1. 歡迎
感謝您參與 Google 推出的 Istio Multi Cloud Burst 程式碼研究室。這個程式碼研究室需要初學者級別的 Kubernetes、Node 和 Go 實作經驗。 事前準備
|
|
學習目標
- 如何在 GKE 上建立 Kubernetes 叢集
- 如何使用 Helm 在 Kubernetes 叢集上安裝 Istio
- 如何使用 Helm 安裝 Istio 多叢集
- 從來源部署網路應用程式至 Kubernetes
- 為 Istio 編寫及套用流量轉送規則
- Prometheus 指標
- 在 Kubernetes 叢集中建構及推送容器映像檔
2. 開始設定
您可以透過下列任一方式,按照本程式碼研究室的操作說明進行操作:
- Google Cloud Shell (建議):瀏覽器內的殼層,內建安裝工具
- 筆記型電腦 (請按照下方說明操作)
開始使用 Google Cloud Platform
- 如果您沒有 GCP 帳戶,請向講師索取免費使用者帳戶卡。
- 前往 Google Cloud 控制台,然後按一下「Select a project」(選取專案):
- 記下專案的「ID」,然後點選專案進行選擇:

選項 1:使用 Google Cloud Shell (建議做法)
Cloud Shell 會在瀏覽器中提供指令列殼層,並自動安裝所需工具,並驗證 Google Cloud Platform 帳戶。(如果您不想在 Cloud Shell 中執行這項練習,請跳至下一節)。
前往 Cloud 控制台,然後按一下右上方工具列中的「啟用 Cloud Shell」:
在 Cloud Shell 中新增工具
您也可以執行下列指令,將兩者都安裝至 ~/.bin,並將其新增至 $PATH:
mkdir -p ~/.bin && \
cd ~/.bin && \
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ahmetb/kubectx/master/kubectx && \
chmod +x kubectx && \
curl -LO https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ahmetb/kubectx/master/kubens && \
chmod +x kubens && \
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-helm/helm-v2.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
tar xzf helm-v2.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
rm helm-v2.12.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
mv linux-amd64/helm ./helm && \
rm -r linux-amd64 && \
export PATH=${HOME}/.bin:${PATH}
以下是一些快速提示,可讓您更輕鬆地使用 Cloud Shell:
1. 將殼層分離至新視窗: |
|
2. 使用檔案編輯器: 按一下右上方的鉛筆圖示,啟動瀏覽器內的檔案編輯器。這會很實用,因為我們會將程式碼片段複製到檔案中。 |
|
3. 啟動新的分頁:如果您需要多個終端機提示。 |
|
4. 放大文字: Cloud Shell 的預設字型大小可能太小,無法清楚辨識。 | Linux 上的 Ctrl-+ 或 Windows 上的 ⌘-+。 |
選項 2:設定筆記型電腦 (不建議)
如果您比較習慣使用自己的工作站環境,而非 Cloud Shell,請設定下列工具:
- 安裝
gcloud:(Cloud Shell 已預先安裝)。請按照操作說明在您的平台上安裝gcloud。我們會使用這個值建立 Kubernetes 叢集。 - 安裝
kubectl:(Cloud Shell 已預先安裝)。執行下列指令安裝:
gcloud components install kubectl
執行下列指令,即可驗證 gcloud。系統會要求您使用 Google 帳戶登入。接著,請選擇預先建立的專案 (如上圖所示) 做為預設專案。(您可以略過設定運算區域的步驟):
gcloud init
3. 設定 GCP 專案
在專案中啟用 GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine)、GCR (Google Container Registry) 和 GCB (Google Cloud Build) API:
gcloud services enable \ cloudapis.googleapis.com \ container.googleapis.com \ containerregistry.googleapis.com \ cloudbuild.googleapis.com
設定環境變數
我們會在設定期間大量使用 Google Cloud 專案,因此請設定環境變數,方便快速參照
export GCLOUD_PROJECT=$(gcloud config get-value project)
我們會在工作坊中建立一些程式碼和設定檔,因此請建立專案目錄並切換至該目錄
mkdir -p src/istio-burst && \ cd src/istio-burst && \ export proj=$(pwd)
4. 建立「primary」Kubernetes 叢集
您可以使用 Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) 輕鬆建立代管 Kubernetes 叢集。
下列指令會建立 Kubernetes 叢集:
- 命名為「primary」
- 在 us-west1-a 區域中,
- 最新的 Kubernetes 版本
- 包含 4 個初始節點
export cluster=primary
export zone=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters create $cluster --zone $zone --username "admin" \
--cluster-version latest --machine-type "n1-standard-2" \
--image-type "COS" --disk-size "100" \
--scopes "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/compute",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.write",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/monitoring",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/servicecontrol",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/service.management.readonly",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/trace.append" \
--num-nodes "4" --network "default" \
--enable-cloud-logging --enable-cloud-monitoring --enable-ip-alias
(這項作業可能需要 5 分鐘的時間。您可以在 Cloud 控制台中查看叢集建立情形。
建立 Kubernetes 叢集後,gcloud 會使用指向叢集的憑證設定 kubectl。
gcloud container clusters get-credentials $cluster --zone=$zone
您現在應該可以使用 kubectl 與新叢集。
執行下列指令,即可列出叢集的 Kubernetes 節點 (這些節點應顯示「Ready」狀態):
kubectl get nodes
修改 Kubeconfig 名稱以利使用
我們會經常切換情境,因此為叢集命名簡短的別名會很方便。
這個指令會將您剛建立的 kubeconfig 項目重新命名為 primary
kubectx ${cluster}=gke_${GCLOUD_PROJECT}_${zone}_${cluster}
設定權限:
您必須是叢集管理員,才能部署 Istio。這個指令會將與 Google Cloud 帳戶相關聯的電子郵件地址設為叢集管理員
kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-admin-binding \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user=$(gcloud config get-value core/account)
5. 建立「爆發」叢集
下列指令會建立 Kubernetes 叢集:
- 命名為「burst」
- 在 us-west1-a 區域中,
- 最新的 Kubernetes 版本
- 包含 1 個初始節點
- 最多可啟用 5 個節點的自動調度資源
export cluster=burst
export zone=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters create $cluster --zone $zone --username "admin" \
--cluster-version latest --machine-type "n1-standard-2" \
--image-type "COS" --disk-size "100" \
--scopes "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/compute",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_only",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.write",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/monitoring",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/servicecontrol",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/service.management.readonly",\
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/trace.append" \
--num-nodes "1" --enable-autoscaling --min-nodes=1 --max-nodes=5 \
--network "default" \
--enable-cloud-logging --enable-cloud-monitoring --enable-ip-alias
(這項作業可能需要 5 分鐘的時間。您可以在 Cloud 控制台中查看叢集建立情形。
建立 Kubernetes 叢集後,gcloud 會使用指向叢集的憑證設定 kubectl。
gcloud container clusters get-credentials $cluster --zone=$zone
您現在應該可以使用 kubectl 與新叢集。
執行下列指令,即可列出叢集的 Kubernetes 節點 (這些節點應顯示「Ready」狀態):
kubectl get nodes
修改 Kubeconfig 名稱以利使用
這個指令會將您剛剛建立的 kubeconfig 項目修改為 burst
kubectx ${cluster}=gke_${GCLOUD_PROJECT}_${zone}_${cluster}
設定權限:
您必須是叢集管理員,才能部署 Istio Remote。這個指令會將與 Google Cloud 帳戶相關聯的電子郵件地址設為叢集管理員
kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-admin-binding \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin \
--user=$(gcloud config get-value core/account)
6. 套用防火牆規則
為了讓兩個叢集彼此通訊,我們需要建立防火牆規則。
執行下列指令,在 Google Cloud Platform 中建立防火牆規則,讓叢集能夠通訊
function join_by { local IFS="$1"; shift; echo "$*"; }
ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS=$(gcloud container clusters list \
--filter="(name=burst OR name=primary) AND zone=$zone" \
--format='value(clusterIpv4Cidr)' | sort | uniq)
ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS=$(join_by , $(echo "${ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS}"))
ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS=$(gcloud compute instances list \
--filter="(metadata.cluster-name=burst OR metadata.cluster-name=primary) AND metadata.cluster-location=us-west1-a" \
--format='value(tags.items.[0])' | sort | uniq)
ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS=$(join_by , $(echo "${ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS}"))
gcloud compute firewall-rules create istio-multicluster-test-pods \
--allow=tcp,udp,icmp,esp,ah,sctp \
--direction=INGRESS \
--priority=900 \
--source-ranges="${ALL_CLUSTER_CIDRS}" \
--target-tags="${ALL_CLUSTER_NETTAGS}" --quiet
我們已設定兩個叢集,並準備在其中部署應用程式和 Istio!
7. Istio 簡介
什麼是 Istio?
