1. 概览
在本实验中,您将学习如何使用 Vertex AI Gen AI Evaluation Service 评估大语言模型。您将使用该 SDK 运行评估作业、比较结果,并根据数据做出有关模型性能和提示设计的决策。
本实验将引导您完成常见的评估工作流程,从简单的基于计算的指标开始,逐步过渡到更精细的基于模型的评估。您还将学习如何创建根据您的特定目标量身定制的自定义指标,以及如何使用 Vertex AI Experiments 跟踪您的工作。
学习内容
在本实验中,您将学习如何执行以下任务:
- 使用基于计算的指标和基于模型的指标评估模型。
- 创建自定义指标,使评估与产品目标保持一致。
- 并排比较不同的提示模板。
- 测试多个基于角色的提示,找出效果最佳的版本。
- 使用 Vertex AI Experiments 跟踪并直观呈现评估运行。
参考
- 代码示例:本实验基于 Google Cloud 生成式 AI 代码库中的示例
- 基于:Vertex AI Gen AI Evaluation 文档
- 数据集:用于指令遵循评估的 OpenOrca 数据集
2. 项目设置
Google 账号
如果您还没有个人 Google 账号,则必须先创建一个 Google 账号。
请使用个人账号,而不是工作账号或学校账号。
登录 Google Cloud 控制台
使用个人 Google 账号登录 Google Cloud 控制台。
启用结算功能
您可以通过以下两种方式启用结算功能。您可以使用个人结算账号,也可以按照以下步骤兑换积分。
兑换 5 美元的 Google Cloud 赠金(可选)
如需参加此研讨会,您需要拥有一个有一定信用额度的结算账号。如果您打算使用自己的结算方式,则可以跳过此步骤。
- 点击此链接,然后使用个人 Google 账号登录。您会看到类似如下的内容:

- 点击点击此处访问您的积分按钮。然后,您会进入一个页面,可以在其中设置结算资料。如果您看到免费试用订阅界面,请点击“取消”,然后继续关联结算信息。
- 点击确认。您现在已关联到 Google Cloud Platform 试用结算账号。
设置个人结算账号
如果您使用 Google Cloud 抵用金设置了结算,则可以跳过此步骤。
如需设置个人结算账号,请点击此处在 Cloud 控制台中启用结算功能。
注意事项:
- 完成本实验的 Cloud 资源费用应不到 1 美元。
- 您可以按照本实验结束时的步骤删除资源,以避免产生更多费用。
- 新用户符合参与 $300 USD 免费试用计划的条件。
创建项目(可选)
如果您没有要用于此实验的当前项目,请在此处创建一个新项目。
3. 设置 Vertex AI Workbench 环境
首先,我们来访问预配置的笔记本环境并安装必要的依赖项。
访问 Vertex AI Workbench
- 在 Google Cloud 控制台中,依次点击导航菜单 ☰ > Vertex AI > 信息中心,前往 Vertex AI。
- 点击启用所有推荐的 API。注意:请等待此步骤完成
- 点击左侧的 Workbench 以创建新的 Workbench 实例。
- 将工作台实例命名为 evaluation-workbench,然后点击创建。
- 等待工作台完成设置。这可能需要几分钟的时间。
- 工作台预配完成后,点击打开 JupyterLab。
- 在工作台中,创建一个新的 Python3 笔记本。
如需详细了解此环境的功能,请参阅 Vertex AI Workbench 的官方文档。
安装软件包并配置环境
- 在笔记本的第一个单元格中,添加并运行以下 import 语句 (SHIFT+ENTER),以安装 Vertex AI SDK(包含评估组件)和其他必需的软件包。
%pip install -U -q google-cloud-aiplatform[evaluation] %pip install -U -q datasets anthropic[vertex] openai - 如需使用新安装的软件包,建议运行以下代码段来重启内核。
# Automatically restart kernel after installation so that your environment can access the new packages. import IPython app = IPython.Application.instance() app.kernel.do_shutdown(True) - 将以下内容替换为您的项目 ID 和位置,然后运行以下单元格。默认位置设置为
europe-west1,但您应使用 Vertex AI Workbench 实例所在的位置。# Configure your project settings PROJECT_ID = "YOUR PROJECT ID" LOCATION = "europe-west1" - 在新的单元中运行以下代码,导入本实验所需的所有 Python 库。
from anthropic import AnthropicVertex from google.auth import default, transport import openai import pandas as pd from vertexai.evaluation import ( EvalTask, MetricPromptTemplateExamples, PairwiseMetric, PointwiseMetric, PointwiseMetricPromptTemplate, ) from vertexai.generative_models import GenerativeModel from vertexai.preview.evaluation import notebook_utils
4. 设置评估数据集
在本教程中,我们将使用 OpenOrca 数据集中的 10 个样本。这样一来,我们就能获得足够的数据来发现模型之间的显著差异,同时保持可管理的评估时间。
💡 专业提示:在生产环境中,您需要 100-500 个示例才能获得具有统计显著性的结果,但 10 个样本非常适合学习和快速原型设计!
