1. 简介
概览
本实验弥合了开发强大的多智能体系统与部署该系统以供实际使用之间的关键差距。虽然在本地构建智能体是一个不错的开始,但生产应用需要一个可扩缩、可靠且安全的平台。
在本实验中,您将使用 Google 智能体开发套件 (ADK) 构建一个多智能体系统,并将其部署到 Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) 上的生产级环境中。
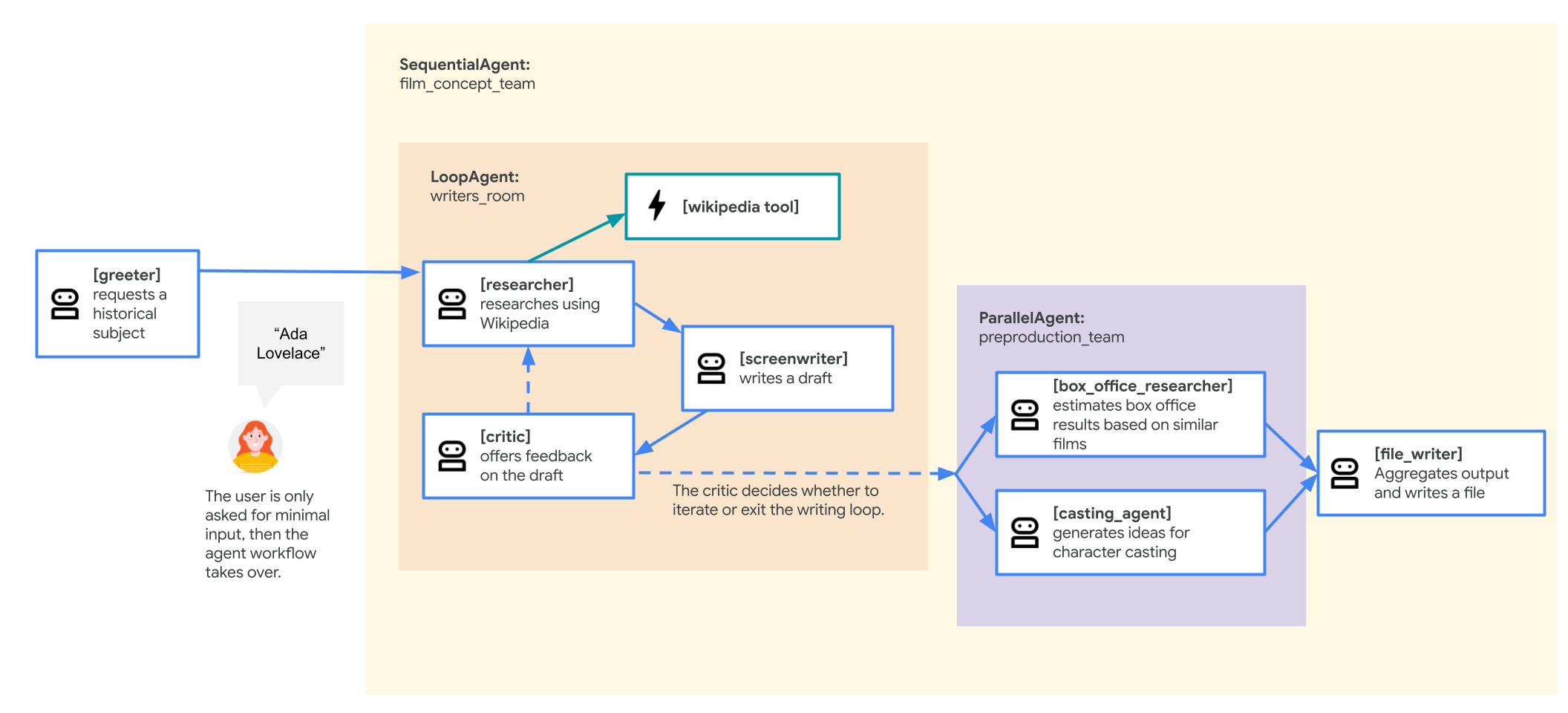
电影概念团队代理
本实验中使用的示例应用是一个“电影概念团队”,由多个协作式智能体组成:研究员、编剧和文件写入器。这些智能体协同工作,帮助用户集思广益,构思有关历史人物的电影推介方案。
为何要部署到 GKE?
