1. 简介
概览
在本实验中,您将超越简单的聊天机器人,构建一个分布式多代理系统。
虽然单个 LLM 可以回答问题,但现实世界的复杂性往往需要专门的角色。您不会让后端工程师设计界面,也不会让设计师优化数据库查询。同样,我们可以创建专注于一项任务的专业 AI 智能体,并让它们相互协调来解决复杂问题。
您将构建一个课程创建系统,该系统包含:
- 研究员智能体:使用
google_search查找最新信息。 - 判断智能体:从质量和完整性方面评价研究。
- Content Builder Agent:将研究转化为结构化课程。
- Orchestrator Agent:管理这些专家之间的工作流和通信。
前提条件
- Python 基础知识。
- 熟悉 Google Cloud 控制台。
您将执行的操作
- 定义一个可以使用工具 (
researcher) 搜索网络的智能体。 - 使用 Pydantic 为
judge实现结构化输出。 - 使用智能体对智能体 (A2A) 协议连接到远程智能体。
- 构建
LoopAgent以在研究人员和法官之间创建反馈环。 - 使用 ADK 在本地运行分布式系统。
- 将多智能体系统部署到 Google Cloud Run。
架构和编排原则
在编写代码之前,我们先来了解一下这些智能体如何协同工作。我们将构建一个课程创建流水线。
系统设计
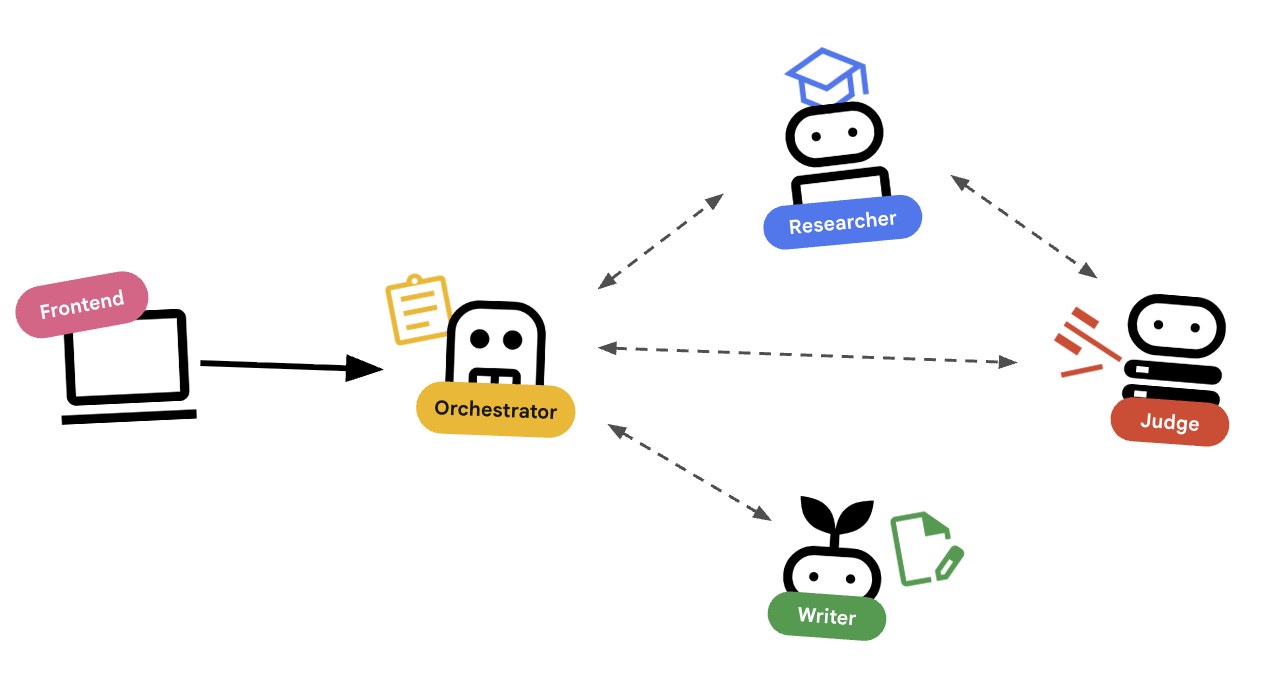
使用代理进行编排
标准代理(例如研究员)确实可以正常工作。编排器代理(例如 LoopAgent 或 SequentialAgent)管理其他代理。它们没有自己的工具;它们的“工具”是委托。
LoopAgent:此函数的作用类似于代码中的while循环。它会重复运行一系列智能体,直到满足某个条件(或达到最大迭代次数)。我们使用此功能进行研究循环:- 研究人员查找信息。
- 裁判会提出批评意见。
- 如果 Judge 显示“失败”,EscalationChecker 会让循环继续。
- 如果 Judge 说“通过”,EscalationChecker 会中断循环。
SequentialAgent:此操作类似于标准脚本执行。它会依次运行各个代理。我们将其用于高级流水线:- 首先,运行研究循环(直到它以良好的数据完成)。
- 然后,运行内容构建器(用于撰写课程)。
通过将这些方法相结合,我们可以创建一个强大的系统,该系统可以在生成最终输出之前进行自我修正。
