1. Introduction
Overview
This lab demonstrates how to securely implement an event driven invocation of an ADK agent deployed on Cloud Run using Eventarc and Pub/Sub services. Most often an agent is called by a user or another agent directly. However, when an agent is getting integrated into existing event-based workflows, making a direct call requires changes to existing software. Triggering an agent invocation based on an event allows incorporating an agent into existing workflows without changes to the workflows.
What you'll do
In this lab you will create a ZooKeeper agentic application that has an AI agent and uses a couple of tools to provide information about animals in the imaginary zoo.

You will deploy the ZooKeeper application as a service to Cloud Run, which is a fully managed, serverless compute platform that runs stateless containers on Google's infrastructure. Then you will set up an Eventarc trigger that will invoke the service endpoint to asynchronously handle messages published to a Pub/Sub topic. You will ensure that the deployment follows best practices including using designated IAM service accounts, granting the least privileged access and minimizing a potential attack surface by exposing the ZooKeeper application's endpoint to Eventarc only. You will do it with the help of the Cloud Shell and Cloud console. You will use ADK and Cloud SDK libraries for Python. To check the behavior you will use gcloud CLI.
What you'll learn
- Deploy your ADK agent to Google Cloud Run.
- Integrate Eventarc trigger with ADK agent running on Google Cloud Run.
- Secure your deployment and integration with Eventarc using principle of the least privilege access principle with help of Google Cloud IAM.
- Publish and pull messages to and from Pub/Sub.
- Minimize public exposure of your application deployed to Google Cloud Run.
What you'll need
- Chrome web browser †
- A personal Google Account ‡
- A Google Cloud Project linked to an active billing account
Note that your account has to have IAM access to the project that lets you provision resources and configure IAM access to these resources.
† User experience using other browsers may differ from one described in the lab.
‡ Using a corporate or school account may be limited in performing some operations described in the lab.
2. Environment setup
To ensure a fully functional development environment for the lab you will use Google Cloud Shell that has all necessary tools pre-installed. Follow the instructions to set up the environment.
If you don't have a Google Account, create a Google Account.
Setup instructions
- Use your Google Account to sign-in to the Google Cloud Console.
- 👉 Open the project picker in the top navigation bar (it might say "Select a project" or show an existing project name) or click
Ctrl+Okeyboard shortcut and choose an existing project or create a new project.It will take a few seconds to create a new project. Wait until it is ready and select it using the project picker.
- 👉 Click the Cloud Shell icon at the top of the Google Cloud console. (marked with the red rectangle):

If asked, click **Authorize** in the pop-up dialog box to approve the Cloud Shell to use your account's credentials.
- 👉💻 Ensure that gcloud CLI is configured to use the project you selected (or created). Run the following command to check the configured project ID:
gcloud config get-value projectYour active configuration is: [cloudshell-19597] [PROJECT_ID]
[PROJECT_ID]will be the ID of the project that you selected or created.👉💻 If you see another value, run the following command to configure your project ID as a default project ID for gcloud CLI commands:gcloud config set project [YOUR_PROJECT_ID]gcloud config set project lab-project-id-example-123
gcloud projects list \ --format='value(projectId)' \ --sort-by='~createTime'
- 👉💻 Set up location for provisioning resources and your project's ID and number in the environment variables:
export LOCATION="us-central1" export PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project) export PROJECT_NUMBER=$(gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format="value(projectNumber)") - 👉💻 Enable Google APIs required for this lab.
gcloud services enable \ aiplatform.googleapis.com \ eventarc.googleapis.com \ run.googleapis.com \ artifactregistry.googleapis.com \ cloudbuild.googleapis.com \ pubsub.googleapis.comOperation "operations/ab12345c-6e7f-8ghi-jkl9-m0e1d23456f7" finished successfully.
3. Deploy ZooKeeper demo application
The following steps provision and configure resources including deployment of the agentic AI application.
Setting up Pub/Sub resources
You will create two Pub/Sub topics. One will be used by third-party service to send events to your agentic AI application. Another for the application to publish results of the event processing.
