关于此 Codelab
1. 简介
Compose 和 View 系统可以结合使用。
在此 Codelab 中,您需要将 Sunflower 的部分植物详情界面迁移到 Compose。我们创建了项目副本,这样一来您可以尝试将一个真实的应用迁移到 Compose。
完成此 Codelab 后,您将能够继续进行迁移,并根据需要转换 Sunflower 剩余的界面。
如果您在学习此 Codelab 的过程中需要获得更多支持,请查看以下配套学习代码:
学习内容
在此 Codelab 中,您将学习:
- 可以遵循的不同迁移路径
- 如何逐步将应用迁移到 Compose
- 如何将 Compose 添加到使用 View 构建的现有界面
- 如何在 Compose 中使用 View
- 如何在 Compose 中创建主题
- 如何测试使用 View 和 Compose 编写的混合界面
前提条件
- 有使用 Kotlin 语法(包括 lambda)的经验
- 了解 Compose 的基础知识
所需条件
2. 迁移策略
Jetpack Compose 从设计之初就考虑到了 View 互操作性。如需迁移到 Compose,我们建议您执行增量迁移(Compose 和 View 在代码库中共存),直到应用完全迁移至 Compose 为止。
推荐的迁移策略如下:
- 使用 Compose 构建新界面
- 在构建功能时,确定可重复使用的元素,并开始创建常见界面组件库
- 一次替换一个界面的现有功能
使用 Compose 构建新界面
使用 Compose 构建覆盖整个界面的新功能是提高 Compose 采用率的最佳方式。借助此策略,您可以添加功能并利用 Compose 的优势,同时仍满足公司的业务需求
一项新功能可能涵盖整个界面,在这种情况下,整个界面都在 Compose 中。如果您使用的是基于 fragment 的导航,这意味着您需要创建一个新的 fragment,并在 Compose 中添加其内容。
您还可以在现有界面中引入新功能。在这种情况下,View 和 Compose 将共存在同一个界面上。例如,假设您要添加的功能是 RecyclerView 中的一种新的视图类型。在这种情况下,新的视图类型将位于 Compose 中,而其他项目保持不变。
构建常见界面组件库
使用 Compose 构建功能时,您很快就会意识到,您最终会构建组件库。您需要确定可重复使用的组件,促使在应用中重复使用这些组件,以便共享组件具有单一可信来源。您构建的功能随后可以依赖于这个库。
使用 Compose 替换现有功能
除了构建新功能之外,您还需要逐步将应用中的现有功能迁移到 Compose。具体采用哪种方法由您决定,下面是一些适合的方法:
- 简单界面 - 包含少数界面元素和动态元素(例如欢迎界面、确认界面或设置界面)的简单界面。这些界面非常适合迁移到 Compose,因为只需几行代码就能搞定。
- 混合 View 和 Compose 界面 - 已包含少量 Compose 代码的界面是另一个不错的选择,因为您可以继续逐步迁移该界面中的元素。如果您的某个界面在 Compose 中只有一个子树,您可以继续迁移该树的其他部分,直到整个界面位于 Compose 中。这称为自下而上的迁移方法。
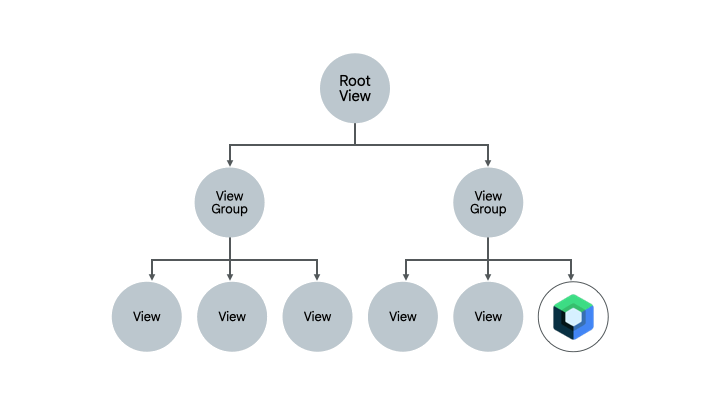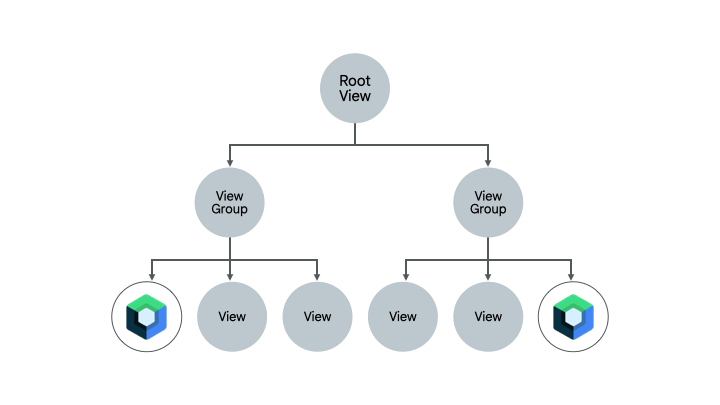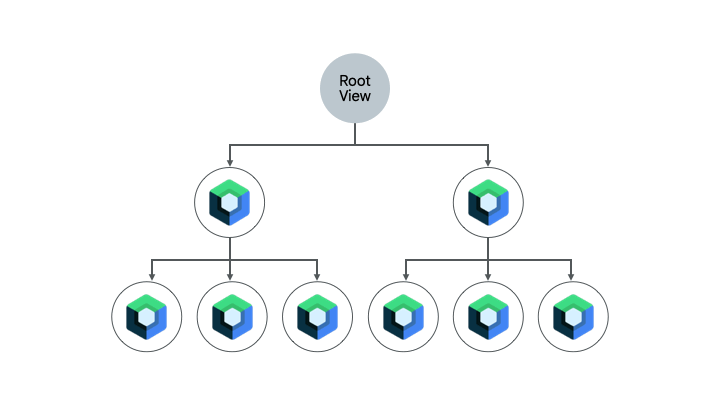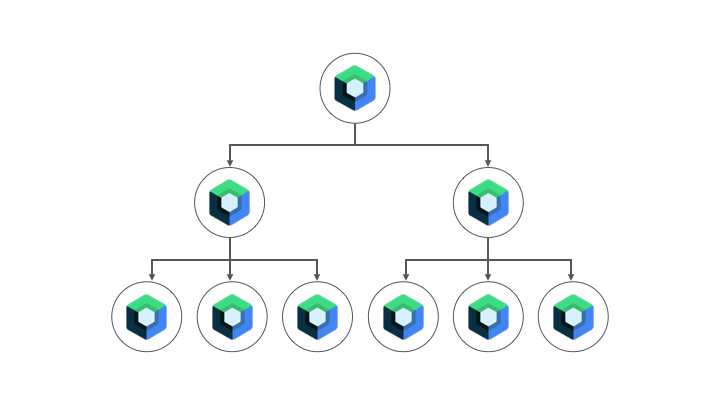
此 Codelab 采用的方法
在此 Codelab 中,您将逐步把 Sunflower 的植物详情界面迁移到 Compose,将 Compose 和 View 结合起来使用。之后,您将掌握足够的知识,可以在需要时继续进行迁移。
3. 准备工作
获取代码
从 GitHub 获取 Codelab 代码:
$ git clone https://github.com/android/codelab-android-compose
或者,您也可以下载 ZIP 文件形式的仓库:
运行示例应用
您刚刚下载的代码包含提供的所有 Compose Codelab 的代码。为了完成此 Codelab,请在 Android Studio 中打开 MigrationCodelab 项目。
在此 Codelab 中,您需要将 Sunflower 的植物详情界面迁移到 Compose。点按植物列表界面中显示的某个植物,即可打开植物详情界面。
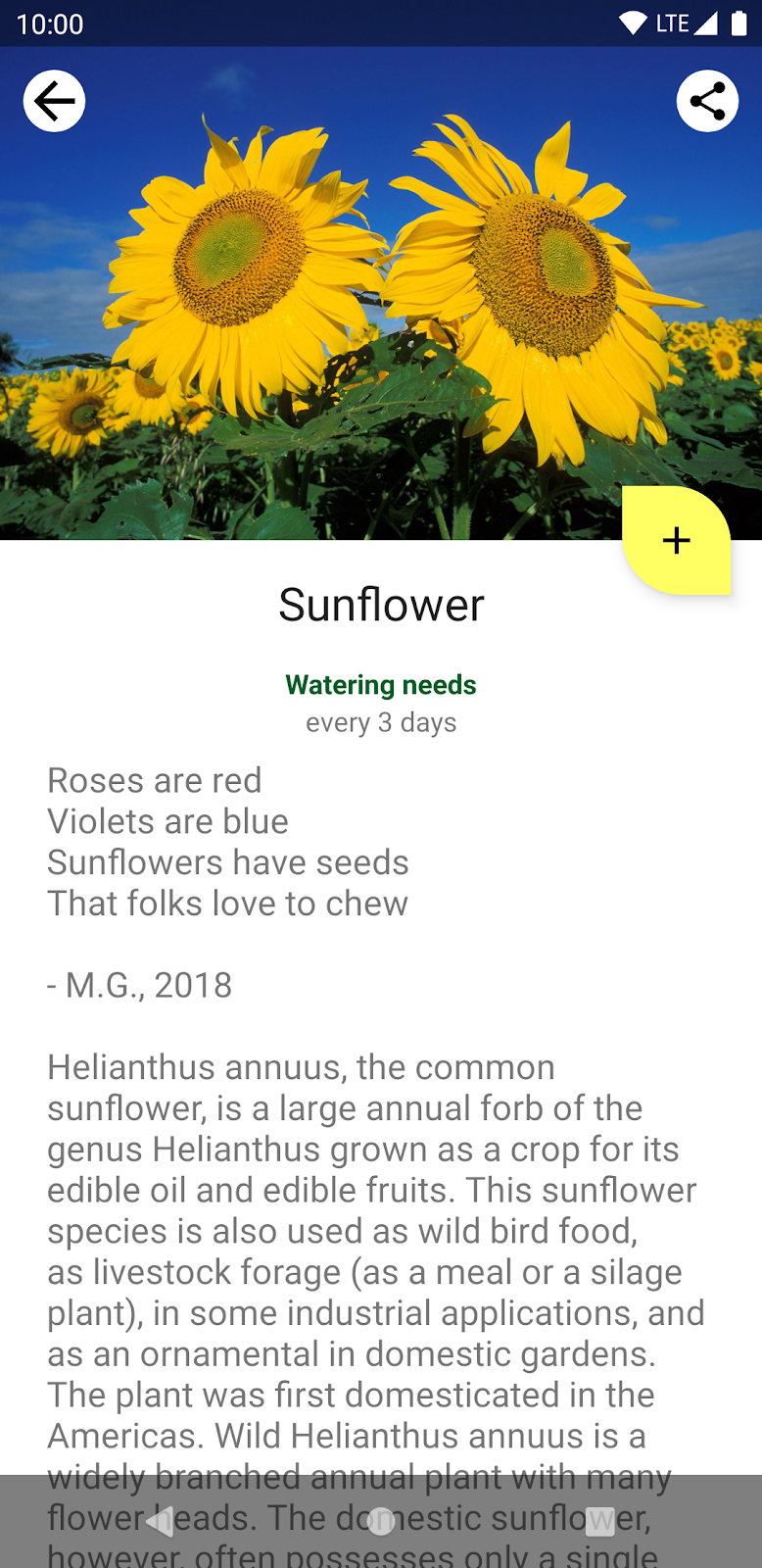
项目设置
此项目使用了多个 Git 分支进行构建:
main分支是此 Codelab 的起点。end包含此 Codelab 的解决方案。
建议您从 main 分支中的代码着手,按照自己的节奏逐步完成此 Codelab。
在本 Codelab 中,系统会为您显示需要添加到项目的代码段。在某些地方,您还需要移除在代码段的注释中明确提及的代码。
如需使用 git 获取 end 分支,请使用 cd 指令进入 MigrationCodelab 项目的目录中,然后使用以下命令:
$ git checkout end
或从此处下载解决方案代码:
常见问题解答
