1. Overview
Last Updated: 2020-07-23
What is Cloud Spanner?
Google Cloud Spanner is a globally distributed, ACID-compliant database that automatically handles replicas, sharding, and transaction processing, so you can quickly scale to meet any usage pattern and ensure success of your products.
Key Features
- Relational database, built for scale: Everything you would expect from a relational database—schemas, SQL queries, and ACID transactions—battle tested and ready to scale globally.
- 99.999% availability: Cloud Spanner delivers industry-leading 99.999% availability for multi-regional instances—10x less downtime than four nines—and provides transparent, synchronous replication across region and multi-region configurations.
- Automatic sharding: Cloud Spanner optimizes performance by automatically sharding the data based on request load and size of the data. As a result, you can spend less time worrying about how to scale your database, and instead focus on scaling your business.
What you'll learn
- Creating Cloud Spanner instances using the Google Cloud Console.
- Creating a new database in a Cloud Spanner instance.
- Using the sampledb to load and query sample data.
- Deleting the Cloud Spanner instance.
2. Setup and Requirements
Self-paced environment setup
If you don't already have a Google Account (Gmail or Google Apps), you must create one. Sign-in to Google Cloud Platform console ( console.cloud.google.com) and create a new project:

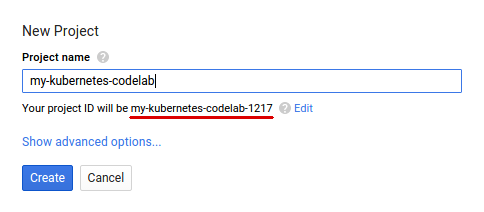
