1. מבוא
בשיעור ה-Lab הזה תלמדו איך לבצע את תהליך העבודה המלא של כוונון מפוקח (SFT) במודל Google Gemini, כדי להתאים אותו למשימה ספציפית: סיכום מאמרים. מודלים גדולים של שפה הם עוצמתיים, אבל בגלל שהם מיועדים לשימוש כללי, אפשר לשפר את היעילות שלהם בתרחישי שימוש ספציפיים באמצעות כוונון עדין. אם תאמנו את המודל על מערך נתונים איכותי של דוגמאות, תוכלו לשפר את העקביות, האיכות והיעילות שלו במשימה שהגדרתם.
תשתמשו ב-Gemini 2.5 Flash, מודל קל וחסכוני, ותבצעו כוונון עדין באמצעות Vertex AI.
סקירה כללית של הארכיטקטורה
אלה הפעולות שנבצע:
- Cloud Shell: סביבת הפיתוח שלכם.
- Cloud Storage: אחסון נתוני אימון/אימות בפורמט JSONL.
- Vertex AI Training: ניהול משימת הכוונון העדין.
- נקודת קצה של Vertex AI: מארחת את המודל שעבר כוונון עדין.
מה תלמדו
- הכנת מערכי נתונים באיכות גבוהה לצורך כוונון מפוקח (SFT).
- הגדרת משימות של כוונון עדין והפעלתן באמצעות Vertex AI SDK ל-Python.
- הערכת מודלים באמצעות מדדים אוטומטיים (ציוני ROUGE).
- השוואה בין מודלים בסיסיים ומודלים שעברו כוונון עדין כדי לכמת את השיפורים.
2. הגדרת הפרויקט
חשבון Google
אם אין לכם חשבון Google אישי, אתם צריכים ליצור חשבון Google.
משתמשים בחשבון לשימוש אישי במקום בחשבון לצורכי עבודה או בחשבון בית ספרי.
כניסה למסוף Google Cloud
נכנסים למסוף Google Cloud באמצעות חשבון Google אישי.
הפעלת חיוב
מימוש קרדיטים בשווי 5 $ל-Google Cloud (אופציונלי)
כדי להשתתף בסדנה הזו, צריך חשבון לחיוב עם יתרה מסוימת. אם אתם מתכננים להשתמש בחיוב משלכם, אתם יכולים לדלג על השלב הזה.
- לוחצים על הקישור הזה ונכנסים לחשבון Google אישי.יופיע מסך כמו זה:

- לוחצים על הלחצן כאן אפשר לגשת לקרדיטים.תועברו לדף להגדרת פרופיל לחיוב
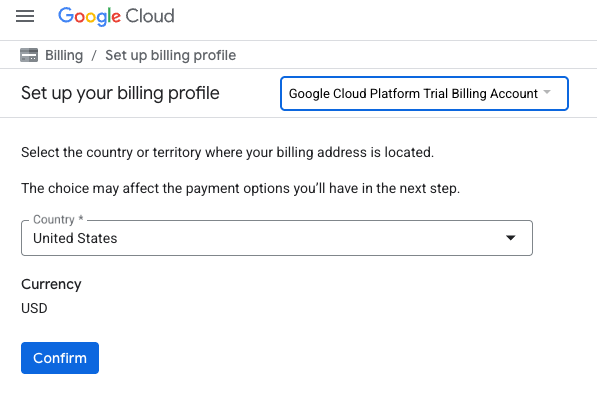
- לוחצים על אישור.
החשבון שלכם מקושר עכשיו לחשבון לחיוב ב-Google Cloud Platform לניסיון.
יצירת פרויקט (אופציונלי)
אם אין לכם פרויקט שאתם רוצים להשתמש בו בסדנה הזו, אתם יכולים ליצור פרויקט חדש כאן.
3. פתיחת Cloud Shell Editor
- כדי לעבור ישירות אל Cloud Shell Editor, לוחצים על הקישור הזה.
