1. 简介
在此实验中,您将学习如何对 Google Gemini 模型执行完整的监督式微调工作流,以使其适应特定任务:文章总结。虽然大语言模型功能强大,但由于其用途广泛,因此可以通过微调来进一步提高其在特定应用场景中的效果。通过使用高质量的示例数据集训练模型,您可以提高模型在目标任务中的一致性、质量和效率。
您将使用轻量级且经济实惠的模型 Gemini 2.5 Flash,并使用 Vertex AI 执行微调。
架构概览
我们将构建以下内容:
- Cloud Shell:您的开发环境。
- Cloud Storage:以 JSONL 格式存储训练/验证数据。
- Vertex AI Training:管理微调作业。
- Vertex AI 端点:用于托管微调后的模型。
学习内容
- 准备高质量的数据集以进行监督式微调。
- 使用 Vertex AI SDK for Python 配置并启动微调作业。
- 使用自动化指标(ROUGE 得分)评估模型。
- 比较基础模型和微调模型,以量化改进效果。
2. 项目设置
Google 账号
如果您还没有个人 Google 账号,则必须先创建一个 Google 账号。
请使用个人账号,而不是工作账号或学校账号。
登录 Google Cloud 控制台
使用个人 Google 账号登录 Google Cloud 控制台。
启用结算功能
兑换 5 美元的 Google Cloud 赠金(可选)
如需参加此研讨会,您需要拥有一个有一定信用额度的结算账号。如果您打算使用自己的结算方式,则可以跳过此步骤。
- 点击此链接,然后使用个人 Google 账号登录。您会看到类似以下内容:

- 点击点击此处以访问您的积分按钮。系统会将您转到用于设置结算资料的页面
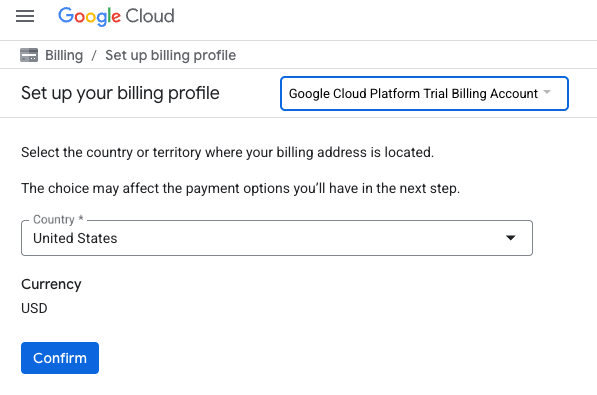
- 点击确认
您现在已关联到 Google Cloud Platform 试用结算账号。
创建项目(可选)
如果您没有要用于此实验的当前项目,请在此处创建一个新项目。
3. 打开 Cloud Shell Editor
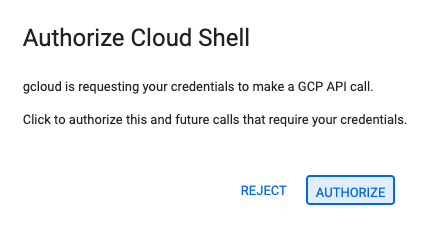
- 点击此链接可直接前往 Cloud Shell 编辑器
- 如果系统在今天任何时间提示您进行授权,请点击授权继续。
- 如果终端未显示在屏幕底部,请打开它:
- 点击查看
- 点击终端
- 在终端中,使用以下命令设置项目:
gcloud config set project [PROJECT_ID]- 示例:
gcloud config set project lab-project-id-example - 如果您不记得自己的项目 ID,可以使用以下命令列出所有项目 ID:
gcloud projects list
- 示例:
- 您应会看到以下消息:
Updated property [core/project].