Remember the project ID, a unique name across all Google Cloud projects (the name above has already been taken and will not work for you, sorry!). It will be referred to later in this codelab as PROJECT_ID.
Next, you'll need to enable billing in the Cloud Console in order to use Google Cloud resources.
Running through this codelab shouldn't cost you more than a few dollars, but it could be more if you decide to use more resources or if you leave them running (see "cleanup" section at the end of this document).
New users of Google Cloud are eligible for a $300 free trial.
3. Open Spanner in Cloud Console
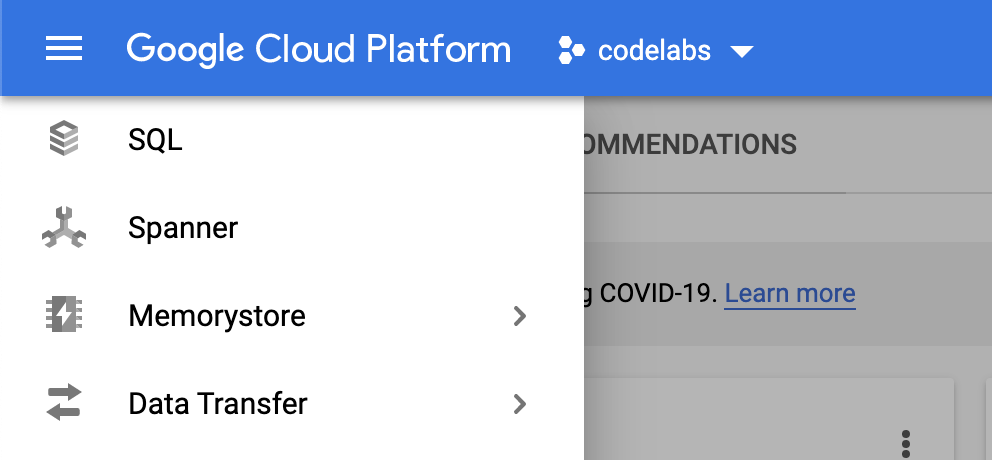
In the Google Cloud Console, click the Menu icon on the top left of the screen for the left navigation.
Scroll down and select "Spanner":
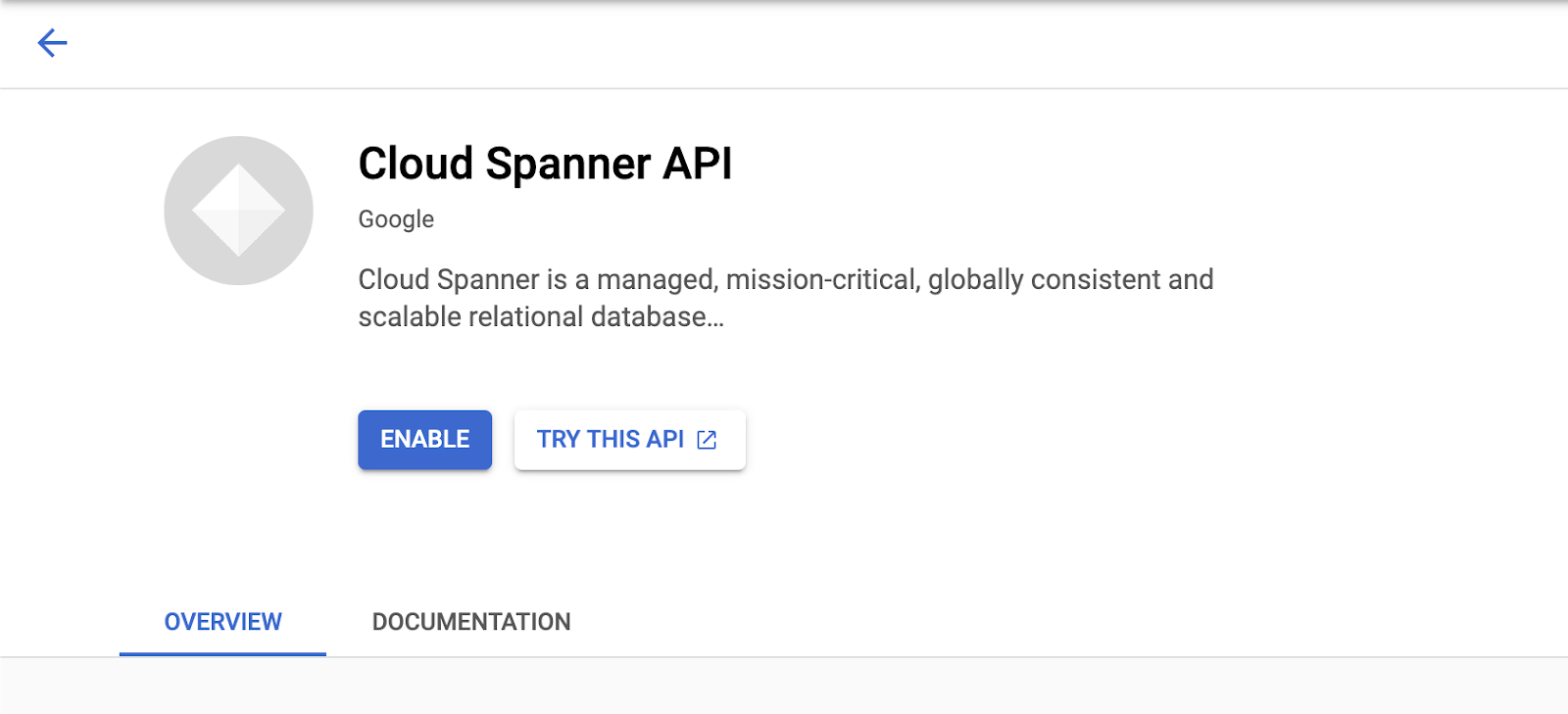
You should now see the Cloud Spanner UI, and assuming you are using a project that hasn't enabled the Cloud Spanner API yet, you will see a dialog asking you to enable it. If you have already enabled the API, you can skip this step.
Click on "Enable" to continue:
4. Create an Instance
First, you will create a Cloud Spanner instance. In the UI, click on "Create Instance" to create a new instance:
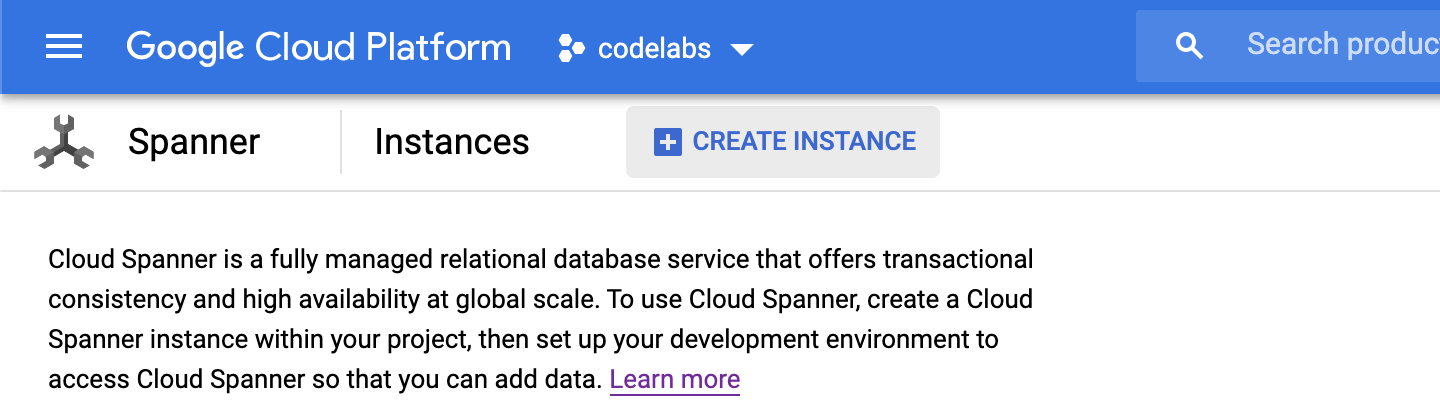
Upon clicking on the "Create Instance", you will be taken to a page to create an instance. Enter an instance name, and choose a configuration.
You can choose either a regional or multi-regional setup. Regional setups will have all the replicas in the same region, multi-regional setups will create read-replicas in multiple regions. You can click on "Compare region configurations" to compare the configuration.
