1. 欢迎
感谢您参加 Google 推出的 Istio 多云突发式扩容 Codelab。若要完成此 Codelab,您需要具备 Kubernetes、Node 和 Go 的初级实践经验。 所需条件
|
|
学习内容
- 如何在 GKE 上创建 Kubernetes 集群
- 如何使用 Helm 在 Kubernetes 集群上安装 Istio
- 如何使用 Helm 安装 Istio 多集群
- 将 Web 应用从源代码部署到 Kubernetes
- 向 Istio 编写和应用流量路由规则
- Prometheus 指标
- 在 Kubernetes 集群内构建和推送容器映像
2. 准备工作
您可以在以下任一平台上按照此 Codelab 进行操作:
- Google Cloud Shell(推荐):浏览器内 Shell,已安装工具
- 笔记本电脑(请按照以下说明操作)
从 Google Cloud Platform 开始
- 如果您没有 GCP 账号,请向讲师领取免费的用户账号卡片。
- 前往 Google Cloud 控制台,然后点击“选择项目”:
- 记下项目的“ID”,然后点击该项目以将其选中:

方法 1:使用 Google Cloud Shell(推荐)
Cloud Shell 在浏览器中提供一个命令行 Shell,其中包含您需要的已安装工具,并会自动对您进行 Google Cloud Platform 账号身份验证。(如果您不想在 Cloud Shell 中运行此练习,请跳至下一部分。)
前往 Cloud 控制台,然后点击右上角工具栏上的“激活 Cloud Shell”:
向 Cloud Shell 添加工具
或者,您也可以运行以下命令将这两个软件包都安装到 ~/.bin 并将其添加到 $PATH:
mkdir -p ~/.bin && \
cd ~/.bin && \
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ahmetb/kubectx/master/kubectx && \
chmod +x kubectx && \
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ahmetb/kubectx/master/kubens && \
chmod +x kubens && \
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-helm/helm-v2.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
tar xzf helm-v2.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
rm helm-v2.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
mv linux-amd64/helm ./helm && \
rm -r linux-amd64 && \
export PATH=${HOME}/.bin:${PATH}
以下是一些有助于更轻松地使用 Cloud Shell 的简要提示:
1. 将 Shell 分离到新窗口: |
|
2. 使用文件编辑器: 点击右上角的铅笔图标,启动浏览器内文件编辑器。这对我们将代码段复制到文件中很有用。 |
|
3. 启动新标签页:如果您需要多个终端提示。 |
|
4. 放大文本: Cloud Shell 上的默认字体大小可能太小,无法阅读。 | 在 Linux/Windows 上按 Ctrl-+,在 macOS 上按 ⌘-+。 |
方法 2:设置笔记本电脑(不推荐)
如果您更喜欢使用自己的工作站环境,而不是 Cloud Shell,请设置以下工具:
- 安装
gcloud:(已预安装在 Cloud Shell 上)。按照说明在您的平台上安装gcloud。我们将使用它创建 Kubernetes 集群。 - 安装
kubectl:(已预安装在 Cloud Shell 上)。运行以下命令进行安装:
gcloud components install kubectl
运行以下命令以对 gcloud 进行身份验证。系统会要求您使用 Google 账号登录。然后,选择预先创建的项目(如上所示)作为默认项目。(您可以跳过配置计算可用区):
gcloud init
3. 设置 GCP 项目
在您的项目中启用 GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine)、GCR (Google Container Registry) 和 GCB (Google Cloud Build) API:
gcloud services enable \ cloudapis.googleapis.com \ container.googleapis.com \ containerregistry.googleapis.com \ cloudbuild.googleapis.com
设置环境变量
在设置过程中,我们将大量使用 Google Cloud 项目,因此我们先设置一个环境变量以供快速参考
export GCLOUD_PROJECT=$(gcloud config get-value project)
我们将在本研讨会期间创建一些代码和配置文件,因此请创建一个项目目录并切换到该目录
mkdir -p src/istio-burst && \ cd src/istio-burst && \ export proj=$(pwd)
4. 创建“主”Kubernetes 集群
您可以使用 Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) 轻松创建托管式 Kubernetes 集群。
以下命令将创建一个 Kubernetes 集群:
- 命名为“primary”
- us-west1-a 区域
- 最新版本的 Kubernetes
- 4 个初始节点
export cluster=primary
export zone=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters create $cluster --zone $zone --username "admin" \
--cluster-version latest --machine-type "n1-standard-2" \
--image-type "COS" --disk-size "100" \
--scopes "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/compute",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.write",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/monitoring",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/servicecontrol",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/service.management.readonly",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/trace.append" \
--num-nodes "4" --network "default" \
--enable-cloud-logging --enable-cloud-monitoring --enable-ip-alias
(此过程可能需要大约 5 分钟。您可以在 Cloud 控制台中监控集群的创建过程。)
创建 Kubernetes 集群后,gcloud 会使用指向集群的凭据配置 kubectl。
gcloud container clusters get-credentials $cluster --zone=$zone
现在,您应该可以将 kubectl 与新集群搭配使用了。
运行以下命令,列出集群的 Kubernetes 节点(它们应显示状态“已就绪”):
kubectl get nodes
修改 Kubeconfig 名称以便于使用
我们将频繁在上下文之间切换,因此为集群设置一个简短的别名会很方便。
此命令会将您刚刚创建的 kubeconfig 条目重命名为 primary
kubectx ${cluster}=gke_${GCLOUD_PROJECT}_${zone}_${cluster}
设置权限:
如需部署 Istio,您必须是集群管理员。此命令会将与您的 Google Cloud 账号关联的电子邮件地址设置为集群管理员
kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-admin-binding \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user=$(gcloud config get-value core/account)
5. 创建“突发”集群
以下命令将创建一个 Kubernetes 集群:
- 名为“burst”
- us-west1-a 区域
- 最新版本的 Kubernetes
- 初始节点数为 1
- 自动扩缩功能已启用(最多 5 个节点)
export cluster=burst
export zone=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters create $cluster --zone $zone --username "admin" \
--cluster-version latest --machine-type "n1-standard-2" \
--image-type "COS" --disk-size "100" \
--scopes "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/compute",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.write",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/monitoring",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/servicecontrol",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/service.management.readonly",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/trace.append" \
--num-nodes "1" --enable-autoscaling --min-nodes=1 --max-nodes=5 \
--network "default" \
--enable-cloud-logging --enable-cloud-monitoring --enable-ip-alias
(此过程可能需要大约 5 分钟。您可以在 Cloud 控制台中监控集群的创建过程。)
创建 Kubernetes 集群后,gcloud 会使用指向集群的凭据配置 kubectl。
gcloud container clusters get-credentials $cluster --zone=$zone
现在,您应该可以将 kubectl 与新集群搭配使用了。
运行以下命令,列出集群的 Kubernetes 节点(它们应显示状态“已就绪”):
kubectl get nodes
修改 Kubeconfig 名称以便于使用
此命令将修改您刚刚对 burst 所做的 kubeconfig 条目
kubectx ${cluster}=gke_${GCLOUD_PROJECT}_${zone}_${cluster}
设置权限:
若要部署 Istio Remote,您必须是集群管理员。此命令会将与您的 Google Cloud 账号关联的电子邮件地址设置为集群管理员
kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-admin-binding \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user=$(gcloud config get-value core/account)
6. 应用防火墙规则
为了让这两个集群能够相互通信,我们需要创建一条防火墙规则。
运行以下命令,在 Google Cloud Platform 中创建一个防火墙规则,以允许我们的集群进行通信
function join_by { local IFS="$1"; shift; echo "$*"; }
ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS=$(gcloud container clusters list \
--filter="(name=burst OR name=primary) AND zone=$zone" \
--format='value(clusterIpv4Cidr)' | sort | uniq)
ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS=$(join_by , $(echo "${ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS}"))
ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS=$(gcloud compute instances list \
--filter="(metadata.cluster-name=burst OR metadata.cluster-name=primary) AND metadata.cluster-location=us-west1-a" \
--format='value(tags.items.[0])' | sort | uniq)
ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS=$(join_by , $(echo "${ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS}"))
gcloud compute firewall-rules create istio-multicluster-test-pods \
--allow=tcp,udp,icmp,esp,ah,sctp \
--direction=INGRESS \
--priority=900 \
--source-ranges="${ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS}" \
--target-tags="${ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS}" --quiet
我们已经设置好这两个集群,可以开始在其上部署应用和 Istio 了!
7. Istio 简介
Istio 是什么?