4. 启用 API
如需使用 Vertex AI 和其他服务,您需要在 Google Cloud 项目中启用必要的 API。
- 在终端中,启用以下 API:
- Vertex AI API (
aiplatform.googleapis.com):启用后,即可使用 Vertex AI 对模型进行微调和提供模型服务。 - Cloud Storage API (
storage.googleapis.com):用于存储数据集和模型制品。
gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com \ storage.googleapis.com - Vertex AI API (
5. 设置项目环境
创建工作目录
- 在终端中,为您的项目创建一个目录,然后进入该目录。
mkdir gemini-finetuning cd gemini-finetuning
设置环境变量
- 在终端中,为您的项目定义环境变量。我们将创建一个
env.sh文件来存储这些变量,以便在会话断开连接时轻松重新加载它们。cat <<EOF > env.sh export PROJECT_ID=\$(gcloud config get-value project) export REGION="us-central1" export BUCKET_NAME="\${PROJECT_ID}-gemini-tuning" EOF source env.sh
创建 Cloud Storage 存储桶
- 在终端中,创建一个存储分区来存储数据集和模型制品。
gcloud storage buckets create gs://$BUCKET_NAME --project=$PROJECT_ID --location=$REGION
设置虚拟环境
- 我们将使用
uv来管理 Python 环境。在终端中,运行以下命令:uv venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate - 在终端中,安装必需的 Python 软件包。
uv pip install google-cloud-aiplatform rouge-score matplotlib pandas tqdm
6. 准备训练数据
优质数据是成功微调的基础。您将使用 WikiLingua 数据集,将其转换为 Gemini 所需的特定 JSONL 格式,然后将其上传到您的存储分区。
- 在终端中,创建一个名为
prepare_data.py的文件。cloudshell edit prepare_data.py - 将以下代码粘贴到
prepare_data.py中。import json import os import pandas as pd from google.cloud import storage import subprocess # Configuration BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"] PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] def download_data(): print("Downloading WikiLingua dataset...") # Using gsutil to copy from public bucket subprocess.run(["gsutil", "cp", "gs://github-repo/generative-ai/gemini/tuning/summarization/wikilingua/*", "."], check=True) def convert_to_gemini_format(input_file, output_file, max_samples=1000): print(f"Converting {input_file} to Gemini format (first {max_samples} samples)...") converted_data = [] with open(input_file, 'r') as f: for i, line in enumerate(f): if i >= max_samples: break obj = json.loads(line) messages = obj.get("messages", []) # Convert messages to Gemini 2.5 format # Input: {"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "..."}, {"role": "model", "content": "..."}]} # Output: {"contents": [{"role": "user", "parts": [{"text": "..."}]}, {"role": "model", "parts": [{"text": "..."}]}]} contents = [] for msg in messages: role = msg["role"] content = msg["content"] contents.append({ "role": role, "parts": [{"text": content}] }) converted_data.append({"contents": contents}) with open(output_file, 'w') as f: for item in converted_data: f.write(json.dumps(item) + "\n") print(f"Saved {len(converted_data)} examples to {output_file}") def upload_to_gcs(local_file, destination_blob_name): print(f"Uploading {local_file} to gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/{destination_blob_name}...") storage_client = storage.Client(project=PROJECT_ID) bucket = storage_client.bucket(BUCKET_NAME) blob = bucket.blob(destination_blob_name) blob.upload_from_filename(local_file) print("Upload complete.") def main(): download_data() # Process Training Data convert_to_gemini_format("sft_train_samples.jsonl", "train_gemini.jsonl") upload_to_gcs("train_gemini.jsonl", "datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl") # Process Validation Data convert_to_gemini_format("sft_val_samples.jsonl", "val_gemini.jsonl") upload_to_gcs("val_gemini.jsonl", "datasets/val/val_gemini.jsonl") print("Data preparation complete!") if __name__ == "__main__": main() - 在终端中,运行数据准备脚本。
python prepare_data.py
7. 建立基准效果
在进行微调之前,您需要一个基准。您将使用 ROUGE 得分来衡量基础 gemini-2.5-flash 模型在摘要任务中的表现。
- 在终端中,创建一个名为
evaluate.py的文件。cloudshell edit evaluate.py - 将以下代码粘贴到