Istio 是服務網格控制層,旨在「連結、保護、控制及觀察服務」。它會以各種方式執行這項操作,但主要會將 Proxy 容器 ( Envoy) 附加到每個已部署的 Kubernetes Pod。Proxy 容器會搭配通用政策和追蹤中心 ( Mixer) 控制微服務之間的所有網路通訊。
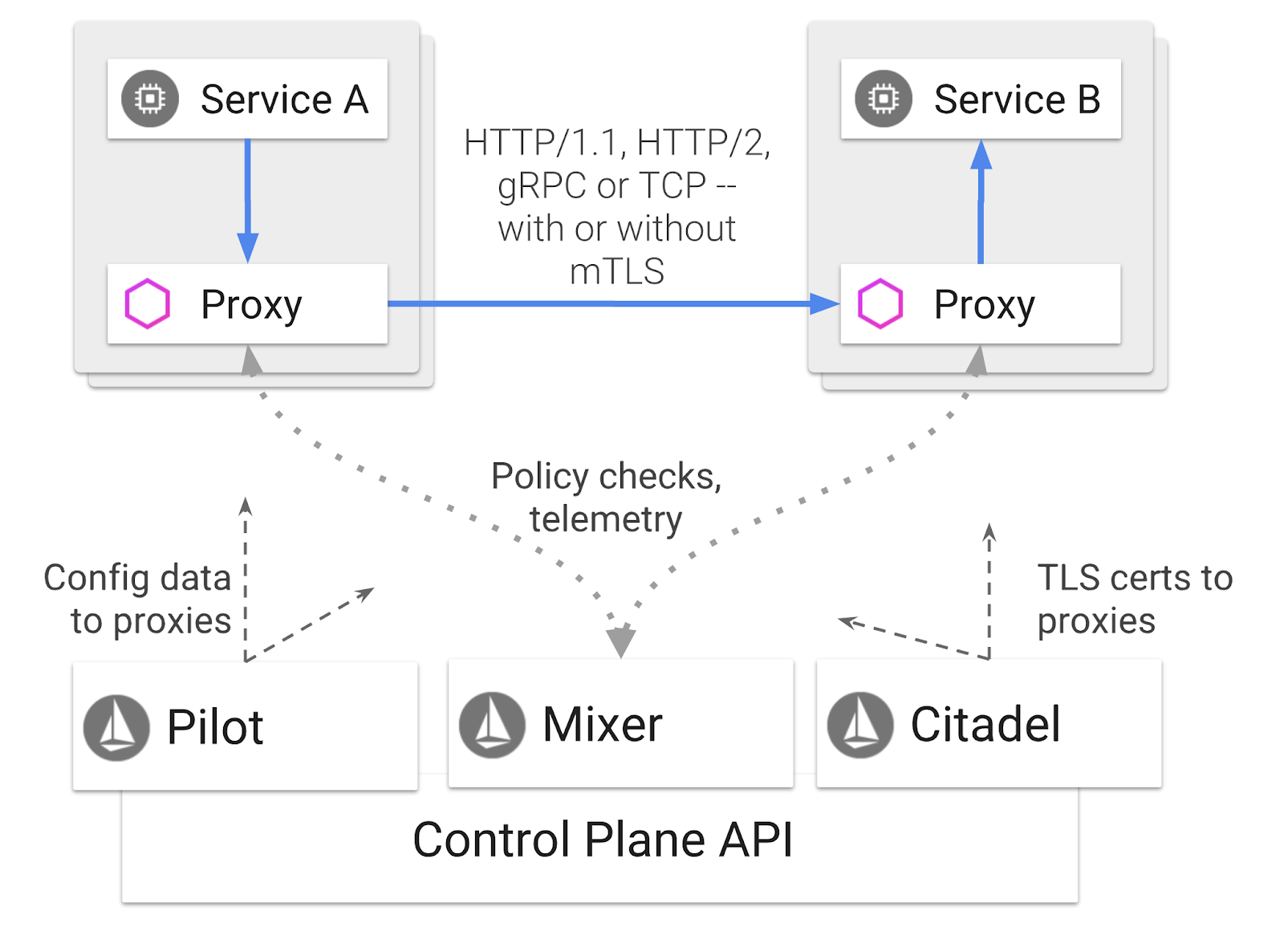
這些政策可獨立於 Kubernetes 部署和服務套用,這表示網路操作員可以觀察網路活動、限制、重新導向或重寫網路政策,而無須重新部署相關應用程式。
Istio 支援的部分流量管理功能包括:
- 斷路器
- 以百分比為準的流量分配
- 網址重寫
- 傳輸層安全標準 (TLS) 終止
- 健康狀態檢查
- 負載平衡
本講習課程將著重於百分比流量分配。
我們將使用的 Istio 術語
VirtualService
VirtualService 會定義一組流量轉送規則,用於在主機位址時套用。
閘道
Gateway 是負載平衡器,會在邊緣網格中運作,用於接收或傳送 HTTP/TCP 連線。閘道可指定通訊埠、SNI 設定等。
DestinationRule
DestinationRule 會定義適用於轉送後,要傳送至服務的流量的政策。這些設定會指定負載平衡、Sidecar 的連線集區大小,以及離群值偵測設定。
Istio 多叢集
您可能注意到,我們建立兩個叢集時,primary 叢集有 4 個節點,但沒有自動調度資源功能,而 burst 叢集有 1 個節點,並可自動調度至最多 5 個節點。
這項設定有兩個原因。
首先,我們要模擬「內部」到「雲端」的情況。在內部部署環境中,您無法存取自動調度資源叢集,因為您有固定的基礎架構。
其次,4 個節點設定 (如上方所述) 是執行 Istio 的最低要求。這就引出一個問題:如果 Istio 至少需要 4 個節點,burst 叢集如何在 1 個節點上執行 Istio?答案是,Istio 多叢集會安裝較少的 Istio 服務,並與主要叢集中的 Istio 安裝作業通訊,以便擷取政策規則並發布遙測資訊。
8. 應用程式架構總覽
元件總覽
我們將使用 NodeJS 和 Redis 部署三層應用程式。
Worker
這個 worker 應用程式是以 NodeJS 編寫,會監聽傳入的 POST HTTP 要求,並對這些要求執行雜湊運算,如果已定義名為 PREFIX 的環境變數,就會在雜湊前方加上該值。計算出雜湊後,應用程式會在指定 Redis 伺服器的「calculation」管道上傳送結果。
我們稍後會使用 PREFIX 環境變數來示範多叢集功能。
供您參考:這些是應用程式使用的套件。
body-parser:可讓我們剖析 HTTP 要求cors:允許使用跨源資源共享dotenv:輕鬆剖析環境變數express:輕鬆託管網站ioredis:用於與 Redis 資料庫通訊的用戶端程式庫morgan:提供精美的結構化記錄
前端
我們的前端也是一個 NodeJS 應用程式,可使用 express 代管網頁。它會根據使用者輸入的頻率,以該頻率向我們的 worker 應用程式傳送要求。這個應用程式也會訂閱名為「calculation」的 Redis 管道訊息,並在網頁中顯示結果。
應用程式會使用下列依附元件。
body-parser:可讓我們剖析 HTTP 要求dotenv:輕鬆剖析環境變數express:輕鬆託管網站ioredis:用於與 Redis 資料庫通訊的用戶端程式庫morgan:提供精美的結構化記錄request::允許提出 HTTP 要求socket.io::允許網頁與伺服器進行雙向通訊
這個網頁使用 Bootstrap 設定樣式,執行時會如下所示:
架構圖
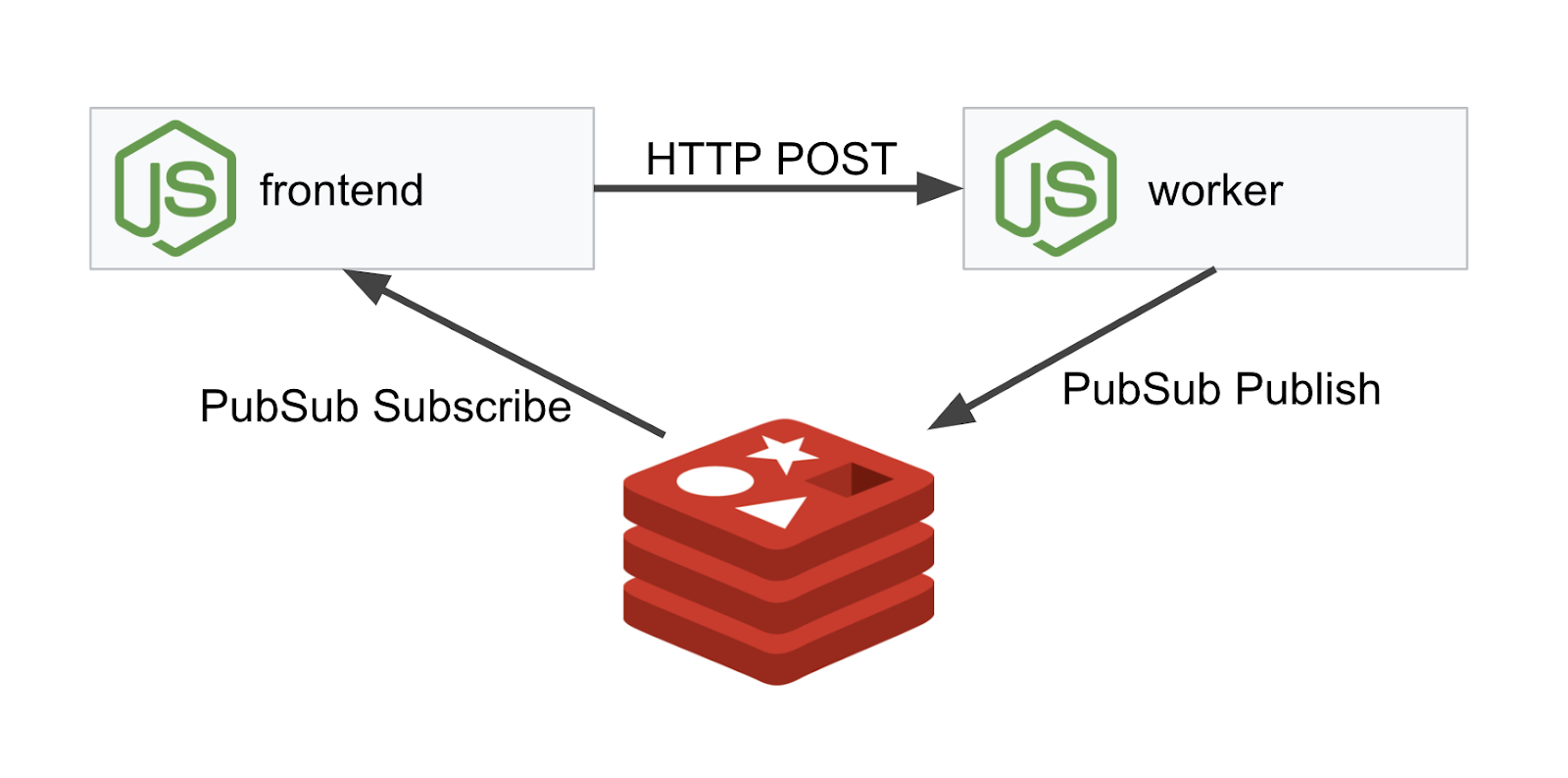
部署圖表
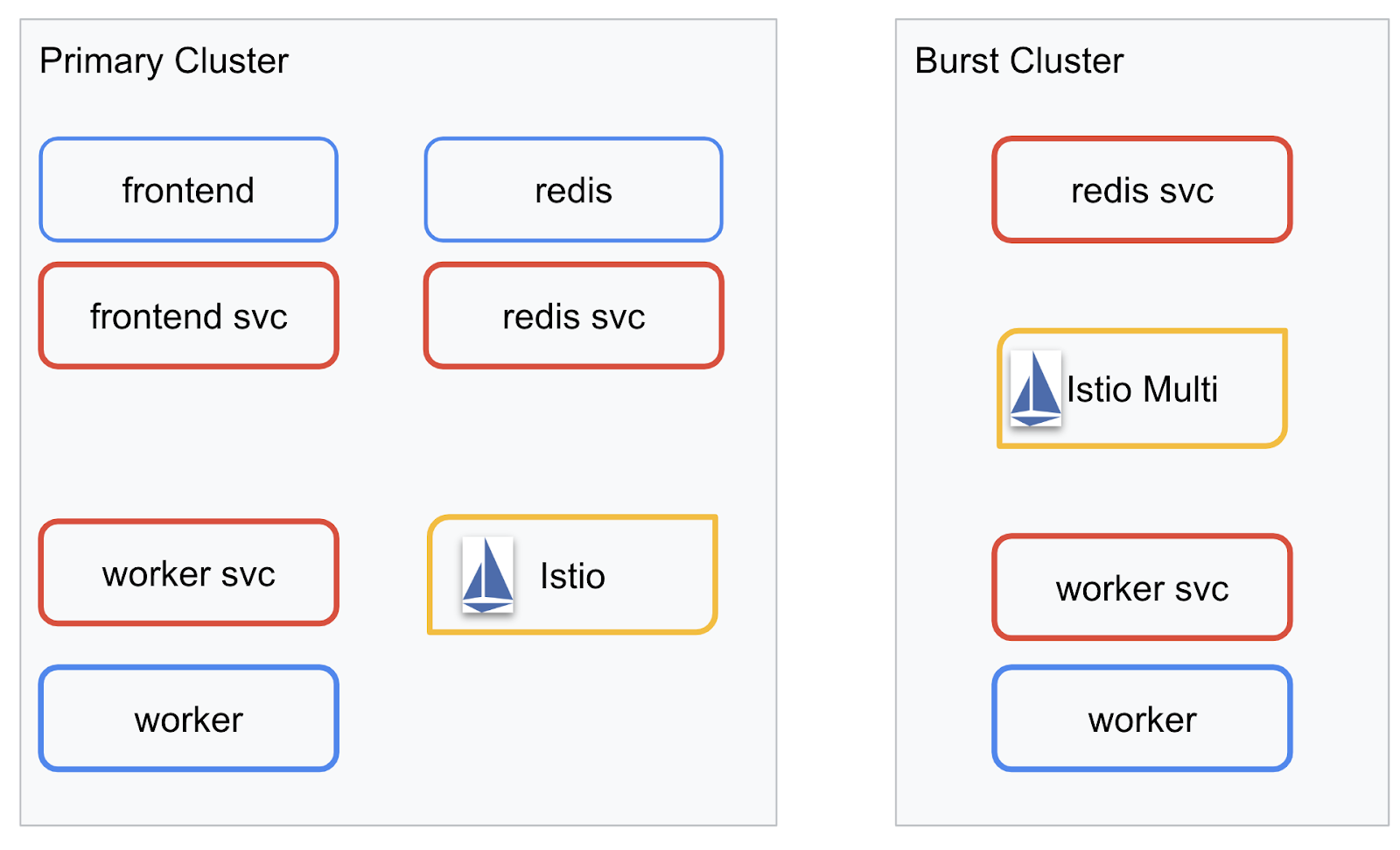
我們將在建立的兩個叢集中部署最終應用程式。primary 叢集會部署所有元件 (frontend、worker 和 Redis),但 burst 叢集只會部署 worker 應用程式。
下圖說明這兩個叢集。紅框代表 Kubernetes 服務,藍框則代表 Kubernetes 部署作業。黃色方塊代表 Istio 安裝作業。
請注意,即使叢集中沒有 Redis 部署項目,burst 叢集仍會部署 Redis 服務。我們需要在叢集中提供這項服務,讓 Kubernetes DNS 能夠解析要求,但在實際提出要求時,Istio Proxy 會將要求重新導向至 primary 叢集中的 Redis 部署。
最終應用程式會在名為 istiowatcher. 的 primary 叢集中執行額外的部署作業,這樣一來,當流量超過特定門檻時,我們就能自動將流量動態重新導向至 burst。
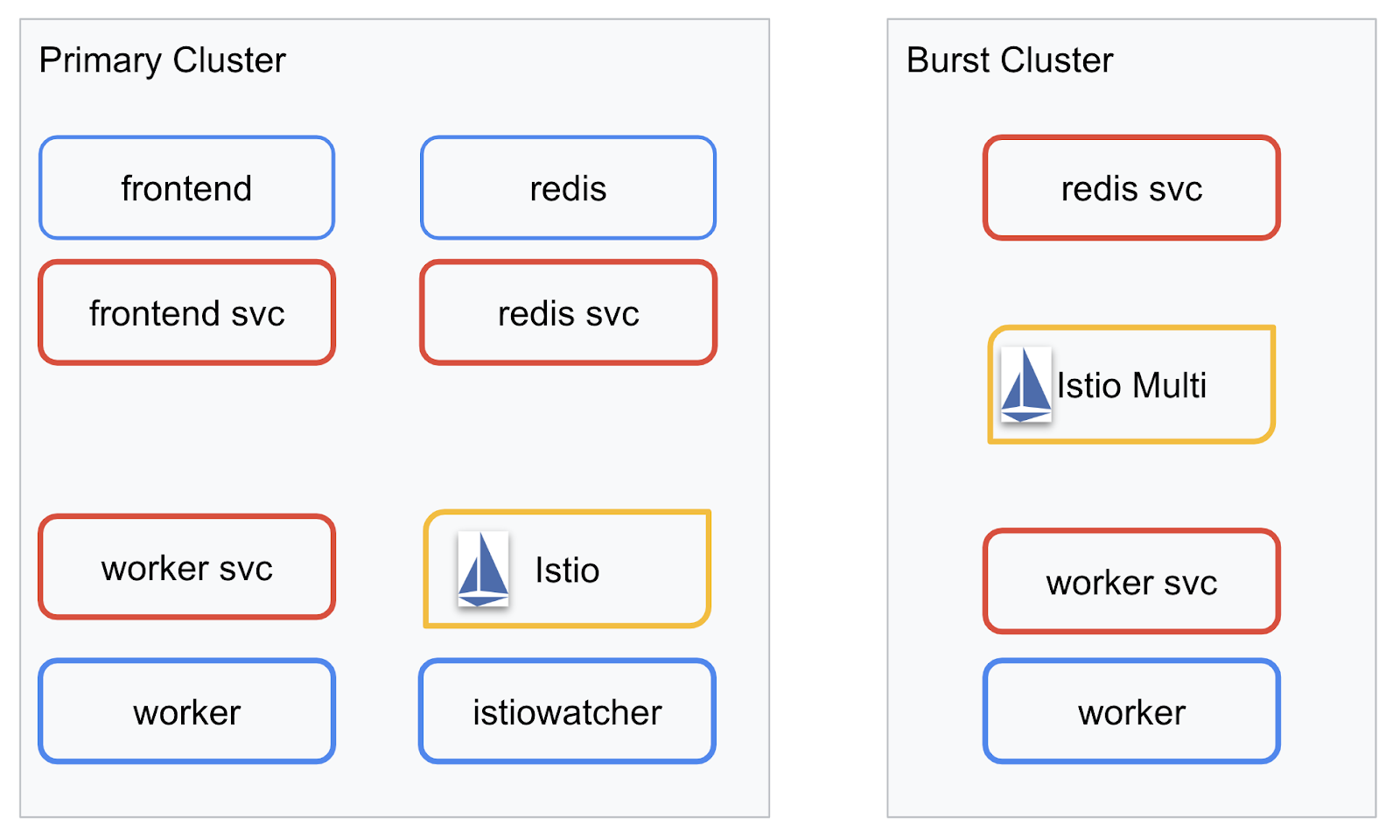
9. 建立應用程式部署檔案
我們需要建立一組 Kubernetes 資訊清單,才能部署應用程式
切換至專案的根目錄,然後建立名為 kubernetes 的新資料夾
mkdir ${proj}/kubernetes && cd ${proj}/kubernetes
編寫 frontend.yaml
這麼做會建立 Kubernetes 部署和服務,以便存取前端映像檔。
將以下內容插入 frontend.yaml。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: frontend-deployment
labels:
app: frontend
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: frontend
image: gcr.io/istio-burst-workshop/frontend
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/_healthz"
port: 8080
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-readiness-probe"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/"
port: 8080