Istio 是一个服务网格控制平面,旨在“连接、保护、控制和观察服务”。它通过多种方式实现此目的,但主要通过将代理容器 ( Envoy) 作为 Sidecar 容器添加到每个已部署的 Kubernetes Pod 中来实现。代理容器会与通用政策和遥测中心 ( Mixer) 协同控制微服务之间的所有网络通信。
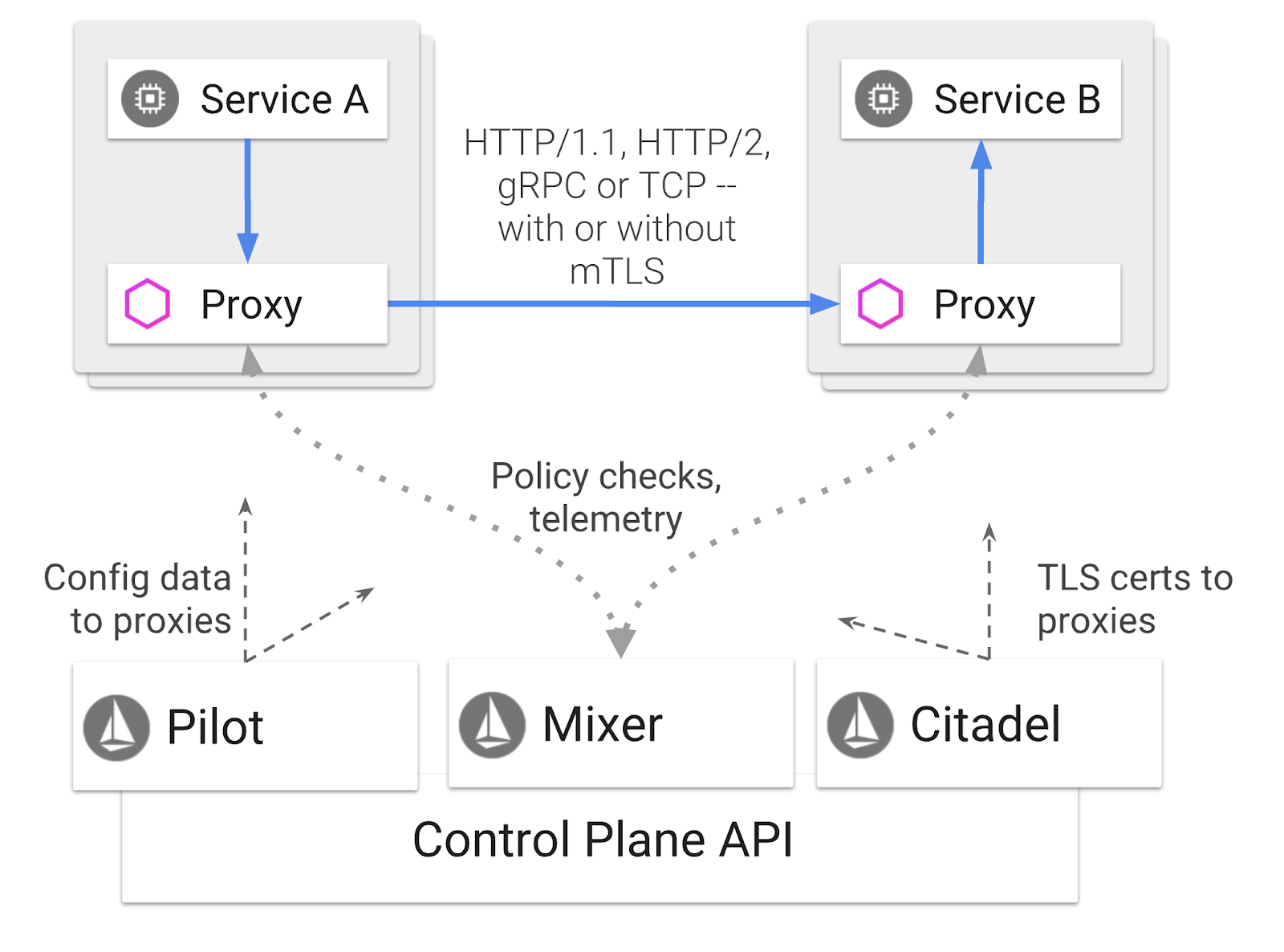
这些政策可独立于您的 Kubernetes 部署和服务应用,这意味着网络运营商无需重新部署关联的应用,即可监控网络活动、限制、重定向或重写网络政策。
Istio 支持的部分流量管理功能包括:
- 断路器
- 基于百分比的流量拆分
- 网址重写
- TLS 终结
- 健康检查
- 负载平衡
在本研讨会中,我们将重点介绍基于百分比的流量分配。
我们将使用的 Istio 术语
VirtualService
VirtualService 定义了一组定向到主机时要应用的流量路由规则。
网关
网关是在网格边缘运行的负载平衡器,用于接收传入或传出 HTTP/TCP 连接。网关可以指定端口、SNI 配置等。
DestinationRule
DestinationRule 用于定义在路由发生后对要路由到服务的流量应用的政策。它们用于指定负载均衡配置、Sidecar 中的连接池大小和离群值检测设置。
Istio 多集群
您可能已经注意到,在创建两个集群时,primary 集群有 4 个节点且不支持自动扩缩,burst 集群有 1 个节点且支持自动扩缩(最多可扩容到 5 个节点)。
之所以采用这种配置,有两个原因。
首先,我们要模拟“本地”到云端的场景。在本地环境中,您无法访问自动扩缩集群,因为您拥有固定的基础架构。
其次,运行 Istio 的最低要求是 4 个节点设置(如上所定义)。这引出了一个问题:如果 Istio 至少需要 4 个节点,那么我们的 burst 集群如何只用 1 个节点运行 Istio?原因在于,Istio Multicluster 会安装一组小得多 Istio 服务,并与主集群中的 Istio 安装进行通信,以检索政策规则并发布遥测信息。
8. 应用架构概览
组件概览
我们将使用 NodeJS 和 Redis 部署一个三层应用。
Worker
该 worker 应用使用 NodeJS 编写,会监听传入的 POST HTTP 请求,对其执行哈希运算,如果定义了名为 PREFIX 的环境变量,则会在哈希前面附加该值。计算出哈希值后,应用会将结果发送到指定 Redis 服务器上的“calculation”通道。
我们稍后将使用 PREFIX 环境变量来演示多集群功能。
备注:以下是应用使用的软件包。
body-parser:允许我们解析 http 请求cors:允许使用跨源资源共享dotenv:轻松解析环境变量express:轻松托管网站ioredis:用于与 Redis 数据库通信的客户端库morgan:提供精美的结构化日志
前端
我们的前端也是一个 NodeJS 应用,使用 express 托管网页。它会采用用户输入的频率,并以该速率向我们的 worker 应用发送请求。此应用还会订阅名为“calculation”的 Redis 通道中的消息,并在网页中显示结果。
该应用使用以下依赖项。
body-parser:允许我们解析 http 请求dotenv:轻松解析环境变量express:轻松托管网站ioredis:用于与 Redis 数据库通信的客户端库morgan:提供结构化日志request:允许发出 HTTP 请求socket.io:允许从网页到服务器进行双向通信
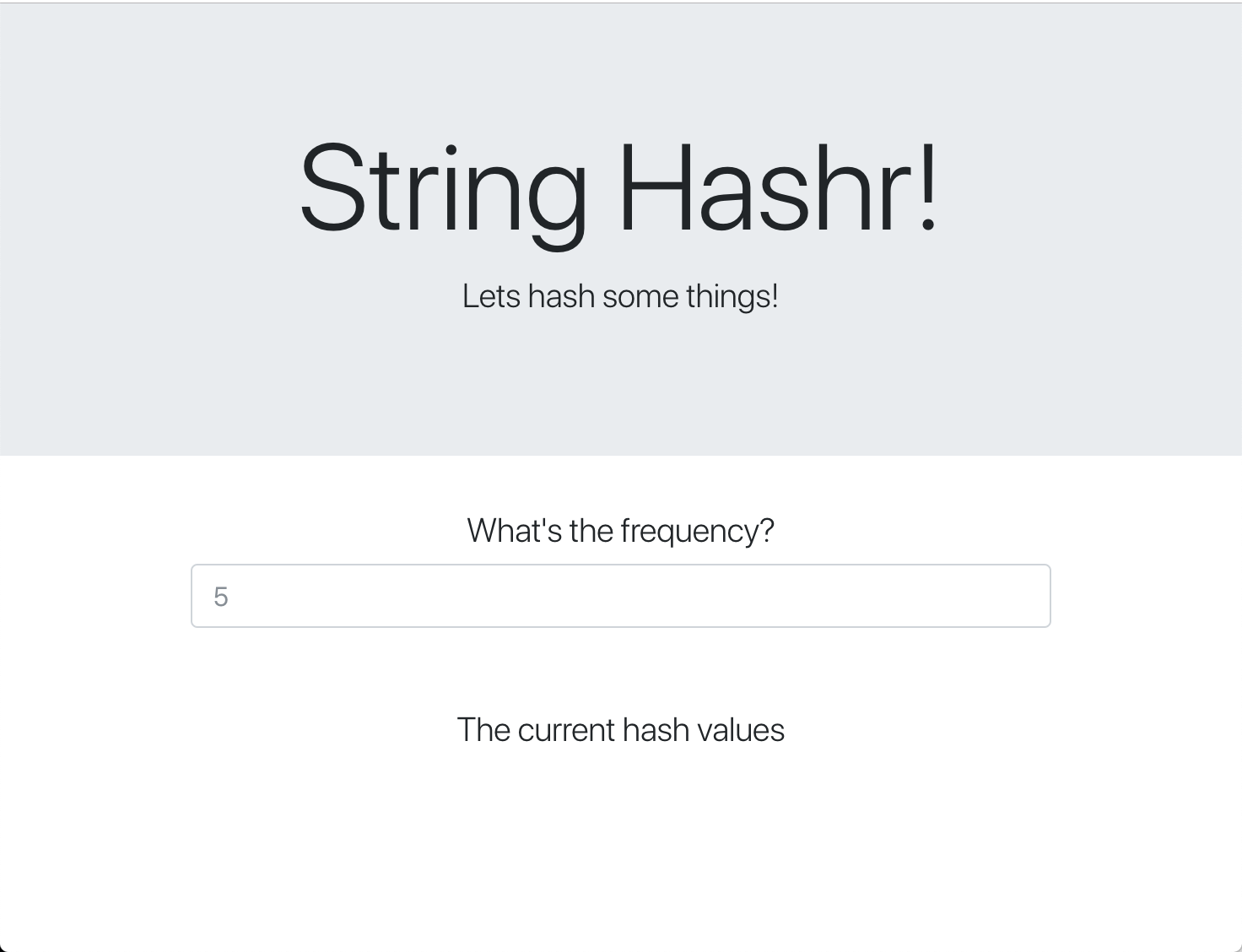
此网页使用 Bootstrap 进行样式设置,运行时如下所示
架构图
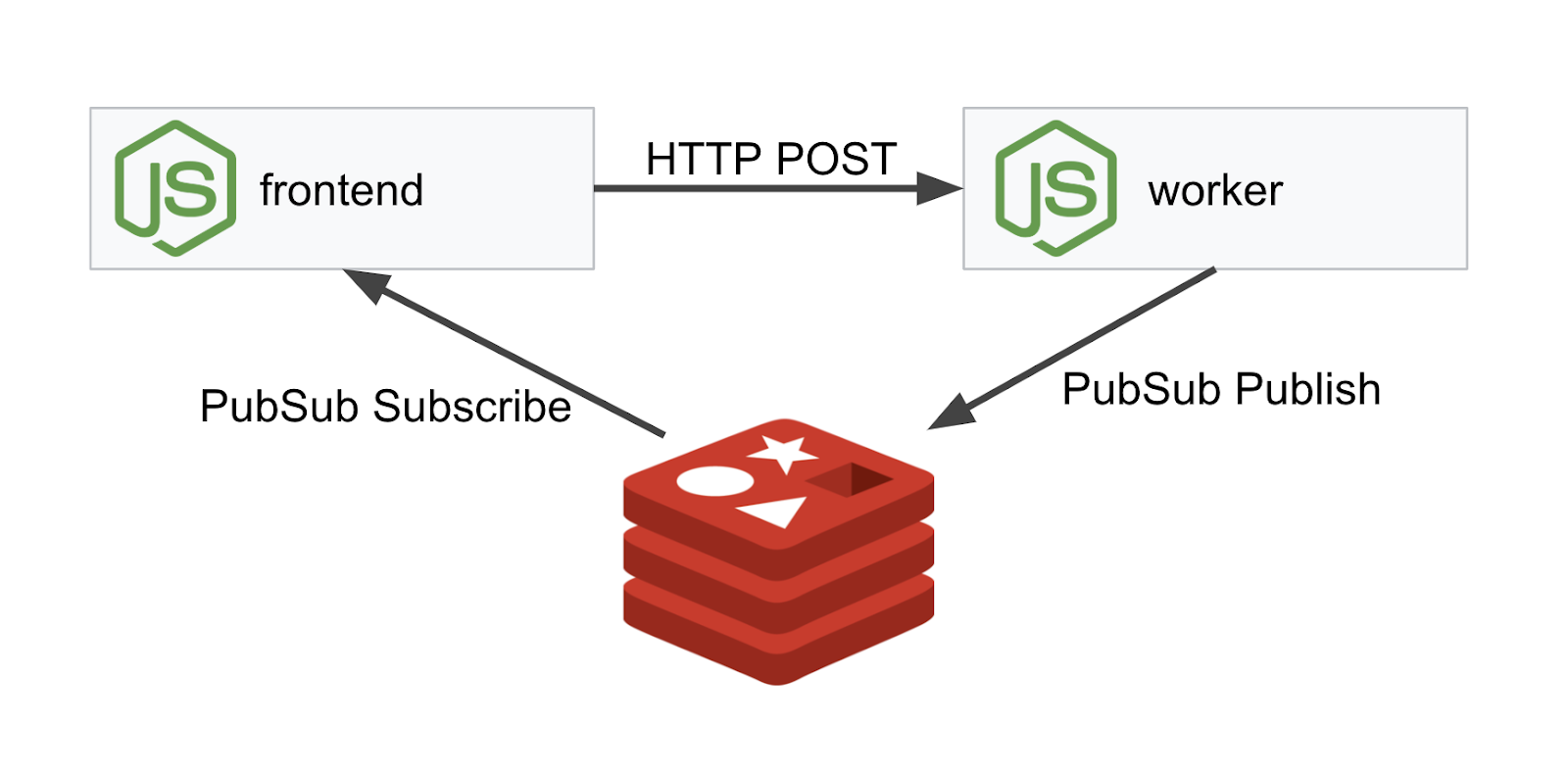
部署图
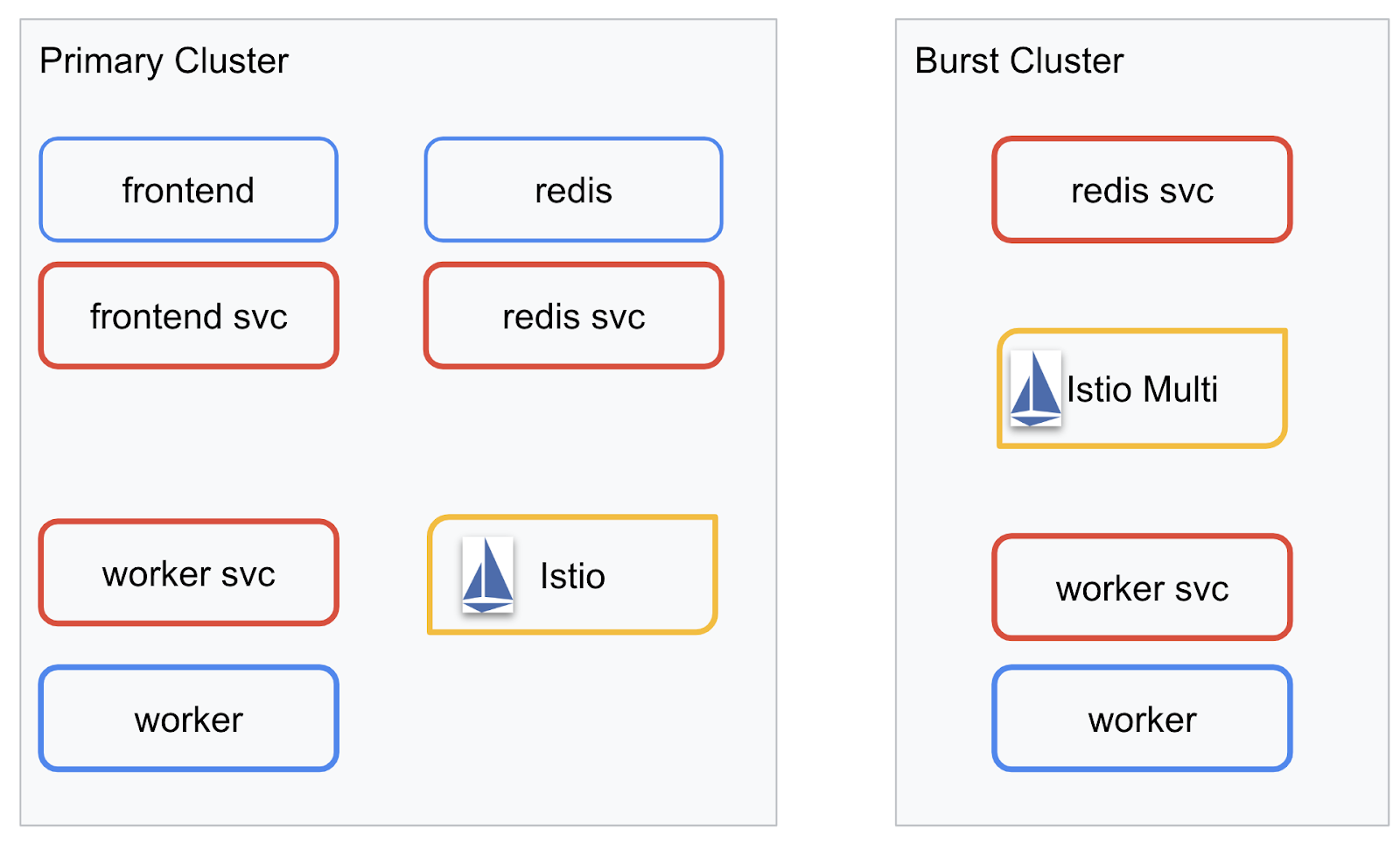
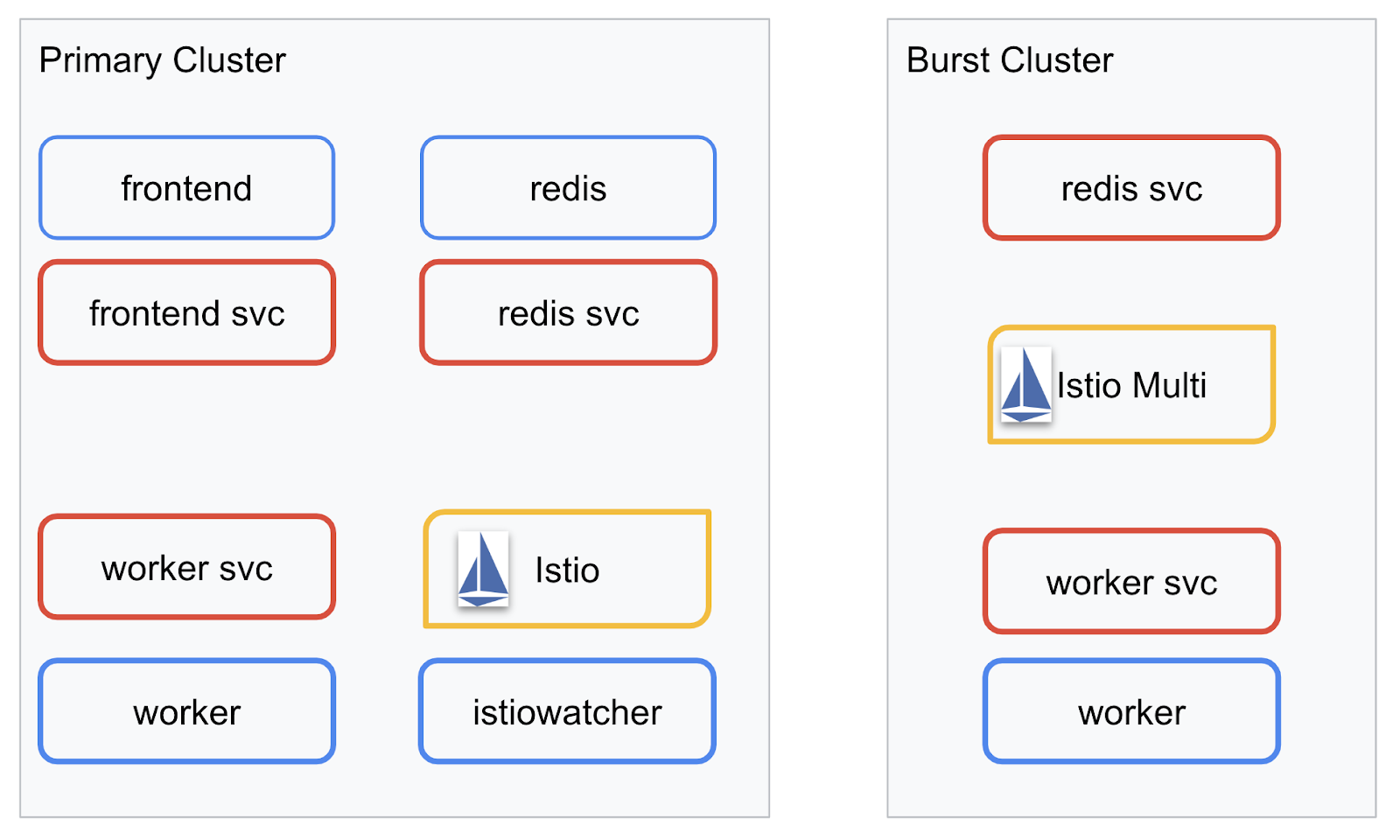
我们将在我们创建的两个集群中部署最终应用。primary 集群将部署所有组件(frontend、worker 和 Redis),但 burst 集群只会部署 worker 应用。
下图展示了这两个集群。红色框框是 Kubernetes 服务,蓝色框框是 Kubernetes 部署。黄色方框表示我们安装了 Istio。
请注意,即使集群中没有 Redis 部署,burst 集群仍部署了 Redis 服务。我们需要在集群中提供此服务,以便 Kubernetes DNS 可以解析请求,但在实际发出请求时,Istio 代理会将请求重新路由到 primary 集群中的 Redis 部署。