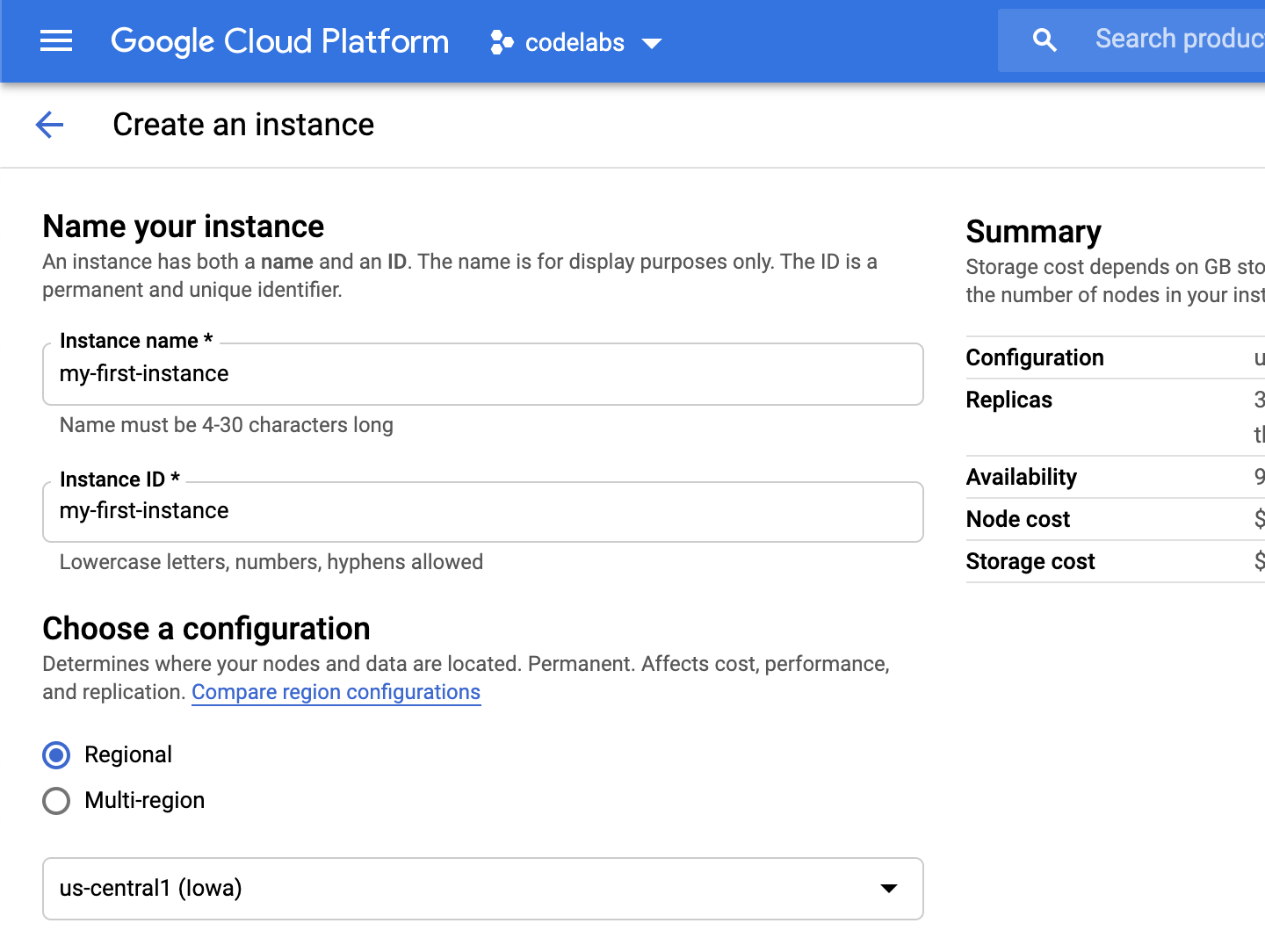
Once you choose a configuration, the summary will be displayed in the right panel:
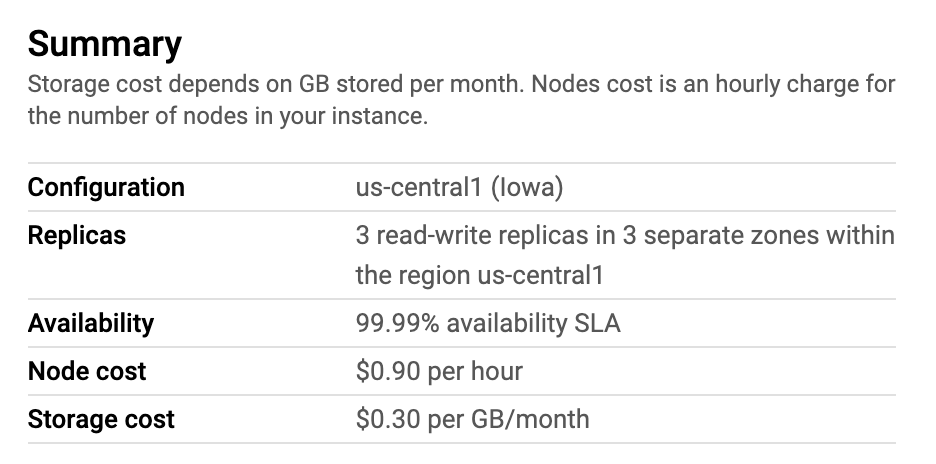
In the future, you can increase the number of nodes to give more resources to your instance, or decrease