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-liveness-probe"
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8080"
- name: PROCESSOR_URL
value: "http://worker-service"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: frontend-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: frontend
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
Deployment 中的重要注意事項
- 我們已將應用程式執行的通訊埠指定為
8080 - 我們已將 worker 的地址設為「
http://worker-service」,並會使用 Kubernetes 內建的 DNS 功能解析產生的服務 - 我們已將
REDIS_URL的地址設為「redis-cache-service:6379」,並會使用 Kubernetes 內建的 DNS 功能來解析產生的 IP 位址。 - 我們也為容器設定
liveness和readiness探針,協助 Kubernetes 瞭解容器何時啟動及運作。
編寫 worker-service.yaml
我們會在單獨的檔案中編寫 Kubernetes 服務定義,而非在部署定義中編寫,因為我們會在多個叢集中重複使用這項服務,但會為每個叢集編寫不同的部署作業。
在 worker-service.yaml 中插入以下內容
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: worker-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: worker
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 8081
編寫 worker-primary.yaml
這是我們要推送至主要叢集的 worker 部署作業。
將以下內容插入 worker-primary.yaml。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: worker-deployment
labels:
app: worker
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: worker
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: worker
cluster-type: primary-cluster
spec:
containers:
- name: worker
image: gcr.io/istio-burst-workshop/worker
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8081
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/_healthz"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-readiness-probe"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-liveness-probe"
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8081"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
請注意,我們在這裡採用相同的模式,提供 liveness 和 readiness 探針,並指定應用程式要使用的 PORT 和 REDIS_URL 環境變數。
這次部署作業還有另一個值得注意的地方,就是缺少 PREFIX 環境變數。也就是說,我們的計算結果將是原始雜湊值 (前面沒有任何前置字串)。
這項部署作業的最後重點是 cluster-type: primary-cluster 標籤。稍後我們會在 Istio 多叢集上進行流量路由時使用這個值
編寫 redis.yaml
工作站與前端的通訊是透過 Redis 管道進行,因此我們需要在叢集中部署 Redis 應用程式。
將下列內容插入 redis.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: redis-cache
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: redis-cache
spec:
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 6379
readinessProbe:
periodSeconds: 5
tcpSocket:
port: 6379
livenessProbe:
periodSeconds: 5
tcpSocket:
port: 6379
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: redis-data
resources:
limits:
memory: 256Mi
cpu: 125m
requests:
cpu: 70m
memory: 200Mi
volumes:
- name: redis-data
emptyDir: {}
這是 Redis 應用程式的半標準部署作業。它會根據 redis:alpine 映像檔建立容器、公開適當的連接埠,並設定合理的資源限制。
編寫 redis-service.yaml
我們需要 Kubernetes 服務才能與 Redis 應用程式通訊
將下列內容插入 redis-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: redis-cache-service