最终应用将在 primary 集群中运行一个名为 istiowatcher. 的额外部署。这样,当流量超出特定阈值时,我们就可以自动将流量动态重定向到 burst。
9. 创建应用部署文件
我们需要创建一组 Kubernetes 清单来部署应用
切换到项目的根目录,然后创建一个名为 kubernetes 的新文件夹
mkdir ${proj}/kubernetes && cd ${proj}/kubernetes
编写 frontend.yaml
这将创建一个 Kubernetes Deployment 和 Service 来访问我们的前端映像。
将以下内容插入 frontend.yaml 中。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: frontend-deployment
labels:
app: frontend
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: frontend
image: gcr.io/istio-burst-workshop/frontend
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/_healthz"
port: 8080
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-readiness-probe"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/"
port: 8080
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-liveness-probe"
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8080"
- name: PROCESSOR_URL
value: "http://worker-service"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: frontend-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: frontend
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
Deployment 中需要注意的重要事项
- 我们已将应用将在哪个端口上运行指定为
8080 - 我们已将 worker 的地址设置为“
http://worker-service”,并将使用 Kubernetes 内置的 DNS 功能解析生成的服务 - 我们已将
REDIS_URL的地址设置为“redis-cache-service:6379”,并将使用 Kubernetes 内置的 DNS 功能解析生成的 IP 地址。 - 我们还为容器设置了
liveness和readiness探测,以便在容器启动并运行时通知 Kubernetes。
编写 worker-service.yaml
我们将 Kubernetes 服务定义写入与部署定义不同的文件,因为我们将在多个集群中重复使用此服务,但会为每个集群编写不同的部署。
在 worker-service.yaml 中插入以下内容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: worker-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: worker
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 8081
编写 worker-primary.yaml
这将是我们要推送到主集群的 worker 部署。
将以下内容插入 worker-primary.yaml 中。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: worker-deployment
labels:
app: worker
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: worker
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: worker