- 👉💻 Create a Pub/Sub topic used to trigger the agentic AI application:
gcloud pubsub topics create invoke_agent export INVOKE_TOPIC_ID=$(gcloud pubsub topics describe invoke_agent --format="value(name)") - 👉💻 Create a Pub/Sub topic where the application can post its responses:
gcloud pubsub topics create agent_responses export RESPONSE_TOPIC_ID=$(gcloud pubsub topics describe agent_responses --format="value(name)") gcloud pubsub subscriptions create agent_responses \ --topic=agent_responses
Setting up service accounts and project-level IAM policies
You will create two service accounts to limit the access scope of the Cloud Run service and the Eventarc trigger to the minimum following the least privilege access principle. The Cloud Run service requires permissions to write logs and traces, to call Gemini LLM on Google Vertex AI and to post results to a Pub/Sub topic. The Eventarc trigger's minimal access requires permissions to call the Cloud Run ZooKeeper service and access Pub/Sub for reading the posted events. These instructions guide you to grant the trigger's service account with the permissions necessary to impersonate the Pub/Sub system service. After you create the Eventarc trigger resource you will run the command that grants the roles/run.invoker role to enable the trigger's service account to call Cloud Run service.
- 👉💻 Create a service account for the Cloud Run service:
gcloud iam service-accounts create zookeeper-cloudrun-sa export ZOOKEEPER_SA="zookeeper-cloudrun-sa@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" - 👉💻 Grant the service account with permissions to write logs and traces and use Gemini models on Vertex AI:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding "${PROJECT_ID}" \ --member="serviceAccount:${ZOOKEEPER_SA}" \ --role="roles/logging.logWriter" \ --condition=None gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding "${PROJECT_ID}" \ --member="serviceAccount:${ZOOKEEPER_SA}" \ --role="roles/cloudtrace.agent" \ --condition=None gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding "${PROJECT_ID}" \ --member="serviceAccount:${ZOOKEEPER_SA}" \ --role="roles/aiplatform.user" \ --condition=None - 👉💻 Grant the service account with permissions to post messages to the ‘agent_responses' topic:
gcloud pubsub topics add-iam-policy-binding agent_responses \ --member="serviceAccount:${ZOOKEEPER_SA}" \ --role="roles/pubsub.publisher" - 👉💻 Create a service account for the Eventarc trigger:
gcloud iam service-accounts create zookeeper-trigger-sa export TRIGGER_SA="zookeeper-trigger-sa@${PROJECT_ID}.iam.gserviceaccount.com" - 👉💻 Grant the Pub/Sub system service account permissions to make authenticated push requests:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding "${TRIGGER_SA}" \ --member="serviceAccount:service-${PROJECT_NUMBER}@gcp-sa-pubsub.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --role="roles/iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator"
Deploying the ZooKeeper app to Cloud Run
You will download the code of the demo application from GitHub. And deploy the code to the Cloud Run.
- 👉💻 Download the agentic AI application:
mkdir zoo-keeper-lab && cd zoo-keeper-lab git init git remote add origin https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos git config set core.sparseCheckout true echo "ai-ml/agent-labs/adk_invoke_with_pubsub/" >> .git/info/sparse-checkout git pull origin main --depth 1 cd ai-ml/agent-labs/adk_invoke_with_pubsub/ - 👉💻 Deploy the agentic AI application to Cloud Run:
gcloud run deploy zookeeper-agent \ --region="${LOCATION}" \ --source="." \ --no-allow-unauthenticated \ --quiet \ --service-account="${ZOOKEEPER_SA}" \ --set-env-vars="REPLY_TOPIC_ID=${RESPONSE_TOPIC_ID}"
Configure Eventarc trigger
After preparing all resources (Pub/Sub topics, IAM service accounts and Cloud Run service), it is time to set up the Eventarc trigger resource. You will create the Eventarc trigger resource and will grant the permissions to call the Cloud Run service to the trigger's service account.