2. 设置
环境设置
打开 Cloud Shell:打开新标签页,然后输入 shell.cloud.google.com
获取起始代码
- 将初始代码库克隆到您的主目录:
cd ~ git clone https://github.com/amitkmaraj/prai-roadshow-lab-1-starter.git cd prai-roadshow-lab-1-starter - 运行 init 脚本,将初始培训积分与结算相关联。
chmod +x ./init.sh ./init.sh - 在编辑器中打开此文件夹。
启用 API
现在您已拥有新项目,请运行以下命令以启用必要的 Google Cloud 服务:
gcloud services enable \
run.googleapis.com \
artifactregistry.googleapis.com \
cloudbuild.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com
这可能需要几秒钟时间。
安装依赖项
我们使用 uv 来快速管理依赖项。
- 安装项目依赖项:
# Ensure you have uv installed: pip install uv uv sync - 设置您的 Google Cloud 项目 ID。
- 提示:您可以在 Cloud 控制台的信息中心内找到项目 ID,也可以通过运行
gcloud config get-value project找到项目 ID。
export GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=$(gcloud config get-value project) - 提示:您可以在 Cloud 控制台的信息中心内找到项目 ID,也可以通过运行
- 设置其余的环境变量:
export GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION=us-central1 export GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI=true
3. 🕵️ 研究员代理
研究员是专家。它的唯一任务是查找信息。为此,它需要访问一个工具:Google 搜索。
为什么要将研究者分开?
深入探讨:为什么不让一个代理完成所有任务?