evaluate.py中。import argparse import json import os import pandas as pd from google.cloud import aiplatform import vertexai from vertexai.generative_models import GenerativeModel, GenerationConfig, HarmCategory, HarmBlockThreshold from rouge_score import rouge_scorer from tqdm import tqdm import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import time # Configuration PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] REGION = os.environ["REGION"] aiplatform.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=REGION) def evaluate(model_name, test_file, max_samples=50, output_json="results.json"): print(f"Evaluating model: {model_name}") # Load Test Data test_df = pd.read_csv(test_file) test_df = test_df.head(max_samples) model = GenerativeModel(model_name) safety_settings = { HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HARASSMENT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_HATE_SPEECH: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, HarmCategory.HARM_CATEGORY_DANGEROUS_CONTENT: HarmBlockThreshold.BLOCK_ONLY_HIGH, } generation_config = GenerationConfig( temperature=0.1, max_output_tokens=1024, ) scorer = rouge_scorer.RougeScorer(['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'], use_stemmer=True) results = [] for index, row in tqdm(test_df.iterrows(), total=len(test_df)): input_text = row['input_text'] reference_summary = row['output_text'] try: response = model.generate_content( input_text, generation_config=generation_config, safety_settings=safety_settings ) generated_summary = response.text scores = scorer.score(reference_summary, generated_summary) results.append({ "generated": generated_summary, "reference": reference_summary, "rouge1": scores['rouge1'].fmeasure, "rouge2": scores['rouge2'].fmeasure, "rougeL": scores['rougeL'].fmeasure }) except Exception as e: print(f"Error processing example {index}: {e}") # Sleep briefly to avoid quota issues if hitting limits time.sleep(1) # Save results with open(output_json, 'w') as f: json.dump(results, f, indent=2) return pd.DataFrame(results) def plot_results(df, title, filename): os.makedirs("plots", exist_ok=True) metrics = ['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'] fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5)) for i, metric in enumerate(metrics): axes[i].hist(df[metric], bins=10, alpha=0.7, color='skyblue', edgecolor='black') axes[i].set_title(f'{metric} Distribution') axes[i].set_xlabel('Score') axes[i].set_ylabel('Count') plt.suptitle(title) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig(f"plots/{filename}") print(f"Plot saved to plots/{filename}") def compare_results(baseline_file, tuned_file): with open(baseline_file, 'r') as f: baseline_data = pd.DataFrame(json.load(f)) with open(tuned_file, 'r') as f: tuned_data = pd.DataFrame(json.load(f)) print("\n--- Comparison ---") metrics = ['rouge1', 'rouge2', 'rougeL'] for metric in metrics: base_mean = baseline_data[metric].mean() tuned_mean = tuned_data[metric].mean() diff = tuned_mean - base_mean print(f"{metric}: Base={base_mean:.4f}, Tuned={tuned_mean:.4f}, Diff={diff:+.4f}") # Comparative Plot os.makedirs("plots", exist_ok=True) comparison_df = pd.DataFrame({ 'Metric': metrics, 'Baseline': [baseline_data[m].mean() for m in metrics], 'Tuned': [tuned_data[m].mean() for m in metrics] }) comparison_df.plot(x='Metric', y=['Baseline', 'Tuned'], kind='bar', figsize=(10, 6)) plt.title('Baseline vs Tuned Model Performance') plt.ylabel('Average Score') plt.xticks(rotation=0) plt.tight_layout() plt.savefig("plots/comparison.png") print("Comparison plot saved to plots/comparison.png") def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, default="gemini-2.5-flash", help="Model resource name") parser.add_argument("--baseline", type=str, help="Path to baseline results json for comparison") parser.add_argument("--output", type=str, default="results.json", help="Output