为了让智能体能够满足生产环境的需求,您需要一个在可伸缩性、安全性和成本效益方面表现出色的平台。Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) 为运行容器化应用提供了强大而灵活的基础。
这为您的生产工作负载带来了以下几点优势:
- 自动扩缩和性能:使用 HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA) 处理不可预测的流量,该工具可根据负载自动添加或移除代理副本。对于要求更高的 AI 工作负载,您可以附加 GPU 和 TPU 等硬件加速器。
- 经济高效的资源管理:借助 GKE Autopilot 优化费用,该功能可自动管理底层基础设施,让您只需为应用请求的资源付费。
- 集成式安全性和可观测性:使用 Workload Identity 安全地连接到其他 Google Cloud 服务,从而避免了管理和存储服务账号密钥的需求。所有应用日志都会自动流式传输到 Cloud Logging,以便进行集中式监控和调试。
- 控制和可移植性:利用开源 Kubernetes 避免受制于特定供应商。您的应用具有可移植性,可以在任何 Kubernetes 集群(本地或其他云端)上运行。
学习内容
在本实验中,您将学习如何执行以下任务:
- 预配 GKE Autopilot 集群。
- 使用 Dockerfile 将应用容器化,并将映像推送到 Artifact Registry。
- 使用 Workload Identity 将应用安全地连接到 Google Cloud API。
- 为 Deployment 和 Service 编写并应用 Kubernetes 清单。
- 使用 LoadBalancer 将应用公开到互联网。
- 使用 HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA) 配置自动扩缩。
2. 项目设置
Google 账号
如果您还没有个人 Google 账号,则必须先创建一个 Google 账号。
请使用个人账号,而不是工作账号或学校账号。
登录 Google Cloud 控制台
使用个人 Google 账号登录 Google Cloud 控制台。
启用结算功能
设置个人结算账号
如果您使用 Google Cloud 抵用金设置了结算,则可以跳过此步骤。
如需设置个人结算账号,请点击此处在 Cloud 控制台中启用结算功能。
注意事项:
- 完成本实验的 Cloud 资源费用应不到 1 美元。
- 您可以按照本实验结束时的步骤删除资源,以避免产生更多费用。
- 新用户符合参与 $300 USD 免费试用计划的条件。
创建项目(可选)
如果您没有要用于此实验的当前项目,请在此处创建一个新项目。
3. 打开 Cloud Shell Editor
- 点击此链接可直接前往 Cloud Shell 编辑器
- 如果系统在今天任何时间提示您进行授权,请点击授权继续。
- 如果终端未显示在屏幕底部,请打开它:
- 点击查看
- 点击终端
- 在终端中,使用以下命令设置项目:
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]- 示例:
gcloud config set project lab-project-id-example - 如果您不记得自己的项目 ID,可以使用以下命令列出所有项目 ID:
gcloud projects list
- 示例:
- 您应会看到以下消息:
Updated property [core/project].
4. 启用 API
如需使用 GKE、Artifact Registry、Cloud Build 和 Vertex AI,您需要在 Google Cloud 项目中启用它们各自的 API。
- 在终端中,启用以下 API:
gcloud services enable \ container.googleapis.com \ artifactregistry.googleapis.com \ cloudbuild.googleapis.com \ aiplatform.googleapis.comOperation "operations/acf.p2-176675280136-b03ab5e4-3483-4ebf-9655-43dc3b345c63" finished successfully.
API 简介
- Google Kubernetes Engine API (
container.googleapis.com) 可让您创建和管理运行代理的 GKE 集群。GKE 提供了一个托管式环境,您可以使用 Google 基础设施在其中部署、管理和扩缩容器化应用。 - Artifact Registry API (
artifactregistry.googleapis.com) 提供了一个安全、私密的制品库,用于存储智能体的容器映像。它是 Container Registry 的下一代产品,可与 GKE 和 Cloud Build 无缝集成。 - Cloud Build API (
cloudbuild.googleapis.com) 由gcloud builds submit命令用于根据您的 Dockerfile 在云端构建容器映像。它是一个无服务器 CI/CD 平台,可在 Google Cloud 基础架构上执行构建。 - Vertex AI API (
aiplatform.googleapis.com) 可让已部署的代理与 Gemini 模型通信,以执行其核心任务。它为 Google Cloud 的所有 AI 服务提供统一的 API。
5. 准备开发环境
创建目录结构
- 在终端中,创建项目目录和必要的子目录:
mkdir -p ~/adk_multiagent_system_gke/workflow_agents cd ~/adk_multiagent_system_gke - 在终端中,运行以下命令以在 Cloud Shell 编辑器资源管理器中打开该目录。
cloudshell open-workspace ~/adk_multiagent_systems - 左侧的“探索器”面板将刷新。现在,您应该会看到您创建的目录。
在接下来的步骤中创建文件时,您会看到文件填充到此目录中。
创建初始文件
现在,您将为应用创建必要的初始文件。
- 在终端中运行以下命令,创建
callback_logging.py。此文件用于处理可观测性的日志记录。cat <<EOF > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/callback_logging.py """ Provides helper functions for observability. Handles formatting and sending agent queries, responses, and tool calls to Google Cloud Logging to aid in monitoring and debugging. """ import logging import google.cloud.logging from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest def log_query_to_model(callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest): cloud_logging_client = google.cloud.logging.Client() cloud_logging_client.setup_logging() if llm_request.contents and llm_request.contents[-1].role == 'user': if llm_request.contents[-1].parts and "text" in llm_request.contents[-1].parts: last_user_message = llm_request.contents[-1].parts[0].text logging.info(f"[query to {callback_context.agent_name}]: " + last_user_message) def log_model_response(callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_response: LlmResponse): cloud_logging_client = google.cloud.logging.Client() cloud_logging_client.setup_logging() if llm_response.content and llm_response.content.parts: for part in llm_response.content.parts: if part.text: logging.info(f"[response from {callback_context.agent_name}]: " + part.text) elif part.function_call: logging.info(f"[function call from {callback_context.agent_name}]: " + part.function_call.name) EOF - 在终端中运行以下命令,创建
workflow_agents/__init__.py。这样便可将相应目录标记为 Python 软件包。cat <<EOF > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/workflow_agents/__init__.py """ Marks the directory as a Python package and exposes the agent module, allowing the ADK to discover and register the agents defined within. """ from . import agent EOF - 在终端中运行以下命令,创建
workflow_agents/agent.py。此文件包含多代理团队的核心逻辑。cat <<EOF > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/workflow_agents/agent.py """ Defines the core multi-agent workflow. Configures individual agents (Researcher, Screenwriter, File Writer), assigns their specific tools, and orchestrates their collaboration using the ADK's SequentialAgent pattern. """ import os import logging import google.cloud.logging from callback_logging import log_query_to_model, log_model_response from dotenv import load_dotenv from google.adk import Agent from google.adk.agents import SequentialAgent, LoopAgent, ParallelAgent from google.adk.tools.tool_context import ToolContext from google.adk.tools.langchain_tool import LangchainTool # import from google.genai import types from langchain_community.tools import WikipediaQueryRun from langchain_community.utilities import WikipediaAPIWrapper cloud_logging_client = google.cloud.logging.Client() cloud_logging_client.setup_logging() load_dotenv() model_name = os.getenv("MODEL") print(model_name) # Tools def append_to_state( tool_context: ToolContext, field: str, response: str ) -> dict[str, str]: """Append new output to an existing state key. Args: field (str): a field name to append to response (str): a string to append to the field Returns: dict[str, str]: {"status": "success"} """ existing_state = tool_context.state.get(field, []) tool_context.state[field] = existing_state + [response] logging.info(f"[Added to {field}] {response}") return {"status": "success"} def write_file( tool_context: ToolContext, directory: str, filename: str, content: str ) -> dict[str, str]: target_path = os.path.join(directory, filename) os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(target_path), exist_ok=True) with open(target_path, "w") as f: f.write(content) return {"status": "success"} # Agents file_writer = Agent( name="file_writer", model=model_name, description="Creates marketing details and saves a pitch document.", instruction=""" PLOT_OUTLINE: { PLOT_OUTLINE? } INSTRUCTIONS: - Create a marketable, contemporary movie title suggestion for the movie described in the PLOT_OUTLINE. If a title has been suggested in PLOT_OUTLINE, you can use it, or replace it with a better one. - Use your 'write_file' tool to create a new txt file with the following arguments: - for a filename, use the movie title - Write to the 'movie_pitches' directory. - For the 'content' to write, extract the following from the PLOT_OUTLINE: - A logline - Synopsis or plot outline """, generate_content_config=types.GenerateContentConfig( temperature=0, ), tools=[write_file], ) screenwriter = Agent( name="screenwriter", model=model_name, description="As a screenwriter, write a logline and plot outline for a biopic