1. 소개
이 실습에서는 Google Gemini 모델에서 지도 미세 조정의 전체 워크플로를 실행하여 특정 작업(기사 요약)에 맞게 조정하는 방법을 알아봅니다. 대규모 언어 모델은 강력하지만 범용적인 특성으로 인해 파인 튜닝을 통해 특정 사용 사례에 더욱 효과적으로 사용할 수 있습니다. 고품질 예시 데이터 세트로 모델을 학습시키면 타겟 작업의 일관성, 품질, 효율성을 개선할 수 있습니다.
경량의 비용 효율적인 모델인 Gemini 2.5 Flash를 사용하고 Vertex AI를 사용하여 파인 튜닝을 실행합니다.
아키텍처 개요
빌드할 항목은 다음과 같습니다.
- Cloud Shell: 개발 환경입니다.
- Cloud Storage: JSONL 형식으로 학습/검증 데이터를 저장합니다.
- Vertex AI Training: 미세 조정 작업을 관리합니다.
- Vertex AI 엔드포인트: 미세 조정된 모델을 호스팅합니다.
학습할 내용
- 지도 미세 조정을 위한 고품질 데이터 세트를 준비합니다.
- Vertex AI SDK for Python을 사용하여 미세 조정 작업을 구성하고 실행합니다.
- 자동 측정항목 (ROUGE 점수)을 사용하여 모델을 평가합니다.
- 기본 모델과 파인 튜닝된 모델을 비교하여 개선사항을 정량화합니다.
2. 프로젝트 설정
Google 계정
아직 개인 Google 계정이 없다면 Google 계정을 만들어야 합니다.
직장 또는 학교 계정 대신 개인 계정을 사용합니다.
Google Cloud 콘솔에 로그인
개인 Google 계정을 사용하여 Google Cloud 콘솔에 로그인합니다.
결제 사용 설정
$5 Google Cloud 크레딧 사용 (선택사항)
이 워크숍을 진행하려면 크레딧이 있는 결제 계정이 필요합니다. 자체 결제를 사용하려는 경우 이 단계를 건너뛰어도 됩니다.
- 이 링크를 클릭하고 개인 Google 계정으로 로그인합니다. 다음과 같이 표시됩니다.

- 여기를 클릭하여 크레딧에 액세스 버튼을 클릭합니다. 그러면 결제 프로필을 설정하는 페이지로 이동합니다.
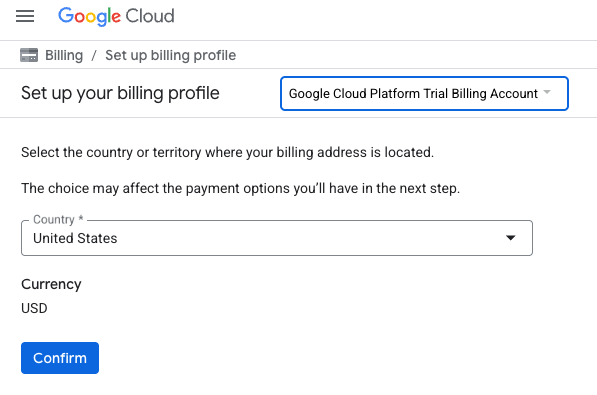
- 확인을 클릭합니다.
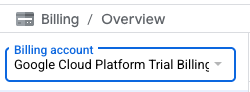
이제 Google Cloud Platform 평가판 결제 계정에 연결되었습니다.
프로젝트 만들기(선택사항)
이 실습에 사용할 현재 프로젝트가 없는 경우 여기에서 새 프로젝트를 만드세요.
3. Cloud Shell 편집기 열기
- 이 링크를 클릭하여 Cloud Shell 편집기로 바로 이동합니다.
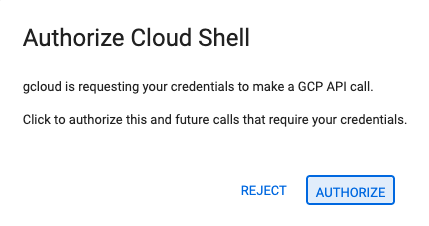
- 오늘 언제든지 승인하라는 메시지가 표시되면 승인을 클릭하여 계속합니다.
- 터미널이 화면 하단에 표시되지 않으면 다음을 실행하여 엽니다.
- 보기를 클릭합니다.
- 터미널을 클릭합니다.
- 터미널에서 다음 명령어를 사용하여 프로젝트를 설정합니다.
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]- 예:
gcloud config set project lab-project-id-example - 프로젝트 ID가 기억나지 않는 경우 다음을 사용하여 모든 프로젝트 ID를 나열할 수 있습니다.
gcloud projects list
- 예:
- 다음 메시지가 표시되어야 합니다.
Updated property [core/project].
4. API 사용 설정
Vertex AI 및 기타 서비스를 사용하려면 Google Cloud 프로젝트에서 필요한 API를 사용 설정해야 합니다.
- 터미널에서 API를 사용 설정합니다.
- Vertex AI API (
aiplatform.googleapis.com): 모델을 미세 조정하고 제공하기 위해 Vertex AI를 사용할 수 있도록 지원합니다. - Cloud Storage API (
storage.googleapis.com): 데이터 세트 및 모델 아티팩트의 저장을 지원합니다.
gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com \ storage.googleapis.com - Vertex AI API (
5. 프로젝트 환경 설정
작업 디렉터리 만들기
- 터미널에서 프로젝트의 디렉터리를 만들고 해당 디렉터리로 이동합니다.
mkdir gemini-finetuning cd gemini-finetuning
환경 변수 설정
- 터미널에서 프로젝트의 환경 변수를 정의합니다. 세션 연결이 끊어질 경우 쉽게 다시 로드할 수 있도록 이러한 변수를 저장하는
env.sh파일을 만듭니다.cat <<EOF > env.sh export PROJECT_ID=\$(gcloud config get-value project) export REGION="us-central1" export BUCKET_NAME="\${PROJECT_ID}-gemini-tuning" EOF source env.sh
Cloud Storage 버킷 만들기
- 터미널에서 데이터 세트와 모델 아티팩트를 저장할 버킷을 만듭니다.
gcloud storage buckets create gs://$BUCKET_NAME --project=$PROJECT_ID --location=$REGION
가상 환경 설정
uv을 사용하여 Python 환경을 관리합니다. 터미널에서 다음을 실행합니다.uv venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate- 터미널에서 필요한 Python 패키지를 설치합니다.
uv pip install google-cloud-aiplatform rouge-score matplotlib pandas tqdm
6. 학습 데이터 준비
양질의 데이터는 성공적인 파인 튜닝의 기반입니다. WikiLingua 데이터 세트를 사용하고, 이를 Gemini에 필요한 특정 JSONL 형식으로 변환한 후 스토리지 버킷에 업로드합니다.
- 터미널에서
prepare_data.py라는 파일을 만듭니다.cloudshell edit prepare_data.py - 다음 코드를
prepare_data.py에 붙여넣습니다.import json import os import pandas as pd from google.cloud import storage import subprocess # Configuration BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"] PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] def download_data(): print("Downloading WikiLingua dataset...") # Using gsutil to copy from public bucket subprocess.run(["gsutil", "cp", "gs://github-repo/generative-ai/gemini/tuning/summarization/wikilingua/*", "."], check=True) def convert_to_gemini_format(input_file, output_file, max_samples=1000): print(f"Converting {input_file} to Gemini format (first {max_samples} samples)...") converted_data = [] with open(input_file, 'r') as f: for i, line in enumerate(f): if i >= max_samples: break obj = json.loads(line) messages = obj.get("messages", []) # Convert messages to Gemini 2.5 format # Input: {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "..."}, {"role": "model", "content": "..."}]} # Output: {"contents": [{"role": "user", "parts": [{"text": "..."}]}, {"role": "model", "parts": [{"text": "..."}]}]} contents = [] for msg in messages: role = msg["role"] content = msg["content"] contents.append({ "role": role, "parts": [{"text": content}] }) converted_data.append({"contents": contents}) with open(output_file, 'w') as f: for item in converted_data: f.write(json.dumps(item) + "\n") print(f"Saved {len(converted_data)} examples to {output_file}") def upload_to_gcs(local_file, destination_blob_name): print(f"Uploading {local_file} to gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/{destination_blob_name}...") storage_client = storage.Client(project=PROJECT_ID) bucket = storage_client.bucket(BUCKET_NAME) blob = bucket.blob(destination_blob_name) blob.upload_from_filename(local_file) print("Upload complete.") def main(): download_data() # Process Training Data convert_to_gemini_format("sft_train_samples.jsonl", "train_gemini.jsonl") upload_to_gcs("train_gemini.jsonl", "datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl") # Process Validation Data convert_to_gemini_format("sft_val_samples.jsonl", "val_gemini.jsonl") upload_to_gcs("val_gemini.jsonl", "datasets/val/val_gemini.jsonl") print("Data preparation complete!") if __name__ == "__main__": main() - 터미널에서 데이터 준비 스크립트를 실행합니다.
python prepare_data.py
7. 기준 성능 설정
미세 조정하기 전에 벤치마크가 필요합니다. ROUGE 점수를 사용하여 기본 gemini-2.5-flash 모델이 요약 작업에서 얼마나 잘 작동하는지 측정합니다.
- 터미널에서
evaluate.py라는 파일을 만듭니다.cloudshell edit evaluate.py - 다음 코드를
evaluate.py에 붙여넣습니다.import argparse import json import os import pandas as pd from google.cloud import aiplatform import vertexai from vertexai.generative_models import GenerativeModel, GenerationConfig, HarmCategory, HarmBlockThreshold from rouge_score import rouge_scorer from tqdm import tqdm import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import time # Configuration PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] REGION = os.environ["REGION"] aiplatform.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=REGION) def evaluate(model_name, test_file, max_samples=50, output_json="results.json"): print(f"Evaluating model: {model_name}") # Load Test Data test_df = pd.read_csv(test_file) test_df = test_df.head(max_samples) model = GenerativeModel(model_name) safety_settings = { HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HARASSMENT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HATE_SPEECH: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, } generation_config = GenerationConfig( temperature=0.1, max_output_tokens=1024, ) scorer = rouge_scorer.RougeScorer(['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'], use_stemmer=True) results = [] for index, row in tqdm(test_df.iterrows(), total=len(test_df)): input_text = row['input_text'] reference_summary = row['output_text'] try: response = model.generate_content( input_text, generation_config=generation_config, safety_settings=safety_settings ) generated_summary = response.text scores = scorer.score(reference_summary, generated_summary) results.append({ "generated": generated_summary, "reference": reference_summary, "rouge1": scores['rouge1'].fmeasure, "rouge2": scores['rouge2'].fmeasure, "rougeL": scores['rougeL'].fmeasure }) except Exception as e: print(f"Error processing example {index}: {e}") # Sleep briefly to avoid quota issues if hitting limits time.sleep(1) # Save results with open(output_json, 'w') as f: json.dump(results, f, indent=2) return pd.DataFrame(results) def plot_results(df, title, filename): os.makedirs("plots", exist_ok=True) metrics = ['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'] fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5)) for i, metric in enumerate(metrics): axes[i].hist(df[metric], bins=10, alpha=0.7, color='skyblue', edgecolor='black') axes[i].set_title(f'{metric} Distribution') axes[i].set_xlabel('Score') axes[i].set_ylabel('Count') plt.suptitle(title) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig(f"plots/{filename}") print(f"Plot saved to plots/{filename}") def compare_results(baseline_file, tuned_file): with open(baseline_file, 'r') as f: baseline_data = pd.DataFrame(json.load(f)) with open(tuned_file, 'r') as f: tuned_data = pd.DataFrame(json.load(f)) print("\n--- Comparison ---") metrics = ['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'] for metric in metrics: base_mean = baseline_data[metric].mean() tuned_mean = tuned_data[metric].mean() diff = tuned_mean - base_mean print(f"{metric}: Base={base_mean:.4f}, Tuned={tuned_mean:.4f}, Diff={diff:+.4f}") # Comparative Plot os.makedirs("plots", exist_ok=True) comparison_df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Metric': metrics, 'Baseline': [baseline_data[m].mean() for m in metrics], 'Tuned': [tuned_data[m].mean() for m in metrics] }) comparison_df.plot(x='Metric', y=['Baseline', 'Tuned'], kind='bar', figsize=(10, 6)) plt.title('Baseline vs Tuned Model Performance') plt.ylabel('Average Score') plt.xticks(rotation=0) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig("plots/comparison.png") print("Comparison plot saved to plots/comparison.png") def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, default="gemini-2.5-flash", help="Model resource name") parser.add_argument("--baseline", type=str, help="Path to baseline results json for comparison") parser.add_argument("--output", type=str, default="results.json", help="Output file for results") args = parser.parse_args() # Ensure test data exists (it was downloaded in prepare_data step) if not os.path.exists("sft_test_samples.csv"): # Fallback download if needed subprocess.run(["gsutil", "cp", "gs://github-repo/generative-ai/gemini/tuning/summarization/wikilingua/sft_test_samples.csv", "."], check=True) df = evaluate(args.model, "sft_test_samples.csv", output_json=args.output) print("\n--- Results Summary ---") print(df.describe()) plot_filename = "baseline_dist.png" if not args.baseline else "tuned_dist.png" plot_results(df, f"ROUGE Scores - {args.model}", plot_filename) if args.baseline: compare_results(args.baseline, args.output) if __name__ == "__main__": main() - 터미널에서 기준 평가를 실행합니다.
python evaluate.py --model "gemini-2.5-flash" --output "baseline.json"plots/baseline_dist.png에baseline.json파일과 플롯이 생성됩니다.
8. 미세 조정 구성 및 실행
이제 Vertex AI에서 관리형 미세 조정 작업을 실행합니다.
- 터미널에서
tune.py라는 파일을 만듭니다.cloudshell edit tune.py - 다음 코드를
tune.py에 붙여넣습니다.import os import time from google.cloud import aiplatform import vertexai from vertexai.preview.tuning import sft # Configuration PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] REGION = os.environ["REGION"] BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"] aiplatform.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=REGION) def train(): print("Launching fine-tuning job...") sft_tuning_job = sft.train( source_model="gemini-2.5-flash", # Using specific version for stability train_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl", validation_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/val/val_gemini.jsonl", epochs=1, # Keep it short for the lab adapter_size=4, learning_rate_multiplier=1.0, tuned_model_display_name="gemini-2.5-flash-wikilingua", ) print(f"Job started: {sft_tuning_job.resource_name}") print("Waiting for job to complete... (this may take ~45 minutes)") # Wait for the job to complete while not sft_tuning_job.has_ended: time.sleep(60) sft_tuning_job.refresh() print(f"Status: {sft_tuning_job.state.name}") print("Job completed!") print(f"Tuned Model Endpoint: {sft_tuning_job.tuned_model_endpoint_name}") return sft_tuning_job.tuned_model_endpoint_name if __name__ == "__main__": train() - 터미널에서 미세 조정 스크립트를 실행합니다.
python tune.py
9. 학습 코드 이해
작업이 실행되는 동안 tune.py 스크립트를 자세히 살펴보고 미세 조정이 어떻게 작동하는지 알아보겠습니다.
관리형 지도 미세 조정
스크립트는 vertexai.tuning.sft.train 메서드를 사용하여 관리형 조정 작업을 제출합니다. 이렇게 하면 인프라 프로비저닝, 학습 배포, 체크포인트 관리의 복잡성이 추상화됩니다.
sft_tuning_job = sft.train(
source_model="gemini-2.5-flash",
train_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl",
# ...
)
LoRA 구성
오픈소스 프레임워크에서와 같이 LoraConfig를 수동으로 정의하는 대신 Vertex AI에서는 이를 몇 가지 주요 파라미터로 간소화합니다.
adapter_size: 이 파라미터 (스크립트에서4로 설정됨)는 LoRA 어댑터의 순위를 제어합니다. 크기가 클수록 모델이 더 복잡한 적응을 학습할 수 있지만 학습 가능한 매개변수의 수가 증가합니다.epochs: 이 실습에서는 학습 시간을 짧게 유지하기 위해 (약 20분)1으로 설정합니다. 프로덕션 시나리오에서는 모델이 데이터에서 더 깊이 학습할 수 있도록 이 값을 늘릴 수 있지만 과적합에 주의해야 합니다.
모델 선택
source_model="gemini-2.5-flash"을 명시적으로 지정합니다. Vertex AI는 다양한 버전의 Gemini를 지원하며 특정 버전을 고정하면 파이프라인이 안정적이고 재현 가능하게 유지됩니다.
10. 모델 비교
미세 조정 작업이 완료되면 새 모델의 성능을 기준과 비교할 수 있습니다.
- 조정된 모델 엔드포인트를 가져옵니다.
tune.py스크립트 끝에 인쇄되었습니다.projects/.../locations/.../endpoints/...와 같이 표시됩니다. - 이번에는 조정된 모델과 비교를 위한 기준 결과를 전달하여 평가 스크립트를 다시 실행합니다.
# Replace [YOUR_TUNED_MODEL_ENDPOINT] with the actual endpoint name export TUNED_MODEL="projects/[YOUR_PROJECT_ID]/locations/[YOUR_REGION]/endpoints/[YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID]" python evaluate.py --model "$TUNED_MODEL" --baseline "baseline.json" --output "tuned.json" - 결과를 확인합니다. 스크립트는 ROUGE 점수를 비교하고 개선사항을 보여주는
plots/comparison.png차트를 생성합니다.Cloud Shell 편집기에서plots폴더를 열어 플롯을 볼 수 있습니다.
11. 삭제
요금이 발생하지 않도록 하려면 생성한 리소스를 삭제합니다.
- 터미널에서 Cloud Storage 버킷과 조정된 모델을 삭제합니다.
gcloud storage rm -r gs://$BUCKET_NAME # Note: You can delete the model endpoint from the Vertex AI Console
12. 축하합니다.
Vertex AI에서 Gemini 2.5 Flash를 미세 조정했습니다.
요약
이 실습에서 학습할 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
- Gemini 미세 조정을 위해 JSONL 형식으로 데이터 세트를 준비했습니다.
- 기본 Gemini 2.5 Flash 모델을 사용하여 기준을 설정했습니다.
- Vertex AI에서 지도 미세 조정 작업을 시작했습니다.
- 파인 튜닝된 모델을 기준과 비교하여 평가했습니다.
다음 단계
이 실습은 Google Cloud를 사용한 프로덕션 레디 AI 학습 과정의 일부입니다.
전체 커리큘럼을 살펴보고 프로토타입에서 프로덕션으로 전환하는 데 필요한 지식을 쌓으세요.
#ProductionReadyAI 해시태그를 사용하여 진행 상황을 공유하세요.