cluster-type: primary-cluster
spec:
containers:
- name: worker
image: gcr.io/istio-burst-workshop/worker
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8081
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/_healthz"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-readiness-probe"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-liveness-probe"
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8081"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
请注意,在此示例中,我们遵循了相同的模式,即提供 liveness 和 readiness 探针,以及指定供应用使用的 PORT 和 REDIS_URL 环境变量。
在此部署中,需要注意的另一点是缺少 PREFIX 环境变量。这意味着,我们的计算结果将是原始哈希值(没有前缀)。
此部署的最后一个要点是 cluster-type: primary-cluster 标签。稍后,我们将在 Istio 多集群上进行流量路由时使用它
编写 redis.yaml
工作器与前端之间的通信是通过 Redis 通道进行的,因此我们需要将 Redis 应用部署到集群中。
将以下内容插入 redis.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-cache
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis-cache
spec:
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
readinessProbe:
periodSeconds: 5
tcpSocket:
port: 6379
livenessProbe:
periodSeconds: 5
tcpSocket:
port: 6379
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: redis-data
resources:
limits:
memory: 256Mi
cpu: 125m
requests:
cpu: 70m
memory: 200Mi
volumes:
- name: redis-data
emptyDir: {}
这是 Redis 应用的半标准部署。它会根据 redis:alpine 映像启动一个容器,公开适当的端口并设置合理的资源限制。
编写 redis-service.yaml
我们需要一个 Kubernetes 服务来与 Redis 应用通信
将以下内容插入 redis-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-cache-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: redis-cache
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
这会提供名为 redis-cache-service 的服务来访问我们的 Redis 部署。
10. 部署应用
现在,我们已将映像推送到 GCR 并编写了 Kubernetes 清单,接下来就可以部署应用并查看其运作方式了!
运行以下命令以部署应用
- 确保我们位于正确的集群
kubectx primary
- 部署 Redis 缓存
kubectl apply -f redis.yaml
- 部署 Redis 服务
kubectl apply -f redis-service.yaml
- 部署前端
kubectl apply -f frontend.yaml
- 部署 Worker
kubectl apply -f worker-primary.yaml
- 部署 Worker 服务
kubectl apply -f worker-service.yaml
我们已将应用部署到 GKE。恭喜!