4. Sunflower 中的 Compose
Compose 已添加到您从 main 分支下载的代码中。不过,我们先来了解一下运行这些代码需要具备哪些条件。
打开应用级 build.gradle 文件后,查看该文件如何导入 Compose 依赖项,以及如何使用 buildFeatures { compose true } 标志让 Android Studio 能够运行 Compose。
app/build.gradle
android {
//...
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = '1.8'
}
buildFeatures {
//...
compose true
}
composeOptions {
kotlinCompilerExtensionVersion '1.3.2'
}
}
dependencies {
//...
// Compose
def composeBom = platform('androidx.compose:compose-bom:2024.09.02')
implementation(composeBom)
androidTestImplementation(composeBom)
implementation "androidx.compose.runtime:runtime"
implementation "androidx.compose.ui:ui"
implementation "androidx.compose.foundation:foundation"
implementation "androidx.compose.foundation:foundation-layout"
implementation "androidx.compose.material3:material3"
implementation "androidx.compose.runtime:runtime-livedata"
implementation "androidx.compose.ui:ui-tooling"
//...
}
这些依赖项的版本在项目级 build.gradle 文件中定义。
5. 欢迎使用 Compose!
在植物详情界面中,我们需要将对植物的说明迁移到 Compose,同时让界面的总体结构保持完好。
Compose 需要有宿主 activity 或 fragment 才能呈现界面。在 Sunflower 中,所有界面都使用 fragment,因此您需要使用 ComposeView:这一 Android View 可以使用其 setContent 方法托管 Compose 界面内容。
移除 XML 代码
我们先从迁移开始!打开 fragment_plant_detail.xml 并执行以下操作:
- 切换到代码视图
- 移除
NestedScrollView中的ConstraintLayout代码和嵌套的 4 个TextView(此 Codelab 会在迁移各项内容时比较和引用 XML 代码,将该代码注释掉会非常有用) - 添加一个
ComposeView,它会改为托管 Compose 代码,并以compose_view作为视图 ID
fragment_plant_detail.xml
<androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView
android:id="@+id/plant_detail_scrollview"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:clipToPadding="false"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/fab_bottom_padding"
app:layout_behavior="@string/appbar_scrolling_view_behavior">
<!-- Step 2) Comment out ConstraintLayout and its children –->
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="@dimen/margin_normal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/plant_detail_name"
...
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
<!-- End Step 2) Comment out until here –->
<!-- Step 3) Add a ComposeView to host Compose code –->
<androidx.compose.ui.platform.ComposeView
android:id="@+id/compose_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView>
添加 Compose 代码
现在,您可以开始将植物详情界面迁移到 Compose 了!