准备数据集
- 在新单元格中,运行以下单元格以加载数据、将其转换为 pandas DataFrame,并将
response列重命名为reference,以便在评估任务中清晰显示,并创建包含 10 个示例的随机样本。from datasets import load_dataset ds = ( load_dataset( "Open-Orca/OpenOrca", data_files="1M-GPT4-Augmented.parquet", split="train[:100]", ) .to_pandas() .drop(columns=["id"]) .rename(columns={"response": "reference"}) ) dataset = ds.sample(n=10) - 上一个单元运行完毕后,在下一个单元中添加并运行以下代码,以显示评估数据集的前几行。
dataset.head()
5. 使用基于计算的指标建立基准
在此任务中,您将使用基于计算的指标建立基准分数。这种方法速度快,可提供客观的基准来衡量未来的改进。
我们将使用 ROUGE(以召回率为导向的摘要评估研究),这是摘要任务的标准指标。其工作原理是将模型生成的回答中的字词序列(N 元语法)与标准答案reference文本中的字词进行比较。
详细了解基于计算的指标。
运行基准评估
- 在新单元格中,添加并运行以下单元格,以定义要测试的模型
gemini-2.0-flash。generation_config包括影响模型输出的参数,例如temperature和max_output_tokens。# Model to be evaluated model = GenerativeModel( "gemini-2.0-flash", generation_config={"temperature": 0.6, "max_output_tokens": 256, "top_k": 1}, )GenerativeModel类是 Vertex AI SDK 中用于与大语言模型交互的主要接口。 - 在下一个单元中,添加并运行以下代码以创建和执行
EvalTask。Vertex AI Evaluation SDK 中的此对象用于编排评估。您需要使用数据集和要计算的指标(在本例中为rouge_l_sum)来配置该函数。# Define an EvalTask with ROUGE-L-SUM metric rouge_eval_task = EvalTask( dataset=dataset, metrics=["rouge_l_sum"], ) rouge_result = rouge_eval_task.evaluate( model=model, prompt_template="# System_prompt\n{system_prompt} # Question\n{question}", ) - 在下一个单元中运行此代码,以显示结果。
notebook_utils.display_eval_result(rouge_result)display_eval_result()实用程序会显示平均(平均值)得分和逐行结果。
6. 可选:使用基于模型的逐点指标进行评估
注意:本部分可能无法在提供的免费抵用金限额内运行。
虽然 ROUGE 非常有用,但它只衡量词汇重叠程度(也就是说,它只统计匹配的字词,而不理解上下文、同义词或释义)。因此,它在确定回答是否流畅或合乎逻辑方面表现不佳。如需更深入地了解模型的性能,您可以使用基于模型的点状指标。
采用这种方法时,另一个 LLM(即“评判模型”)会根据一组预定义的标准(例如流畅度或连贯性)单独评估每条回答。
详细了解基于模型的指标。
运行逐点评估
- 在新的单元格中运行以下代码,以创建交互式下拉菜单。对于此运行,请从列表中选择 coherence。
#Select a pointwise metric to use import ipywidgets as widgets pointwise_single_turn_metrics = [ metric for metric in MetricPromptTemplateExamples.list_example_metric_names() if not metric.startswith("pairwise") and not metric.startswith("multi_turn") ] dropdown = widgets.Dropdown( options=pointwise_single_turn_metrics, description="Select a metric:", font_weight="bold", style={"description_width": "initial"}, ) def dropdown_eventhandler(change): global POINTWISE_METRIC if change["type"] == "change" and change["name"] == "value": POINTWISE_METRIC = change.new print("Selected:", change.new) POINTWISE_METRIC = dropdown.value dropdown.observe(dropdown_eventhandler, names="value") display(dropdown) - 在新单元格中,再次运行
EvalTask,这次使用基于所选模型的指标。Vertex AI Evaluation Service 会为评判模型构建提示,其中包含原始提示、参考答案、候选模型的回答以及所选指标的说明。评判模型会返回一个数值分数,并说明其评分的原因。注意:此步骤需要几分钟时间才能运行。pointwise_result = EvalTask( dataset=dataset, metrics=[POINTWISE_METRIC], ).evaluate( model=model, prompt_template="# System_prompt\n{system_prompt} # Question\n{question}", )
显示结果
评估完成后,下一步是分析输出。
- 在新单元中运行以下代码,以查看摘要指标,其中显示了所选指标的平均得分。
notebook_utils.display_eval_result(pointwise_result) - 在下一个单元中运行以下代码,查看逐行细分结果,其中包括评判模型针对其得分给出的书面理由。这种定性反馈有助于您了解为什么系统会以某种方式对回答进行评分。
notebook_utils.display_explanations(pointwise_result, num=1, metrics=[POINTWISE_METRIC])
7. 构建自定义指标以获得更深入的分析洞见
流畅度等预构建指标非常有用,但对于特定产品,您通常需要根据自己的目标衡量效果。借助自定义逐点指标,您可以定义自己的评估标准和评分标准。