it if your instance doesn't need extra resources.
Click on "Create" to create the instance.

Your Cloud Spanner instance is now ready to use.
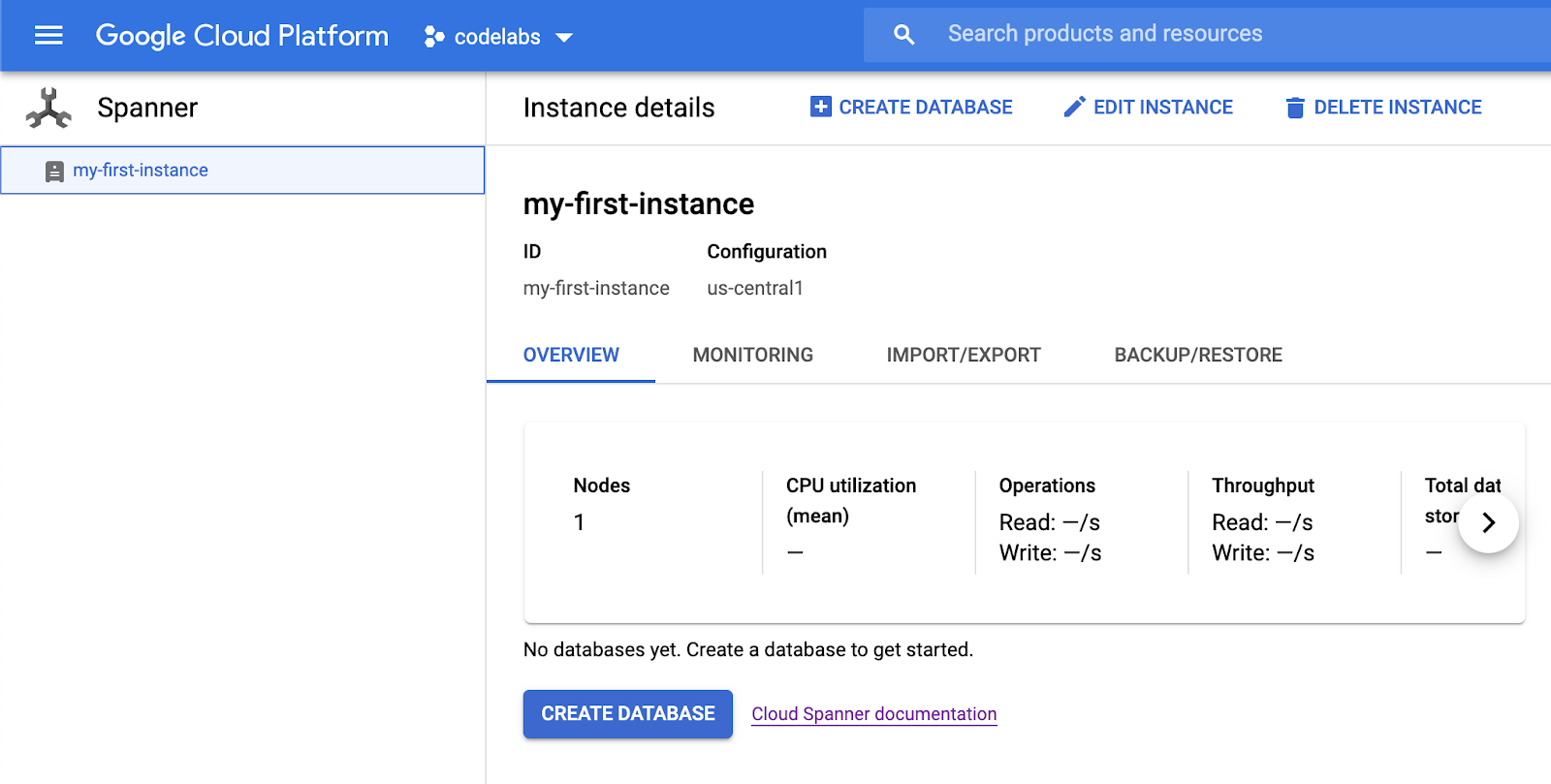
5. Create a Database
In order to create a new database, click on the "Create Database":