- אם תתבקשו לאשר בשלב כלשהו היום, תצטרכו ללחוץ על אישור כדי להמשיך.
- אם הטרמינל לא מופיע בתחתית המסך, פותחים אותו:
- לוחצים על הצגה.
- לוחצים על Terminal (מסוף)
 .
.
- בטרמינל, מגדירים את הפרויקט באמצעות הפקודה הבאה:
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]- דוגמה:
gcloud config set project lab-project-id-example - אם אתם לא זוכרים את מזהה הפרויקט, אתם יכולים להציג רשימה של כל מזהי הפרויקטים באמצעות הפקודה:
gcloud projects list
- דוגמה:
- תוצג ההודעה הבאה:
Updated property [core/project].
4. הפעלת ממשקי API
כדי להשתמש ב-Vertex AI ובשירותים אחרים, צריך להפעיל את ממשקי ה-API הנדרשים בפרויקט בענן שלכם ב-Google Cloud.
- בטרמינל, מפעילים את ממשקי ה-API:
- Vertex AI API (
aiplatform.googleapis.com): מאפשר שימוש ב-Vertex AI לצורך כוונון עדין והצגת מודלים. - Cloud Storage API (
storage.googleapis.com): מאפשר אחסון של מערכי נתונים וארטיפקטים של מודלים.
gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com \ storage.googleapis.com - Vertex AI API (
5. הגדרת סביבת הפרויקט
יצירת ספריית עבודה
- בטרמינל, יוצרים ספרייה לפרויקט ועוברים אליה.
mkdir gemini-finetuning cd gemini-finetuning
הגדרה של משתני סביבה
- בטרמינל, מגדירים את משתני הסביבה של הפרויקט. ניצור קובץ
env.shכדי לאחסן את המשתנים האלה, כך שאפשר יהיה לטעון אותם מחדש בקלות אם הסשן יתנתק.cat <<EOF > env.sh export PROJECT_ID=\$(gcloud config get-value project) export REGION="us-central1" export BUCKET_NAME="\${PROJECT_ID}-gemini-tuning" EOF source env.sh
יצירת קטגוריה של Cloud Storage
- בטרמינל, יוצרים קטגוריה לאחסון מערך הנתונים ופריטי המודל.
gcloud storage buckets create gs://$BUCKET_NAME --project=$PROJECT_ID --location=$REGION
הגדרת סביבה וירטואלית
- אנחנו נשתמש ב-
uvכדי לנהל את סביבת Python שלנו. בטרמינל, מריצים את הפקודה:uv venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate - בטרמינל, מתקינים את חבילות Python הנדרשות.
uv pip install google-cloud-aiplatform rouge-score matplotlib pandas tqdm
6. הכנת נתוני האימון
נתונים איכותיים הם הבסיס לשיפור מוצלח של המודל. תשתמשו במערך הנתונים WikiLingua, תמירו אותו לפורמט JSONL הספציפי שנדרש ל-Gemini ותעלו אותו לקטגוריה שלכם ב-Cloud Storage.
- בטרמינל, יוצרים קובץ בשם
prepare_data.py.cloudshell edit prepare_data.py - הדביקו את הקוד הבא ב-
prepare_data.py.import json import os import pandas as pd from google.cloud import storage import subprocess # Configuration BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"] PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] def download_data(): print("Downloading WikiLingua dataset...") # Using gsutil to copy from public bucket subprocess.run(["gsutil", "cp", "gs://github-repo/generative-ai/gemini/tuning/summarization/wikilingua/*", "."], check=True) def convert_to_gemini_format(input_file, output_file, max_samples=1000): print(f"Converting {input_file} to Gemini format (first {max_samples} samples)...") converted_data = [] with open(input_file, 'r') as f: for i, line in enumerate(f): if i >= max_samples: break obj = json.loads(line) messages = obj.get("messages", []) # Convert messages to Gemini 2.5 format # Input: {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "..."}, {"role": "model", "content": "..."}]} # Output: {"contents": [{"role": "user", "parts": [{"text": "..."}]}, {"role": "model", "parts": [{"text": "..."}]}]} contents = [] for msg in messages: role = msg["role"] content = msg["content"] contents.append({ "role": role, "parts": [{"text": content}] }) converted_data.append({"contents": contents}) with open(output_file, 'w') as f: for item in converted_data: f.write(json.dumps(item) + "\n") print(f"Saved {len(converted_data)} examples to {output_file}") def upload_to_gcs(local_file, destination_blob_name): print(f"Uploading {local_file} to gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/{destination_blob_name}...") storage_client = storage.Client(project=PROJECT_ID) bucket = storage_client.bucket(BUCKET_NAME) blob = bucket.blob(destination_blob_name) blob.upload_from_filename(local_file) print("Upload complete.") def main(): download_data() # Process Training Data convert_to_gemini_format("sft_train_samples.jsonl", "train_gemini.jsonl") upload_to_gcs("train_gemini.jsonl", "datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl") # Process Validation Data convert_to_gemini_format("sft_val_samples.jsonl", "val_gemini.jsonl") upload_to_gcs("val_gemini.jsonl", "datasets/val/val_gemini.jsonl") print("Data preparation complete!") if __name__ == "__main__": main() - בטרמינל, מריצים את סקריפט הכנת הנתונים.
python prepare_data.py
7. קביעת ביצועים בסיסיים
לפני שמבצעים התאמה עדינה, צריך להגדיר מדד השוואה. תמדדו את הביצועים של מודל הבסיס gemini-2.5-flash במשימת הסיכום באמצעות ציוני ROUGE.
- בטרמינל, יוצרים קובץ בשם
evaluate.py.cloudshell edit evaluate.py - הדביקו את הקוד הבא ב-
evaluate.py.import argparse import json import os import pandas as pd from google.cloud import aiplatform import vertexai from vertexai.generative_models import GenerativeModel, GenerationConfig, HarmCategory, HarmBlockThreshold from rouge_score import rouge_scorer from tqdm import tqdm import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import time # Configuration PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] REGION = os.environ["REGION"] aiplatform.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=REGION) def evaluate(model_name, test_file, max_samples=50, output_json="results.json"): print(f"Evaluating model: {model_name}") # Load Test Data test_df = pd.read_csv(test_file) test_df = test_df.head(max_samples) model = GenerativeModel(model_name) safety_settings = { HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HARASSMENT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HATE_SPEECH: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, } generation_config = GenerationConfig( temperature=0.1, max_output_tokens=1024, ) scorer = rouge_scorer.RougeScorer(['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'], use_stemmer=True) results = [] for index, row in tqdm(test_df.iterrows(), total=len(test_df)): input_text = row['input_text'] reference_summary = row['output_text'] try: response = model.generate_content( input_text, generation_config=generation_config, safety_settings=safety_settings ) generated_summary = response.text scores = scorer.score(reference_summary, generated_summary) results.append({ "generated": generated_summary, "reference": reference_summary, "rouge1": scores['rouge1'].fmeasure, "rouge2": scores['rouge2'].fmeasure, "rougeL": scores['rougeL'].fmeasure }) except Exception as e: print(f"Error processing example {index}: {e}") # Sleep briefly to avoid quota issues if hitting