小巧且专注的智能体更易于评估和调试。如果研究结果不理想,请迭代研究人员的提示。如果课程格式不佳,您可以在内容构建器中进行迭代。在“包罗万象”的单体提示中,修复一个问题往往会导致另一个问题。
- 如果您在 Cloud Shell 中工作,请运行以下命令以打开 Cloud Shell 编辑器:
cloudshell workspace . - 打开
agents/researcher/agent.py。 - 您会看到一个包含 TODO 的框架。
- 添加以下代码以定义
researcher代理:# ... existing imports ... # Define the Researcher Agent researcher = Agent( name="researcher", model=MODEL, description="Gathers information on a topic using Google Search.", instruction=""" You are an expert researcher. Your goal is to find comprehensive and accurate information on the user's topic. Use the `google_search` tool to find relevant information. Summarize your findings clearly. If you receive feedback that your research is insufficient, use the feedback to refine your next search. """, tools=[google_search], ) root_agent = researcher
主要概念:工具使用
请注意,我们传递了 tools=[google_search]。ADK 会处理向 LLM 描述此工具的复杂性。当模型确定需要信息时,它会生成结构化的工具调用,ADK 会执行 Python 函数 google_search,并将结果反馈给模型。
4. ⚖️ Judge 代理
研究者很努力,但 LLM 可能会很懒惰。我们需要评审员来审核作业。Judge 接受研究并返回结构化的通过/未通过评估结果。
结构化输出
深入探讨:为了实现工作流自动化,我们需要可预测的输出。杂乱无章的文字评价很难以程序化方式进行解析。通过强制执行 JSON 架构(使用 Pydantic),我们确保 Judge 返回布尔值 pass 或 fail,以便我们的代码能够可靠地采取行动。
- 打开
agents/judge/agent.py。 - 定义
JudgeFeedback架构和judge代理。# 1. Define the Schema class JudgeFeedback(BaseModel): """Structured feedback from the Judge agent.""" status: Literal["pass", "fail"] = Field( description="Whether the research is sufficient ('pass') or needs more work ('fail')." ) feedback: str = Field( description="Detailed feedback on what is missing. If 'pass', a brief confirmation." ) # 2. Define the Agent judge = Agent( name="judge", model=MODEL, description="Evaluates research findings for completeness and accuracy.", instruction=""" You are a strict editor. Evaluate the 'research_findings' against the user's original request. If the findings are missing key info, return status='fail'. If they are comprehensive, return status='pass'. """, output_schema=JudgeFeedback, # Disallow delegation because it should only output the schema disallow_transfer_to_parent=True, disallow_transfer_to_peers=True, ) root_agent = judge
核心概念:限制代理行为
我们设置了 disallow_transfer_to_parent=True 和 disallow_transfer_to_peers=True。这会强制 Judge 仅返回结构化 JudgeFeedback。它无法决定是否与用户“聊天”,也无法委托给其他代理。这使其成为逻辑流程中的确定性组件。
5. 🧪 隔离测试
在连接它们之前,我们可以验证每个代理是否正常运行。借助 ADK,您可以单独运行代理。
主要概念:互动式运行时
adk run 会启动一个轻量级环境,您是该环境中的“用户”。这样,您就可以单独测试代理的指令和工具使用情况。如果代理在此处失败(例如,无法使用 Google 搜索),则在编排中肯定会失败。