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: redis-cache
ports:
- port: 6379
targetPort: 6379
這會提供名為 redis-cache-service 的服務,用於存取 Redis 部署。
10. 部署應用程式
將映像檔推送至 GCR 並編寫 Kubernetes 資訊清單後,現在是部署應用程式並查看其運作方式的好時機!
執行下列指令來部署應用程式
- 確認我們位於正確的叢集
kubectx primary
- 部署 Redis Cache
kubectl apply -f redis.yaml
- 部署 Redis 服務
kubectl apply -f redis-service.yaml
- 部署前端
kubectl apply -f frontend.yaml
- 部署 worker
kubectl apply -f worker-primary.yaml
- 部署 Worker 服務
kubectl apply -f worker-service.yaml
我們已將應用程式部署至 GKE。恭喜!
測試
等待 Pod 上線
kubectl get pods -w
所有 Pod 都處於「Running」狀態後,請按下 Ctrl + C
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE frontend-deployment-695d95fbf7-76sd8 1/1 Running 0 2m redis-cache-7475999bf5-nxj8x 1/1 Running 0 2m worker-deployment-5b9cf9956d-g975p 1/1 Running 0 2m
您會發現我們並未透過 LoadBalancer 公開前端。這是因為稍後我們會透過 Istio 存取應用程式。為了測試所有服務是否都已啟用及運作,我們會使用 kubectl port-forward. 執行下列指令,將本機 (或 Cloud Shell) 電腦上的通訊埠 8080 轉送至執行 frontend 部署作業的通訊埠 8080。
kubectl port-forward \
$(kubectl get pods -l app=frontend -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') \
8080:8080
如果您是在本機上執行:請開啟網路瀏覽器,然後前往 http://localhost:8080
如果您在 Cloud Shell 中執行:請按一下「網頁預覽」按鈕,然後選取「透過以下通訊埠預覽:8080」。
您應該會看到前端!如果您在「頻率」方塊中輸入數字,系統就會開始顯示井字號
恭喜!一切都已完成!
按下 Ctrl+C 即可停止轉送通訊埠。
11. 清理已部署的應用程式
我們將在叢集中套用 Istio,然後重新部署應用程式,因此請先清除目前的應用程式。
執行下列指令,即可刪除所有剛建立的部署作業和服務
- 刪除「
redis-cache-service」
kubectl delete -f redis-service.yaml
- 刪除「
redis」
kubectl delete -f redis.yaml
- 刪除「
frontend」
kubectl delete -f frontend.yaml
- 刪除「
worker」
kubectl delete -f worker-primary.yaml
- 刪除「
worker-service」
kubectl delete -f worker-service.yaml
12. 在主要叢集上安裝 Istio
取得 Istio
Istio 的發布版本由 GitHub 託管。下列指令會下載 1.0.0 版的 istio 並解壓縮。
- 變更至專案根目錄
cd ${proj}
- 下載封存檔案
curl -LO https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.0.0/istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
- 解壓縮及移除封存檔
tar xzf istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz && rm istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
建立 Istio 範本
執行下列 Helm 指令可建立範本,以便在叢集中安裝 Istio。
helm template istio-1.0.0/install/kubernetes/helm/istio \ --name istio --namespace istio-system \ --set prometheus.enabled=true \ --set servicegraph.enabled=true > istio-primary.yaml
這樣會在目前目錄中建立名為 istio-primary.yaml 的檔案,其中包含部署及執行 Istio 所需的所有定義和規格。
請注意兩個 --set 參數。這些功能可為 Istio 系統新增 Prometheus 和 ServiceGraph 支援功能。我們稍後會在本研究室中使用 Prometheus 服務。
部署 Istio
如要部署 Istio,我們必須先建立名為 istio-system 的命名空間,讓 Istio 部署和服務能夠在其中執行。
kubectl create namespace istio-system
最後,套用我們使用 Helm 建立的 istio-primary.yaml 檔案
kubectl apply -f istio-primary.yaml
標籤預設命名空間
Istio 會將補充 Proxy 服務插入每個部署作業。這項功能是採用選擇加入的方式,因此我們需要使用 istio-injection=enabled 為 default 命名空間加上標籤,讓 Istio 自動為我們插入補充資訊。
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
恭喜!我們已建立叢集並啟用 Istio,準備部署應用程式!
