │
│ [{"species":"lion","name":"Leo","age":7,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah │
│ Heights"},{"species":"lion","name":"Nala","age":6,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah │
│ Heights"},{"species":"lion","name":"Simba","age":3,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah │
│ Heights"},{"species":"lion","name":"King","age":8,"enclosure":"The Big Cat │
│ Plains","trail":"Savannah Heights"}] │
╰───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────╯
✦ Lions can be found in The Big Cat Plains on the Savannah Heights.
デバッグ
次のようなエラーが表示された場合:
✕ Unknown command: /find --animal="lions"
/mcp の実行を試み、zoo-remote - Disconnected が出力された場合は、再デプロイするか、次のコマンドを再度実行する必要があります。
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \
--member=user:$(gcloud config get-value account) \
--role='roles/run.invoker'
export PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects describe $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT --format="value(projectNumber)")
export ID_TOKEN=$(gcloud auth print-identity-token)
12. おわりに
おめでとうございます!セキュアなリモート MCP サーバーをデプロイして接続しました。
次のラボに進む
このラボは、3 部構成のシリーズの最初のラボです。2 つ目のラボでは、ADK エージェントで作成した MCP サーバーを使用します。
ADK エージェントで Cloud Run の MCP サーバーを使用する
(省略可)クリーンアップ
次のラボに進まず、作成したものをクリーンアップする場合は、Cloud プロジェクトを削除して、追加の課金が発生しないようにします。
サービスが使用されていない場合、Cloud Run の料金は発生しませんが、コンテナ イメージを Artifact Registry に保存すると課金される場合があります。Cloud プロジェクトを削除すると、そのプロジェクト内で使用されているすべてのリソースに対する課金が停止します。
必要に応じて、プロジェクトを削除します。
gcloud projects delete $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT
不要なリソースを Cloud Shell ディスクから削除することもできます。次のことが可能です。
- Codelab プロジェクト ディレクトリを削除します。
rm -rf ~/mcp-on-cloudrun - 警告: この操作は元に戻せません。Cloud Shell のすべてのデータを削除して空き容量を増やす場合は、ホーム ディレクトリ全体を削除できます。残しておきたいものはすべて別の場所に保存されていることを確認してください。
sudo rm -rf $HOME