测试
等待 pod 上线
kubectl get pods -w
当所有 Pod 都处于“Running”状态后,按 Ctrl + C
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE frontend-deployment-695d95fbf7-76sd8 1/1 Running 0 2m redis-cache-7475999bf5-nxj8x 1/1 Running 0 2m worker-deployment-5b9cf9956d-g975p 1/1 Running 0 2m
您会发现,我们并未通过 LoadBalancer 公开前端。这是因为稍后我们将通过 Istio 访问该应用。为了测试所有内容是否已启动并正常运行,我们将使用 kubectl port-forward. 运行以下命令,将本地(或 Cloud Shell)计算机上的端口 8080 转发到运行 frontend 部署的端口 8080。
kubectl port-forward \
$(kubectl get pods -l app=frontend -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') \
8080:8080
如果您在本地运行:打开网络浏览器,然后前往 http://localhost:8080
如果您是在 Cloud Shell 中运行:点击“网页预览”按钮,然后选择“在端口 8080 上预览”
您应该会看到前端!如果您在“频次”框中输入数字,则应该会看到开始显示哈希值
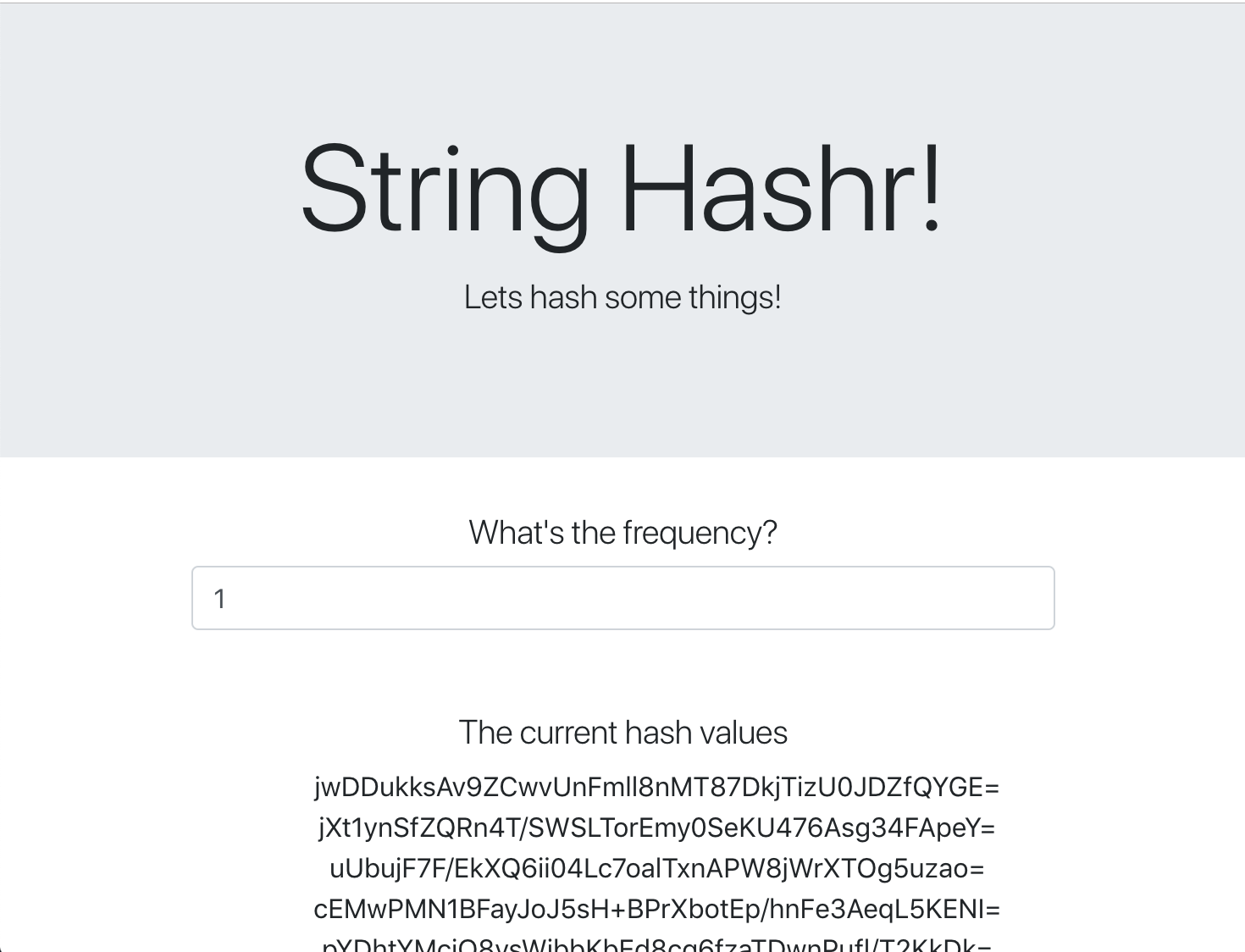
恭喜,一切顺利!
按 Ctrl+C 即可停止转发端口。
11. 清理已部署的应用
我们将对集群应用 Istio,然后重新部署应用,因此请先清理当前的应用。
运行以下命令,删除您刚刚创建的所有部署和服务
- 删除
redis-cache-service
kubectl delete -f redis-service.yaml
- 删除
redis
kubectl delete -f redis.yaml
- 删除
frontend
kubectl delete -f frontend.yaml
- 删除
worker
kubectl delete -f worker-primary.yaml
- 删除
worker-service
kubectl delete -f worker-service.yaml
12. 在主集群上安装 Istio
获取 Istio
Istio 的版本托管在 GitHub 上。以下命令将下载 1.0.0 版 Istio 并将其解压缩。
- 切换到项目的根目录
cd ${proj}
- 下载归档文件
curl -LO https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.0.0/istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
- 解压缩并移除归档文件
tar xzf istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz && rm istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
创建 Istio 模板
运行以下 Helm 命令将创建用于将 Istio 安装到集群中的模板。
helm template istio-1.0.0/install/kubernetes/helm/istio \ --name istio --namespace istio-system \ --set prometheus.enabled=true \ --set servicegraph.enabled=true > istio-primary.yaml
这会在当前目录中创建一个名为 istio-primary.yaml 的文件,其中包含部署和运行 Istio 所需的所有定义和规范。
请注意两个 --set 参数。这些更改为 Istio 系统添加了 Prometheus 和 ServiceGraph 支持。我们将在稍后的实验中使用 Prometheus 服务。
部署 Istio
如需部署 Istio,我们首先需要创建一个名为 istio-system 的命名空间,以便 Istio 部署和服务在其中运行。
kubectl create namespace istio-system
最后,应用我们使用 Helm 创建的 istio-primary.yaml 文件
kubectl apply -f istio-primary.yaml
标签默认命名空间
Istio 的工作原理是将边车代理服务注入到您的每个部署中。此操作是可选的,因此我们需要使用 istio-injection=enabled 为 default 命名空间添加标签,以便 Istio 可以自动为我们注入 sidecar。
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
恭喜!我们已成功启动集群并安装了 Istio,现在可以部署应用了!
13. 使用 Istio 流量管理功能部署应用
创建 Istio 流量管理配置文件
Istio 的运作方式与 Kubernetes 类似,因为它使用 yaml 文件进行配置。同样,我们需要创建一组文件,告知 Istio 如何公开和路由我们的流量。
创建名为 istio-manifests 的目录,并进入该目录
mkdir ${proj}/istio-manifests && cd ${proj}/istio-manifests
编写 frontend-gateway.yaml
此文件将以与 GKE LoadBalancer 类似的方式公开我们的 Kubernetes 集群,并将所有传入流量路由到我们的前端服务。
创建一个名为 frontend-gateway.yaml 的文件,并插入以下内容。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: frontend-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway # use Istio default gateway implementation
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: frontend-ingress-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- frontend-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: frontend-service
port:
number: 80
编写 redis-virtualservice.yaml
创建一个名为 redis-virtualservice.yaml 的文件,并插入以下内容
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: redis-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- redis-cache-service
gateways:
- mesh
tcp:
- route:
- destination:
host: redis-cache-service.default.svc.cluster.local
编写 worker-virtualservice.yaml
创建一个名为 worker-virtualservice.yaml 的文件,并插入以下内容
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
部署 Istio 流量管理政策
部署 Istio 政策的方式与其他 Kubernetes 资源相同,使用 kubectl apply
- 应用我们的网关
kubectl apply -f frontend-gateway.yaml
- 应用 Redis VirtualService
kubectl apply -f redis-virtualservice.yaml
- 应用我们的 Worker VirtualService
kubectl apply -f worker-virtualservice.yaml
部署应用
- 切换回
kubernetes目录
cd ${proj}/kubernetes
- 部署 Redis 缓存
kubectl apply -f redis.yaml
- 部署 Redis 服务
kubectl apply -f redis-service.yaml
- 部署前端
kubectl apply -f frontend.yaml
- 部署 Worker
kubectl apply -f worker-primary.yaml
- 部署 Worker 服务
kubectl apply -f worker-service.yaml
验证
至此,我们已在集群上重新部署了应用,并配置了 Istio 和流量管理政策。
我们来等待所有工作负载都上线
所有这些 pod 都上线后,获取我们在 frontend-ingressgateway.yaml 中配置的 IngressGateway
$ kubectl -n istio-system get svc istio-ingressgateway NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.36.3.112 35.199.158.10 80:31380/TCP,
浏览到 <EXTERNAL-IP> 地址,或使用 curl 命令访问该地址,您应该会看到前端!
$ curl 35.199.158.10
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>String Hashr</title>
<!-- Bootstrap -->
...
14. 在“突发”集群上安装 Istio
我们花了大量时间在 primary 集群上进行设置和部署,但我们还有另一个完整的集群需要部署到!