13. 使用 Istio 流量管理功能部署應用程式
建立 Istio 流量管理設定檔
Istio 的運作方式與 Kubernetes 相似,因為它會使用 yaml 檔案進行設定。因此,我們需要建立一組檔案,告訴 Istio 如何公開及轉送流量。
建立名為 istio-manifests 的目錄,然後切換至該目錄
mkdir ${proj}/istio-manifests && cd ${proj}/istio-manifests
編寫 frontend-gateway.yaml
這個檔案會以類似 GKE LoadBalancer 的方式公開 Kubernetes 叢集,並將所有傳入流量轉送至前端服務。
建立名為 frontend-gateway.yaml 的檔案,並插入以下內容。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: frontend-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway # use Istio default gateway implementation
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: frontend-ingress-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- frontend-gateway
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: frontend-service
port:
number: 80
編寫 redis-virtualservice.yaml
建立名為 redis-virtualservice.yaml 的檔案,並插入以下內容
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: redis-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- redis-cache-service
gateways:
- mesh
tcp:
- route:
- destination:
host: redis-cache-service.default.svc.cluster.local
編寫 worker-virtualservice.yaml
建立名為 worker-virtualservice.yaml 的檔案,並插入以下內容
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
部署 Istio 流量管理政策
部署 Istio 政策的方式與其他 Kubernetes 資源相同,使用 kubectl apply
- 套用閘道
kubectl apply -f frontend-gateway.yaml
- 套用 Redis VirtualService
kubectl apply -f redis-virtualservice.yaml
- 套用我們的 Worker VirtualService
kubectl apply -f worker-virtualservice.yaml
部署應用程式
- 變更回
kubernetes目錄
cd ${proj}/kubernetes
- 部署 Redis Cache
kubectl apply -f redis.yaml
- 部署 Redis 服務
kubectl apply -f redis-service.yaml
- 部署前端
kubectl apply -f frontend.yaml
- 部署 worker
kubectl apply -f worker-primary.yaml
- 部署 Worker 服務
kubectl apply -f worker-service.yaml
驗證
目前,我們已在叢集中重新部署應用程式,並套用 Istio 和流量管理政策。
請等候所有工作負載上線
所有節點都上線後,請取得我們在 frontend-ingressgateway.yaml 中設定的 IngressGateway
$ kubectl -n istio-system get svc istio-ingressgateway NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.36.3.112 35.199.158.10 80:31380/TCP,
請瀏覽 <EXTERNAL-IP> 位址,或使用 curl 命令,您應該會看到前端!
$ curl 35.199.158.10
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>String Hashr</title>
<!-- Bootstrap -->
...
14. 在「burst」叢集中安裝 Istio
我們花了許多時間在 primary 叢集中進行設定及部署作業,但我們還有另一個叢集要部署!
在本節中,我們需要從兩個叢集中擷取設定變數,因此請密切留意每個指令指向哪個叢集。
建立 Istio 遠端資訊清單
就像我們將 Istio 部署至 primary 叢集一樣,我們會使用 Helm 將 Istio 遠端部署作業模板化,以便部署至 burst 叢集。不過,我們必須先取得 primary 叢集的相關資訊
收集主要叢集資訊
變更為 primary 叢集
kubectx primary
下列指令會擷取主要叢集中各個 Pod 的 IP 位址。Istio Remote 會使用這些資訊,與主要叢集進行通訊。
export PILOT_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio=pilot -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export POLICY_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio-mixer-type=policy -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export STATSD_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio=statsd-prom-bridge -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export TELEMETRY_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l istio-mixer-type=telemetry -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.podIP}')
export ZIPKIN_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l app=jaeger -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.status.podIP}{end}')
建立遙控器範本
我們現在將使用 helm 建立名為 istio-remote-burst.yaml 的檔案,然後部署至 burst 叢集。
變更為專案根目錄
cd $proj
helm template istio-1.0.0/install/kubernetes/helm/istio-remote --namespace istio-system \
--name istio-remote \
--set global.remotePilotAddress=${PILOT_POD_IP} \
--set global.remotePolicyAddress=${POLICY_POD_IP} \
--set global.remoteTelemetryAddress=${TELEMETRY_POD_IP} \
--set global.proxy.envoyStatsd.enabled=true \
--set global.proxy.envoyStatsd.host=${STATSD_POD_IP} \
--set global.remoteZipkinAddress=${ZIPKIN_POD_IP} > istio-remote-burst.yaml
在爆發叢集上安裝 Istio Remote
如要在 burst 叢集中安裝 Istio,請按照在 primary 叢集中安裝時的步驟操作,但請改用 istio-remote-burst.yaml 檔案。
將 kubecontext 變更為 burst
kubectx burst
建立 istio-system 命名空間
kubectl create ns istio-system
套用 istio-burst.yaml
kubectl apply -f istio-remote-burst.yaml
標籤預設命名空間
同樣地,我們需要標記 default 命名空間,讓 Proxy 能夠自動插入。
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
恭喜!目前,我們已在 burst 叢集上設定 Istio Remote。不過,叢集目前仍無法進行通訊。我們需要為 burst 叢集產生 kubeconfig 檔案,以便部署至 primary 叢集,並將兩者連結在一起。
為「burst」叢集建立 kubeconfig
變更為突發叢集
kubectx burst
設定環境
我們需要收集叢集的相關資訊,才能為叢集建立 kubeconfig 檔案。
- 取得叢集名稱
CLUSTER_NAME=$(kubectl config view --minify=true -o "jsonpath={.clusters[].name}")
- 取得叢集伺服器名稱
SERVER=$(kubectl config view --minify=true -o "jsonpath={.clusters[].cluster.server}")
- 取得
istio-multi服務帳戶憑證授權單位的密鑰名稱
SECRET_NAME=$(kubectl get sa istio-multi -n istio-system -o jsonpath='{.secrets[].name}')
- 取得先前機密金鑰中儲存的憑證授權單位資料
CA_DATA=$(kubectl get secret ${SECRET_NAME} -n istio-system -o "jsonpath={.data['ca\.crt']}")
- 取得先前機密中儲存的權杖
TOKEN=$(kubectl get secret ${SECRET_NAME} -n istio-system -o "jsonpath={.data['token']}" | base64 --decode)
建立 kubeconfig 檔案
設定所有環境變數後,我們需要建立 kubeconfig 檔案
cat <<EOF > burst-kubeconfig
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: ${CA_DATA}
server: ${SERVER}
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
contexts:
- context:
cluster: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
user: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
current-context: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
user:
token: ${TOKEN}
EOF
這會在目前目錄中建立名為 burst-kubeconfig 的新檔案,primary 叢集可使用這個檔案驗證及管理 burst 叢集。
改回主要叢集
kubectx primary
建立密鑰並加上標籤,套用「burst」的 kubeconfig
kubectl create secret generic burst-kubeconfig --from-file burst-kubeconfig -n istio-system
為密鑰加上標籤,讓 Istio 知道要將其用於多叢集驗證
kubectl label secret burst-kubeconfig istio/multiCluster=true -n istio-system
恭喜!我們已驗證兩個叢集,並透過 Istio 多叢集功能相互通訊。讓我們部署跨叢集應用程式
15. 部署跨叢集應用程式
建立部署作業
切換至 kubernetes 目錄
cd ${proj}/kubernetes
為「burst」叢集建立 worker 部署作業:worker-burst.yaml
建立名為 worker-burst.yaml 的檔案,並插入以下內容:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: worker-deployment
labels:
app: worker
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: worker
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: worker
cluster-type: burst-cluster
spec:
containers:
- name: worker
image: gcr.io/istio-burst-workshop/worker
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8081
readinessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/_healthz"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-readiness-probe"
livenessProbe:
initialDelaySeconds: 10
httpGet:
path: "/"
port: 8081
httpHeaders:
- name: "Cookie"
value: "istio_session-id=x-liveness-probe"
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8081"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
- name: PREFIX
value: "bursty-"
請注意,這幾乎與先前建立的 worker-primary.yaml 完全相同。兩者之間有兩個主要差異。
第一個主要差異是我們新增了 PREFIX 環境變數,其值為「bursty-」
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8081"
- name: REDIS_URL
value: "redis-cache-service:6379"
- name: PREFIX
value: "bursty-"
這表示 burst 叢集中的工作者會在傳送的所有雜湊前方加上「bursty-」,我們可以利用這項資訊判斷應用程式是否確實跨叢集。
第二個主要差異是,我們將此部署作業的 cluster-type 標籤從 primary-cluster 變更為 burst-cluster
labels:
app: worker
cluster-type: burst-cluster
我們會在稍後更新 VirtualService 時使用這個標籤。
修改 Istio 服務
目前,我們的 Istio 服務並未充分利用這兩個部署項目。100% 的流量都會轉送至「primary」叢集。我們來調整一下吧!
切換至 istio-manifests 目錄
cd ${proj}/istio-manifests
編輯 worker-virtualservice.yaml 以加入 DestinationRules
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 50
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 50
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: worker-destination-rule
spec:
host: worker-service
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: RANDOM
subsets:
- name: primary
labels:
cluster-type: primary-cluster
- name: burst
labels:
cluster-type: burst-cluster
您可以看到我們已在 VirtualService 中新增第二個目的地。它仍會參照相同的主機 (worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local)),但 50% 的流量會路由至 primary 子集,而其他 50% 會路由至 burst 子集。
我們將 primary 子集定義為標籤為 cluster-type: primary-cluster 的部署,而 burst 子集則是標籤為 cluster-type: burst-cluster 的部署。
這樣一來,兩個叢集的流量就會以 50/50 的比例分配。
部署至叢集
將 redis-service.yaml 部署至爆發叢集
變更為 burst kubeconfig
kubectx burst
變更至專案根目錄
cd ${proj}
然後部署
將 redis-service.yaml 部署至爆發叢集
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/redis-service.yaml
將 worker-burst.yaml 部署至 burst 叢集
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/worker-burst.yaml
將 worker-service.yaml 部署至爆發叢集
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/worker-service.yaml
套用 Istio VirtualServices
變更為 primary kubeconfig
kubectx primary
然後部署
kubectl apply -f istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml
驗證是否運作正常
如要確認是否正常運作,請瀏覽 Istio Ingress 點,並注意約 50% 的雜湊字串前置字串為「burst-」。
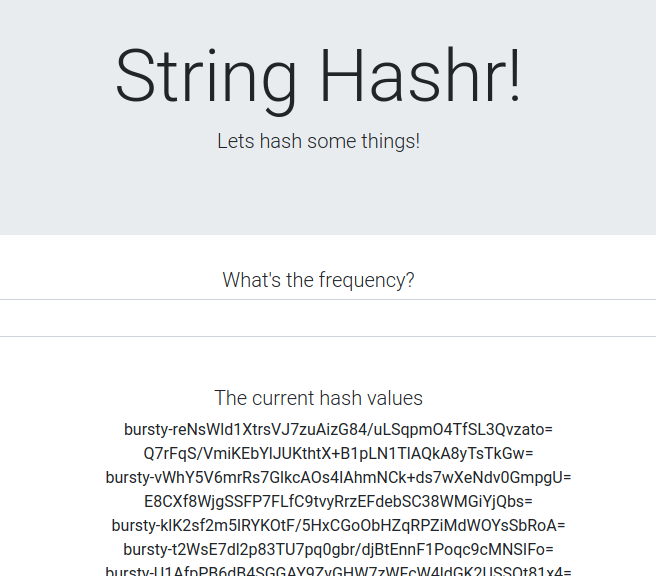
這表示我們已成功跨叢集通訊!請嘗試變更不同服務的權重,並套用 worker-virtualservice.yaml 檔案。這是平衡叢集間流量的好方法,但如果能自動執行這項操作,那就更棒了。
16. 善用 Prometheus 指標
Prometheus 簡介
Prometheus 是開放原始碼系統監控與快訊工具包,最初是在 SoundCloud 上打造。這個資料集會維護多維度資料模型,其中時間序列資料會以指標名稱和鍵/值組合來識別。
以下是 Prometheus 架構圖,供您參考:
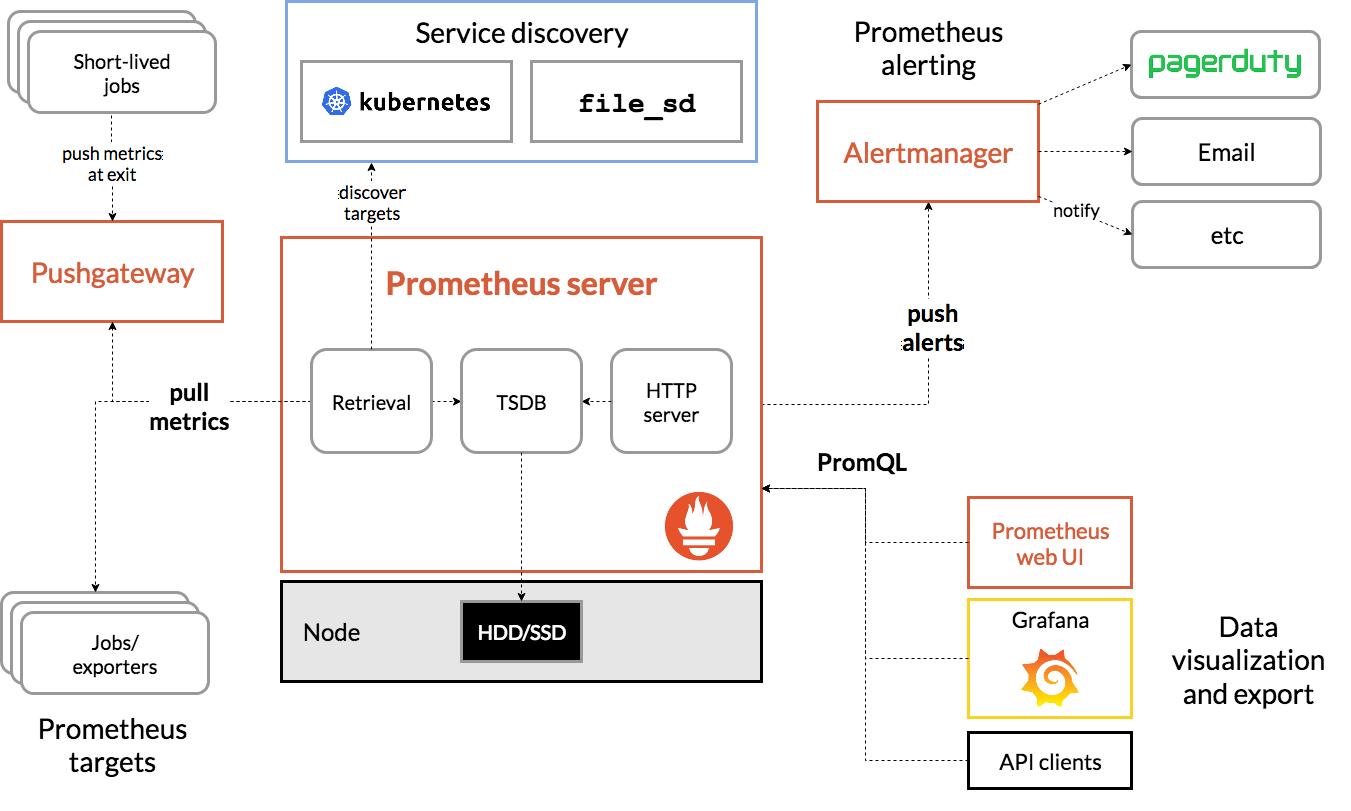
當 Istio 與 Prometheus 一併部署時,會自動將各種指標回報至 Prometheus 伺服器。我們可以使用這些指標即時管理叢集。
探索 Prometheus 指標
首先,我們需要公開 Prometheus 部署作業。
前往 GKE 的「Workloads」(工作負載) 分頁,然後深入查看「prometheus」工作負載。
查看部署作業詳細資料後,請依序前往「Actions」>「Expose」。
選擇轉送至 9090 通訊埠,然後輸入「負載平衡器」
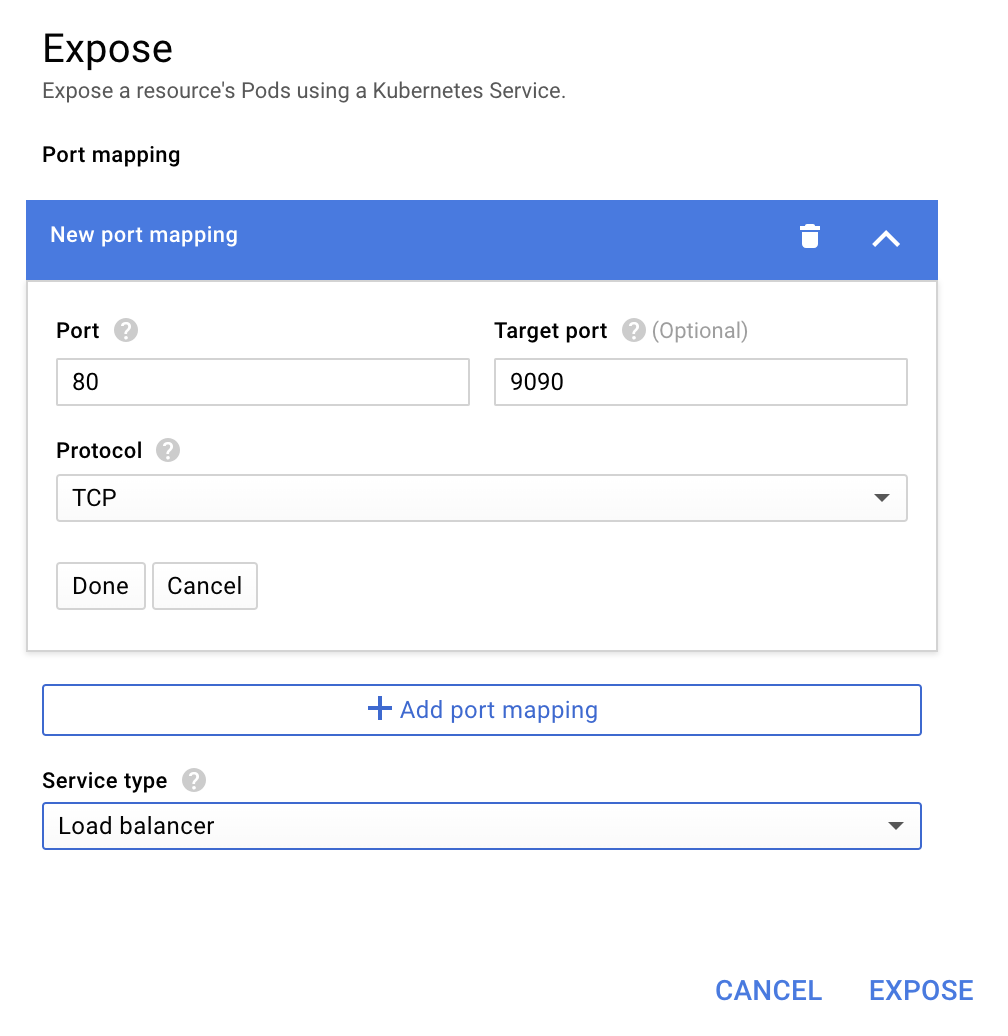
並選擇「曝光」。
這會在可公開存取的 IP 位址上建立服務,我們可以用來探索 Prometheus 指標
等待端點開始運作,然後按一下「外部端點」旁的 IP 位址 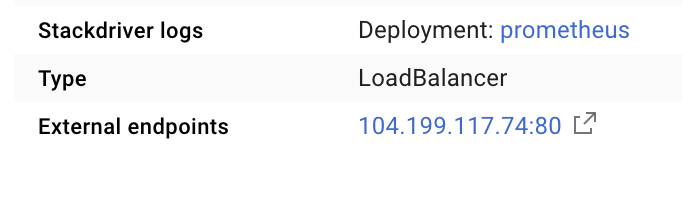
您現在應該會看到 Prometheus UI。
Prometheus 提供足夠的指標,可做為單獨的工作坊。不過,我們先來探討 istio_requests_total 指標。
執行這項查詢會傳回大量資料。這是所有透過 Istio 服務網格傳送的要求的指標,而且數量龐大!我們會修改運算式,篩選出我們真正感興趣的內容:
要求的目的服務為 worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local,且來源為 frontend-deployment,且限制在過去 15 秒內
查詢如下所示:
istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s]
並提供更容易管理的資料
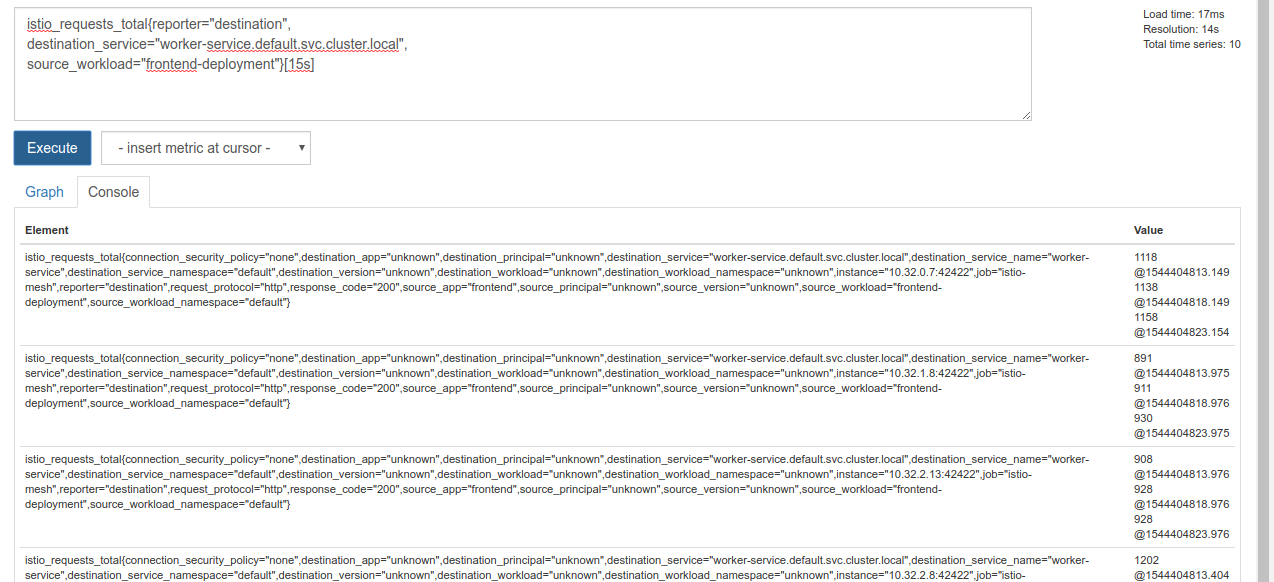
但還是有點密集。我們想知道每秒的請求次數,而不是所有要求。
為此,我們可以使用內建的 rate 函式
rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s])

這有助於我們更接近目標,但我們需要進一步將這些指標縮減為邏輯群組。
為此,我們可以使用 sum 和 by 關鍵字來分組及加總結果
sum(rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s])) by (source_workload,
source_app, destination_service)
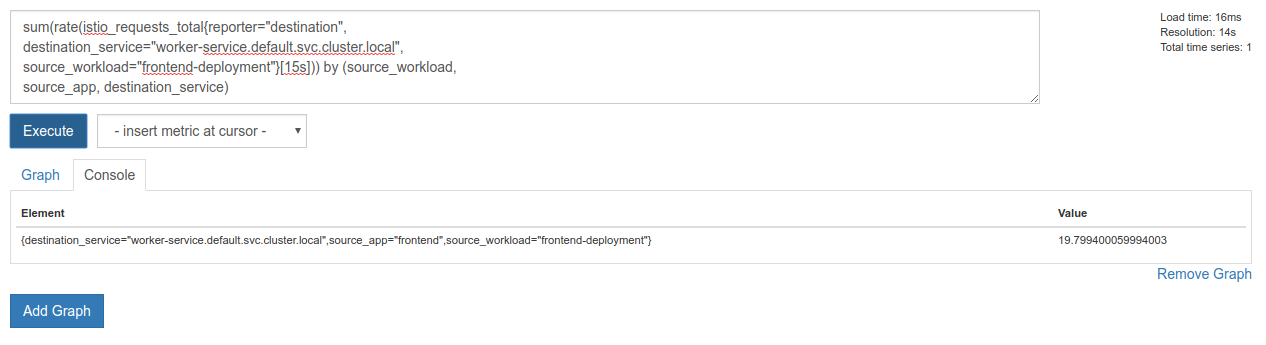
太棒了,我們可以從 Prometheus 取得所需的確切指標。
最終 Prometheus 查詢
根據我們所學到的一切,我們需要向 Prometheus 提出的最終查詢為
sum(rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",
destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s])) by (source_workload,
source_app, destination_service)
我們現在可以使用他們的 HTTP API 取得指標。
我們可以透過發出 HTTP GET 要求,以自己的查詢來查詢 Prometheus 的 API,請按照以下方式進行。請將 <prometheus-ip-here> 替換為 Prometheus 的 IP 位址。