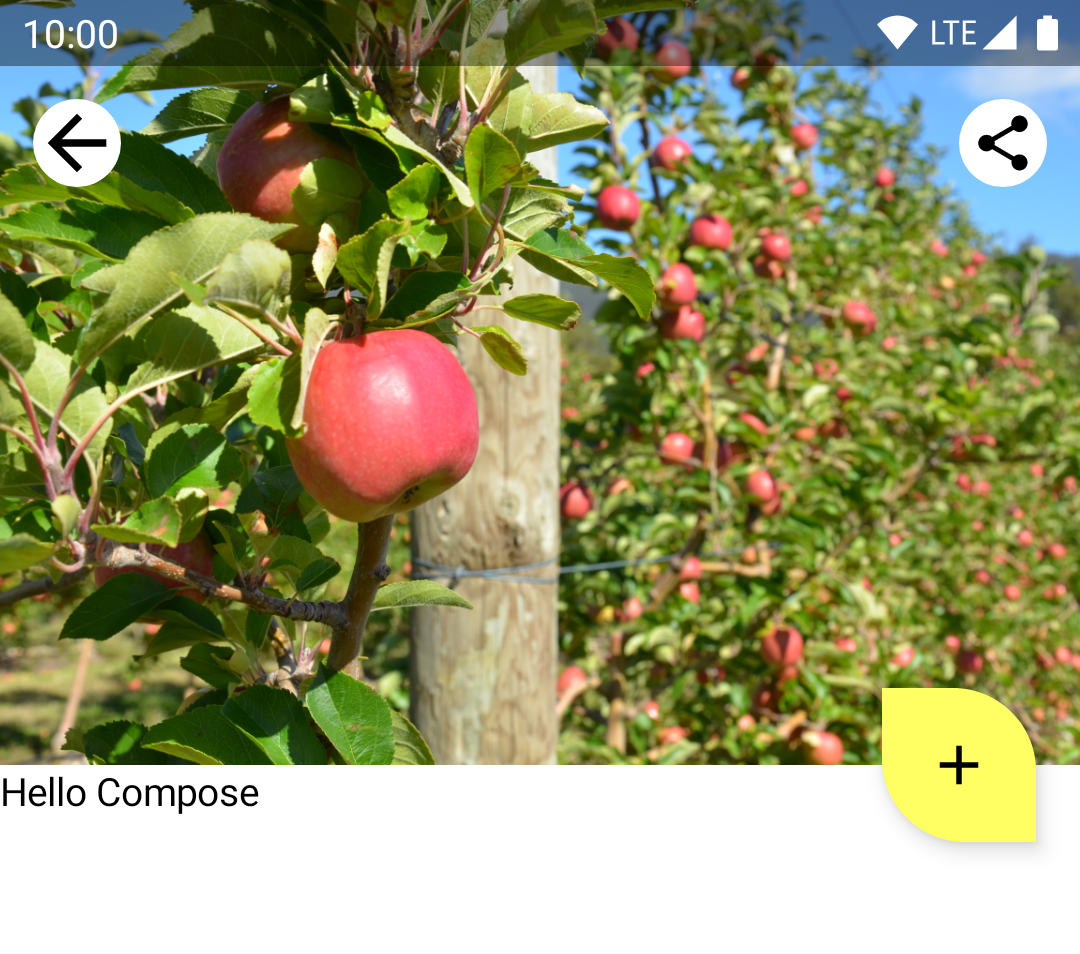
在整个 Codelab 中,您都需要将 Compose 代码添加到 plantdetail 文件夹下的 PlantDetailDescription.kt 文件中。打开该文件,看看项目中是否有占位符 "Hello Compose" 文本。
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Composable
fun PlantDetailDescription() {
Surface {
Text("Hello Compose")
}
}
我们从在上一步中添加的 ComposeView 中调用此可组合项,即可在界面上显示此内容。打开 PlantDetailFragment.kt。
界面使用的是数据绑定,因此您可以直接访问 composeView 并调用 setContent,以便在界面上显示 Compose 代码。您需要在 MaterialTheme 内调用 PlantDetailDescription 可组合项,因为 Sunflower 使用的是 Material Design。
PlantDetailFragment.kt
class PlantDetailFragment : Fragment() {
// ...
override fun onCreateView(...): View? {
val binding = DataBindingUtil.inflate<FragmentPlantDetailBinding>(
inflater, R.layout.fragment_plant_detail, container, false
).apply {
// ...
composeView.setContent {
// You're in Compose world!
MaterialTheme {
PlantDetailDescription()
}
}
}
// ...
}
}
如果您运行该应用,界面上会显示“Hello Compose”。
6. 使用 XML 创建可组合项
我们首先迁移植物的名称。更确切地说,就是您在 fragment_plant_detail.xml 中移除的 ID 为 @+id/plant_detail_name 的 TextView。XML 代码如下:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/plant_detail_name"
...
android:layout_marginStart="@dimen/margin_small"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/margin_small"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="@{viewModel.plant.name}"
android:textAppearance="?attr/textAppearanceHeadline5"
... />
请查看它是否为 textAppearanceHeadline5 样式,水平外边距为 8.dp,以及是否在界面上水平居中。不过,要显示的标题是从由代码库层的 PlantDetailViewModel 公开的 LiveData 中观察到的。
如何观察 LiveData 将在稍后介绍,因此先假设我们有可用的名称,并以参数形式将其传递到我们在 PlantDetailDescription.kt 文件中创建的新 PlantName 可组合项。稍后,将从 PlantDetailDescription 可组合项调用此可组合项。
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Composable
private fun PlantName(name: String) {
Text(
text = name,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall,
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(horizontal = dimensionResource(R.dimen.margin_small))
.wrapContentWidth(Alignment.CenterHorizontally)
)
}
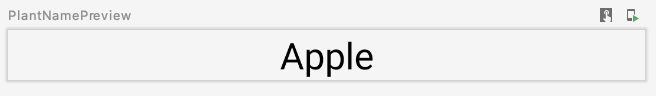
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantNamePreview() {
MaterialTheme {
PlantName("Apple")
}
}
预览如下:
其中:
Text的样式为MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall,类似于 XML 代码中的textAppearanceHeadline5。- 修饰符会修饰 Text,使其看起来像 XML 版本:
- 使用
fillMaxWidth修饰符,使其占据最大可用宽度。此修饰符对应于 XML 代码中layout_width属性的match_parent值。 - 使用
padding修饰符,以便应用水平内边距值margin_small。这对应于 XML 中的marginStart和marginEnd声明。margin_small值也是使用dimensionResource辅助函数提取的现有尺寸资源。 wrapContentWidth修饰符用于对齐文本,以使其水平居中。这类似于在 XML 中gravity为center_horizontal。
7. ViewModel 和 LiveData
现在,我们将标题连接到界面。如需执行此操作,您需要使用 PlantDetailViewModel 加载数据。为此,Compose 集成了 ViewModel 和 LiveData。
ViewModels
由于在 fragment 中使用了 PlantDetailViewModel 的实例,因此我们可以将其作为参数传递给 PlantDetailDescription,就这么简单。
打开 PlantDetailDescription.kt 文件,然后将 PlantDetailViewModel 参数添加到 PlantDetailDescription:
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Composable
fun PlantDetailDescription(plantDetailViewModel: PlantDetailViewModel) {
//...