在此任务中,您将从头开始创建一个名为 summarization_helpfulness 的新指标。
定义和运行自定义指标
- 在新的单元格中运行以下代码,以定义自定义指标。
PointwiseMetricPromptTemplate包含指标的构建块:- criteria:告知评判模型要评估的具体维度:“关键信息”“简洁性”和“无扭曲”。
- rating_rubric:提供 5 分制评分标准,用于定义每个分数的含义。
- input_variables:将数据集中的其他列传递给评判模型,以便该模型获得执行评估所需的上下文。
# This new custom metric evaluates the actual quality and usefulness of the summary. summarization_helpfulness_metric = PointwiseMetric( metric="summarization_helpfulness", metric_prompt_template=PointwiseMetricPromptTemplate( criteria={ "Key Information": "Does the summary capture the most critical pieces of information from the original text? It should not miss the main topic or key takeaways.", "Conciseness": "Is the summary brief and to the point? It should avoid unnecessary words or repetitive information.", "No Distortion": "Does the summary introduce information or opinions that were NOT present in the original text? It must accurately reflect the source material without adding hallucinations." }, rating_rubric={ "5": "Excellent: Captures all key information, is highly concise, and has zero distortion.", "4": "Good: Captures most key information with minor omissions, is concise, and has no distortion.", "3": "Satisfactory: Captures the main idea but misses some key details OR is not very concise.", "2": "Unsatisfactory: Misses the main idea of the original text OR contains minor distortions/hallucinations.", "1": "Poor: Is completely irrelevant, fails to summarize the text, OR contains significant distortions.", }, input_variables=["prompt", "reference"], ), ) - 在下一个单元格中运行以下代码,以使用新的自定义指标执行
EvalTask。# You would then update the EvalTask to use this new metric pointwise_result = EvalTask( dataset=dataset, metrics=[summarization_helpfulness_metric], ).evaluate( model=model, prompt_template="# System_prompt\n{system_prompt} # Question\n{question}", ) - 在新单元格中运行以下命令以显示结果。
notebook_utils.display_eval_result(pointwise_result)
8. 使用成对评估比较模型
当您需要确定两个模型在特定任务上的表现哪个更好时,可以使用基于模型的成对评估。此方法是一种 A/B 测试,其中评判模型会确定获胜者,从而为以数据为依据的模型选择提供直接比较。
模型:
- 候选模型:模型变量(之前定义为
gemini-2.0-flash)会传递到.evaluate()方法中。这是您要测试的主要模型。 - 基准模型:在 PairwiseMetric 类中指定第二个模型
gemini-2.0-flash-lite。这是您要比较的模型。
运行成对评估
- 在新单元格中,添加并运行以下代码,以创建交互式下拉菜单。这样,您就可以选择要使用哪个成对指标进行比较。在此次运行中,选择 pairwise_summarization_quality。
from IPython.display import display import ipywidgets as widgets pairwise_single_turn_metrics = [ metric for metric in MetricPromptTemplateExamples.list_example_metric_names() if metric.startswith("pairwise") and "multi_turn" not in metric ] dropdown = widgets.Dropdown( options=pairwise_single_turn_metrics, description="Select a metric:", font_weight="bold", style={"description_width": "initial"}, ) def dropdown_eventhandler(change): global POINTWISE_METRIC if change["type"] == "change" and change["name"] == "value": POINTWISE_METRIC = change.new print("Selected:", change.new) def dropdown_eventhandler(change): global PAIRWISE_METRIC_NAME if change["type"] == "change" and change["name"] == "value": PAIRWISE_METRIC_NAME = change.new print("Selected:", change.new) PAIRWISE_METRIC_NAME = dropdown.value dropdown.observe(dropdown_eventhandler, names="value") display(dropdown) - 在下一个单元格中,添加并运行以下代码以配置和执行