- 👉💻 Create Eventarc trigger:
gcloud eventarc triggers create invoke-agent \ --location="${LOCATION}" \ --destination-run-service="zookeeper-agent" \ --destination-run-path="/zookeeper" \ --destination-run-region="${LOCATION}" \ --event-filters="type=google.cloud.pubsub.topic.v1.messagePublished" \ --transport-topic="${INVOKE_TOPIC_ID}" \ --service-account="${TRIGGER_SA}" - 👉💻 Grant permissions to the trigger's service account to invoke the Cloud Run service:
gcloud run services add-iam-policy-binding zookeeper-agent \ --region="${LOCATION}" \ --member="serviceAccount:${TRIGGER_SA}" \ --role="roles/run.invoker"
4. Review how the solution works
Now review what you just deployed. The following diagram reflects all resources and how they interact with one another. You will use gcloud CLI to publish a message to the ‘invoke_agent' topic. This will simulate an event that a third-party service logs to the messaging service to invoke the agentic AI application.
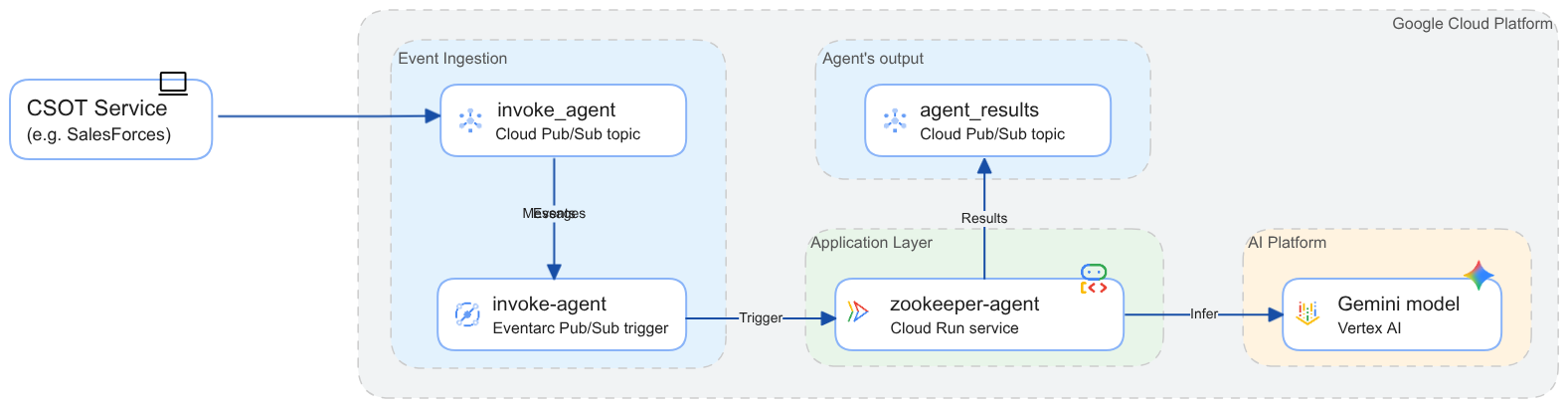
The deployment is secured following least privilege access. Cloud Run service enforces authentication (see --no-allow-unauthenticated argument in step #9 in the previous section). Only identities with the roles/run.invoker or similar permissions can call the service. And this role is granted only to the Eventarc trigger's service account. Similarly the access to the ‘invoke_agent' topic is minimized to disallow unauthorized publishing of events.. It is still possible to call the ZooKeeper agent directly bypassing the posting to the Pub/Sub topic. See section 6 to learn how to hide the endpoint of the application from public access.
Run the workflow
You will emulate an external event by publishing a question in the natural language to ZooKeeper.
👉💻 Use the following command to post a message to the Pub/Sub topic:
gcloud pubsub topics publish invoke_agent \
--message='{"user_id": "important_app", "prompt": "How many animals are in the zoo?"}'
In reality the event information will probably have a less-readable form. In order to process it, an agentic AI application will need to have detailed instructions regarding the event's format, the data and what the agent should do with the event information.
You can check that the agent received the event, processes the request and posted the response to the ‘agent_responses' topic. To read the response, you will use the ‘agent_responses' subscription (the codelab uses the same ID for both the topic and subscription for the responses).
👉💻 Use the following command to read the agent's response from the Pub/Sub subscription:
gcloud pubsub subscriptions pull agent_responses --auto-ack
The output will print a table with the message metadata and the payload containing the answer that there are 33 species in the zoo. The --auto-ack flag automatically acknowledges the message after it has been pulled, so it will not be delivered again.
How it works
See the source code of the agentic AI application by opening Cloud Shell Editor and viewing the files under ~/zoo-keeper-lab folder. You also can view the source code on GitHub.
- The main.py implements a basic FastAPI web application with a single handler that processes Eventarc events.
- The processor.py parses the event's message to retrieve the user ID and the request. Then it creates a new session in the ADK runner and calls the Zookeeper agent to process the request. The response from the agent is posted to the ‘agent_responses' Pub/Sub topic.
- The subfolder zookeeper_agent hosts source code of the ADK agent. You can run the command
adk run zookeeper_agentfrom the root folder of the application to interact with the agent using adk CLI.
How to troubleshoot
In the event any of the previous commands fails, read the error message carefully. If the deployment to Cloud Run fails the first step would be to determine at which stage of the process the failure occurred.
- If the output of the "gcloud run deploy..." command reports that the build failed, see the build logs URL in the output and open it in a separate window.
- If the output says something like "service failed to start" or similar, it means that the service deploys but then execution fails healthcheck. In this case open the Logs Explorer or see the following paragraph for gcloud CLI command. Read logs to find the root cause of the failure.
What if you posted a message to Pub/Sub but the agent does not respond or the response looks strange?
👉💻 Use the following command to read the application logs posted from the recent execution:
gcloud logging read \
'resource.type = "cloud_run_revision" AND \
resource.labels.service_name = "zookeeper-agent" AND \
resource.labels.location = "us-central1"'
The logs track the execution and report errors such as incorrect or unparsable message payload, invalid response from the gemini model, invalid environment settings and other possible issues.
5. Harden deployment security
The Cloud Run service you deployed exposes a public endpoint that can be called by anyone on the internet. While the endpoint is protected for unauthorized invocation and rigorously validates the structure of the request, it still leaves this attack vector which allows denial-of-service and denial-of-wallet attacks. Because the sole invocation path for the service in the current design is through the Eventarc trigger, the service does not need to expose its endpoint to the internet.
👉💻 Close this attack vector by restricting the calls to the service to be only from the limited collection of sources including Eventarc triggers:
gcloud run services update zookeeper-agent --region=${LOCATION} --ingress=internal
Now, if you try to call the service's URL from your local machine you will get a "404 Page not found" error.
👉💻 Use curl to send a request to the service endpoint:
URL=$(gcloud run services describe zookeeper-agent --region=${LOCATION} --format='value(status.url)')
curl -X POST -d '{}' "${URL}/zookeeper"
You will see an output similar to the following:
<html><head> <meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8"> <title>404 Page not found</title> </head> <body text=#000000 bgcolor=#ffffff> <h1>Error: Page not found</h1> <h2>The requested URL was not found on this server.</h2> <h2></h2> </body></html>
After this change, it is no longer possible to invoke the ZooKeeper directly by calling the Cloud Run service endpoint unless you make the call from the VPC in the same project, the Shared VPC network that your revision is configured to send traffic to or a host that is a part of the VPC Service Controls perimeter.
6. Summary
Congratulations! You've successfully set up an environment to asynchronously invoke your agentic AI application triggered by incoming events.
Clean up
Note that keeping the resources you provisioned may charges on your billing account. If you don't plan to use this environment for more experiments and to avoid upcoming charges it is recommended that you delete the resources that were created during this codelab.
There are two methods to do it:
Method 1: Shutting down the project
Shutting down (deleting) the project releases all resources and data of the project and unlinks the billing account. Using this method prevents further charges from being imposed for any resources or data used for this codelab. Use the following command to shut down the project:
gcloud projects delete $(gcloud config get-value project) --quiet
Method 2: Deleting resources in the project
Deleting the Cloud Run service protects against further charges for using the serverless platform. Note that this method does not completely remove all data generated during the codelab such as Cloud Build and application logs, container images, etc. Run the following command to delete the service:
gcloud run services delete zookeeper-agent --region=${LOCATION}
The Eventarc trigger definition and Pub/Sub topics don't impose management costs (see Eventarc pricing and Pub/Sub pricing for more details).
Learn more about shutting down the project.
What's next
- Learn more about the code by reviewing the demo at GitHub.
- Review the architecture orchestrating access to disparate enterprise systems
- Learn how to trigger Cloud Run using Eventarc triggers
- Learn more about ADK