}
现在,请在从 fragment 调用此可组合项时传递 ViewModel 实例:
PlantDetailFragment.kt
class PlantDetailFragment : Fragment() {
...
override fun onCreateView(...): View? {
...
composeView.setContent {
MaterialTheme {
PlantDetailDescription(plantDetailViewModel)
}
}
}
}
LiveData
有了 LiveData,您已有权访问 PlantDetailViewModel 的 LiveData<Plant> 字段,以获取植物的名称。
如需从可组合项观察 LiveData,请使用 LiveData.observeAsState() 函数。
由于 LiveData 发出的值可以是 null,因此您需要将其用例封装在 null 检查中。有鉴于此,以及为了实现可重用性,最好将 LiveData 的使用和监听拆分到不同的可组合项中。因此,我们来创建一个名为 PlantDetailContent 的新可组合项,用于显示 Plant 信息。
完成这些更新后,PlantDetailDescription.kt 文件现在应如下所示:
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Composable
fun PlantDetailDescription(plantDetailViewModel: PlantDetailViewModel) {
// Observes values coming from the VM's LiveData<Plant> field
val plant by plantDetailViewModel.plant.observeAsState()
// If plant is not null, display the content
plant?.let {
PlantDetailContent(it)
}
}
@Composable
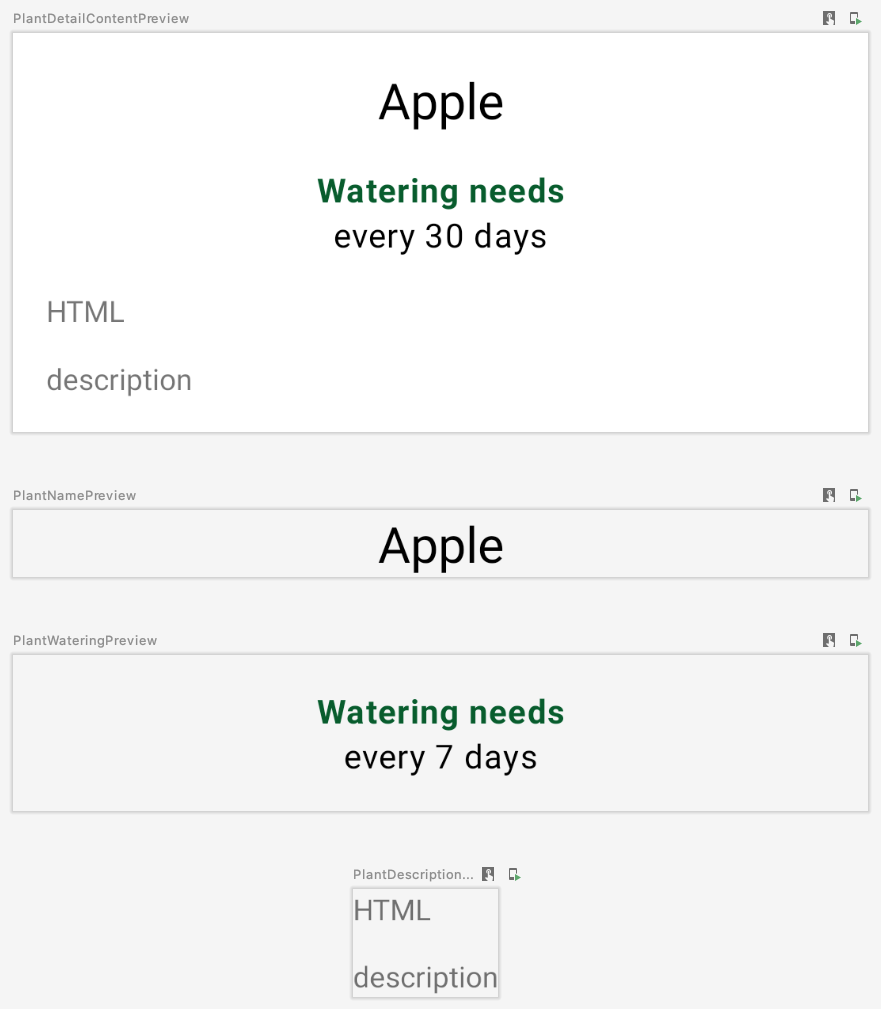
fun PlantDetailContent(plant: Plant) {
PlantName(plant.name)
}
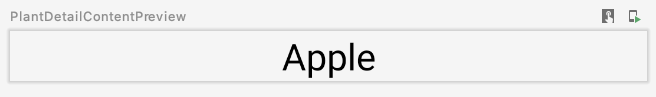
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantDetailContentPreview() {
val plant = Plant("id", "Apple", "description", 3, 30, "")
MaterialTheme {
PlantDetailContent(plant)
}
}
PlantNamePreview 应反映我们的更改,而无需直接更新,因为 PlantDetailContent 仅调用 PlantName:
现在,您已连接 ViewModel,使植物名称能在 Compose 中显示。在接下来的几部分中,您将构建其余可组合项,并以类似的方式将它们连接到 ViewModel。
8. 更多 XML 代码迁移
现在,我们可以更轻松地将界面中缺少的内容补充完整:浇水信息和植物说明。您已经可以按照与之前类似的方法迁移界面的其余部分了。
您之前从 fragment_plant_detail.xml 移除的浇水信息 XML 代码由两个 ID 为 plant_watering_header 和 plant_watering 的 TextView 组成。
<TextView
android:id="@+id/plant_watering_header"
...
android:layout_marginStart="@dimen/margin_small"
android:layout_marginTop="@dimen/margin_normal"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/margin_small"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="@string/watering_needs_prefix"
android:textColor="?attr/colorAccent"
android:textStyle="bold"
... />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/plant_watering"
...