EvalTask。请注意,PairwiseMetric类用于定义基准模型 (gemini-2.0-flash-lite),而候选模型 (gemini-2.0-flash) 会传递到.evaluate()方法中。pairwise_result = EvalTask( dataset=dataset, metrics=[ PairwiseMetric( metric=PAIRWISE_METRIC_NAME, metric_prompt_template=MetricPromptTemplateExamples.get_prompt_template( PAIRWISE_METRIC_NAME ), # Define a baseline model to compare against baseline_model=GenerativeModel("gemini-2.0-flash-lite"), ) ], ).evaluate( # Specify a candidate model for pairwise comparison model=model, prompt_template="# System_prompt\n{system_prompt} # Question\n{question}", ) - 在新的单元格中,添加并运行以下代码以显示结果。总结表格将显示每个模型的“胜出率”,指明 Judge Model 更偏好哪个模型。
notebook_utils.display_eval_result(pairwise_result)
9. 可选:评估基于角色的提示
注意:本部分可能无法在提供的免费抵用金限额内运行。
在此任务中,您将测试多个提示模板,这些模板会指示模型采用不同的角色。此流程通常称为“提示工程”或“提示设计”,可让您系统地找到针对特定使用情形的最有效提示。
准备总结数据集
若要执行此评估,数据集需要包含以下字段:
instruction:我们提供给模型的核心任务。在这种情况下,提示很简单,就是“总结以下文章:”。context:模型需要处理的源文本。这里提供了四条不同的新闻片段。reference:事实依据或“黄金标准”摘要。系统会将模型生成的输出与此文本进行比较,以计算 ROUGE 和摘要质量等指标的分数。
- 在新单元格中,添加并运行以下代码,以创建用于总结任务的
pandas.DataFrame。instruction = "Summarize the following article: \n" context = [ "Typhoon Phanfone has killed at least one person, a US airman on Okinawa who was washed away by high waves. Thousands of households have lost power and Japan's two largest airlines have suspended many flights. The storm also forced the suspension of the search for people missing after last week's volcanic eruption. The storm-tracking website Tropical Storm Risk forecasts that Phanfone will rapidly lose power over the next few hours as it goes further into the Pacific Ocean. Typhoon Phanfone was downgraded from an earlier status of a super typhoon, but the Japan Meteorological Agency had warned it was still a dangerous storm. Japan averages 11 typhoons a year, according to its weather agency. The typhoon made landfall on Monday morning near the central city of Hamamatsu, with winds of up to 180 km/h (112 mph). The airman was one of three US military personnel swept away by high waves whipped up by the typhoon off southern Okinawa island, where the US has a large military base. The remaining two are still missing. A police spokesman said they had been taking photographs of the sea. A university student who was surfing off the seas of Kanagawa Prefecture, south of Tokyo, was also missing, national broadcast NHK reports. It said at least 10 people had been injured and 9,500 houses were without power. The storm was expected to deposit about 100mm of rain on Tokyo over 24 hours, according to the Transport Ministry website. Many schools were closed on Monday and two car companies in Japan halted production at some plants ahead of the storm. More than 174 domestic flights were affected nationwide, NHK state broadcaster said on Sunday. On Sunday, heavy rain delayed the Japanese Formula One Grand Prix in Suzaka. French driver Jules Bianchi lost control in the wet conditions and crashed, sustaining a severe head injury.", "The blaze started at the detached building in Drivers End in Codicote, near Welwyn, during the morning. There was another fire at the building 20 years ago, after which fire-proof foil was placed under the thatch, which is protecting the main building. More than 15 fire engines and support vehicles were called to tackle the blaze. Roads in the area were closed and traffic diverted.", 'The 18-year-old fell at the New Charter Academy on Broadoak Road in Ashton-under-Lyne at about 09:10 BST, Greater Manchester Police (GMP) said. GMP said he had gone to Manchester Royal Infirmary and his condition was "serious". Principal Jenny Langley said the school would remain "fully open" while police investigated. "Our thoughts are with the family and we\'re doing everything we can to support them along with staff and pupils," she said.', 'But Belgian-born Dutchman Max Verstappen was unable to drive a car legally on his own in either country. That all changed on Wednesday when the youngster turned 18 and passed his driving test at the first attempt. Despite having competed in 14 grands prix since his debut in Australia in March, Verstappen admitted to feeling the pressure during his test. "It\'s a relief," said the Toro Rosso driver, who finished ninth in Japan on Sunday and had only started driving lessons a week ago. "I was a bit nervous to make mistakes, but the exam went well." A bonus of turning 18 is that Verstappen will now be able to drink the champagne if he ever makes it onto the podium.', ] reference = [ "A powerful typhoon has brought many parts of Japan to a standstill and briefly battered Tokyo before heading out to sea.", "A major fire has been burning in the thatched roof of a large property in Hertfordshire.", "A student has been taken to hospital after falling from a balcony at a Greater Manchester school.", "He is Formula 1's youngest ever driver and in charge of a car that can reach over 200mph.", ] response = [ "Typhoon Phanfone, while downgraded from super typhoon status, caused significant disruption and tragedy in Japan. One US airman died after being swept away by high waves, with two more missing. The storm caused power outages for thousands, flight cancellations, and the suspension of rescue efforts for missing volcano victims. Heavy rain and strong winds led to school and factory closures, transportation disruptions, and at least 10 injuries. The typhoon is expected to weaken as it moves over the Pacific Ocean.", "A large fire broke out in a detached thatched building in Codicote, near Welwyn. This is the second fire at the building in 20 years. Thankfully, fire-proof foil installed after the previous fire is protecting the main building. Over 15 fire engines and support vehicles responded, closing roads and diverting traffic in the area.", "An 18-year-old student at New Charter Academy in Ashton-under-Lyne suffered a serious fall and was hospitalized. The incident is under investigation by Greater Manchester Police, but the school remains open. The principal expressed support for the student's family and the school community.", "Max Verstappen, a Formula One driver, was finally able to get his driver's license at age 18. Despite already competing in 14 Grand Prix races, he was not of legal driving age in his native countries. He admitted to being nervous but passed the test on his first attempt. As an added bonus of turning 18, Verstappen can now enjoy champagne on the podium if he places.", ] eval_dataset = pd.DataFrame( { "instruction": instruction, "context": context, "reference": reference, } )
运行提示评估任务
准备好总结数据集后,您就可以运行此任务的核心实验了:比较多个提示模板,看看哪个模板能让模型生成最优质的输出。
- 在下一个单元格中,创建一个
EvalTask,该对象将用于每个提示实验。通过设置experiment参数,系统会自动将此任务的所有评估运行记录到 Vertex AI Experiments 中并进行分组。EXPERIMENT_NAME = "eval-sdk-prompt-engineering" # @param {type:"string"} summarization_eval_task = EvalTask( dataset=eval_dataset, metrics=[ "rouge_l_sum", "bleu", "fluency", "coherence", "safety", "groundedness", "summarization_quality", "verbosity", "instruction_following", "text_quality", ], experiment=EXPERIMENT_NAME, )rouge_l_sum和bleu等计算指标到各种基于模型的指标(fluency、coherence、summarization_quality、instruction_following等)。这样一来,我们就能全面了解每个提示对模型输出质量的影响。 - 在新的单元中,添加并运行以下代码,以定义和评估四种以角色为导向的提示策略。
for循环会遍历每个模板并运行评估。每个模板都旨在通过为模型提供特定角色或目标来生成不同风格的摘要:- 角色 #1(标准):中性、直截了当的总结请求。
- 角色 2(高管):要求以要点形式提供总结,重点关注结果和影响,这符合忙碌的高管的偏好。
- 角色 3(五年级学生):指示模型使用简单语言,测试其调整输出复杂程度的能力。
- 角色 4(技术分析师):要求提供高度基于事实的摘要,其中保留了关键统计数据和实体,用于测试模型的精确度。请注意,这些新模板中的占位符(例如
{context}和{instruction})与您为此任务创建的eval_dataset中的新列名称相匹配。
# Define prompt templates that target different user personas prompt_templates = [ # Persona 1: Standard, neutral summary "Article: {context}. Task: {instruction}. Summary:", # Persona 2: For a busy executive (bullet points) "Instruction: {instruction} into three key bullet points for a busy executive. Focus on the main outcome and impact. Article: {context}. Summary:", # Persona 3: For a 5th grader (simple language) "Instruction: {instruction} such that you're explaining it to a 10-year-old. Use simple words. Article: {context}. Summary:", # Persona 4: For a technical analyst (fact-focused) "Instruction: Provide a detailed, factual summary of the following text, ensuring all key statistics, names, and locations are preserved. Article: {context}. Summary:", ] eval_results = [] for i, prompt_template in enumerate(prompt_templates): eval_result = summarization_eval_task.evaluate( prompt_template=prompt_template, model=GenerativeModel( "gemini-2.0-flash", generation_config={ "temperature": 0.3, "max_output_tokens": 256, "top_k": 1, }, ), evaluation_service_qps=5, ) eval_results.append((f"Prompt Persona #{i+1}", eval_result))
分析和直观呈现结果
运行实验是第一步。真正的价值在于分析结果,以便根据数据做出决策。在此任务中,您将使用 SDK 的可视化工具来解读提示角色实验的输出。
- 在新单元中运行以下代码,以显示您测试的四种提示角色的总结结果。这样一来,您就可以从宏观上以量化方式了解效果。
for title, eval_result in eval_results: notebook_utils.display_eval_result(title=title, eval_result=eval_result) - 在新单元中,添加并运行以下代码,以查看每个角色的