about a historical character.", instruction=""" INSTRUCTIONS: Your goal is to write a logline and three-act plot outline for an inspiring movie about a historical character(s) described by the PROMPT: { PROMPT? } - If there is CRITICAL_FEEDBACK, use those thoughts to improve upon the outline. - If there is RESEARCH provided, feel free to use details from it, but you are not required to use it all. - If there is a PLOT_OUTLINE, improve upon it. - Use the 'append_to_state' tool to write your logline and three-act plot outline to the field 'PLOT_OUTLINE'. - Summarize what you focused on in this pass. PLOT_OUTLINE: { PLOT_OUTLINE? } RESEARCH: { research? } CRITICAL_FEEDBACK: { CRITICAL_FEEDBACK? } """, generate_content_config=types.GenerateContentConfig( temperature=0, ), tools=[append_to_state], ) researcher = Agent( name="researcher", model=model_name, description="Answer research questions using Wikipedia.", instruction=""" PROMPT: { PROMPT? } PLOT_OUTLINE: { PLOT_OUTLINE? } CRITICAL_FEEDBACK: { CRITICAL_FEEDBACK? } INSTRUCTIONS: - If there is a CRITICAL_FEEDBACK, use your wikipedia tool to do research to solve those suggestions - If there is a PLOT_OUTLINE, use your wikipedia tool to do research to add more historical detail - If these are empty, use your Wikipedia tool to gather facts about the person in the PROMPT - Use the 'append_to_state' tool to add your research to the field 'research'. - Summarize what you have learned. Now, use your Wikipedia tool to do research. """, generate_content_config=types.GenerateContentConfig( temperature=0, ), tools=[ LangchainTool(tool=WikipediaQueryRun(api_wrapper=WikipediaAPIWrapper())), append_to_state, ], ) film_concept_team = SequentialAgent( name="film_concept_team", description="Write a film plot outline and save it as a text file.", sub_agents=[ researcher, screenwriter, file_writer ], ) root_agent = Agent( name="greeter", model=model_name, description="Guides the user in crafting a movie plot.", instruction=""" - Let the user know you will help them write a pitch for a hit movie. Ask them for a historical figure to create a movie about. - When they respond, use the 'append_to_state' tool to store the user's response in the 'PROMPT' state key and transfer to the 'film_concept_team' agent """, generate_content_config=types.GenerateContentConfig( temperature=0, ), tools=[append_to_state], sub_agents=[film_concept_team], ) EOF
您的文件结构现在应如下所示:
设置虚拟环境
- 在终端中,使用
uv创建并激活虚拟环境。这样可确保项目依赖项不会与系统 Python 发生冲突。uv venv source .venv/bin/activate
安装要求
- 在终端中运行以下命令,以创建
requirements.txt文件。cat <<EOF > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/requirements.txt # Lists all Python dependencies required to run the multi-agent system, # including the Google ADK, LangChain community tools, and web server libraries. langchain-community==0.3.20 wikipedia==1.4.0 google-adk==1.8.0 fastapi==0.121.2 uvicorn==0.38.0 EOF - 在终端中将必需的软件包安装到虚拟环境中。
uv pip install -r requirements.txt
设置环境变量
- 在终端中使用以下命令创建
.env文件,并自动插入您的项目 ID 和区域。cat <<EOF > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/.env GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT="$(gcloud config get-value project)" GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT_NUMBER="$(gcloud projects describe $(gcloud config get-value project) --format='value(projectNumber)')" GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION="us-central1" GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI=true MODEL="gemini-2.5-flash" EOF - 在终端中,将变量加载到 shell 会话中。
source .env
回顾
在本部分中,您为项目建立了本地基础:
- 创建了目录结构和必要的代理启动器文件(
agent.py、callback_logging.py、requirements.txt)。 - 使用虚拟环境 (