android:layout_marginStart="@dimen/margin_small"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/margin_small"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
app:wateringText="@{viewModel.plant.wateringInterval}"
.../>
与您之前的操作类似,请创建一个名为 PlantWatering 的新可组合项并添加 Text 可组合项,以在界面上显示浇水信息:
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@OptIn(ExperimentalComposeUiApi::class)
@Composable
private fun PlantWatering(wateringInterval: Int) {
Column(Modifier.fillMaxWidth()) {
// Same modifier used by both Texts
val centerWithPaddingModifier = Modifier
.padding(horizontal = dimensionResource(R.dimen.margin_small))
.align(Alignment.CenterHorizontally)
val normalPadding = dimensionResource(R.dimen.margin_normal)
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.watering_needs_prefix),
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primaryContainer,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
modifier = centerWithPaddingModifier.padding(top = normalPadding)
)
val wateringIntervalText = pluralStringResource(
R.plurals.watering_needs_suffix, wateringInterval, wateringInterval
)
Text(
text = wateringIntervalText,
modifier = centerWithPaddingModifier.padding(bottom = normalPadding)
)
}
}
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantWateringPreview() {
MaterialTheme {
PlantWatering(7)
}
}
预览如下:
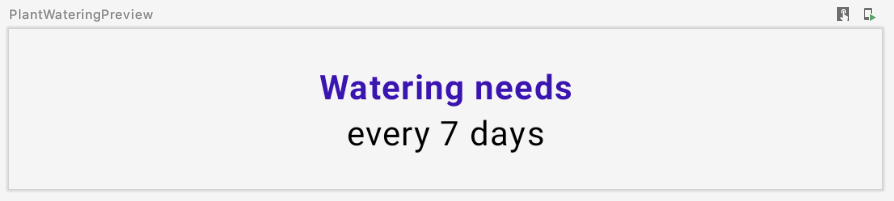
需要注意以下几点:
- 由于
Text可组合项会共享水平内边距和对齐修饰,因此您可以将修饰符分配给局部变量(即centerWithPaddingModifier),以重复使用修饰符。修饰符是标准的 Kotlin 对象,因此可以重复使用。 - Compose 的
MaterialTheme与plant_watering_header中使用的colorAccent不完全匹配。现在,我们可以使用将在互操作性主题设置部分中加以改进的MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primaryContainer。 - 在 Compose 1.2.1 中,必须选择启用
ExperimentalComposeUiApi才能使用pluralStringResource。在将来的 Compose 版本中,可能不再需要这样做。
我们将各个部分组合在一起,然后同样从 PlantDetailContent 调用 PlantWatering。我们一开始移除的 ConstraintLayout XML 代码的外边距为 16.dp,我们需要将该值添加到 Compose 代码中。
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="@dimen/margin_normal">
请在 PlantDetailContent 中创建一个 Column 以同时显示名称和浇水信息,并将其作为内边距。另外,为了确保背景颜色和所用的文本颜色均合适,请添加 Surface 用于处理这种设置。
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Composable
fun PlantDetailContent(plant: Plant) {
Surface {
Column(Modifier.padding(dimensionResource(R.dimen.margin_normal))) {
PlantName(plant.name)
PlantWatering(plant.wateringInterval)
}
}
}
刷新预览后,您会看到以下内容:
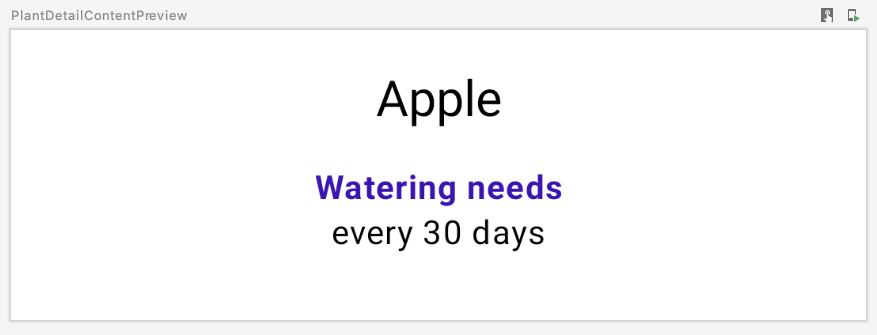
9. Compose 代码中的 View
现在,我们来迁移植物说明。fragment_plant_detail.xml 中的代码具有包含 app:renderHtml="@{viewModel.plant.description}" 的 TextView,用于告知 XML 在界面上显示哪些文本。renderHtml 是一个绑定适配器,可在 PlantDetailBindingAdapters.kt 文件中找到。该实现使用 HtmlCompat.fromHtml 在 TextView 上设置文本!
但是,Compose 目前不支持 Spanned 类,也不支持显示 HTML 格式的文本。因此,我们需要在 Compose 代码中使用 View 系统中的 TextView 来绕过此限制。
由于 Compose 目前还无法呈现 HTML 代码,因此您需要使用 AndroidView API 程序化地创建一个 TextView,从而实现此目的。