在本部分中,我们需要从两个集群中获取配置变量,因此请仔细注意每个命令指向的是哪个集群。
创建 Istio 远程清单
与将 Istio 部署到 primary 集群时类似,我们将使用 Helm 为将 Istio 远程部署到 burst 集群创建模板。不过,在此之前,我们需要获取一些有关 primary 集群的信息
收集主要集群信息
更改为 primary 集群
kubectx primary
以下命令会检索主集群中各个 Pod 的 IP 地址。Istio Remote 使用这些端口与主集群进行通信。
export PILOT_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio=pilot -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export POLICY_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio-mixer-type=policy -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export STATSD_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio=statsd-prom-bridge -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export TELEMETRY_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio-mixer-type=telemetry -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export ZIPKIN_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l app=jaeger -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.status.podIP}{end}')
创建远程模板
现在,我们将使用 helm 创建一个名为 istio-remote-burst.yaml 的文件,然后将其部署到 burst 集群。
切换到项目根目录
cd $proj
helm template istio-1.0.0/install/kubernetes/helm/istio-remote --namespace istio-system \
--name istio-remote \
--set global.remotePilotAddress=${PILOT_POD_IP} \
--set global.remotePolicyAddress=${POLICY_POD_IP} \
--set global.remoteTelemetryAddress=${TELEMETRY_POD_IP} \
--set global.proxy.envoyStatsd.enabled=true \
--set global.proxy.envoyStatsd.host=${STATSD_POD_IP} \
--set global.remoteZipkinAddress=${ZIPKIN_POD_IP} > istio-remote-burst.yaml
在突发集群上安装 Istio Remote
如需在 burst 集群上安装 Istio,我们需要遵循与在 primary 集群上安装时相同的步骤,但需要改用 istio-remote-burst.yaml 文件。
将 kubecontext 更改为 burst
kubectx burst
创建 istio-system 命名空间
kubectl create ns istio-system
应用 istio-burst.yaml
kubectl apply -f istio-remote-burst.yaml
标签默认命名空间
再次提醒一下,我们需要为 default 命名空间添加标签,以便自动注入代理。
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
恭喜!至此,我们已在 burst 集群上设置 Istio Remote。不过,此时这些集群仍无法通信。我们需要为 burst 集群生成一个 kubeconfig 文件,以便将其部署到 primary 集群以将它们关联起来。
为“突发”集群创建 kubeconfig
改用突发集群
kubectx burst
设置环境
我们需要收集有关集群的一些信息,以便为其创建 kubeconfig 文件。
- 获取集群的名称
CLUSTER_NAME=$(kubectl config view --minify=true -o "jsonpath={.clusters[].name}")
- 获取集群服务器名称
SERVER=$(kubectl config view --minify=true -o "jsonpath={.clusters[].cluster.server}")
- 获取
istio-multi服务账号证书颁发机构的 Secret 名称
SECRET_NAME=$(kubectl get sa istio-multi -n istio-system -o jsonpath='{.secrets[].name}')
- 获取存储在先前 Secret 中的证书颁发机构数据
CA_DATA=$(kubectl get secret ${SECRET_NAME} -n istio-system -o "jsonpath={.data['ca\.crt']}")
- 获取存储在上一个 Secret 中的令牌
TOKEN=$(kubectl get secret ${SECRET_NAME} -n istio-system -o "jsonpath={.data['token']}" | base64 --decode)
创建 kubeconfig 文件
设置所有这些环境变量后,我们需要创建 kubeconfig 文件
cat <<EOF > burst-kubeconfig
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: ${CA_DATA}
server: ${SERVER}
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
contexts:
- context:
cluster: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
user: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
current-context: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
user:
token: ${TOKEN}
EOF
这将在当前目录中创建一个名为 burst-kubeconfig 的新文件,primary 集群可以使用该文件对 burst 集群进行身份验证和管理。
改回主集群
kubectx primary
通过创建 Secret 并为其添加标签,为“burst”应用 kubeconfig
kubectl create secret generic burst-kubeconfig --from-file burst-kubeconfig -n istio-system
为 Secret 添加标签,以便 Istio 知道将其用于多集群身份验证
kubectl label secret burst-kubeconfig istio/multiCluster=true -n istio-system
恭喜!我们已对这两个集群进行了身份验证,并通过 Istio 多集群实现了它们之间的通信。我们来跨集群部署应用
15. 部署跨集群应用
创建部署
切换到 kubernetes 目录
cd ${proj}/kubernetes
为“burst”集群创建工作器部署:worker-burst.yaml
创建一个名为 worker-burst.yaml 的文件,并将以下内容插入其中:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: worker-deployment
labels:
app: worker
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: worker
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: worker
cluster-type: burst-cluster
spec:
containers:
- name: worker
image: gcr.io/istio-burst-workshop/worker
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8081
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/_healthz"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-readiness-probe"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-liveness-probe"
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8081"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
- name: PREFIX
value: "bursty-"
请注意,这与我们之前创建的 worker-primary.yaml 几乎完全相同。这两者之间有两个主要区别。
第一个主要区别是,我们添加了值为“bursty-”的 PREFIX 环境变量
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8081"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
- name: PREFIX
value: "bursty-"
这意味着,burst 集群中的 worker 会在发送的所有哈希的前面添加“bursty-”,我们可以通过此方法了解我们的应用是否真正跨集群。
第二个主要区别是,我们将此部署的 cluster-type 标签从 primary-cluster 更改为 burst-cluster
labels:
app: worker
cluster-type: burst-cluster
我们稍后在更新 VirtualService 时会使用此标签。
修改 Istio 服务
目前,我们的 Istio 服务无法同时利用这两项部署。100% 的流量都被路由到“主”集群。我们来修改一下。
切换到 istio-manifests 目录
cd ${proj}/istio-manifests
修改 worker-virtualservice.yaml 以添加 DestinationRule
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 50
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 50
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: worker-destination-rule
spec:
host: worker-service
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: RANDOM
subsets:
- name: primary
labels:
cluster-type: primary-cluster
- name: burst
labels:
cluster-type: burst-cluster
您可以看到,我们已向 VirtualService 添加了第二个目的地。它仍然引用同一主机 (worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local)),但 50% 的流量会路由到 primary 子集,另外 50% 的流量会路由到 burst 子集。
我们将 primary 子集定义为具有标签 cluster-type: primary-cluster 的部署,将 burst 子集定义为具有标签 cluster-type: burst-cluster 的部署。
这样,流量就会在两个集群之间按 50/50 的比例有效拆分。
部署到集群
将 redis-service.yaml 部署到突发集群
更改为 burst kubeconfig
kubectx burst
切换到项目根目录
cd ${proj}
然后部署
将 redis-service.yaml 部署到突发集群
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/redis-service.yaml
将 worker-burst.yaml 部署到突发集群
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/worker-burst.yaml
将 worker-service.yaml 部署到突发集群
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/worker-service.yaml
应用 Istio VirtualService
更改为 primary kubeconfig
kubectx primary
然后部署
kubectl apply -f istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml
验证是否正常运行
如需验证其是否正常运行,请浏览您的 Istio Ingress 点,并注意大约 50% 的哈希前缀为“burst-”。
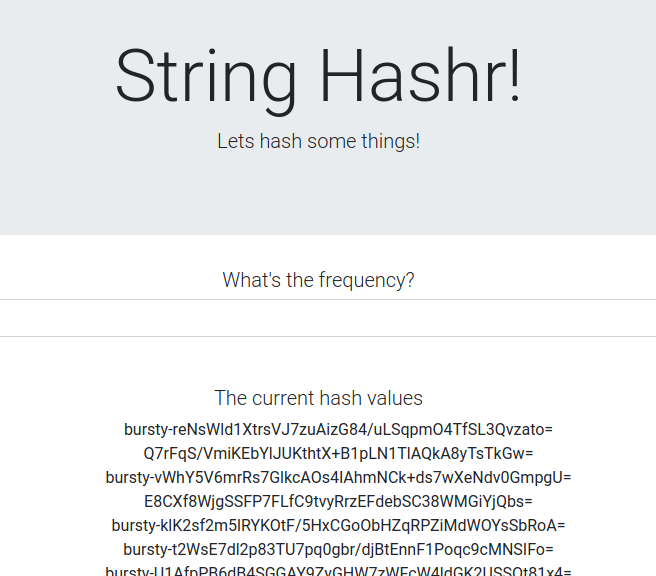
这意味着我们已成功跨集群通信!请尝试更改不同服务的权重,然后应用 worker-virtualservice.yaml 文件。这是一种很好的在集群之间平衡流量的方式,但如果我们可以自动执行此操作,该怎么办?