uv) 隔离依赖项。 - 配置了环境变量 (
.env),用于存储项目特定的详细信息,例如项目 ID 和区域。
6. 探索代理文件
您已设置本实验的源代码,其中包括一个预先编写的多代理系统。在部署应用之前,最好先了解代理的定义方式。核心代理逻辑位于 workflow_agents/agent.py 中。
- 在 Cloud Shell 编辑器中,使用左侧的文件浏览器导航到
adk_multiagent_system_gke/workflow_agents/,然后打开agent.py文件。 - 请花点时间浏览一下该文件。您无需理解每一行代码,但需要注意其高级结构:
- 各个代理:该文件定义了三个不同的
Agent对象:researcher、screenwriter和file_writer。每个代理都会获得一个特定的instruction(即提示)以及一个允许使用的tools列表(例如WikipediaQueryRun工具或自定义write_file工具)。 - 代理组合:各个代理链接在一起,形成一个称为
film_concept_team的SequentialAgent。这会告知 ADK 依次运行这些代理,并将状态从一个代理传递到下一个代理。 - 根代理:定义了一个
root_agent(命名为“greeter”),用于处理初始用户互动。当用户提供提示时,此代理会将其保存到应用的状态,然后将控制权转移到film_concept_team工作流。
- 各个代理:该文件定义了三个不同的
了解此结构有助于明确您即将部署的内容:不仅是单个代理,还是由 ADK 编排的专业代理协调团队。
7. 创建 GKE Autopilot 集群
准备好环境后,下一步是预配代理应用将运行的基础设施。您将创建一个 GKE Autopilot 集群,作为部署的基础。我们使用 Autopilot 模式,因为它可处理集群底层节点、扩缩和安全性的复杂管理,让您能够专注于部署应用。
- 在终端中,创建一个名为
adk-cluster的新 GKE Autopilot 集群。gcloud container clusters create-auto adk-cluster \ --location=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION \ --project=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT - 创建集群后,在终端中运行以下命令,将
kubectl配置为连接到该集群:gcloud container clusters get-credentials adk-cluster \ --location=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION \ --project=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT~/.kube/config)。从这一刻起,kubectl命令行工具将通过身份验证,并被定向为与您的adk-cluster通信。
回顾
在本部分中,您预配了以下基础架构:
- 使用
gcloud创建了完全托管的 GKE Autopilot 集群。 - 配置了本地
kubectl工具,以对新集群进行身份验证并与之通信。
8. 将应用容器化并推送
您的代理的代码目前仅存在于 Cloud Shell 环境中。如需在 GKE 上运行该应用,您必须先将其打包为容器映像。容器映像是一个静态的便携式文件,可将应用的代码及其所有依赖项捆绑在一起。运行此映像时,它会变成一个正在运行的容器。
此流程包含三个关键步骤:
- 创建入口点:定义一个
main.py文件,将代理逻辑转换为可运行的网络服务器。 - 定义容器映像:创建 Dockerfile,作为构建容器映像的蓝图。
- 构建并推送:使用 Cloud Build 执行 Dockerfile,创建容器映像并将其推送到 Google Artifact Registry(一个用于存储映像的安全代码库)。
准备应用以进行部署
您的 ADK 代理需要一个 Web 服务器来接收请求。main.py 文件将充当此入口点,使用 FastAPI 框架通过 HTTP 公开代理的功能。
- 在 终端的
adk_multiagent_system_gke目录的根目录中,创建一个名为main.py的新文件。cat <<EOF > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/main.py """ Serves as the application entry point. Initializes the FastAPI web server, discovers the agents defined in the workflow directory, and exposes them via HTTP endpoints for interaction. """ import os import uvicorn from fastapi import FastAPI from google.adk.cli.fast_api import get_fast_api_app # Get the directory where main.py is located AGENT_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # Configure the session service (e.g., SQLite for local storage) SESSION_SERVICE_URI = "sqlite:///./sessions.db" # Configure CORS to allow requests from various origins for this lab ALLOWED_ORIGINS = ["http://localhost", "http://localhost:8080", "*"] # Enable the ADK's built-in web interface SERVE_WEB_INTERFACE = True # Call the ADK function to discover agents and create the FastAPI app app: FastAPI = get_fast_api_app( agents_dir=AGENT_DIR, session_service_uri=SESSION_SERVICE_URI, allow_origins=ALLOWED_ORIGINS, web=SERVE_WEB_INTERFACE, ) # You can add more FastAPI routes or configurations below if needed # Example: # @app.get("/hello") # async def read_root(): # return {"Hello": "World"} if __name__ == "__main__": # Get the port from the PORT environment variable provided by the container runtime # Run the Uvicorn server, listening on all available network interfaces (0.0.0.0) uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=int(os.environ.get("PORT", 8080))) EOFuvicorn服务器运行此应用,监听主机0.0.0.0以接受来自任何 IP 地址的连接,并监听PORT环境变量指定的端口,我们将在稍后的 Kubernetes 清单中设置此环境变量。
此时,您在 Cloud Shell 编辑器的资源管理器面板中看到的文件结构应如下所示: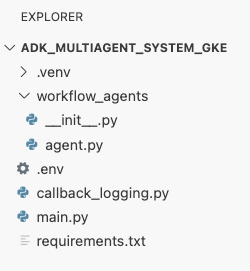
使用 Docker 将 ADK 代理容器化
为了将应用部署到 GKE,我们首先需要将其打包到容器映像中,该映像会将应用的代码与运行所需的所有库和依赖项捆绑在一起。我们将使用 Docker 来创建此容器映像。