AndroidView 使您能够在 View 的 factory lamba 中构建该 View。它还提供了一个 update lambda,它会在 View 膨胀和后续重组时被调用。
为此,请创建新的 PlantDescription 可组合项。此可组合项将调用 AndroidView,后者会在 factory lambda 中构造 TextView。在 factory lambda 中,初始化显示 HTML 格式文本的 TextView,然后将 movementMethod 设置为 LinkMovementMethod 的实例。最后,在 update lambda 中将 TextView 的文本设置为 htmlDescription。
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Composable
private fun PlantDescription(description: String) {
// Remembers the HTML formatted description. Re-executes on a new description
val htmlDescription = remember(description) {
HtmlCompat.fromHtml(description, HtmlCompat.FROM_HTML_MODE_COMPACT)
}
// Displays the TextView on the screen and updates with the HTML description when inflated
// Updates to htmlDescription will make AndroidView recompose and update the text
AndroidView(
factory = { context ->
TextView(context).apply {
movementMethod = LinkMovementMethod.getInstance()
}
},
update = {
it.text = htmlDescription
}
)
}
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantDescriptionPreview() {
MaterialTheme {
PlantDescription("HTML<br><br>description")
}
}
预览:
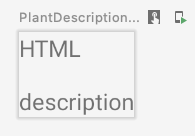
请注意,htmlDescription 会记住作为参数传递的指定 description 的 HTML 说明。如果 description 参数发生变化,系统会再次执行 remember 中的 htmlDescription 代码。
因此,如果 htmlDescription 发生变化,AndroidView 更新回调将重组。在 update lambda 中读取的任何状态都会导致重组。
我们将 PlantDescription 添加到 PlantDetailContent 可组合项,并更改预览代码,以便同样显示 HTML 说明:
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Composable
fun PlantDetailContent(plant: Plant) {
Surface {
Column(Modifier.padding(dimensionResource(R.dimen.margin_normal))) {
PlantName(plant.name)
PlantWatering(plant.wateringInterval)
PlantDescription(plant.description)
}
}
}
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantDetailContentPreview() {
val plant = Plant("id", "Apple", "HTML<br><br>description", 3, 30, "")
MaterialTheme {
PlantDetailContent(plant)
}
}
预览如下:
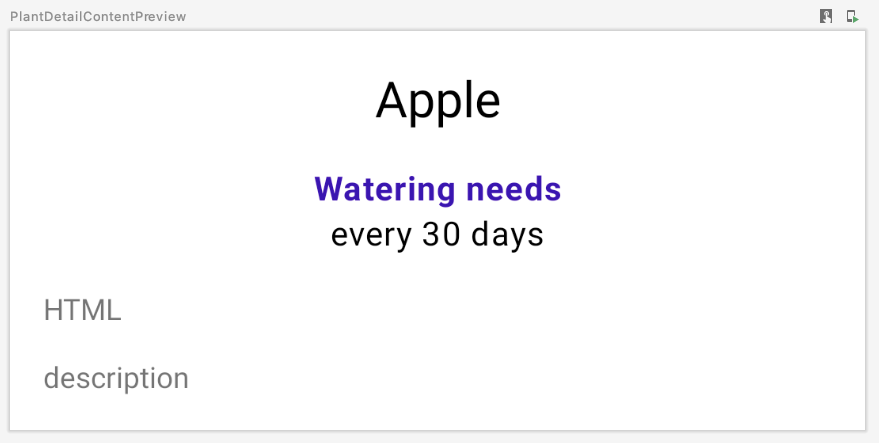
现在,您已将原始 ConstraintLayout 中的所有内容迁移到 Compose。您可以运行该应用,检查其是否按预期运行。
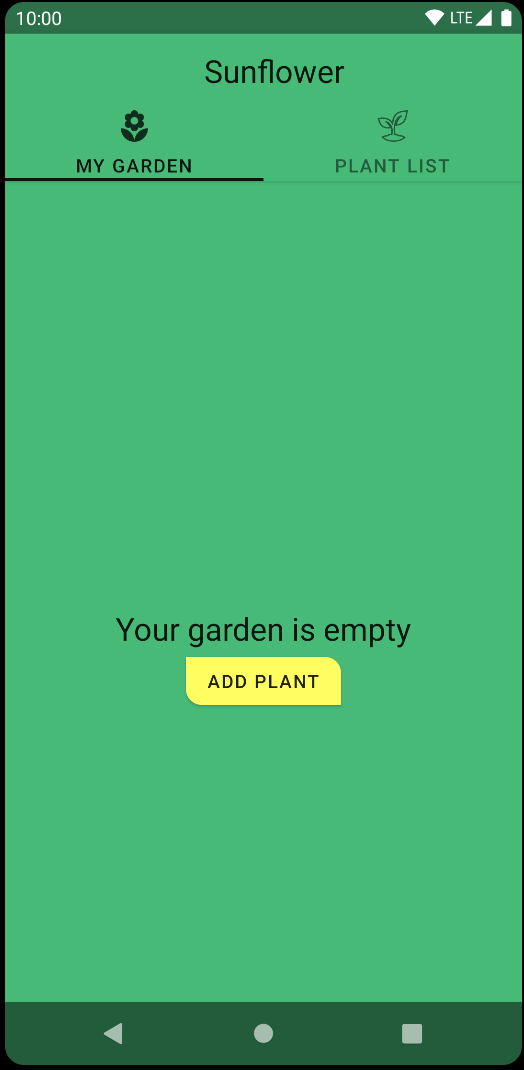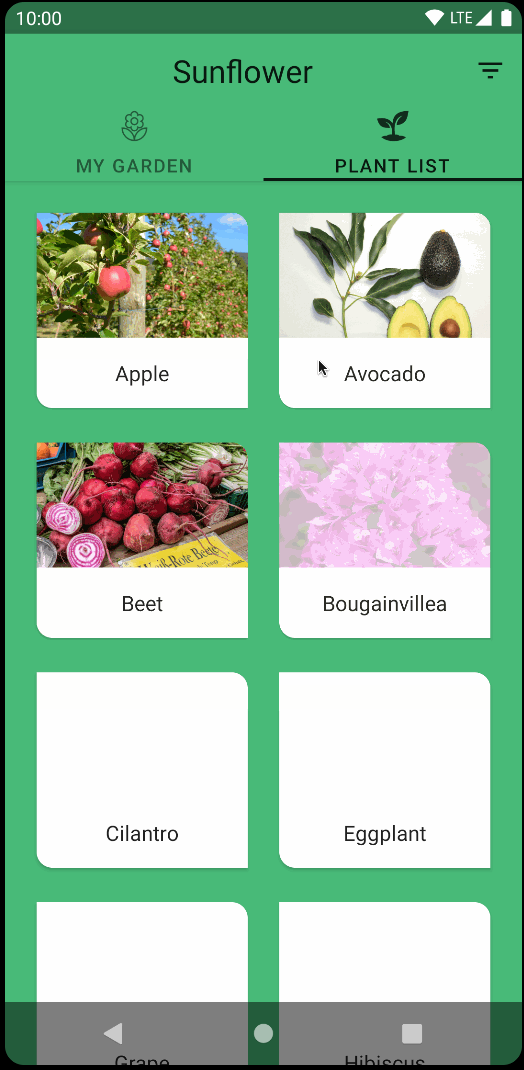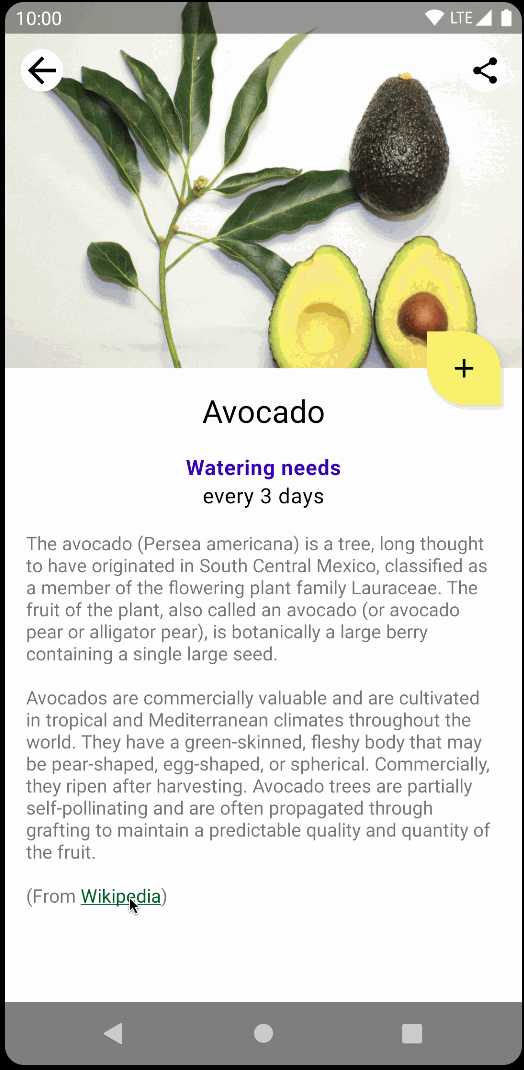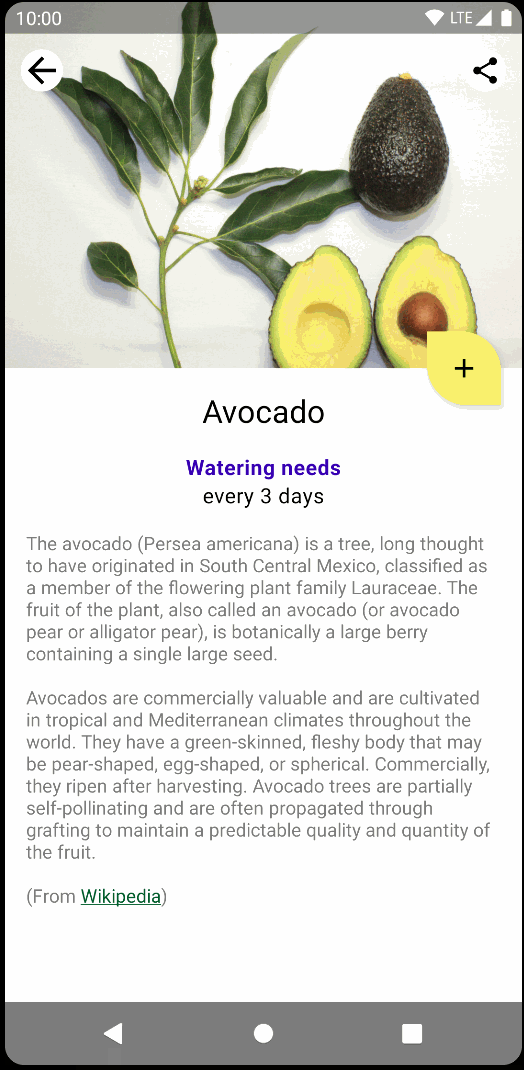
10. ViewCompositionStrategy
只要 ComposeView 与窗口分离,Compose 就会处理组合。如果 fragment 中使用了 ComposeView,这种情况是不可取的,原因有两个:
- 组合必须遵循 fragment 的视图生命周期,Compose 界面
View类型才能保存状态。 - 发生过渡时,底层
ComposeView将处于分离状态。不过,在这些过渡期间,Compose 界面元素仍然可见。
如需修改此行为,请使用适当的 ViewCompositionStrategy 调用 setViewCompositionStrategy,使其改为遵循 fragment 的视图生命周期。具体而言,您需要在 fragment 的 LifecycleOwner 被销毁时使用 DisposeOnViewTreeLifecycleDestroyed 策略处置组合。
由于 PlantDetailFragment 包含进入和退出过渡(如需了解详情,请查看 nav_garden.xml),并且我们稍后会在 Compose 中使用 View 类型,因此我们需要确保 ComposeView 使用 DisposeOnViewTreeLifecycleDestroyed 策略。不过,在 fragment 中使用 ComposeView 时,最好始终设置此策略。
PlantDetailFragment.kt
import androidx.compose.ui.platform.ViewCompositionStrategy
...