16. 利用 Prometheus 指标
Prometheus 简介
Prometheus 是一个开源系统监控和提醒工具包,最初在 SoundCloud 上构建而成。它维护一个多维数据模型,其中时间序列数据由指标名称和键值对标识。
下面是 Prometheus 架构图,供您参考:
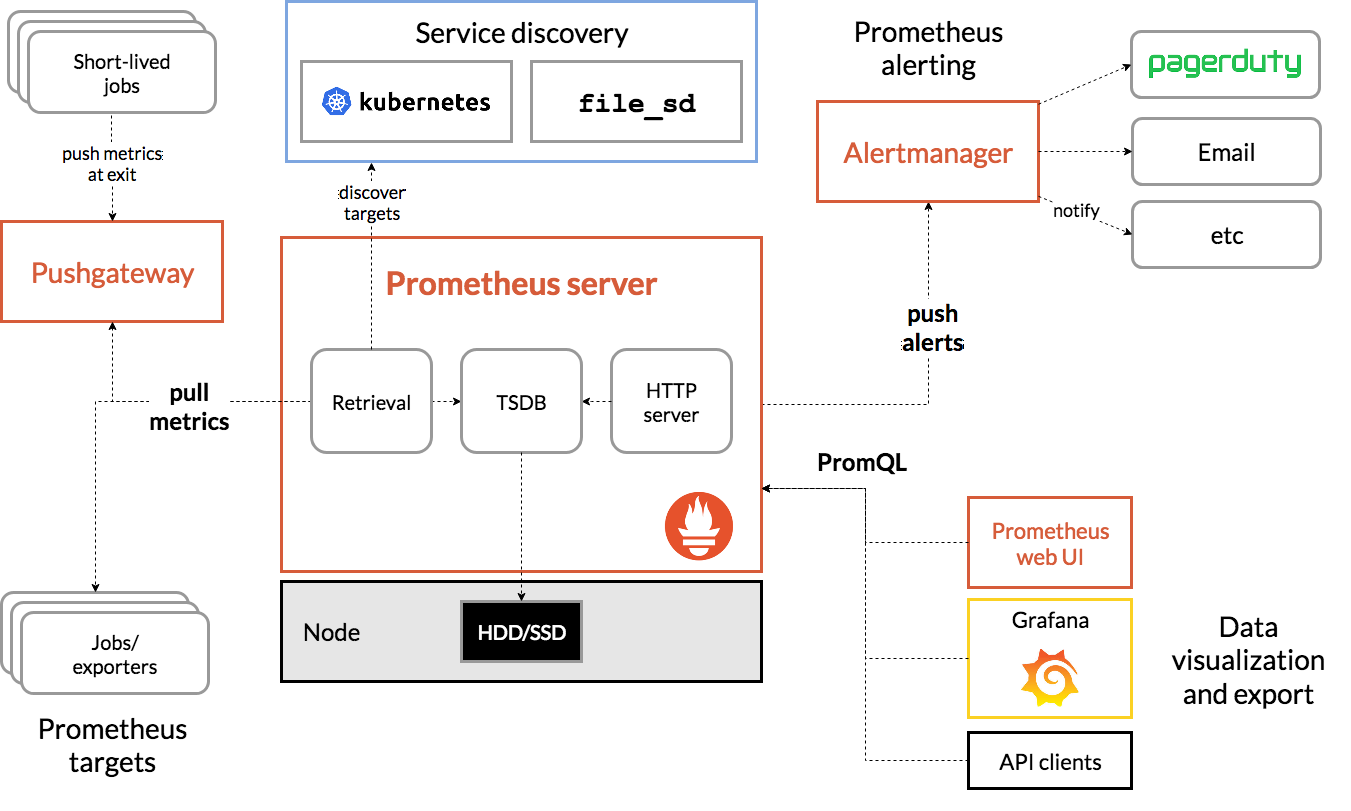
与 Prometheus 一起部署时,Istio 会自动向 Prometheus 服务器报告各种指标。我们可以使用这些指标来动态管理集群。
探索 Prometheus 指标
首先,我们需要公开 Prometheus 部署。
前往 GKE 中的“Workloads”(工作负载)标签页,然后展开“prometheus”工作负载。
查看部署的详细信息后,依次选择“操作”->“公开”。
选择转发到端口 9090,然后输入“负载平衡器”
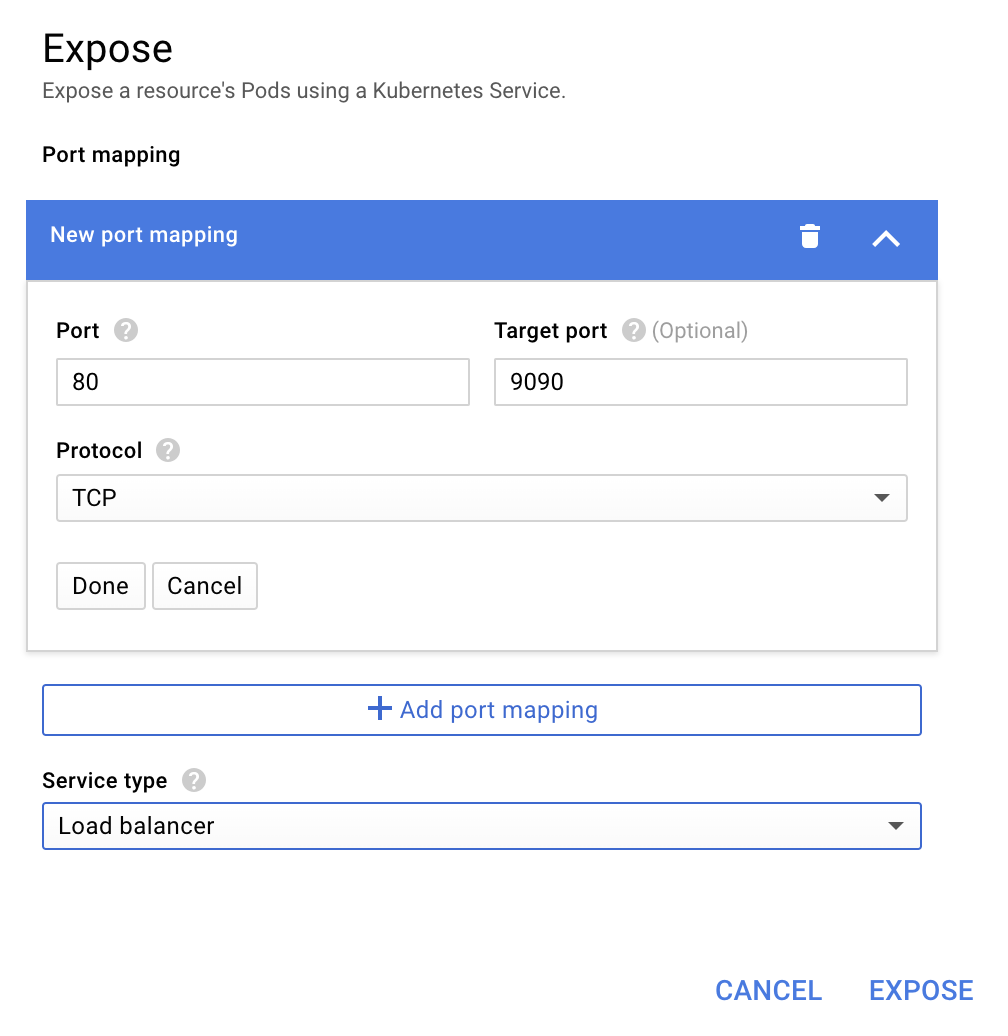
然后选择“公开”
这将在一个可公开访问的 IP 地址上创建一个服务,我们可以使用该服务来探索 Prometheus 指标
等待端点变为可用状态,然后点击“外部端点”旁边的 IP 地址 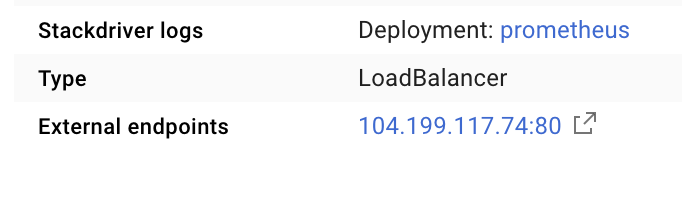
您现在应该看到 Prometheus 界面。
Prometheus 提供了足够的指标,可以作为自己的工作坊。不过,我们先来探索一下 istio_requests_total 指标。
执行该查询会返回大量数据。它包含通过 Istio 服务网格传输的所有请求的相关指标,数量非常多!我们将更改表达式,以过滤出我们真正感兴趣的内容:
目标服务为 worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local 且来源为 frontend-deployment 的请求(仅限过去 15 秒内)
该查询如下所示:
istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s]
这样,我们就可以处理更易于管理的数据
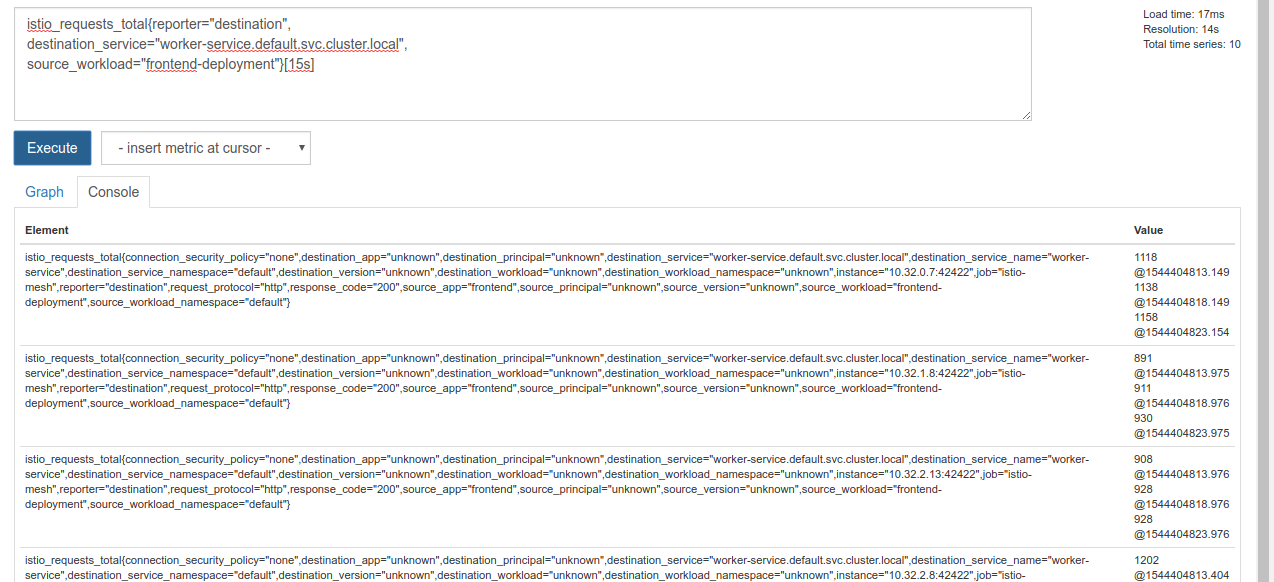
但仍有点密集。我们想知道每秒请求数,而不是所有请求数。
为此,我们可以使用内置的 rate 函数
rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s])

我们已经接近目标了,但还需要进一步将这些指标缩减为一个逻辑组。
为此,我们可以使用 sum 和 by 关键字对结果进行分组和求和
sum(rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s])) by (source_workload,
source_app, destination_service)
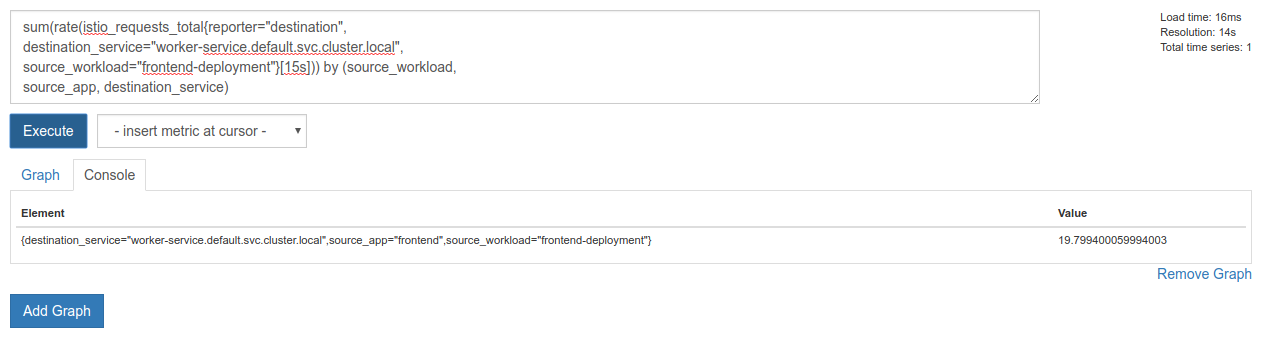
太好了!我们可以从 Prometheus 中获取所需的确切指标。
最终的 Prometheus 查询
综合我们学到的所有知识,我们需要向 Prometheus 发出最后一个查询:
sum(rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s])) by (source_workload,
source_app, destination_service)
现在,我们可以使用其 HTTP API 来获取该指标。
我们可以通过发出 http GET 请求来查询其 API,如下所示。请替换 <prometheus-ip-here>
curl http://<prometheus-ip-here>/api/v1/query?query=sum\(rate\(istio_requests_total%7Breporter%3D%22destination%22%2C%0Adestination_service%3D%22worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local%22%2C%0Asource_workload%3D%22frontend-deployment%22%7D%5B15s%5D\)\)%20by%20\(source_workload%2C%0Asource_app%2C%20destination_service\)
以下是示例响应:
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"resultType": "vector",
"result": [
{
"metric": {
"destination_service": "worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
"source_app": "frontend",
"source_workload": "frontend-deployment"
},
"value": [
1544404907.503,
"18.892886390062788"
]
}
]
}
}
现在,我们可以从 JSON 中提取指标值
清理
我们需要删除刚才用于公开 Prometheus 的服务。在 Google Cloud 控制台中,找到我们刚刚创建的服务顶部,然后点击“删除”
后续步骤:
我们已经找到了一种方法来发现流量是如何在集群中流动的以及流速是多少,下一步是编写一个小型二进制文件,用于定期查询 Prometheus,如果每秒对 worker 的请求数超过特定阈值,则对我们的 worker 虚拟服务应用不同的目标权重,以将所有流量发送到 burst 集群。每秒请求数低于较低阈值后,将所有流量发回 primary。
17. 创建跨集群突发流量
设置
将 worker-service 的所有流量设置为流向主集群
我们将将所有以 worker-service 为目的地的流量路由到 primary 集群视为应用的“默认”状态
修改 $proj/istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml,使其如下所示
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 100
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 0
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: worker-destination-rule
spec:
host: worker-service
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: RANDOM
subsets:
- name: primary
labels:
cluster-type: primary-cluster
- name: burst
labels:
cluster-type: burst-cluster
确保您已连接到 primary 集群
kubectx primary
应用 istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml
kubectl apply -f istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml
编写 istiowatcher 守护程序
我们将使用 Go 编写此服务,因为它速度快且可移植。应用的整体流程将是启动,然后每秒查询 Prometheus,
在 src 中创建一个名为 istiowatcher 的新目录
mkdir -p ${proj}/src/istiowatcher && cd ${proj}/src/istiowatcher
我们将从容器内调用 istioctl,以便从集群内操控 Istio 控制平面。
编写 istiowatcher.go
在该目录中创建一个名为 istiowatcher.go 的文件,并将以下内容插入其中
package main
import (
"github.com/tidwall/gjson"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"os/exec"
"time"
)
func main() {
//These are in requests per second
var targetLow float64 = 10
var targetHigh float64 = 15
// This is for the ticker in milliseconds
ticker := time.NewTicker(1000 * time.Millisecond)
isBurst := false
// Our prometheus query
reqQuery := `/api/v1/query?query=sum(rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s]))by(source_workload,source_app,destination_service)`
for t := range ticker.C {
log.Printf("Checking Prometheus at %v", t)
// Check prometheus