- 以交互方式运行研究者。请注意,我们指向的是特定的代理目录:
# This runs the researcher agent in interactive mode uv run adk run agents/researcher - 在聊天提示中,输入:
Find the population of Tokyo in 2020export GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=$(gcloud config get-value project) export GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION=us-central1 export GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI=true - 退出聊天 (Ctrl+C)。
- 以交互方式运行 Judge:
uv run adk run agents/judge - 在聊天提示中,模拟输入:
Topic: Tokyo. Findings: Tokyo is a city.status='fail',因为发现内容过于简短。
6. ✍️ 内容构建智能体
内容构建器是创意撰稿人。它会根据已获批准的研究成果制作课程。
- 打开
agents/content_builder/agent.py。 - 定义
content_builder代理。content_builder = Agent( name="content_builder", model=MODEL, description="Transforms research findings into a structured course.", instruction=""" You are an expert course creator. Take the approved 'research_findings' and transform them into a well-structured, engaging course module. **Formatting Rules:** 1. Start with a main title using a single `#` (H1). 2. Use `##` (H2) for main section headings. 3. Use bullet points and clear paragraphs. 4. Maintain a professional but engaging tone. Ensure the content directly addresses the user's original request. """, ) root_agent = content_builder
关键概念:上下文传播
您可能想知道:“内容构建器如何知道研究者找到了什么?”在 ADK 中,流水线中的代理共享一个 session.state。稍后,在 Orchestrator 中,我们将配置 Researcher 和 Judge,以将其输出保存到此共享状态。内容构建器的提示实际上可以访问此历史记录。
7. 🎻 Orchestrator
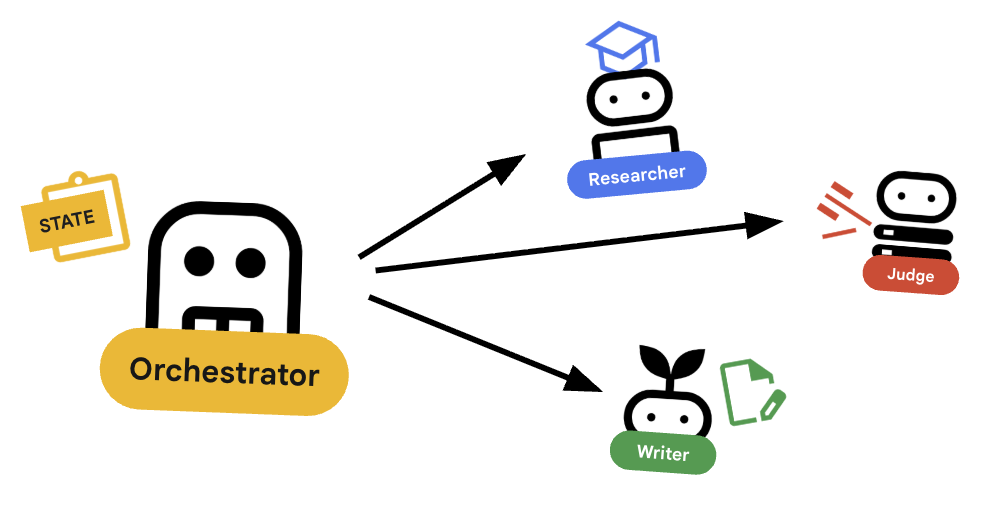
编排程序是我们多代理团队的管理器。与执行特定任务的专家代理(研究员、评判员、内容构建器)不同,编排器的任务是协调工作流程并确保信息在它们之间正确流动。
🌐 架构:代理对代理 (A2A)
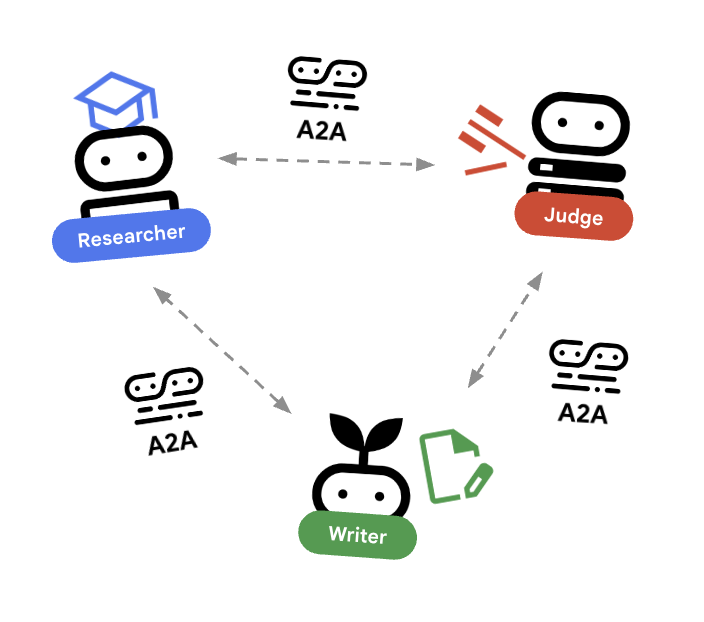
在本实验中,我们将构建一个分布式系统。我们没有在单个 Python 进程中运行所有代理,而是将它们部署为独立的微服务。这样一来,每个代理都可以独立扩缩,并且即使发生故障也不会导致整个系统崩溃。
为了实现这一点,我们使用了代理对代理 (A2A) 协议。
A2A 协议
深入探讨:在生产系统中,代理在不同的服务器(甚至不同的云)上运行。A2A 协议为它们提供了一种标准方式,以便通过 HTTP 相互发现和通信。RemoteA2aAgent 是相应协议的 ADK 客户端。
- 打开
agents/orchestrator/agent.py。 - 找到注释
# TODO: Define Remote Agents或远程代理定义部分。 - 添加以下代码以定义连接。请务必将此代码放在导入代码之后,并放在任何其他代理定义之前。
# ... existing code ... # Connect to the Researcher (Localhost port 8001) researcher_url = os.environ.get("RESEARCHER_AGENT_CARD_URL", "http://localhost:8001/a2a/agent/.well-known/agent-card.json") researcher = RemoteA2aAgent( name="researcher", agent_card=researcher_url, description="Gathers information using Google Search.", # IMPORTANT: Save the output to state for the Judge to see after_agent_callback=create_save_output_callback("research_findings"), # IMPORTANT: Use authenticated client for communication httpx_client=create_authenticated_client(researcher_url) ) # Connect to the Judge (Localhost port 8002) judge_url = os.environ.get("JUDGE_AGENT_CARD_URL", "http://localhost:8002/a2a/agent/.well-known/agent-card.json") judge = RemoteA2aAgent( name="judge", agent_card=judge_url, description="Evaluates research.", after_agent_callback=create_save_output_callback("judge_feedback"), httpx_client=create_authenticated_client(judge_url) ) # Content Builder (Localhost port 8003) content_builder_url = os.environ.get("CONTENT_BUILDER_AGENT_CARD_URL", "http://localhost:8003/a2a/agent/.well-known/agent-card.json") content_builder = RemoteA2aAgent( name="content_builder", agent_card=content_builder_url, description="Builds the course.", httpx_client=create_authenticated_client(content_builder_url) )
8. 🛑 升级检查工具
循环需要一种停止方式。如果 Judge 说“通过”,我们希望立即退出循环并转到 Content Builder。
使用 BaseAgent 实现自定义逻辑
深入探讨:并非所有智能体都使用 LLM。有时,您需要简单的 Python 逻辑。BaseAgent 可让您定义仅运行代码的代理。在这种情况下,我们会检查会话状态,并使用 EventActions(escalate=True) 向 LoopAgent 发出停止信号。
- 仍处于“
agents/orchestrator/agent.py”阶段。 - 找到
EscalationCheckerTODO 占位符。 - 将其替换为以下实现:
class EscalationChecker(BaseAgent): """Checks the judge's feedback and escalates (breaks the loop) if it passed.""" async def _run_async_impl( self, ctx: InvocationContext ) -> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]: # Retrieve the feedback saved by the Judge feedback = ctx.session.state.get("judge_feedback") print(f"[EscalationChecker] Feedback: {feedback}") # Check for 'pass' status is_pass = False if isinstance(feedback, dict) and feedback.get("status") == "pass": is_pass = True # Handle string fallback if JSON parsing failed elif isinstance(feedback, str) and '"status": "pass"' in feedback: is_pass = True if is_pass: # 'escalate=True' tells the parent LoopAgent to stop looping yield Event(author=self.name, actions=EventActions(escalate=True)) else: # Continue the loop yield Event(author=self.name) escalation_checker = EscalationChecker(name="escalation_checker")
关键概念:通过事件控制流程
代理不仅通过文本进行通信,还通过事件进行通信。通过使用 escalate=True 生成事件,此代理会向上级(即 LoopAgent)发送信号。LoopAgent 已编程为捕获此信号并终止循环。
9. 🔁 研究循环
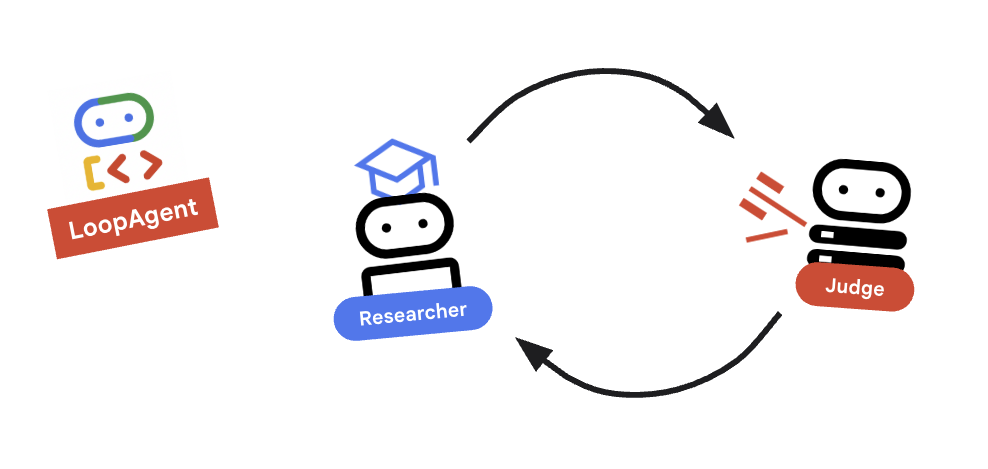
我们需要一个反馈环:研究 -> 判断 ->(失败)-> 研究 -> ...
- 仍处于“
agents/orchestrator/agent.py”阶段。 - 添加
research_loop定义。将此 放置在EscalationChecker类和escalation_checker实例之后。research_loop = LoopAgent( name="research_loop", description="Iteratively researches and judges until quality standards are met.", sub_agents=[researcher, judge, escalation_checker], max_iterations=3, )
主要概念:LoopAgent
LoopAgent 会按顺序循环遍历其 sub_agents。
researcher:查找数据。judge:评估数据。escalation_checker:决定是否要yield Event(escalate=True)。如果发生escalate=True,则循环会提前中断。否则,它会从研究员重新开始(最多max_iterations)。
10. 🔗 最终流水线
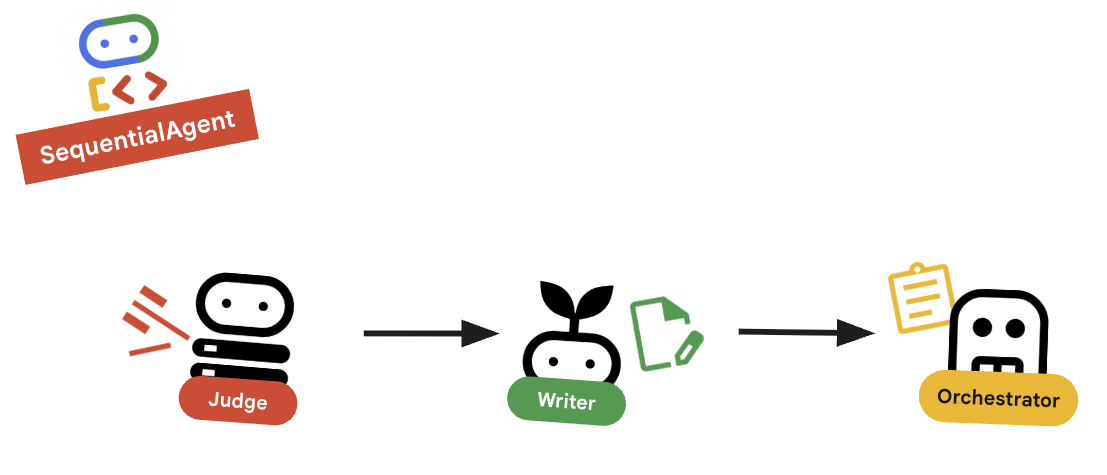
最后,将所有内容整合在一起。
- 仍处于“
agents/orchestrator/agent.py”阶段。 - 在文件底部定义
root_agent。确保此占位符替换任何现有的root_agent = None占位符。root_agent = SequentialAgent( name="course_creation_pipeline", description="A pipeline that researches a topic and then builds a course from it.", sub_agents=[research_loop, content_builder], )
主要概念:分层组合
请注意,research_loop 本身也是一个代理(一个 LoopAgent)。我们将其视为 SequentialAgent 中的任何其他子代理。这种可组合性让您可以通过嵌套简单模式(序列中的循环、路由器中的序列等)来构建复杂的逻辑。
11. 💻 在本地运行
在运行所有内容之前,我们先来看看 ADK 如何在本地模拟分布式环境。
深入了解:本地开发的运作方式
在微服务架构中,每个代理都以自己的服务器身份运行。部署后,您将拥有 4 项不同的 Cloud Run 服务。如果您必须打开 4 个终端标签页并运行 4 个命令,那么在本地模拟此操作可能会很麻烦。
此脚本会为 Researcher(端口 8001)、Judge(8002)和 Content Builder(8003)启动 uvicorn 进程。它会设置 RESEARCHER_AGENT_CARD_URL 等环境变量,并将这些变量传递给 Orchestrator(端口 8004)。这正是我们稍后在云端配置它的方式!
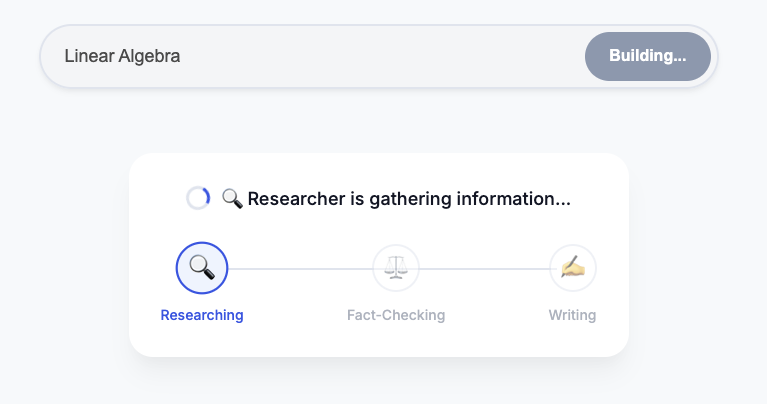
- 运行编排脚本:
./run_local.sh - 测试:
- 如果使用 Cloud Shell:点击网页预览按钮(位于终端的右上角)-> 在端口 8080 上预览 -> 将更改端口更改为
8000。 - 如果是在本地运行:在浏览器中打开
http://localhost:8000。 - 提示:“创建一个关于咖啡历史的课程。”
- 观察:Orchestrator 将致电研究人员。输出会发送给 Judge。如果 Judge 失败,则循环继续!
- “Internal Server Error”(内部服务器错误)/ 身份验证错误:如果您看到身份验证错误(例如与
google-auth相关),请确保您已运行gcloud auth application-default login(如果在本地计算机上运行)。在 Cloud Shell 中,确保已正确设置GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT环境变量。 - 终端错误:如果该命令在新终端窗口中失败,请记得重新导出环境变量(
GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT等)。
- 如果使用 Cloud Shell:点击网页预览按钮(位于终端的右上角)-> 在端口 8080 上预览 -> 将更改端口更改为
- 单独测试代理:即使整个系统都在运行,您也可以通过直接定位特定代理的端口来测试这些代理。这有助于调试特定组件,而无需触发整个链。
- 仅限研究人员(端口 8001):
http://localhost:8001 - 仅评判(端口 8002):
http://localhost:8002 - 仅限内容构建器(端口 8003):
http://localhost:8003 - Orchestrator(端口 8004):
http://localhost:8004(直接访问 Orchestrator 逻辑)
- 仅限研究人员(端口 8001):
12. 🚀 部署到 Cloud Run
最终验证在云端运行。我们将每个代理部署为单独的服务。
了解部署配置
将代理部署到 Cloud Run 时,我们会传递多个环境变量来配置其行为和连接:
GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT:确保代理使用正确的 Google Cloud 项目进行日志记录和 Vertex AI 调用。GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI:告知代理框架 (ADK) 使用 Vertex AI 进行模型推理,而不是直接调用 Gemini API。[AGENT]_AGENT_CARD_URL:这对编排程序至关重要。它会告知 Orchestrator 在何处查找远程代理。通过将此属性设置为已部署的 Cloud Run 网址(特别是代理卡路径),我们可以让 Orchestrator 通过互联网发现 Researcher、Judge 和 Content Builder 并与之通信。
- 部署研究者:
gcloud run deploy researcher \ --source agents/researcher/ \ --region us-central1 \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --labels dev-tutorial=prod-ready-1 \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI="true"RESEARCHER_URL=$(gcloud run services describe researcher --region us-central1 --format='value(status.url)') echo $RESEARCHER_URL - 部署 Judge:
gcloud run deploy judge \ --source agents/judge/ \ --region us-central1 \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --labels dev-tutorial=prod-ready-1 \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI="true"JUDGE_URL=$(gcloud run services describe judge --region us-central1 --format='value(status.url)') echo $JUDGE_URL - 部署内容构建器:
gcloud run deploy content-builder \ --source agents/content_builder/ \ --region us-central1 \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --labels dev-tutorial=prod-ready-1 \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI="true"CONTENT_BUILDER_URL=$(gcloud run services describe content-builder --region us-central1 --format='value(status.url)') echo $CONTENT_BUILDER_URL - 部署 Orchestrator:使用捕获的环境变量配置 Orchestrator。
gcloud run deploy orchestrator \ --source agents/orchestrator/ \ --region us-central1 \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --labels dev-tutorial=prod-ready-1 \ --set-env-vars RESEARCHER_AGENT_CARD_URL=$RESEARCHER_URL/a2a/agent/.well-known/agent-card.json \ --set-env-vars JUDGE_AGENT_CARD_URL=$JUDGE_URL/a2a/agent/.well-known/agent-card.json \ --set-env-vars CONTENT_BUILDER_AGENT_CARD_URL=$CONTENT_BUILDER_URL/a2a/agent/.well-known/agent-card.json \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI="true"ORCHESTRATOR_URL=$(gcloud run services describe orchestrator --region us-central1 --format='value(status.url)') echo $ORCHESTRATOR_URL - 部署前端:
gcloud run deploy course-creator \ --source app \ --region us-central1 \ --allow-unauthenticated \ --labels dev-tutorial=prod-ready-1 \ --set-env-vars AGENT_SERVER_URL=$ORCHESTRATOR_URL \ --set-env-vars GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT - 测试远程部署:打开已部署的 Orchestrator 的网址。现在,它完全在云端运行,利用 Google 的无服务器基础架构来扩缩代理!提示:您可以在 Cloud Run 界面中找到所有微服务及其网址
13. 总结
恭喜!您已成功构建并部署了一个可用于生产环境的分布式多代理系统。
我们取得的成就
- 分解复杂任务:我们没有使用一个庞大的提示,而是将工作拆分为专门的角色(研究员、评判员、内容构建者)。
- 实施质量控制:我们使用
LoopAgent和结构化Judge来确保只有高质量的信息才能进入最后一步。 - 为生产环境而打造:通过使用智能体到智能体 (A2A) 协议和 Cloud Run,我们创建了一个系统,其中每个智能体都是一个独立的可扩缩微服务。这比在单个 Python 脚本中运行所有内容要稳健得多。
- 编排:我们使用
SequentialAgent和LoopAgent定义清晰的控制流模式。
后续步骤
现在,您已经掌握了基础知识,可以扩展此系统了:
- 添加更多工具:向研究员授予对内部文档或 API 的访问权限。
- 改进 Judge:添加更具体的标准,甚至添加“人工干预”步骤。
- 交换模型:尝试为不同的代理使用不同的模型(例如,为 Judge 使用更快的模型,为 Content Writer 使用更强大的模型)。
您现在可以开始在 Google Cloud 上构建复杂可靠的智能体工作流了!