- 在 终端的
adk_multiagent_system_gke目录的根目录中,创建一个名为Dockerfile的新文件。cat <<'EOF' > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/Dockerfile # Defines the blueprint for the container image. Installs dependencies, # sets up a secure non-root user, and specifies the startup command to run the # agent web server. # Use an official lightweight Python image as the base FROM python:3.13-slim # Set the working directory inside the container WORKDIR /app # Create a non-root user for security best practices RUN adduser --disabled-password --gecos "" myuser # Copy and install dependencies first to leverage Docker's layer caching COPY requirements.txt . RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt # Copy all application code into the container COPY . . # Create the directory where the agent will write files at runtime # The -p flag ensures the command doesn't fail if the directory already exists RUN mkdir -p movie_pitches # Change ownership of EVERYTHING in /app to the non-root user # Without this, the running agent would be denied permission to write files. RUN chown -R myuser:myuser /app # Switch the active user from root to the non-root user USER myuser # Add the user's local binary directory to the system's PATH ENV PATH="/home/myuser/.local/bin:$PATH" # Define the command to run when the container starts CMD ["sh", "-c", "uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port $PORT"] EOF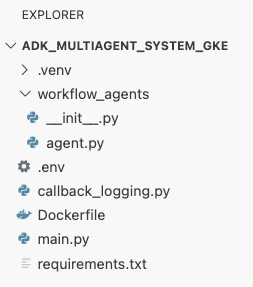
构建容器映像并将其推送到 Artifact Registry
现在,您已经有了 Dockerfile,接下来将使用 Cloud Build 构建映像并将其推送到 Artifact Registry。Artifact Registry 是与 Google Cloud 服务集成的安全私有注册表。GKE 将从该注册表中拉取映像以运行您的应用。
- 在终端中,创建一个新的 Artifact Registry 制品库来存储您的容器映像。
gcloud artifacts repositories create adk-repo \ --repository-format=docker \ --location=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION \ --description="ADK repository" - 在终端中,使用
gcloud builds submit构建容器映像并将其推送到代码库。gcloud builds submit \ --tag $GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION-docker.pkg.dev/$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT/adk-repo/adk-agent:latest \ --project=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \ .Dockerfile中的步骤。它会在云端构建映像,使用 Artifact Registry 代码库的地址标记该映像,并自动将其推送到该代码库。 - 在终端中,验证映像是否已构建:
gcloud artifacts docker images list \ $GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION-docker.pkg.dev/$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT/adk-repo \ --project=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT
回顾
在本部分中,您将代码打包以进行部署:
- 创建了一个
main.py入口点,用于将代理封装在 FastAPI Web 服务器中。 - 定义了
Dockerfile,用于将代码和依赖项捆绑到可移植的映像中。 - 使用 Cloud Build 构建映像并将其推送到安全的 Artifact Registry 仓库。
9. 创建 Kubernetes 清单
现在,您的容器映像已构建并存储在 Artifact Registry 中,您需要指示 GKE 如何运行该映像。这涉及两项主要活动:
- 配置权限:您将在集群内为代理创建专用身份,并授予该身份对所需 Google Cloud API(特别是 Vertex AI)的安全访问权限。
- 定义应用状态:您将编写一个 Kubernetes 清单文件(一个 YAML 文档),以声明方式定义应用运行所需的一切内容,包括容器映像、环境变量以及应如何向网络公开应用。
为 Vertex AI 配置 Kubernetes 服务账号
您的代理需要获得与 Vertex AI API 通信的权限,才能访问 Gemini 模型。在 GKE 中授予此权限最安全且推荐的方法是使用工作负载身份。借助 Workload Identity,您可以将 Kubernetes 原生身份(即 Kubernetes 服务账号)与 Google Cloud 身份(即 IAM 服务账号)相关联,从而完全避免下载、管理和存储静态 JSON 密钥。
- 在终端中,创建 Kubernetes 服务账号 (
adk-agent-sa)。这会在 GKE 集群中为您的代理创建一个身份,供您的 Pod 使用。kubectl create serviceaccount adk-agent-sa - 在终端中,通过创建政策绑定,将 Kubernetes 服务账号关联到 Google Cloud IAM。此命令会向您的
adk-agent-sa授予aiplatform.user角色,使其能够安全地调用 Vertex AI API。gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding projects/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} \ --role=roles/aiplatform.user \ --member=principal://iam.googleapis.com/projects/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT_NUMBER}/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.svc.id.goog/subject/ns/default/sa/adk-agent-sa \ --condition=None
创建 Kubernetes 清单文件
Kubernetes 使用 YAML 清单文件来定义应用的期望状态。您将创建一个 deployment.yaml 文件,其中包含两个重要的 Kubernetes 对象:Deployment 和 Service。
- 在终端中,生成
deployment.yaml文件。cat <<EOF > ~/adk_multiagent_systems/deployment.yaml # Defines the Kubernetes resources required to deploy the application to GKE. # Includes the Deployment (to run the container pods) and the Service # (to expose the application via a Load Balancer). apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: adk-agent spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: adk-agent template: metadata: labels: app: adk-agent spec: # Assign the Kubernetes Service Account for Workload Identity serviceAccountName: adk-agent-sa containers: - name: adk-agent imagePullPolicy: Always # The path to the container image in Artifact Registry image: ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION}-docker.pkg.dev/${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}/adk-repo/adk-agent:latest # Define the resources for GKE Autopilot to provision resources: limits: memory: "1Gi" cpu: "1000m" ephemeral-storage: "512Mi" requests: memory: "1Gi" cpu: "1000m" ephemeral-storage: "512Mi" ports: - containerPort: 8080 # Environment variables passed to the application env: - name: PORT value: "8080" - name: GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT value: ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT} - name: GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION value: ${GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION} - name: GOOGLE_GENAI_USE_VERTEXAI value: "true" - name: MODEL value: "gemini-2.5-flash" --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: adk-agent spec: # Create a public-facing Network Load Balancer with an external IP type: LoadBalancer ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 8080 selector: app: adk-agent EOF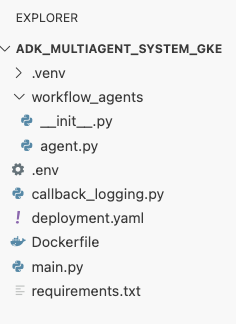
回顾
在此部分中,您定义了安全和部署配置:
- 创建了 Kubernetes 服务账号,并使用 Workload Identity 将其与 Google Cloud IAM 相关联,从而使您的 pod 可以安全地访问 Vertex AI,而无需管理密钥。
- 生成了一个
deployment.yaml文件,用于定义 Deployment(如何运行 pod)和 Service(如何通过负载平衡器公开 pod)。
10. 将应用部署到 GKE
定义清单文件并将容器映像推送到 Artifact Registry 后,您现在可以部署应用了。在此任务中,您将使用 kubectl 将配置应用到 GKE 集群,然后监控状态以确保代理正确启动。
- 在终端中,将
deployment.yaml清单应用到您的集群。kubectl apply -f deployment.yamlkubectl apply命令会将您的deployment.yaml文件发送到 Kubernetes API 服务器。然后,服务器会读取您的配置,并协调创建 Deployment 和 Service 对象。 - 在终端中,实时查看部署状态。等待 pod 处于
Running状态。kubectl get pods -l=app=adk-agent --watch- 待处理:Pod 已被集群接受,但容器尚未创建。
- 正在创建容器:GKE 正在从 Artifact Registry 拉取容器映像并启动容器。
- 运行:成功!容器正在运行,并且您的代理应用已上线。
- 当状态显示为
Running时,在终端中按 CTRL+C 停止 watch 命令并返回到命令提示符。
回顾
在本部分中,您启动了工作负载:
- 使用
kubectlapply 将清单发送到集群。 - 监控 Pod 生命周期(Pending -> ContainerCreating -> Running),确保应用已成功启动。
11. 与代理互动
您的 ADK 代理现已在 GKE 上实时运行,并通过公共负载平衡器向互联网公开。您将连接到代理的 Web 界面以与其互动,并验证整个系统是否正常运行。
查找服务的外部 IP 地址
如需访问代理,您首先需要获取 GKE 为您的服务预配的公共 IP 地址。
- 在终端中,运行以下命令以获取服务的详细信息。
kubectl get service adk-agent - 在
EXTERNAL-IP列中查找相应值。首次部署服务后,可能需要一两分钟才能分配 IP 地址。如果显示为pending,请稍等片刻,然后再次运行该命令。输出将类似于以下内容:NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE adk-agent-service LoadBalancer 10.120.12.234 34.123.45.67 80:31234/TCP 5mEXTERNAL-IP下列出的地址(例如 34.123.45.67)是代理的公共入口点。
测试已部署的智能体
现在,您可以使用公共 IP 地址直接从浏览器访问 ADK 的内置 Web 界面。
- 从终端中复制外部 IP 地址 (
EXTERNAL-IP)。 - 在网络浏览器中打开一个新标签页,然后输入
http://[EXTERNAL-IP],将[EXTERNAL-IP]替换为您复制的 IP 地址。 - 您现在应该会看到 ADK Web 界面。
- 确保在代理下拉菜单中选择了 workflow_agents。
- 开启令牌流式传输。
- 输入
hello并按 Enter 键即可开始新对话。 - 观察结果。代理应快速回复问候语:“我可以帮助您撰写热门电影的推介。您想拍摄哪位历史人物的电影?