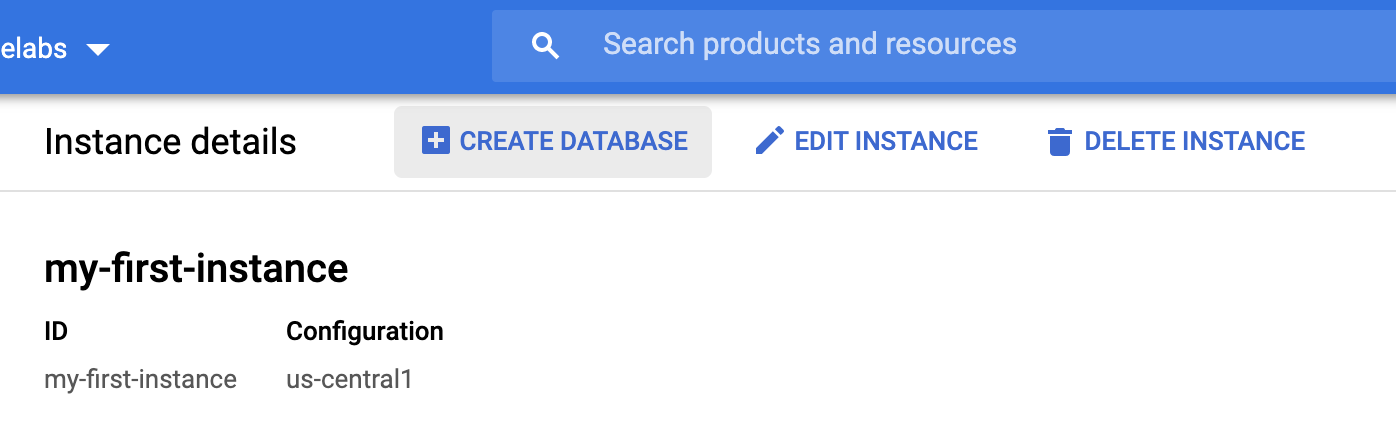
Enter a name for your new database. Optionally, you can also provide a schema at this point.
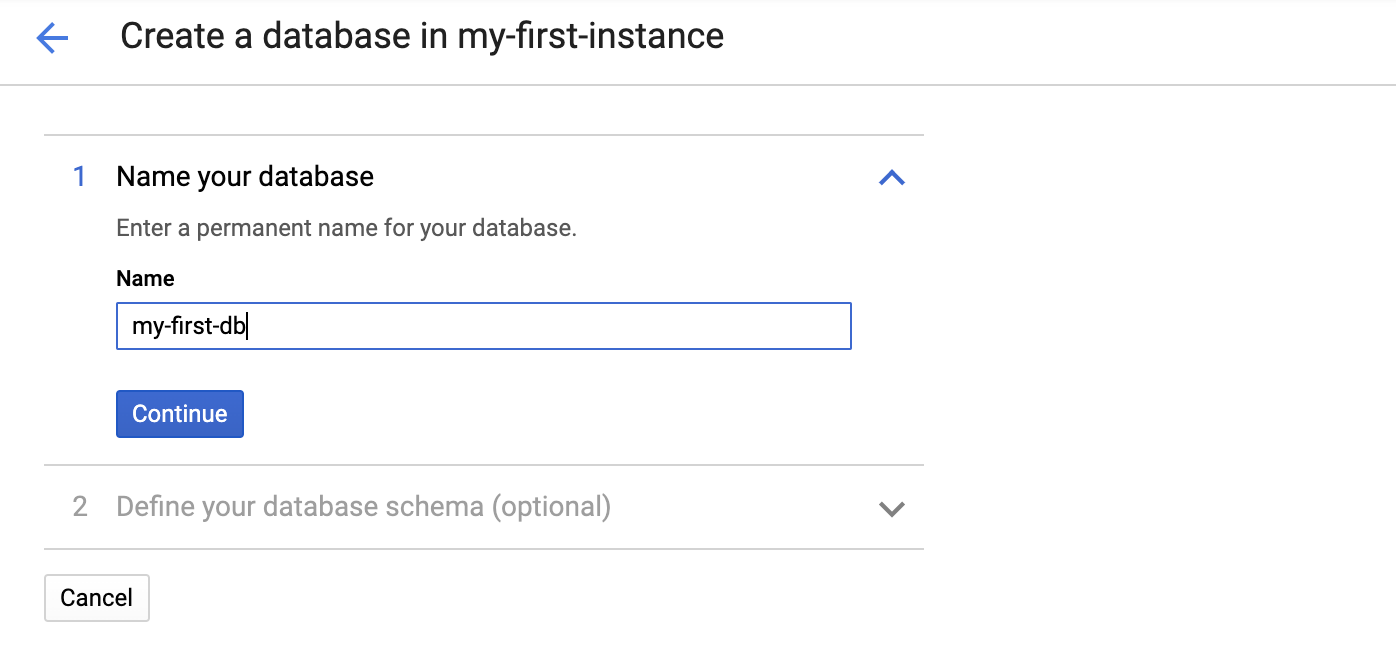
We will skip providing a schema at this step, and click on "Create" to create an empty database.