// Note that b/c we are querying over the past 5 minutes, we are getting a very SLOW ramp of our reqs/second
// If we wanted this to be a little "snappier" we can scale it down to say 30s
resp, err := http.Get("http://prometheus.istio-system.svc.cluster.local:9090" + reqQuery)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error: %v", err)
continue
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
val := gjson.Get(string(body), "data.result.0.value.1")
log.Printf("Value: %v", val)
currentReqPerSecond := val.Float()
log.Printf("Reqs per second %f", currentReqPerSecond)
if currentReqPerSecond > targetHigh && !isBurst {
applyIstio("burst.yaml")
log.Println("Entering burst mode")
isBurst = true
} else if currentReqPerSecond < targetLow && isBurst {
applyIstio("natural.yaml")
log.Println("Returning to natural state.")
isBurst = false
}
}
}
func applyIstio(filename string) {
cmd := exec.Command("istioctl", "replace", "-f", filename)
if err := cmd.Run(); err != nil {
log.Printf("Error hit applying istio manifests: %v", err)
}
}
编写 Dockerfile
创建一个名为 Dockerfile 的新文件,并将以下内容插入其中。
FROM golang:1.11.2-stretch as base
FROM base as builder
WORKDIR /workdir
RUN curl -LO https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.0.0/istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
RUN tar xzf istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
RUN cp istio-1.0.0/bin/istioctl ./istioctl
FROM base
WORKDIR /go/src/istiowatcher
COPY . .
COPY --from=builder /workdir/istioctl /usr/local/bin/istioctl
RUN go get -d -v ./...
RUN go install -v ./...
CMD ["istiowatcher"]
此多阶段 Dockerfile 会在第一个阶段下载并解压缩 Istio 1.0.0 版本。第二阶段会将目录中的所有内容复制到映像中,然后将 istioctl 从构建阶段复制到 /usr/local/bin(以便应用可以调用它),获取依赖项、编译代码并将 CMD 设置为“istiowatcher”
编写 burst.yaml
当 frontend 向 worker 发出的请求/秒数超过 15 时,istiowatcher 将应用此文件。
创建一个名为 burst.yaml 的新文件,并将以下内容插入其中。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 0
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 100
编写 natural.yaml
当 frontend 到 worker 的每秒请求数低于 10 时,我们会将其视为返回的“自然”状态。在此状态下,100% 的流量都会路由到 primary 集群。
创建一个名为 natural.yaml 的新文件,并将以下内容插入其中
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 100
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 0
构建并推送 istiowatcher
运行以下命令可将当前目录发送到 Google Cloud Build (GCB),GCB 会在 GCR 中构建并标记映像。
gcloud builds submit -t gcr.io/${GCLOUD_PROJECT}/istiowatcher
部署 istiowatcher
切换到 kubernetes 目录
cd ${proj}/kubernetes/
编写部署文件:istiowatcher.yaml
创建一个名为 istiowatcher.yaml 的文件,然后插入以下内容(替换 <your-project-id>)。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: istiowatcher-deployment
labels:
app: istiowatcher
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: istiowatcher
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: istiowatcher
spec:
serviceAccountName: istio-pilot-service-account
automountServiceAccountToken: true
containers:
- name: istiowatcher
image: gcr.io/<your-project-id>/istiowatcher
imagePullPolicy: Always
部署
确保我们在主集群中运行
kubectx primary
在 istio-system 命名空间中部署 istiowatcher.yaml
kubectl apply -n istio-system -f istiowatcher.yaml
请务必注意 yaml 中的 serviceAccountName 和 automountServiceAccountToken 指令。这样,我们就可以获得从集群中运行 istioctl 所需的凭据。
我们还需要在 istio-system 命名空间中部署此服务,以确保我们拥有 istio-pilot-service-account 的凭据。(它不存在于 default 命名空间中)。
观看流量自动切换!
现在,进入神奇时刻!我们前往前端,将每秒请求次数提高到 20
请注意,这需要几秒钟的时间,但我们会逐步提高速度,并且所有哈希都带有“bursty-”前缀!
这是因为我们是在 15s 范围内对 Prometheus 进行采样,这会导致响应时间略有延迟。如果我们希望更精确地设置带宽,可以将 Prometheus 查询更改为 5s.
18. 接下来做什么?
清理
如果您使用的是本研讨会提供的临时账号,则无需进行清理。
您可以删除 Kubernetes 集群、防火墙规则和 GCR 中的映像
gcloud container clusters delete primary --zone=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters delete burst --zone=us-west1-a
gcloud compute firewall-rules delete istio-multicluster-test-pods
gcloud container images delete gcr.io/$GCLOUD_PROJECT/istiowatcher
后续措施
- 参加一些 Istio 讲座!
- 获取认证:使用 Kubernetes + Istio 构建您的下一个应用
- 主题演讲:Kubernetes、Istio、Knative:全新的开放式云端堆栈 - Google Kubernetes 统筹产品经理 Aparna Sinha
- 教程:使用 Istio - Lee Calcote 和 Girish Ranganathan(SolarWinds)
- Istio - The Packet's-Eye View - Matt Turner, Tetrate
- Istio 是史上最先进的下一代防火墙吗?- John Morello,Twistlock
- 阅读 Istio 文档
- 加入 Istio 工作组
- 在 Twitter 上关注 @IstioMesh