file for results") args = parser.parse_args() # Ensure test data exists (it was downloaded in prepare_data step) if not os.path.exists("sft_test_samples.csv"): # Fallback download if needed subprocess.run(["gsutil", "cp", "gs://github-repo/generative-ai/gemini/tuning/summarization/wikilingua/sft_test_samples.csv", "."], check=True) df = evaluate(args.model, "sft_test_samples.csv", output_json=args.output) print("\n--- Results Summary ---") print(df.describe()) plot_filename = "baseline_dist.png" if not args.baseline else "tuned_dist.png" plot_results(df, f"ROUGE Scores - {args.model}", plot_filename) if args.baseline: compare_results(args.baseline, args.output) if __name__ == "__main__": main() - 在终端中,运行基准评估。
python evaluate.py --model "gemini-2.5-flash" --output "baseline.json"plots/baseline_dist.png中生成一个baseline.json文件和一个图表。
8. 配置并启动微调
现在,您将在 Vertex AI 上启动受管理的微调作业。
- 在终端中,创建一个名为
tune.py的文件。cloudshell edit tune.py - 将以下代码粘贴到
tune.py中。import os import time from google.cloud import aiplatform import vertexai from vertexai.preview.tuning import sft # Configuration PROJECT_ID = os.environ["PROJECT_ID"] REGION = os.environ["REGION"] BUCKET_NAME = os.environ["BUCKET_NAME"] aiplatform.init(project=PROJECT_ID, location=REGION) def train(): print("Launching fine-tuning job...") sft_tuning_job = sft.train( source_model="gemini-2.5-flash", # Using specific version for stability train_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl", validation_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/val/val_gemini.jsonl", epochs=1, # Keep it short for the lab adapter_size=4, learning_rate_multiplier=1.0, tuned_model_display_name="gemini-2.5-flash-wikilingua", ) print(f"Job started: {sft_tuning_job.resource_name}") print("Waiting for job to complete... (this may take ~45 minutes)") # Wait for the job to complete while not sft_tuning_job.has_ended: time.sleep(60) sft_tuning_job.refresh() print(f"Status: {sft_tuning_job.state.name}") print("Job completed!") print(f"Tuned Model Endpoint: {sft_tuning_job.tuned_model_endpoint_name}") return sft_tuning_job.tuned_model_endpoint_name if __name__ == "__main__": train() - 在终端中,运行微调脚本。
python tune.py
9. 了解训练代码
在作业运行期间,我们来详细了解一下 tune.py 脚本,以便了解微调的运作方式。
受管理的监督式微调
该脚本使用 vertexai.tuning.sft.train 方法提交受管理的调优作业。这样可以免去预配基础设施、分配训练和管理检查点的复杂性。
sft_tuning_job = sft.train(
source_model="gemini-2.5-flash",
train_dataset=f"gs://{BUCKET_NAME}/datasets/train/train_gemini.jsonl",
# ...
)
LoRA 配置
与您在开源框架中手动定义 LoraConfig 不同,Vertex AI 将此简化为几个关键参数:
adapter_size:此形参(在我们的脚本中设置为4)用于控制 LoRA 适配器的秩。尺寸越大,模型可以学习的复杂自适应就越多,但可训练的参数数量也会增加。epochs:在本实验中,我们将此值设置为1,以缩短训练时间(约 20 分钟)。在实际应用场景中,您可以增加此值,以便模型从数据中更深入地学习,但应注意避免过拟合。
模型选择
我们明确指定了 source_model="gemini-2.5-flash"。Vertex AI 支持各种版本的 Gemini,固定特定版本可确保流水线保持稳定且可重现。
10. 比较模型
微调作业完成后,您可以将新模型的性能与基准进行比较。
- 获取调优后模型的端点。它是在
tune.py脚本结束时打印的。其格式应为projects/.../locations/.../endpoints/...。 - 再次运行评估脚本,这次传递您的调优模型和基准结果以进行比较。
# Replace [YOUR_TUNED_MODEL_ENDPOINT] with the actual endpoint name export TUNED_MODEL="projects/[YOUR_PROJECT_ID]/locations/[YOUR_REGION]/endpoints/[YOUR_ENDPOINT_ID]" python evaluate.py --model "$TUNED_MODEL" --baseline "baseline.json" --output "tuned.json" - 查看结果。该脚本将输出 ROUGE 得分比较结果,并生成一个显示改进情况的
plots/comparison.png图表。您可以在 Cloud Shell 编辑器中打开plots文件夹来查看这些图表。
11. 清理
为避免产生费用,请删除您创建的资源。
- 在终端中,删除 Cloud Storage 存储分区和已调优的模型。
gcloud storage rm -r gs://$BUCKET_NAME # Note: You can delete the model endpoint from the Vertex AI Console
12. 恭喜!
您已成功在 Vertex AI 上对 Gemini 2.5 Flash 进行微调!
回顾
您此实验中,您将执行以下操作:
- 准备了 JSONL 格式的数据集,用于 Gemini 微调。
- 使用基础 Gemini 2.5 Flash 模型建立了基准。
- 在 Vertex AI 上启动了监督式微调作业。
- 评估了微调模型并将其与基准模型进行了比较。
后续步骤
本实验是可用于生产用途的 AI 与 Google Cloud 学习路线的组成部分。
使用 #ProductionReadyAI 标签分享您的进度。