curl http://<prometheus-ip-here>/api/v1/query?query=sum\(rate\(istio_requests_total%7Breporter%3D%22destination%22%2C%0Adestination_service%3D%22worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local%22%2C%0Asource_workload%3D%22frontend-deployment%22%7D%5B15s%5D\)\)%20by%20\(source_workload%2C%0Asource_app%2C%20destination_service\)
回覆範例如下:
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"resultType": "vector",
"result": [
{
"metric": {
"destination_service": "worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",
"source_app": "frontend",
"source_workload": "frontend-deployment"
},
"value": [
1544404907.503,
"18.892886390062788"
]
}
]
}
}
我們現在可以從 JSON 中擷取指標值
清除
我們需要刪除剛剛用來公開 Prometheus 的服務。在 Google Cloud 控制台中,前往我們剛建立的服務頂端,然後點選「刪除」
後續步驟:
我們已經找到方法,瞭解流量如何在叢集中移動,以及移動速度,接下來要做的是編寫一個小型二進位檔,定期查詢 Prometheus。如果 worker 的每秒要求數超過特定門檻,就會在 worker 虛擬服務上套用不同的目的地權重,將所有流量傳送至 burst 叢集。當每秒要求次數低於較低門檻時,請將所有流量傳回 primary。
17. 建立跨叢集爆發事件
設定方式
將 worker-service 的所有流量設為主要叢集
我們會將所有目的地為 worker-service 的流量,且已路由至 primary 叢集的流量視為應用程式的「預設」狀態
請將 $proj/istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml 編輯成如下所示
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 100
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 0
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: worker-destination-rule
spec:
host: worker-service
trafficPolicy:
loadBalancer:
simple: RANDOM
subsets:
- name: primary
labels:
cluster-type: primary-cluster
- name: burst
labels:
cluster-type: burst-cluster
確認您已連線至 primary 叢集
kubectx primary
套用 istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml
kubectl apply -f istio-manifests/worker-virtualservice.yaml
編寫 istiowatcher 守護程式
我們將使用 Go 編寫這項服務,以便享有速度和可攜性。應用程式的整體流程會啟動,並每秒查詢 Prometheus。
在 src 中建立名為 istiowatcher 的新目錄
mkdir -p ${proj}/src/istiowatcher && cd ${proj}/src/istiowatcher
我們會從容器內呼叫 istioctl,以便在叢集中操控 Istio 控制平面。
編寫 istiowatcher.go
在該目錄中建立名為 istiowatcher.go 的檔案,並在其中插入下列內容
package main
import (
"github.com/tidwall/gjson"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"os/exec"
"time"
)
func main() {
//These are in requests per second
var targetLow float64 = 10
var targetHigh float64 = 15
// This is for the ticker in milliseconds
ticker := time.NewTicker(1000 * time.Millisecond)
isBurst := false
// Our prometheus query
reqQuery := `/api/v1/query?query=sum(rate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination",destination_service="worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local",source_workload="frontend-deployment"}[15s]))by(source_workload,source_app,destination_service)`
for t := range ticker.C {
log.Printf("Checking Prometheus at %v", t)
// Check prometheus
// Note that b/c we are querying over the past 5 minutes, we are getting a very SLOW ramp of our reqs/second
// If we wanted this to be a little "snappier" we can scale it down to say 30s
resp, err := http.Get("http://prometheus.istio-system.svc.cluster.local:9090" + reqQuery)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Error: %v", err)
continue
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
val := gjson.Get(string(body), "data.result.0.value.1")
log.Printf("Value: %v", val)
currentReqPerSecond := val.Float()
log.Printf("Reqs per second %f", currentReqPerSecond)
if currentReqPerSecond > targetHigh && !isBurst {
applyIstio("burst.yaml")
log.Println("Entering burst mode")
isBurst = true
} else if currentReqPerSecond < targetLow && isBurst {
applyIstio("natural.yaml")
log.Println("Returning to natural state.")
isBurst = false
}
}
}
func applyIstio(filename string) {