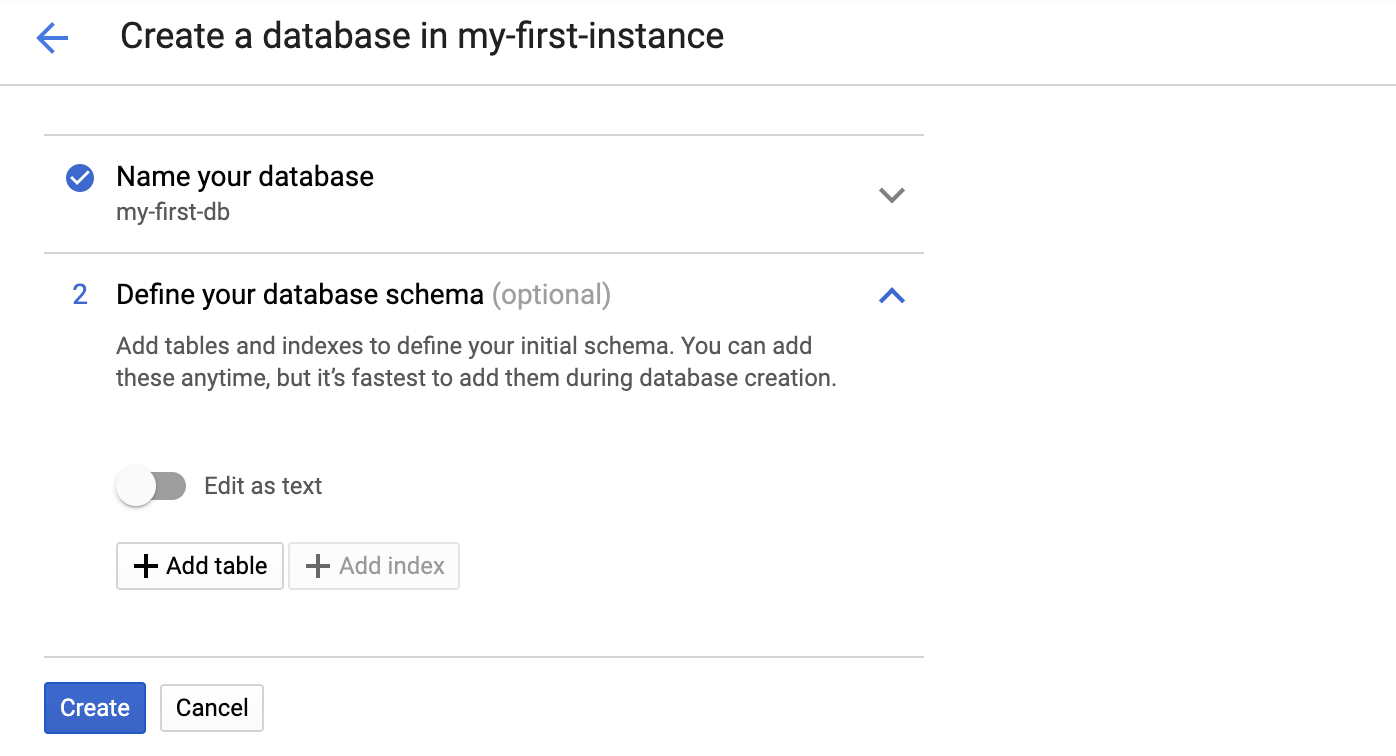
After clicking on "Create", a new database will be created:
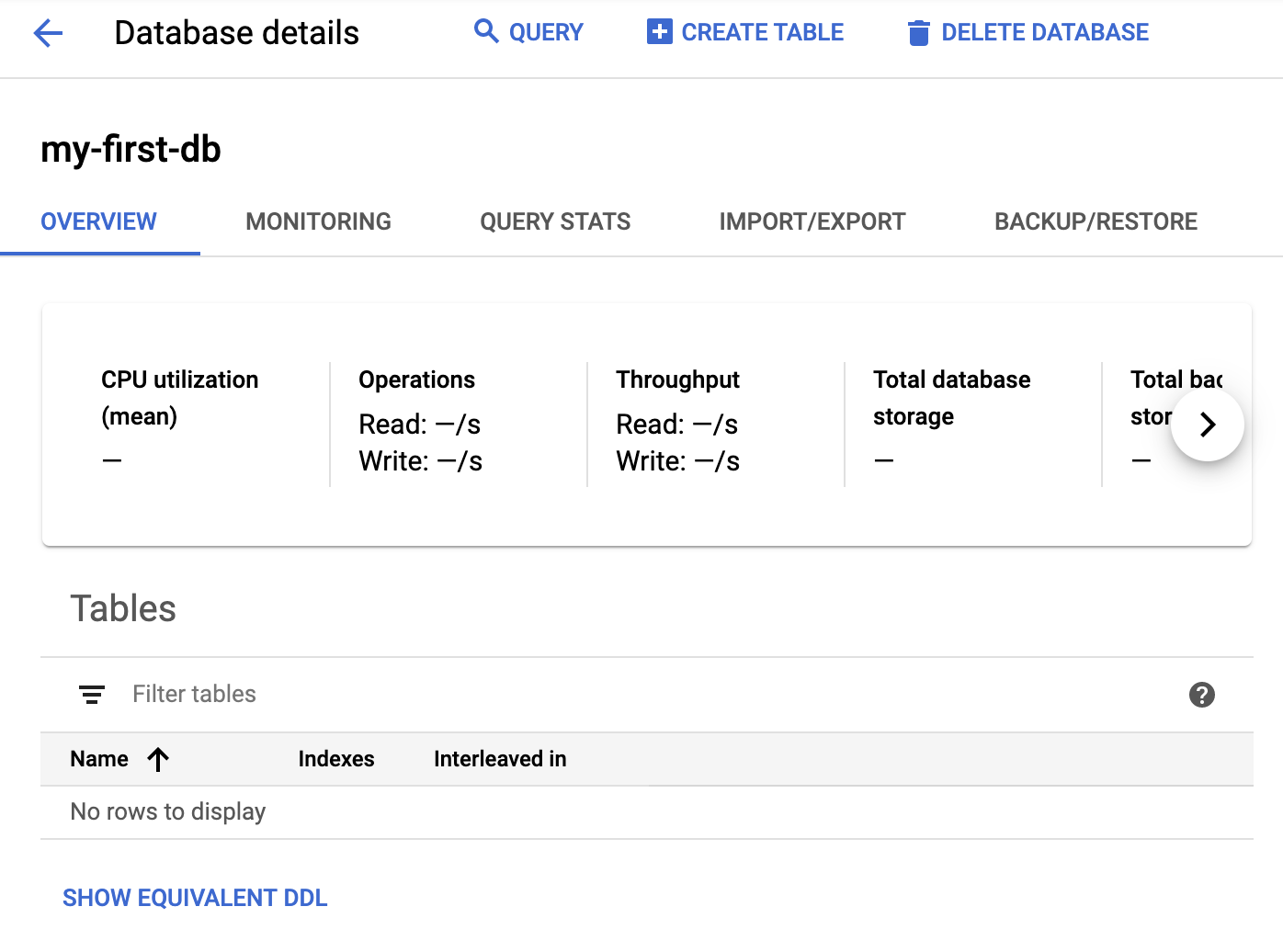
6. Load and Query Sample Data
In this codelab, we are going to load and query sample data by using the sampledb. Sampledb contains various datasets and can import data to your existing databases.
We will run the program in Google Cloud Shell. If this is the first time you have used the Google Cloud Shell for this project, you will see the Google Cloud Shell logo on the top navigation bar. Activate Cloud Shell by pressing on it.
Once activated, you will see a console at the bottom:
In the console, clone the sampledb repository and follow the instructions to install the dependencies:
$ git clone https://github.com/cloudspannerecosystem/sampledb.git
After successfully cloning the repository, navigate into the new directory, create a virtual environment and install the needed requirements:
$ cd sampledb $ virtualenv env $ source env/bin/activate $ pip install -r requirements.txt
Once the dependencies are installed, you can run sampledb to create a new database with sample data:
$ python batch_import.py my-first-instance my-sample-db
Once succeeds, you will be able to see the "my-sample-db" with two new tables (comments and stories):
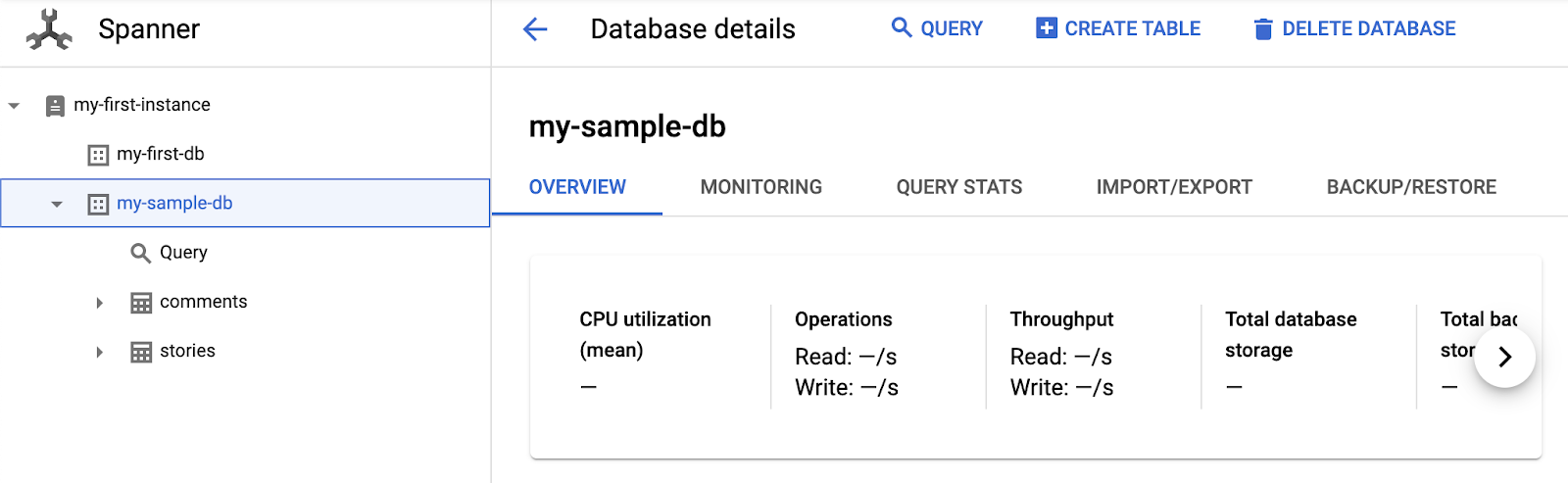
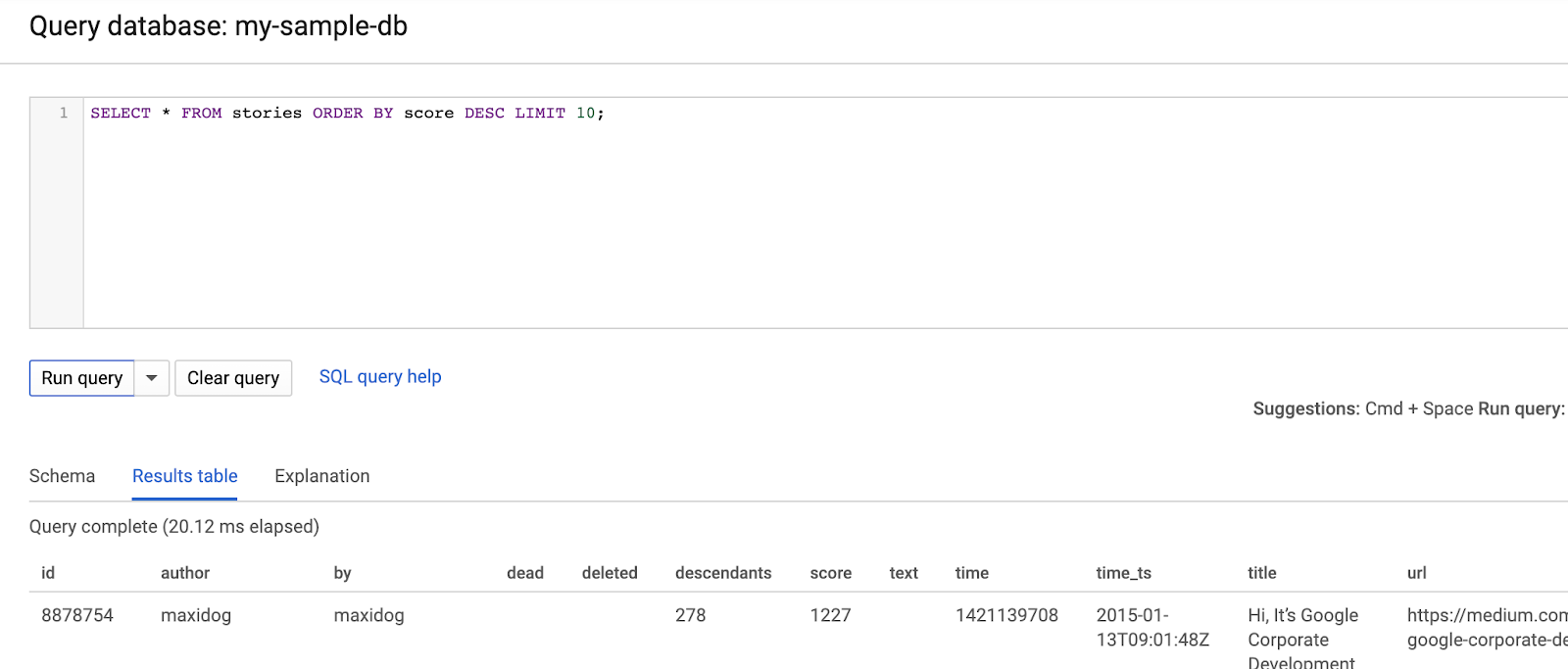
The sample dataset contains stories and comments from Hacker News. You can click on the "Query" to start querying and browsing the data:
7. Clean up
This step is optional. If you want to continue to experiment with your Cloud Spanner instance, you do not need to clean it up at this time. However, the project you are using will continue to be charged for the instance. If you have no further need for this instance, then you should delete it at this time to avoid these charges.