limits time.sleep(1) # Save results with open(output_json, 'w') as f: json.dump(results, f, indent=2) return pd.DataFrame(results) def plot_results(df, title, filename): os.makedirs("plots", exist_ok=True) metrics = ['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'] fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5)) for i, metric in enumerate(metrics): axes[i].hist(df[metric], bins=10, alpha=0.7, color='skyblue', edgecolor='black') axes[i].set_title(f'{metric} Distribution') axes[i].set_xlabel('Score') axes[i].set_ylabel('Count') plt.suptitle(title) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig(f"plots/{filename}") print(f"Plot saved to plots/{filename}") def compare_results(baseline_file, tuned_file): with open(baseline_file, 'r') as f: baseline_data = pd.DataFrame(json.load(f)) with open(tuned_file, 'r') as f: tuned_data = pd.DataFrame(json.load(f)) print("\n--- Comparison ---") metrics = ['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'] for metric in metrics: base_mean = baseline_data[metric].mean() tuned_mean = tuned_data[metric].mean() diff = tuned_mean - base_mean print(f"{metric}: Base={base_mean:.4f}, Tuned={tuned_mean:.4f}, Diff={diff:+.4f}") # Comparative Plot os.makedirs("plots", exist_ok=True) comparison_df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Metric': metrics, 'Baseline': [baseline_data[m].mean() for m in metrics], 'Tuned': [tuned_data[m].mean() for m in metrics] }) comparison_df.plot(x='Metric', y=['Baseline', 'Tuned'], kind='bar', figsize=(10, 6)) plt.title('Baseline vs Tuned Model Performance') plt.ylabel('Average Score') plt.xticks(rotation=0) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig("plots/comparison.png") print("Comparison plot saved to plots/comparison.png") def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, default="gemini-2.5-flash", help="Model resource name") parser.add_argument("--baseline", type=str, help="Path to baseline results json for comparison") parser.add_argument("--output", type=str, default="results.json", help="Output file for results") args = parser.parse_args() # Ensure test data exists (it was downloaded in prepare_data step) if not os.path.exists("sft_test_samples.csv"): # Fallback download if needed subprocess.run(["gsutil", "cp", "gs://github-repo/generative-ai/gemini/tuning/summarization/wikilingua/sft_test_samples.csv", "."], check=True) df = evaluate(args.model, "sft_test_samples.csv", output_json=args.output) print("\n--- Results Summary ---") print(df.describe()) plot_filename = "baseline_dist.png" if not args.baseline else "tuned_dist.png" plot_results(df, f"ROUGE Scores - {args.model}", plot_filename) if args.baseline: compare_results(args.baseline, args.output) if __name__ == "__main__": main() - במסוף, מריצים את ההערכה הראשונית.
python evaluate.py --model "gemini-2.5-flash" --output "baseline.json"baseline.jsonוגרף ב-plots/baseline_dist.png.
8. הגדרה והפעלה של כוונון עדין
עכשיו מפעילים משימת כוונון עדין מנוהלת ב-Vertex AI.
- בטרמינל, יוצרים קובץ בשם
tune.py.cloudshell edit tune.py - הדביקו את הקוד הבא ב-
tune.py.import os import time from google.cloud import aiplatform import vertexai from vertexai.preview.tuning import sft # Configuration PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] REGION = os.environ["REGION"] BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"] aiplatform.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=REGION) def train(): print("Launching fine-tuning job...") sft_tuning_job = sft.train( source_model="gemini-2.5-flash", # Using specific version for stability train_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl", validation_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/val/val_gemini.jsonl", epochs=1, # Keep it short for the lab adapter_size=4, learning_rate_multiplier=1.0, tuned_model_display_name="gemini-2.5-flash-wikilingua", ) print(f"Job started: {sft_tuning_job.resource_name}") print("Waiting for job to complete... (this may take ~45 minutes)") # Wait for the job to complete while not sft_tuning_job.has_ended: time.sleep(60) sft_tuning_job.refresh() print(f"Status: {sft_tuning_job.state.name}") print("Job completed!") print(f"Tuned Model Endpoint: {sft_tuning_job.tuned_model_endpoint_name}") return sft_tuning_job.tuned_model_endpoint_name if __name__ == "__main__": train() - במסוף, מריצים את סקריפט הכוונון העדין.
python tune.py
9. הסבר על קוד האימון
בזמן שההרצה של המשימה מתבצעת, נבחן מקרוב את הסקריפט tune.py כדי להבין איך מתבצעת ההתאמה העדינה.