cmd := exec.Command("istioctl", "replace", "-f", filename)
if err := cmd.Run(); err != nil {
log.Printf("Error hit applying istio manifests: %v", err)
}
}
編寫 Dockerfile
建立名為 Dockerfile 的新檔案,並在其中插入下列內容。
FROM golang:1.11.2-stretch as base
FROM base as builder
WORKDIR /workdir
RUN curl -LO https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.0.0/istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
RUN tar xzf istio-1.0.0-linux.tar.gz
RUN cp istio-1.0.0/bin/istioctl ./istioctl
FROM base
WORKDIR /go/src/istiowatcher
COPY . .
COPY --from=builder /workdir/istioctl /usr/local/bin/istioctl
RUN go get -d -v ./...
RUN go install -v ./...
CMD ["istiowatcher"]
這個多階段 Dockerfile 會在第一個階段下載並解壓縮 Istio 1.0.0 版本。第二個階段會將目錄中的所有內容複製到映像檔,然後將 istioctl 從建構階段複製到 /usr/local/bin (以便讓應用程式呼叫),取得依附元件、編譯程式碼,並將 CMD 設為「istiowatcher」。
編寫 burst.yaml
當 frontend 對 worker 的每秒要求次數超過 15 時,istiowatcher 就會套用這個檔案。
建立名為 burst.yaml 的新檔案,並在其中插入下列內容。
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 0
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 100
編寫 natural.yaml
當 frontend 到 worker 的每秒要求次數低於 10 時,我們會將此視為「自然」狀態。在這個狀態下,100% 的流量都會轉送至 primary 叢集。
建立名為 natural.yaml 的新檔案,並在其中插入下列內容
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: worker-virtual-service
spec:
hosts:
- worker-service
gateways:
- mesh
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: primary
port:
number: 80
weight: 100
- destination:
host: worker-service.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: burst
port:
number: 80
weight: 0
建構及推送 istiowatcher
執行下列指令,將目前目錄傳送至 Google Cloud Build (GCB),GCB 會在 GCR 中建構並標記映像檔。
gcloud builds submit -t gcr.io/${GCLOUD_PROJECT}/istiowatcher
部署 istiowatcher
切換至 kubernetes 目錄
cd ${proj}/kubernetes/
編寫部署檔案:istiowatcher.yaml
建立名為 istiowatcher.yaml 的檔案,然後插入以下內容 (請替換 <your-project-id>)。
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: istiowatcher-deployment
labels:
app: istiowatcher
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: istiowatcher
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: istiowatcher
spec:
serviceAccountName: istio-pilot-service-account
automountServiceAccountToken: true
containers:
- name: istiowatcher
image: gcr.io/<your-project-id>/istiowatcher
imagePullPolicy: Always
部署
確認我們是在主要叢集中執行
kubectx primary
在 istio-system 命名空間中部署 istiowatcher.yaml
kubectl apply -n istio-system -f istiowatcher.yaml
請注意 yaml 中的 serviceAccountName 和 automountServiceAccountToken 指令。這樣一來,我們就能取得在叢集內執行 istioctl 所需的憑證。
我們也需要在 istio-system 命名空間中部署這項作業,確保我們擁有 istio-pilot-service-account 的憑證。(它不存在於 default 命名空間中)。
觀看流量自動切換!
接下來是神奇時刻!讓我們前往前端,將每秒要求次數調高至 20
請注意,這項作業需要幾秒鐘的時間,但我們會加快速度,所有雜湊都會加上「bursty-」前置字串!
這是因為我們會在 15s 範圍內取樣 Prometheus,因此回應時間會稍微延遲。如果想縮小頻寬,可以將 Prometheus 查詢變更為 5s.
18. 接下來要做什麼?
清除
如果您使用的是本工作坊提供的臨時帳戶,則不需要清理。
您可以刪除 Kubernetes 叢集、防火牆規則和 GCR 中的映像檔
gcloud container clusters delete primary --zone=us-west1-a
gcloud container clusters delete burst --zone=us-west1-a
gcloud compute firewall-rules delete istio-multicluster-test-pods
gcloud container images delete gcr.io/$GCLOUD_PROJECT/istiowatcher
未來展望
- 參加 Istio 講座!
- 取得認證:使用 Kubernetes 和 Istio 建構下一個應用程式
- Keynote:Kubernetes、Istio、Knative:新的開放式雲端技術堆疊 - Google Kubernetes 產品群經理 Aparna Sinha
- 教學課程:使用 Istio - SolarWinds 的 Lee Calcote 和 Girish Ranganathan
- Istio - The Packet's-Eye View - Matt Turner, Tetrate
- Istio 是否為有史以來最先進的新一代防火牆?- Twistlock 的 John Morello
- 參閱 Istio 說明文件
- 加入 Istio 工作群組
- 在 Twitter 上追蹤 @IstioMesh