summarization_quality指标的理由。for title, eval_result in eval_results: notebook_utils.display_explanations( eval_result, metrics=["summarization_quality"], num=2 ) - 生成雷达图,直观呈现每个提示的不同质量指标之间的权衡取舍。在新的单元中,添加并运行以下代码。
notebook_utils.display_radar_plot( eval_results, metrics=["instruction_following", "fluency", "coherence", "text_quality"], ) - 如需更直接的并列比较,请创建条形图。在新的单元中,添加并运行以下代码。
notebook_utils.display_bar_plot( eval_results, metrics=["instruction_following", "fluency", "coherence", "text_quality"], )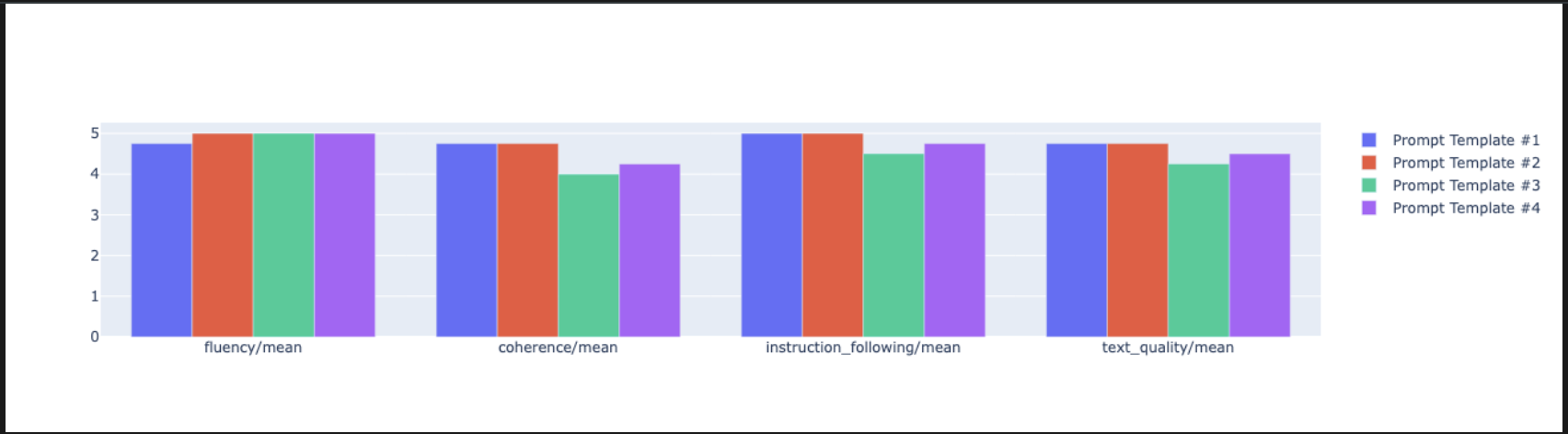
- 现在,您可以查看已记录到 Vertex AI 实验中的所有运行作业的摘要。这有助于您跟踪一段时间内的工作情况。在新的单元中,添加并运行以下代码:
summarization_eval_task.display_runs()
10. 清理实验
为保持项目井井有条并避免产生不必要的费用,最佳做法是清理您创建的资源。在本实验中,每次评估运行都记录到了 Vertex AI 实验中。以下代码会删除此父实验,同时也会移除所有关联的运行作业及其底层数据。
- 在新单元格中运行此代码,以删除 Vertex AI 实验及其关联的运行作业。
delete_experiment = True # Please set your LOCATION to the same one used during Vertex AI SDK initialization. LOCATION = "YOUR LOCATION" # @param {type:"string"} if delete_experiment: from google.cloud import aiplatform aiplatform.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=LOCATION) experiment = aiplatform.Experiment(EXPERIMENT_NAME) experiment.delete()
11. 从实践到生产
您在本实验中学习的技能是创建可靠 AI 应用的基础。不过,从手动运行的笔记本过渡到生产级评估系统需要额外的基础设施和更系统的方法。本部分概述了在扩大规模时需要考虑的关键实践和战略框架。
制定生产评估策略
若要在生产环境中应用本实验中的技能,最好将这些技能转化为可重复使用的策略。以下框架概述了常见场景(例如模型选择、提示优化和持续监控)中的关键注意事项。
对于模型选择:
# Evaluation strategy for choosing models
evaluation_strategy = {
"dataset_size": "100+ examples for statistical significance",
"metrics": ["task-specific", "general quality", "efficiency"],
"comparison_type": "pairwise with statistical testing",
"baseline": "established_model_or_human_benchmark"
}
提示优化
# Systematic prompt improvement workflow
prompt_optimization = {
"hypothesis": "Clear statement of what you're testing",
"variants": "3-5 different prompt strategies",
"evaluation": "Same metrics across all variants",
"analysis": "Statistical significance + qualitative review"
}
用于持续监控
# Production evaluation pipeline
production_eval = {
"frequency": "Every model update + weekly monitoring",
"automation": "CI/CD integration with quality gates",
"metrics": "Speed + quality + cost tracking",
"alerting": "Performance degradation detection"
}
成本效益注意事项
大规模的基于模型的评估可能成本高昂。经济高效的制作策略会针对不同目的采用不同的方法。下表总结了不同评估类型在速度、费用和应用场景方面的权衡:
评估类型 | 时间 | 每次抽样的费用 | 最适合的用途 |
ROUGE/BLEU | 秒 | 约为 0.001 美元 | 大批量筛查 |
基于模型的 Pointwise | 约 1-2 秒 | 约 0.01 美元 | 质量评估 |
成对比较 | 约 2-3 秒 | 约 0.02 美元 | 模型选择 |
人工评估 | 分钟 | $1-10 | 黄金标准验证 |
通过 CI/CD 和监控实现自动化
手动运行笔记本无法扩容。在持续集成/持续部署 (CI/CD) 流水线中自动执行评估。
- 创建质量门禁:将评估任务集成到 CI/CD 流水线中(例如,Cloud Build)。自动对新提示或模型运行评估,并在关键质量得分低于您定义的阈值时阻止部署。
- 监控趋势:将评估运行的摘要指标导出到 Google Cloud Monitoring 等服务。构建信息中心以跟踪一段时间内的质量,并设置自动提醒,以便在出现任何明显的性能下降时通知您的团队。
12. 总结
您已完成本实验。您已学习了评估生成式 AI 模型的基本技能。
本实验是“可用于生产用途的 AI 与 Google Cloud”学习路线的组成部分。
- 探索完整课程,弥合从原型设计到生产的差距。
- 使用 #
ProductionReadyAI分享您的进度。
回顾
在本实验中,您学习了如何执行以下任务:
- 使用
EvalTask框架应用评估最佳实践。 - 使用不同的指标类型,从基于计算的评估者到基于模型的评估者。
- 通过测试不同版本的提示来优化提示。
- 构建可重现的实验跟踪工作流。
可供持续学习的资源
您在本实验中学习的系统评估方法将为构建可靠、高质量的 AI 应用奠定基础。请记住:良好的评估是实验性 AI 与生产成功之间的桥梁。