כוונון מפוקח מנוהל (SFT)
הסקריפט משתמש בשיטה vertexai.tuning.sft.train כדי לשלוח משימת שיפור מנוהלת. הפלטפורמה מסתירה את המורכבות של הקצאת התשתית, הפצת ההדרכה וניהול נקודות הבדיקה.
sft_tuning_job = sft.train(
source_model="gemini-2.5-flash",
train_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl",
# ...
)
הגדרת LoRA
במקום להגדיר LoraConfig באופן ידני כמו במסגרות קוד פתוח, ב-Vertex AI התהליך הזה פשוט יותר וכולל כמה פרמטרים מרכזיים:
-
adapter_size: הפרמטר הזה (שמוגדר ל-4בסקריפט שלנו) שולט בדרגה של מתאמי LoRA. גודל גדול יותר מאפשר למודל ללמוד התאמות מורכבות יותר, אבל מגדיל את מספר הפרמטרים שאפשר לאמן. -
epochs: הגדרנו את הערך הזה ל-1במעבדה הזו כדי לקצר את זמן ההכשרה (כ-20 דקות). בתרחיש ייצור, יכול להיות שתגדילו את הערך הזה כדי לאפשר למודל ללמוד יותר לעומק מהנתונים שלכם, אבל חשוב להיזהר מהתאמת יתר.
בחירת מודל
אנחנו מציינים במפורש את source_model="gemini-2.5-flash". Vertex AI תומך בגרסאות שונות של Gemini, וצימוד של גרסה ספציפית מבטיח שהצינור יישאר יציב וניתן לשחזור.
10. השוואה בין מודלים
אחרי שמשימת הכוונון העדין מסתיימת, אפשר להשוות בין הביצועים של המודל החדש לבין הביצועים של המודל הבסיסי.
- מקבלים את נקודת הקצה של המודל המכוון. הוא הודפס בסוף התסריט
tune.py. היא תיראה בערך כך:projects/.../locations/.../endpoints/.... - מריצים שוב את סקריפט ההערכה, הפעם מעבירים את המודל המשופר ואת תוצאות הבסיס להשוואה.
# Replace [YOUR_TUNED_MODEL_ENDPOINT] with the actual endpoint name export TUNED_MODEL="projects/[YOUR_PROJECT_ID]/locations/[YOUR_REGION]/endpoints/[YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID]" python evaluate.py --model "$TUNED_MODEL" --baseline "baseline.json" --output "tuned.json" - מעיינים בתוצאות. הסקריפט יציג השוואה של ציוני ROUGE וייצור תרשים
plots/comparison.pngשמציג את השיפור.אפשר לראות את התרשימים על ידי פתיחת התיקייהplotsב-Cloud Shell Editor.
11. הסרת המשאבים
כדי להימנע מחיובים, מומלץ למחוק את המשאבים שיצרתם.
- בטרמינל, מוחקים את קטגוריה של Cloud Storage ואת המודל שעבר התאמה.
gcloud storage rm -r gs://$BUCKET_NAME # Note: You can delete the model endpoint from the Vertex AI Console
12. מעולה!
השלמת בהצלחה את תהליך הכוונון העדין של Gemini 2.5 Flash ב-Vertex AI.
Recap
בשיעור ה-Lab הזה:
- הכנתם מערך נתונים בפורמט JSONL לצורך כוונון עדין של Gemini.
- יצרנו בסיס באמצעות מודל הבסיס Gemini 2.5 Flash.
- הפעלתם פעולת כוונון מפוקח (SFT) ב-Vertex AI.
- הערכה והשוואה של המודל שעבר כוונון עדין לעומת המודל הבסיסי.
המאמרים הבאים
ה-Lab הזה הוא חלק מתוכנית הלימודים Production-Ready AI with Google Cloud.
כאן אפשר לעיין בתוכנית הלימודים המלאה כדי לגשר על הפער בין אב טיפוס לייצור.
שתפו את ההתקדמות שלכם באמצעות ההאשטאג #ProductionReadyAI.