- 当系统提示您选择历史人物时,选择您感兴趣的人物。以下是一些建议:
the most successful female pirate in historythe woman who invented the first computer compilera legendary lawman of the American Wild West
回顾
在本部分中,您验证了部署:
- 检索了由 LoadBalancer 分配的外部 IP 地址。
- 通过浏览器访问 ADK Web 界面,确认多智能体系统响应迅速且功能正常。
12. 配置自动扩缩
生产环境中的一个主要挑战是处理不可预测的用户流量。像您在上一个任务中那样对副本数量进行硬编码,意味着您要么为闲置资源支付过高的费用,要么在流量高峰期间面临性能不佳的风险。GKE 通过自动扩缩功能解决了这一问题。
您将配置 HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA),这是一个 Kubernetes 控制器,可根据实时 CPU 利用率自动调整部署中正在运行的 pod 数量。
- 在 Cloud Shell 编辑器的终端中,在
adk_multiagent_system_gke目录的根目录下创建一个新的hpa.yaml文件。cloudshell edit ~/adk_multiagent_systems/hpa.yaml - 将以下内容添加到新的
hpa.yaml文件中:# Configures the HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA) to automatically scale # the number of running agent pods up or down based on CPU utilization # to handle varying traffic loads. apiVersion: autoscaling/v1 kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler metadata: name: adk-agent-hpa spec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: adk-agent minReplicas: 1 maxReplicas: 5 targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 50adk-agentDeployment 为目标。它可确保始终至少有 1 个 Pod 处于运行状态,最多设置 5 个 Pod,并会添加/移除副本,以使平均 CPU 利用率保持在 50% 左右。此时,您在 Cloud Shell 编辑器中的探索器面板中看到的文件结构应如下所示:
- 将以下内容粘贴到终端中,以将 HPA 应用到您的集群。
kubectl apply -f hpa.yaml
验证自动扩缩器
HPA 现在处于有效状态,并正在监控您的部署。您可以检查其状态,看看它是否在运行。
- 在终端中运行以下命令,以获取 HPA 的状态。
kubectl get hpa adk-agent-hpaNAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE adk-agent-hpa Deployment/adk-agent 0%/50% 1 5 1 30s
回顾
在本部分中,您针对生产流量进行了优化:
- 创建了
hpa.yaml清单来定义扩缩规则。 - 部署了 HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA),以根据 CPU 利用率自动调整 Pod 副本的数量。
13. 为生产进行准备
注意:以下部分仅供参考,不包含要执行的后续步骤。这些指南旨在为将应用投入生产环境提供背景信息和最佳实践。
通过资源分配调整效果
在 GKE Autopilot 中,您可以通过在 deployment.yaml 中指定资源 requests 来控制为应用预配的 CPU 和内存量。
如果您发现代理因内存不足而运行缓慢或崩溃,可以通过修改 deployment.yaml 中的 resources 块来增加其资源分配,然后使用 kubectl apply 重新应用该文件。
例如,如需将内存增加一倍:
# In deployment.yaml
# ...
resources:
requests:
memory: "2Gi" # Increased from 1Gi
cpu: "1000m"
# ...
使用 CI/CD 自动执行工作流
在本实验中,您手动运行了命令。专业做法是创建 CI/CD(持续集成/持续部署)流水线。通过将源代码库(例如 GitHub)与 Cloud Build 触发器相关联,您可以实现整个部署流程的自动化。
借助流水线,每次推送代码更改时,Cloud Build 都可以自动执行以下操作:
- 构建新的容器映像。
- 将该映像推送到 Artifact Registry。
- 将更新后的 Kubernetes 清单应用于 GKE 集群。
安全地管理密钥
在本实验中,您将配置存储在 .env 文件中,并将其传递给应用。这对于开发来说很方便,但对于 API 密钥等敏感数据来说并不安全。建议的最佳实践是使用 Secret Manager 安全地存储 Secret。
GKE 与 Secret Manager 原生集成,可让您将 Secret 直接装载到 Pod 中,作为环境变量或文件,而无需将它们签入源代码。
您请求的清理资源部分已插入到总结部分之前。
14. 清理资源
为避免因本教程中使用的资源导致您的 Google Cloud 账号产生费用,请删除包含这些资源的项目,或者保留项目但删除各个资源。
删除 GKE 集群
在本实验中,GKE 集群是主要费用因素。删除该实例会停止计算费用。
- 在终端中,运行以下命令:
gcloud container clusters delete adk-cluster \ --location=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION \ --quiet
删除 Artifact Registry 代码库
存储在 Artifact Registry 中的容器映像会产生存储费用。
- 在终端中,运行以下命令:
gcloud artifacts repositories delete adk-repo \ --location=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION \ --quiet
删除项目(可选)
如果您专门为此实验创建了一个新项目,并且不打算再次使用该项目,那么最简单的清理方法是删除整个项目。
- 在终端中,运行以下命令(将
[YOUR_PROJECT_ID]替换为您的实际项目 ID):gcloud projects delete [YOUR_PROJECT_ID]
15. 总结
恭喜!您已成功将多代理 ADK 应用部署到生产级 GKE 集群。这是一项重大成就,涵盖了现代云原生应用的核心生命周期,为您部署自己的复杂智能体系统奠定了坚实的基础。
回顾
在本实验中,您学习了如何执行以下操作:
- 预配 GKE Autopilot 集群。
- 使用
Dockerfile构建容器映像并将其推送到 Artifact Registry - 使用 Workload Identity 安全地连接到 Google Cloud API。
- 为 Deployment 和 Service 编写 Kubernetes 清单。
- 使用 LoadBalancer 将应用公开到互联网。
- 使用 HorizontalPodAutoscaler (HPA) 配置自动扩缩。