class PlantDetailFragment : Fragment() {
...
override fun onCreateView(...): View? {
val binding = DataBindingUtil.inflate<FragmentPlantDetailBinding>(
inflater, R.layout.fragment_plant_detail, container, false
).apply {
...
composeView.apply {
// Dispose the Composition when the view's LifecycleOwner
// is destroyed
setViewCompositionStrategy(
ViewCompositionStrategy.DisposeOnViewTreeLifecycleDestroyed
)
setContent {
MaterialTheme {
PlantDetailDescription(plantDetailViewModel)
}
}
}
}
...
}
}
11. Material 主题设置
我们已将植物详情的文本内容迁移到 Compose。不过,您可能已经注意到,Compose 使用的主题颜色有误。当植物名称应该使用绿色时,它使用的是紫色。
如需使用正确的主题颜色,您需要通过定义自己的主题并提供主题的颜色来自定义 MaterialTheme。
自定义 MaterialTheme
如需创建自己的主题,请打开 theme 软件包下的 Theme.kt 文件。Theme.kt 定义了一个名为 SunflowerTheme 的可组合项,它接受内容 lambda 并将其传递给 MaterialTheme。
它尚不会执行任何有趣的操作,接下来,您可以对其进行自定义。
Theme.kt
import androidx.compose.material3.MaterialTheme
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
@Composable
fun SunflowerTheme(
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
MaterialTheme(content = content)
}
MaterialTheme 允许您自定义其颜色、排版和形状。现在,请通过在 Sunflower View 的主题中提供相同的颜色来自定义颜色。SunflowerTheme 还可以接受一个名为 darkTheme 的布尔值参数,如果系统处于深色模式,该参数默认为 true,否则为 false。使用此参数,我们可以将正确的颜色值传递给 MaterialTheme,以匹配当前设置的系统主题。
Theme.kt
@Composable
fun SunflowerTheme(
darkTheme: Boolean = isSystemInDarkTheme(),
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
val lightColors = lightColorScheme(
primary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_green_500),
primaryContainer = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_green_700),
secondary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_yellow_500),
background = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_green_500),
onPrimary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_black),
onSecondary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_black),
)
val darkColors = darkColorScheme(
primary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_green_100),
primaryContainer = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_green_200),
secondary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_yellow_300),
onPrimary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_black),
onSecondary = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_black),
onBackground = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_black),
surface = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_green_100_8pc_over_surface),
onSurface = colorResource(id = R.color.sunflower_white),
)
val colors = if (darkTheme) darkColors else lightColors
MaterialTheme(
colorScheme = colors,
content = content
)
}
如需使用此库,请不要使用 MaterialTheme,改为使用 SunflowerTheme。例如,在 PlantDetailFragment 中:
PlantDetailFragment.kt
class PlantDetailFragment : Fragment() {
...
composeView.apply {
...