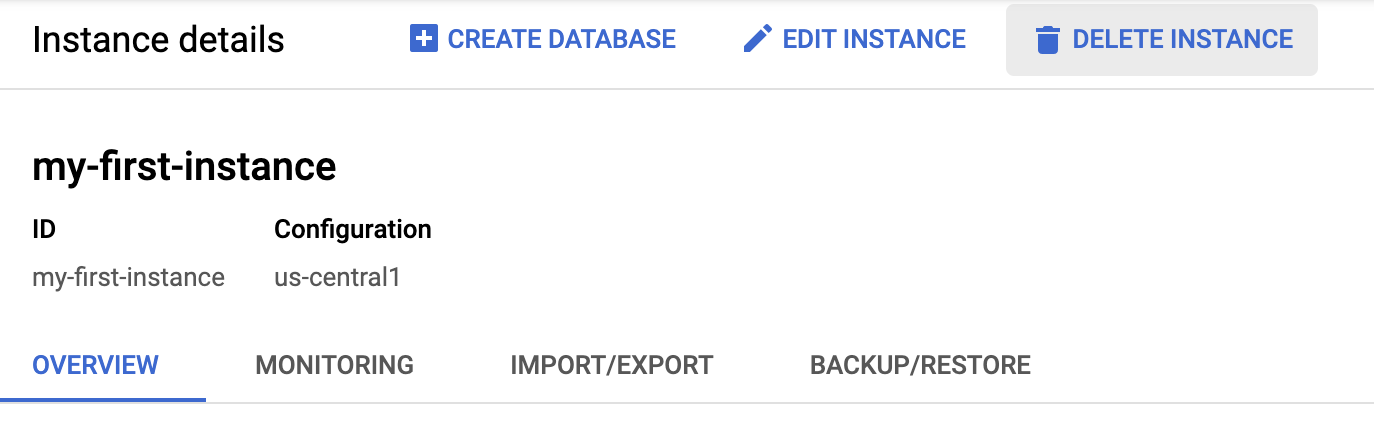
Return to the instance page by clicking on "my-first-instance" in the upper left corner:
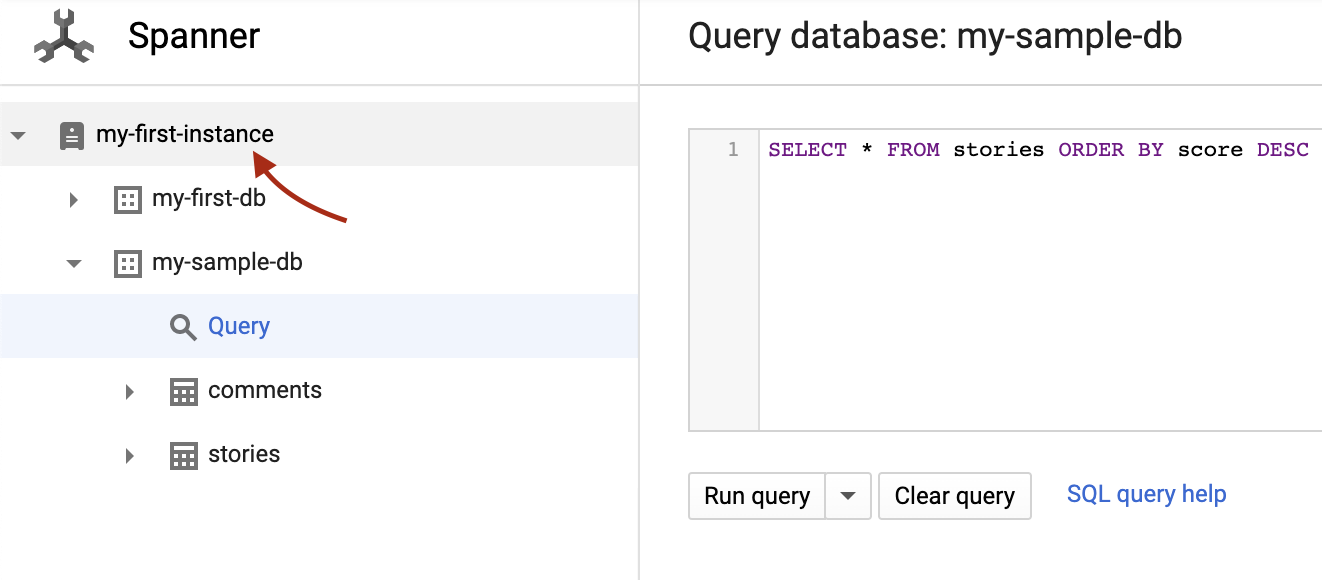
Click on "Delete" button to delete the instance:
Deleting an instance is permanent! The data from that instance cannot be recovered. To help prevent accidentally deleting the wrong instance, you must confirm the deletion by entering the instance name in a confirmation dialog:
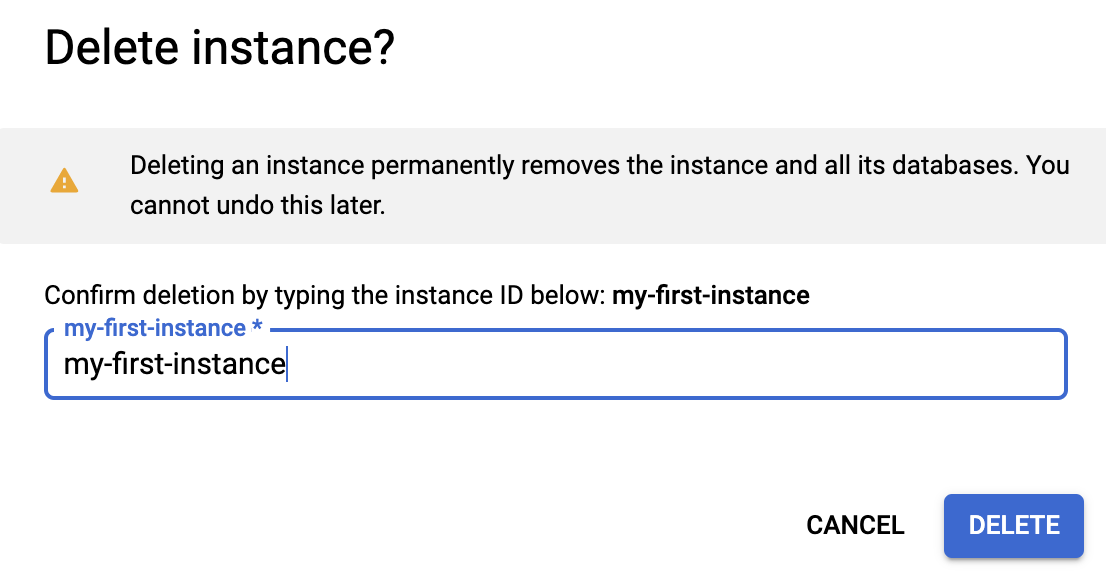
Enter your instance name and press "Delete".
8. Congratulations!
You have created a new Cloud Spanner instance, created an empty database, loaded sample data, and (optionally) deleted the Cloud Spanner instance.
What we've covered
- Creating Cloud Spanner instances via the Google Cloud Console.
- Creating a new database in a Cloud Spanner instance.
- Using the sampledb to load and query sample data.
- Deleting the Cloud Spanner instance.
Learn More
- View the Google Cloud Spanner documentation.
- Read about Google Cloud Spanner APIs and client libraries.