setContent {
SunflowerTheme {
PlantDetailDescription(plantDetailViewModel)
}
}
}
}
此外还有 PlantDetailDescription.kt 文件中的所有预览可组合项:
PlantDetailDescription.kt
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantDetailContentPreview() {
val plant = Plant("id", "Apple", "HTML<br><br>description", 3, 30, "")
SunflowerTheme {
PlantDetailContent(plant)
}
}
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantNamePreview() {
SunflowerTheme {
PlantName("Apple")
}
}
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantWateringPreview() {
SunflowerTheme {
PlantWatering(7)
}
}
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PlantDescriptionPreview() {
SunflowerTheme {
PlantDescription("HTML<br><br>description")
}
}
在预览中您可以看到,颜色现在应与 Sunflower 主题的颜色一致。
您还可以在深色主题中预览界面,方法是创建新函数并将 Configuration.UI_MODE_NIGHT_YES 传递给预览的 uiMode:
import android.content.res.Configuration
...
@Preview(uiMode = Configuration.UI_MODE_NIGHT_YES)
@Composable
private fun PlantDetailContentDarkPreview() {
val plant = Plant("id", "Apple", "HTML<br><br>description", 3, 30, "")
SunflowerTheme {
PlantDetailContent(plant)
}
}
预览如下:

如果您运行应用,它在浅色主题和深色主题下的行为都将与迁移前完全相同:
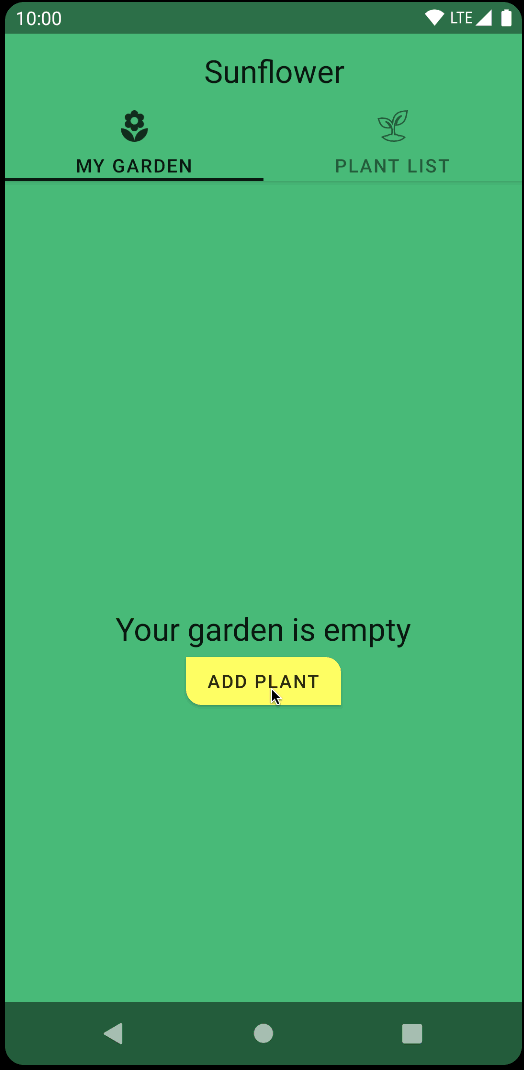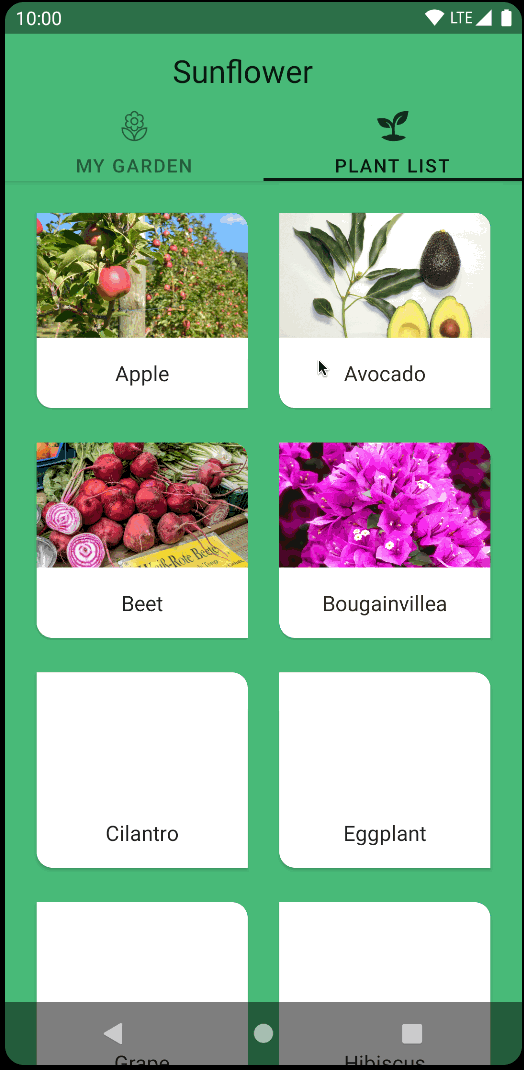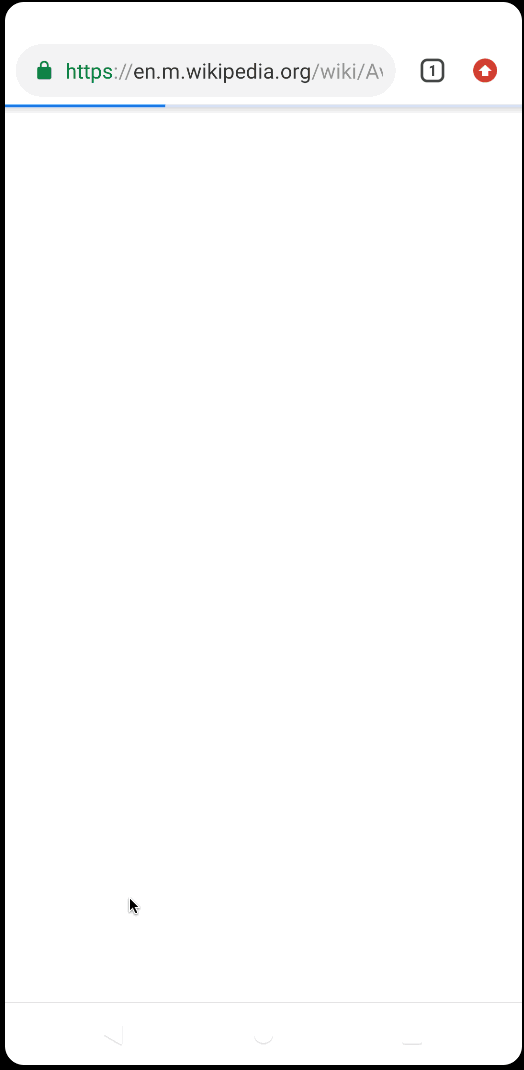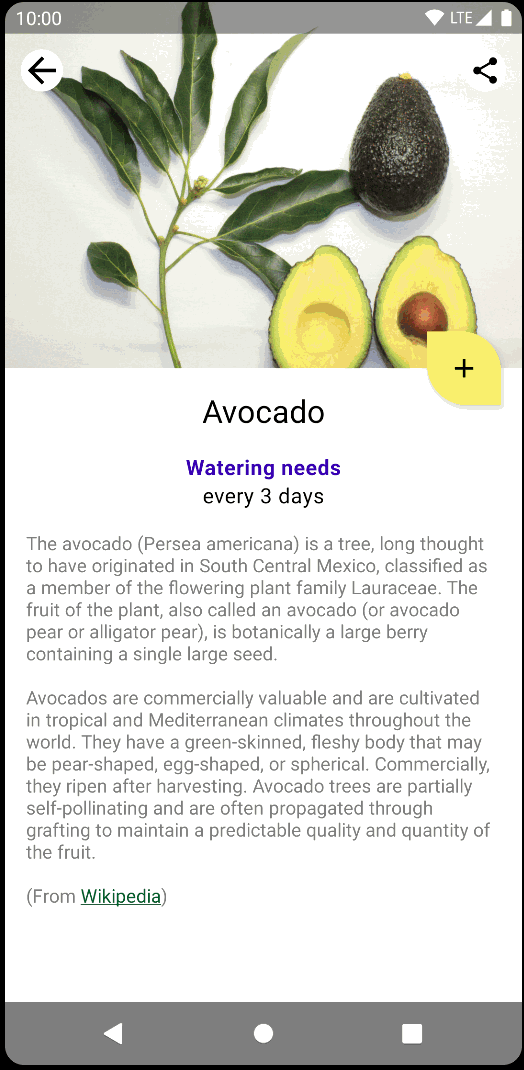
12. 测试
将植物详情界面的各个部分迁移到 Compose 之后,务必要进行测试,确保您没有损坏任何内容。
在 Sunflower 中,位于 androidTest 文件夹的 PlantDetailFragmentTest 用于测试应用的某些功能。请打开该文件并查看当前的代码:
testPlantName用于检查界面上的植物名称testShareTextIntent用于检查点按分享按钮后是否触发了正确的 intent
当 activity 或 fragment 使用 Compose 时,您不需要使用 ActivityScenarioRule,而需要使用 createAndroidComposeRule,它将 ActivityScenarioRule 与 ComposeTestRule 集成,让您可以测试 Compose 代码。
在 PlantDetailFragmentTest 中,将用法 ActivityScenarioRule 替换为 createAndroidComposeRule。如果需要使用 activity 规则来配置测试,请使用 createAndroidComposeRule 中的 activityRule 属性,具体代码如下所示:
@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4::class)
class PlantDetailFragmentTest {
@Rule
@JvmField
val composeTestRule = createAndroidComposeRule<GardenActivity>()
...
@Before
fun jumpToPlantDetailFragment() {
populateDatabase()
composeTestRule.activityRule.scenario.onActivity { gardenActivity ->
activity = gardenActivity
val bundle = Bundle().apply { putString("plantId", "malus-pumila") }
findNavController(activity, R.id.nav_host).navigate(R.id.plant_detail_fragment, bundle)
}
}
...
}
如果您运行测试,testPlantName 会失败!testPlantName 检查界面上是否存在 TextView。不过,您已将这部分的界面迁移到 Compose。因此,您需要改用 Compose 断言:
@Test
fun testPlantName() {
composeTestRule.onNodeWithText("Apple").assertIsDisplayed()
}
如果运行测试,您会看到所有测试均会通过。
13. 恭喜
恭喜,您已成功完成此 Codelab!
原始 Sunflower GitHub 项目的 compose 分支会将植物详细信息界面完全迁移到 Compose。除了您在此 Codelab 中完成的操作之外,该分支还会模拟 CollapsingToolbarLayout 的行为。这些行为包括:
- 使用 Compose 加载图片
- 动画
- 更出色的尺寸处理
- 等等!
后续操作
请查看 Compose 开发者在线课程中的其他 Codelab:
