1. Overview
This lab focuses on utilizing Gemini Code Assist, an AI-powered agent in Google Cloud. You will learn to use Gemini Code Assist for common developer tasks, including understanding existing codebases, generating documentation and unit tests, refactoring both UI and backend components of a Python web application.
What you will learn
In this lab, you will learn how to do the following:
- How to use Gemini Code Assist for common developer tasks.
Prerequisites
- This lab assumes familiarity with the Cloud Console and Cloud Shell environments.
2. Setup and Requirements
Cloud Project setup
- Sign-in to the Google Cloud Console and create a new project or reuse an existing one. If you don't already have a Gmail or Google Workspace account, you must create one.

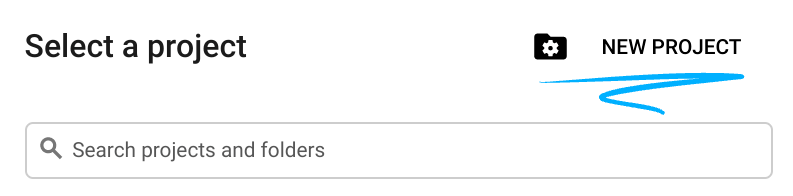
- The Project name is the display name for this project's participants. It is a character string not used by Google APIs. You can always update it.
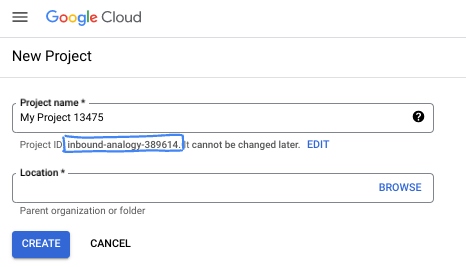
- The Project ID is unique across all Google Cloud projects and is immutable (cannot be changed after it has been set). The Cloud Console auto-generates a unique string; usually you don't care what it is. In most codelabs, you'll need to reference your Project ID (typically identified as
PROJECT_ID). If you don't like the generated ID, you might generate another random one. Alternatively, you can try your own, and see if it's available. It can't be changed after this step and remains for the duration of the project. - For your information, there is a third value, a Project Number, which some APIs use. Learn more about all three of these values in the documentation.
- Next, you'll need to enable billing in the Cloud Console to use Cloud resources/APIs. Running through this codelab won't cost much, if anything at all. To shut down resources to avoid incurring billing beyond this tutorial, you can delete the resources you created or delete the project. New Google Cloud users are eligible for the $300 USD Free Trial program.
Environment Setup
Open Gemini chat.
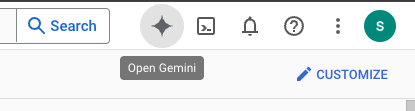
Or type "Ask Gemini" in the search bar.
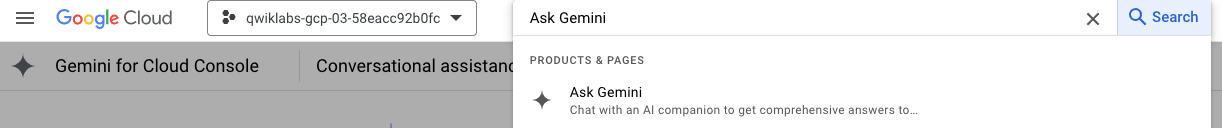
Enable Gemini for Google Cloud API:
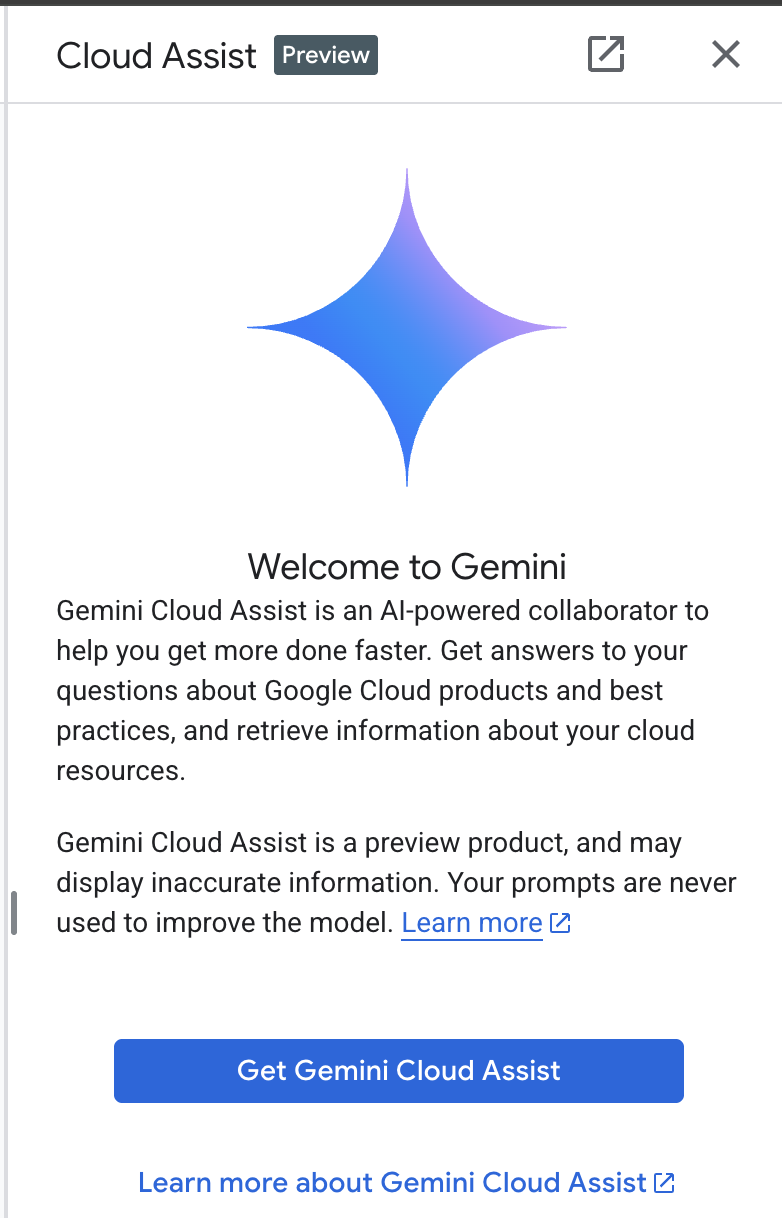
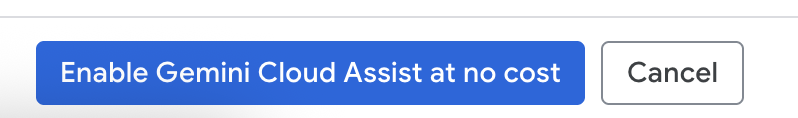
Enable GCA on the next screen.
Click "Start chatting" and follow one of the sample questions or type your own prompt to try it out.
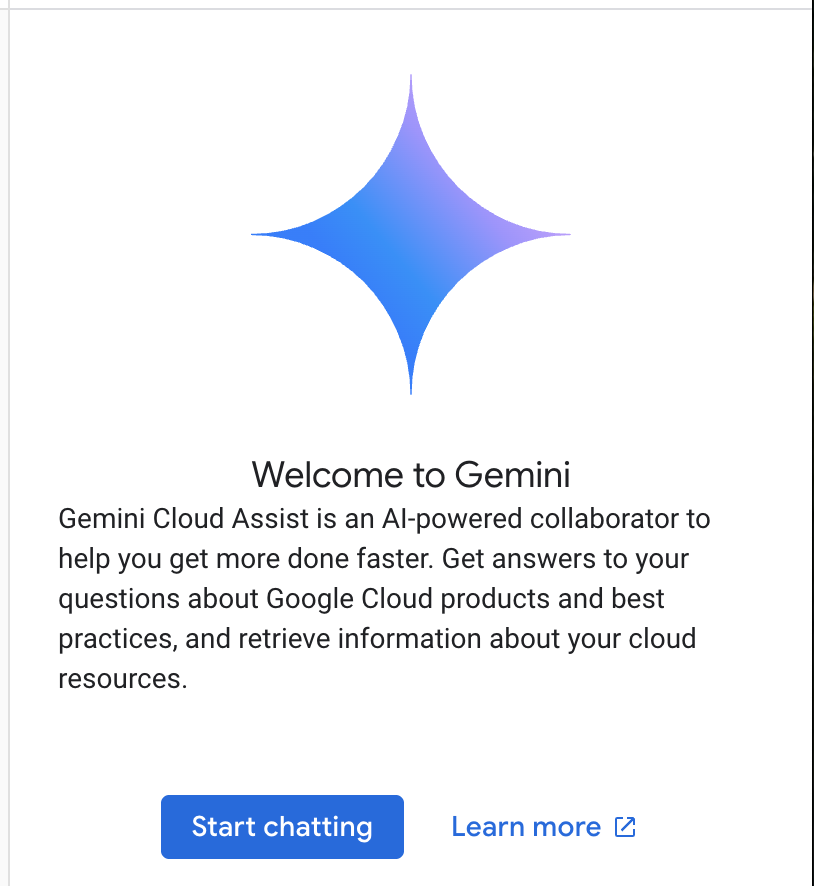
Prompts to try:
- Explain Cloud Run in 5 key points.
- You are Google Cloud Run Product Manager, explain Cloud Run to a student in 5 short key points.
- You are Google Cloud Run Product Manager, explain Cloud Run to a Certified Kubernetes Developer in 5 short key points.
- You are Google Cloud Run Product Manager, explain when you would use Cloud Run versus GKE to a Senior Developer in 5 short key points.
Close the Gemini Cloud Assist chat window after you are done.
Check out Prompt Guide to learn more about writing better prompts.
How Gemini for Google Cloud uses your data
Google's privacy commitment
Google was one of the first in the industry to publish an AI/ML privacy commitment, which outlines our belief that customers should have the highest level of security and control over their data that's stored in the cloud.
Data you submit and receive
The questions that you ask Gemini, including any input information or code that you submit to Gemini to analyze or complete, are called prompts. The answers or code completions that you receive from Gemini are called responses. Gemini doesn't use your prompts or its responses as data to train its models.
Encryption of prompts
When you submit prompts to Gemini, your data is encrypted in-transit as input to the underlying model in Gemini.
Program data generated from Gemini
Gemini is trained on first-party Google Cloud code as well as selected third-party code. You're responsible for the security, testing, and effectiveness of your code, including any code completion, generation, or analysis that Gemini offers you.
Learn more how Google handles your prompts.
3. Options to test prompts
If you would like to change existing prompts, you have several options for that.
Vertex AI Studio is a part of Google Cloud's Vertex AI platform, specifically designed to simplify and accelerate the development and use of generative AI models.
Google AI Studio is a web-based tool for prototyping and experimenting with prompt engineering and the Gemini API.
- Gemini Web App (gemini.google.com)
The Google Gemini web app (gemini.google.com) is a web-based tool designed to help you explore and utilize the power of Google's Gemini AI models.
- Google Gemini mobile app for Android and Google app on iOS
4. Download and examine the application
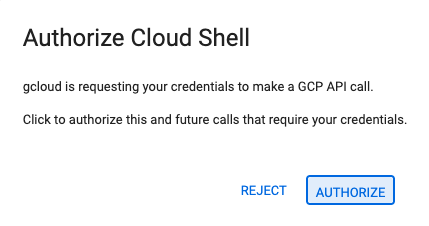
Activate Cloud Shell by clicking on the icon to the right of the search bar.

If prompted to authorize, click "Authorize" to continue.
In the terminal, run the commands below to clone the Git repository locally.
git clone https://github.com/gitrey/calendar-app-lab
cd calendar-app-lab
Start "Cloud Shell Editor".

Open the "calendar-app-lab" folder.
Start a new terminal in the Cloud Shell Editor.
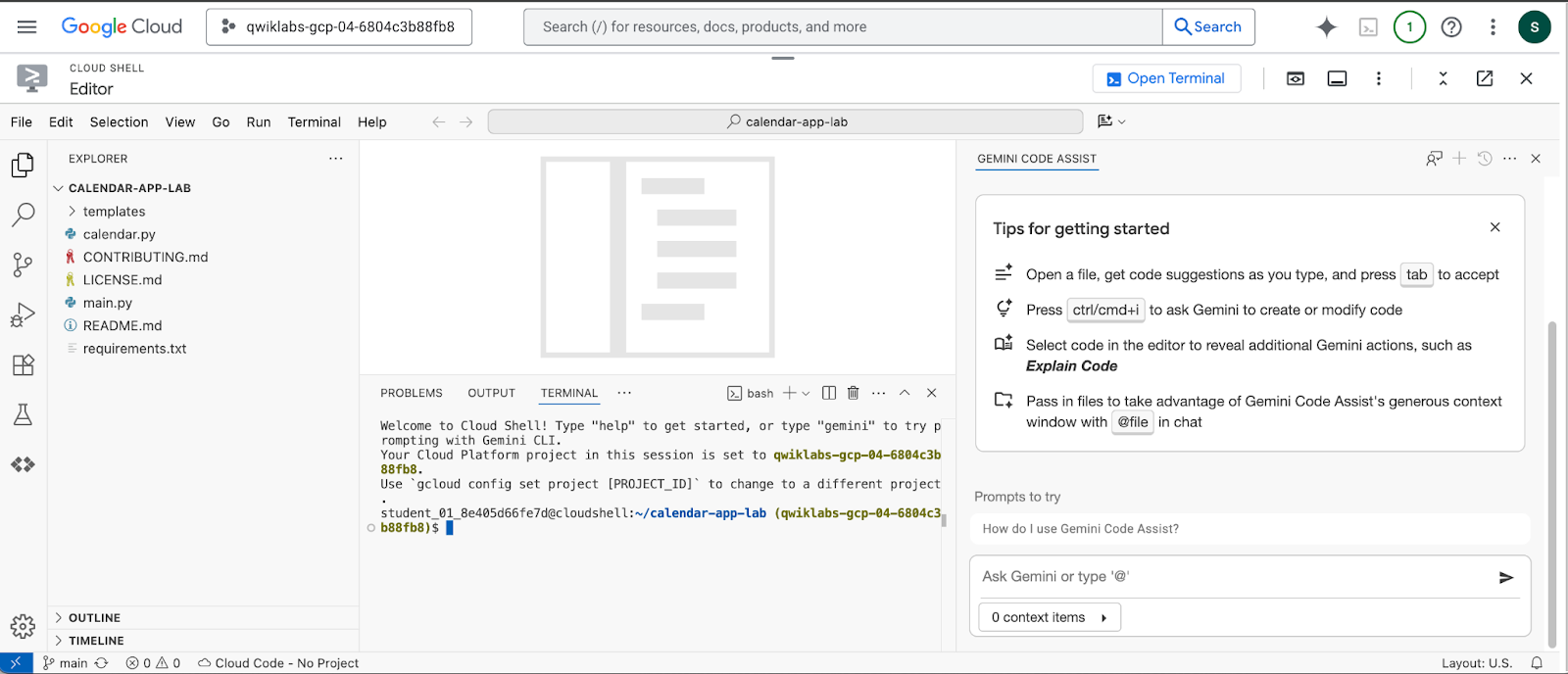
Your environment should look similar to the screenshot below.
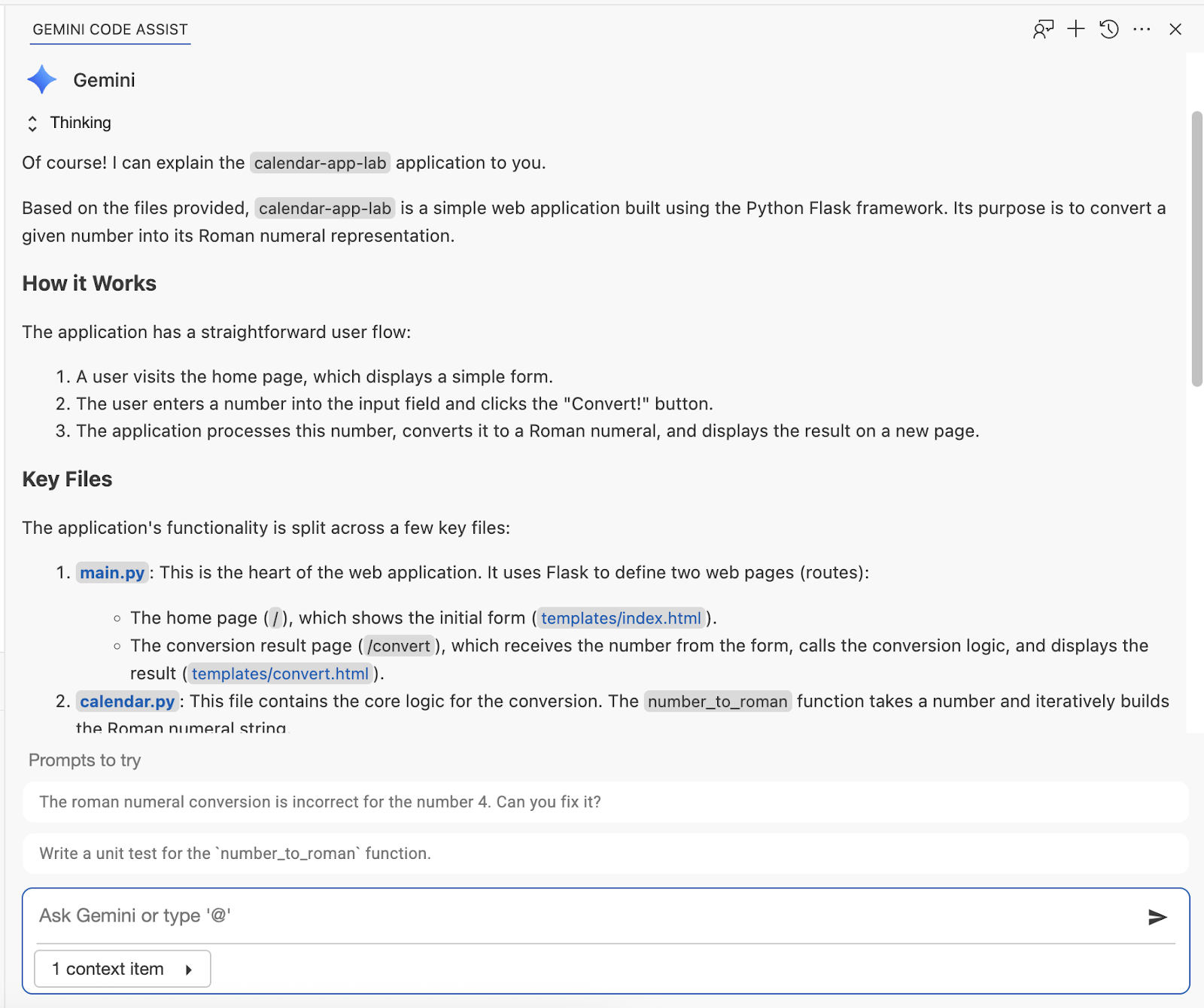
In the Gemini Code Assist chat window, send this prompt:
Don't suggest any changes. Explain this codebase to me.
Sample output:
5. Start the application locally
In the chat window, send this prompt:
How do I set up a virtual environment and run this app locally?
Run suggested commands in the terminal:
Install the dependencies:
Start the app:
Click on the link to preview application:
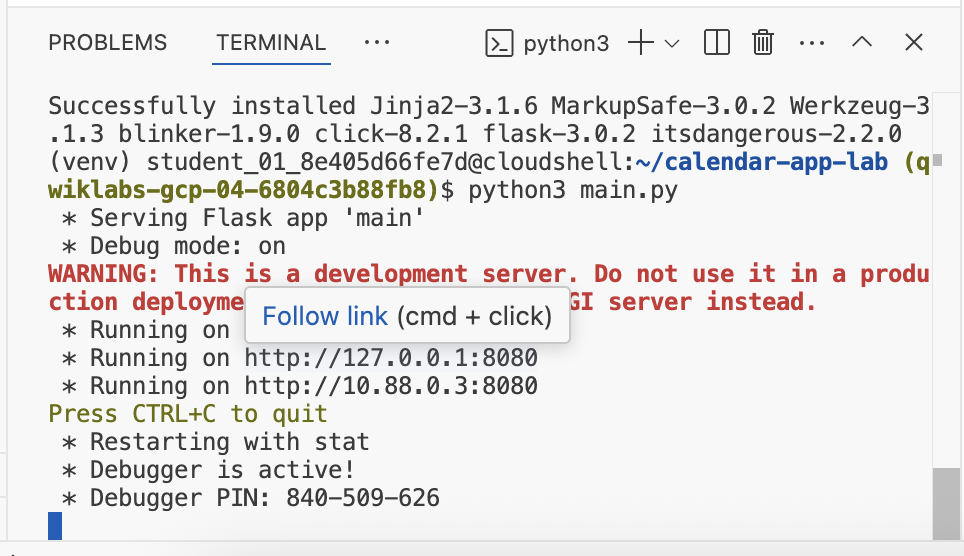
Sample output:

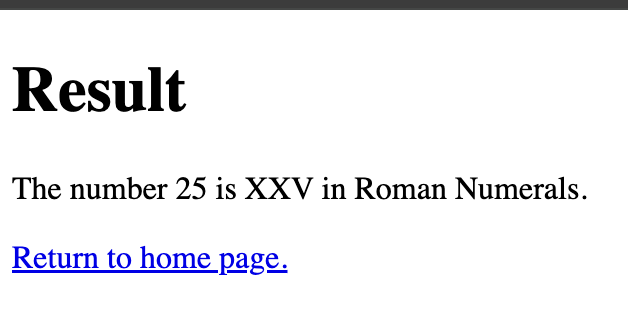
6. Adding documentation
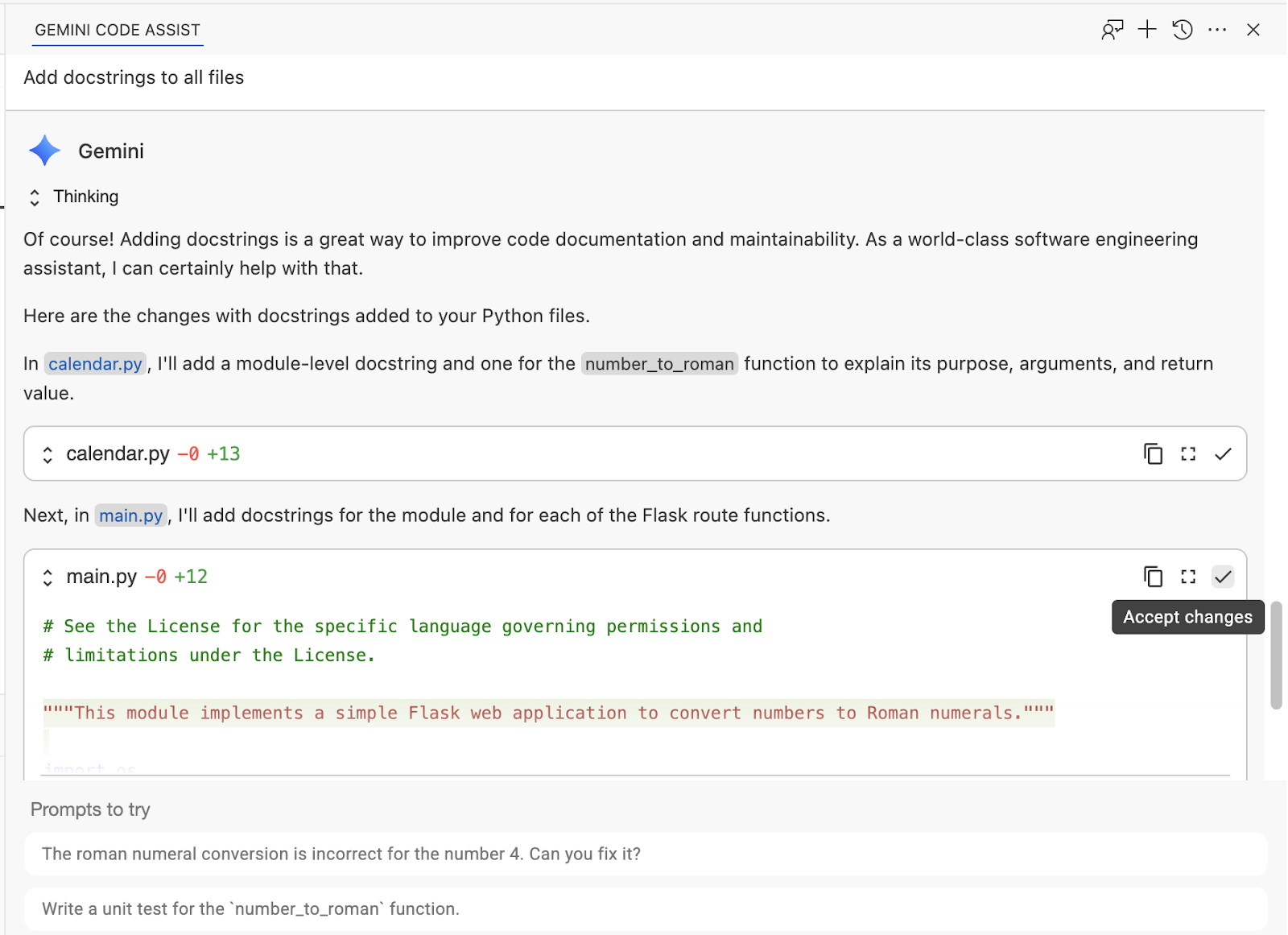
In the chat window, send this prompt:
Add docstrings to all files
Review suggested changes and accept them in the chat:
In the chat window, send this prompt:
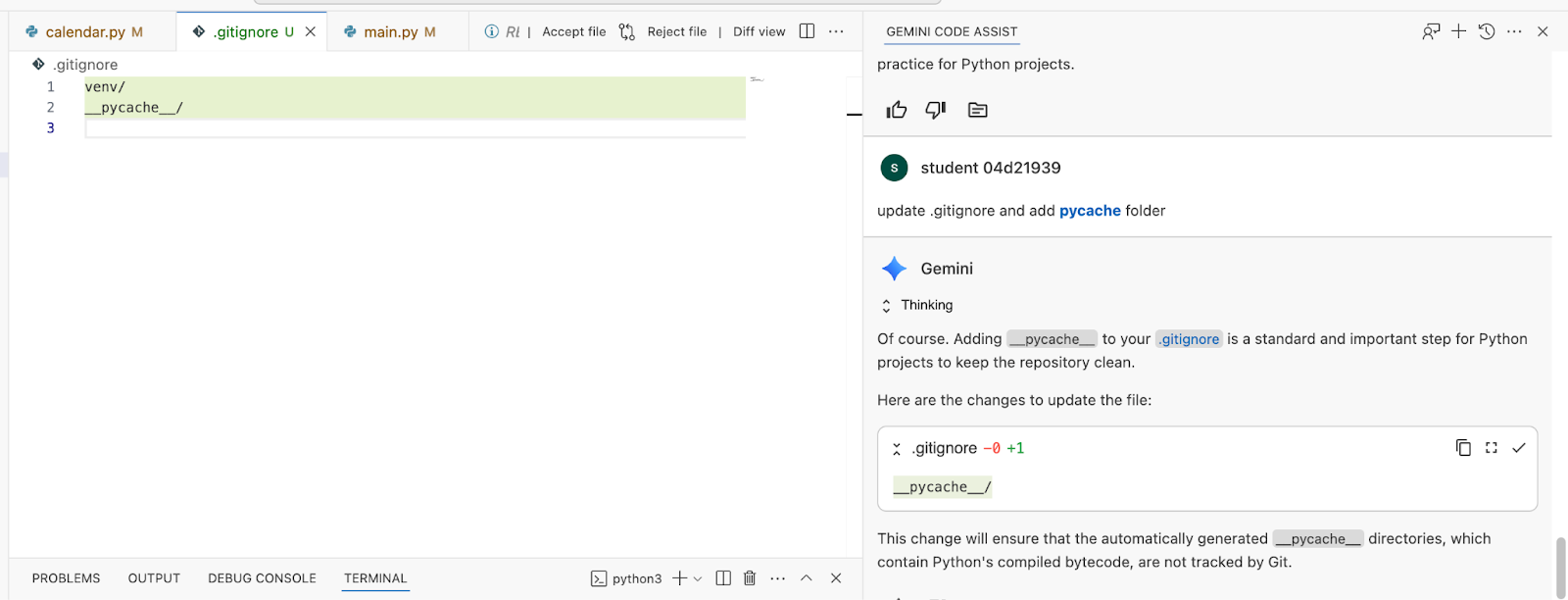
update .gitignore and add venv/* folder
Followed by this prompt:
update .gitignore and add __pycache__ folder
Sample output:
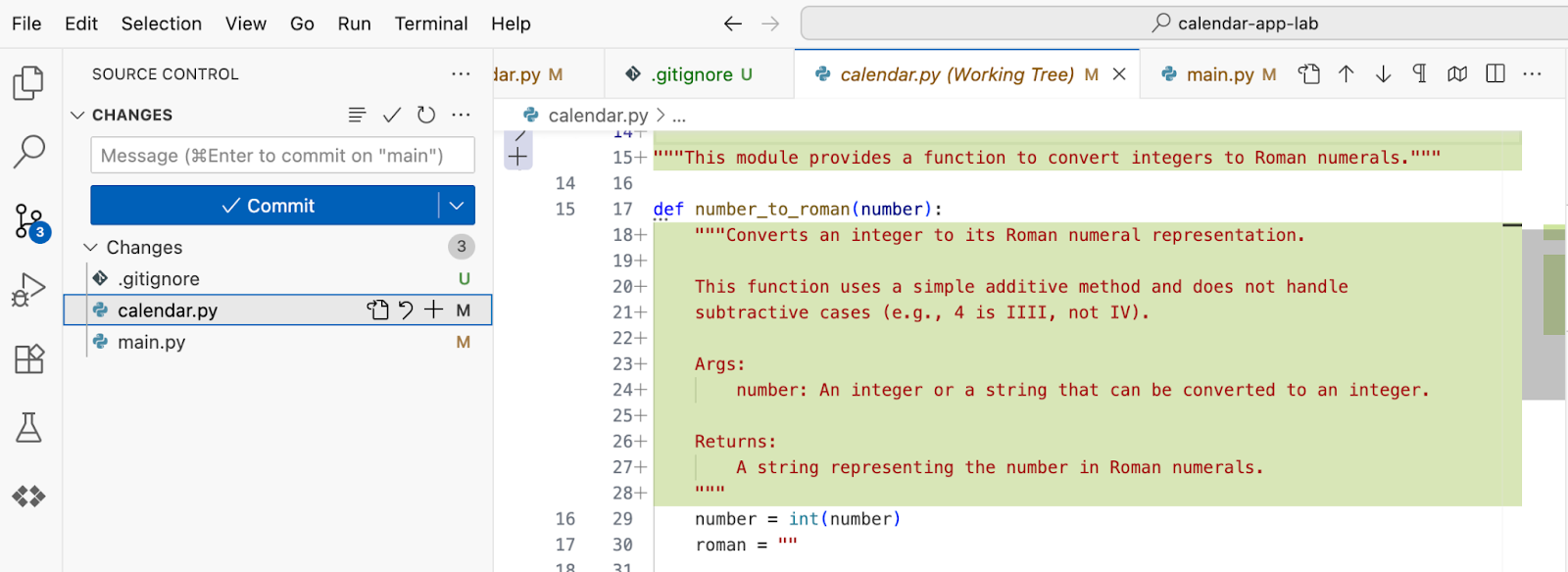
Switch to Source Control view and review changes that you made so far:
7. Adding Unit Tests
Open calendar.py file and from context menu select Gemini Code Assist >> Generate Unit Tests
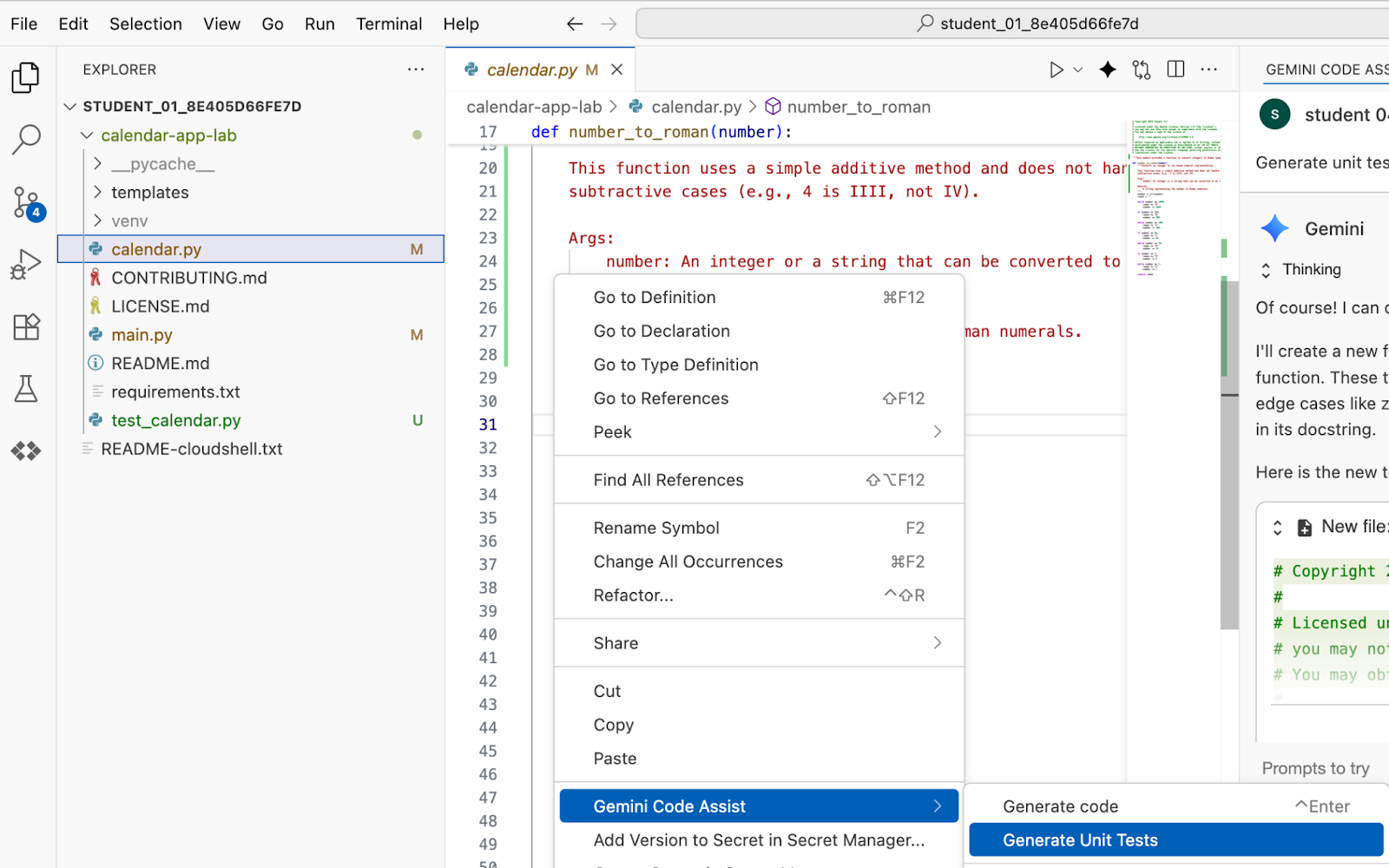
Hit enter in the Gemini Code Assist chat window. Review the changes and accept them.
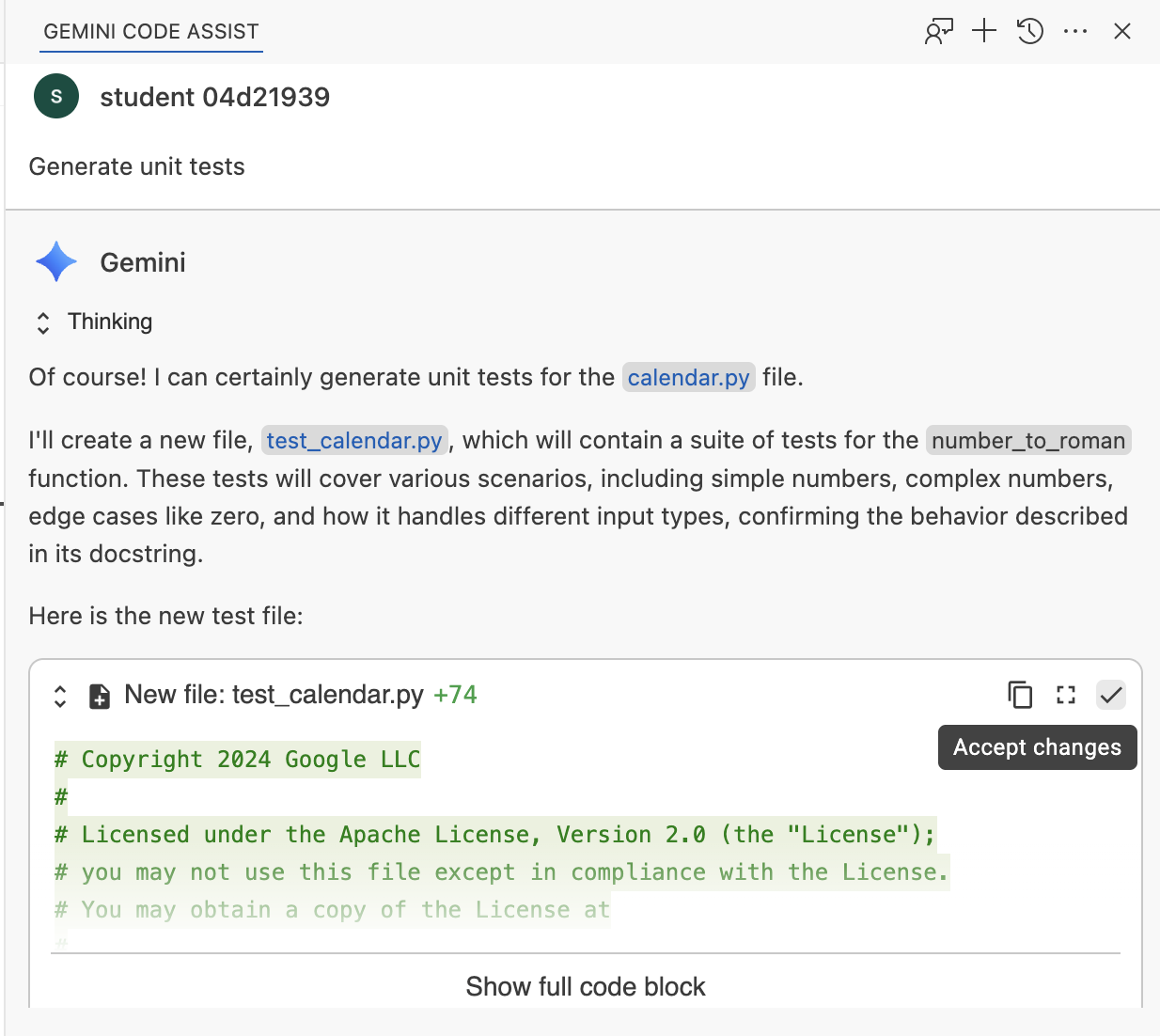
Ask Gemini how to run the tests:
How do I run the tests?
Run the suggested commands in the terminal and review the output.
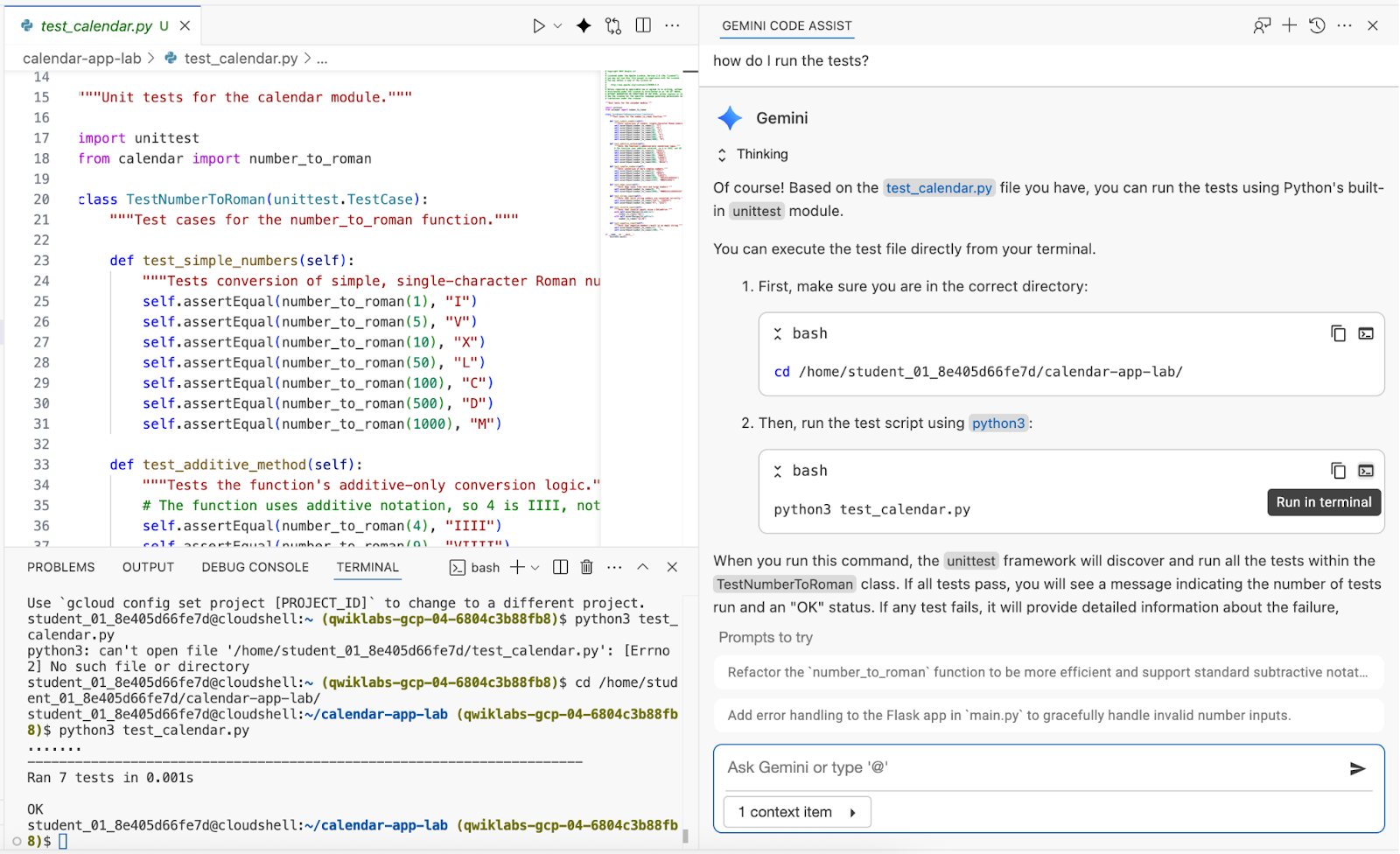
8. Check for bugs
Open calendar.py file and in the chat window send this prompt:
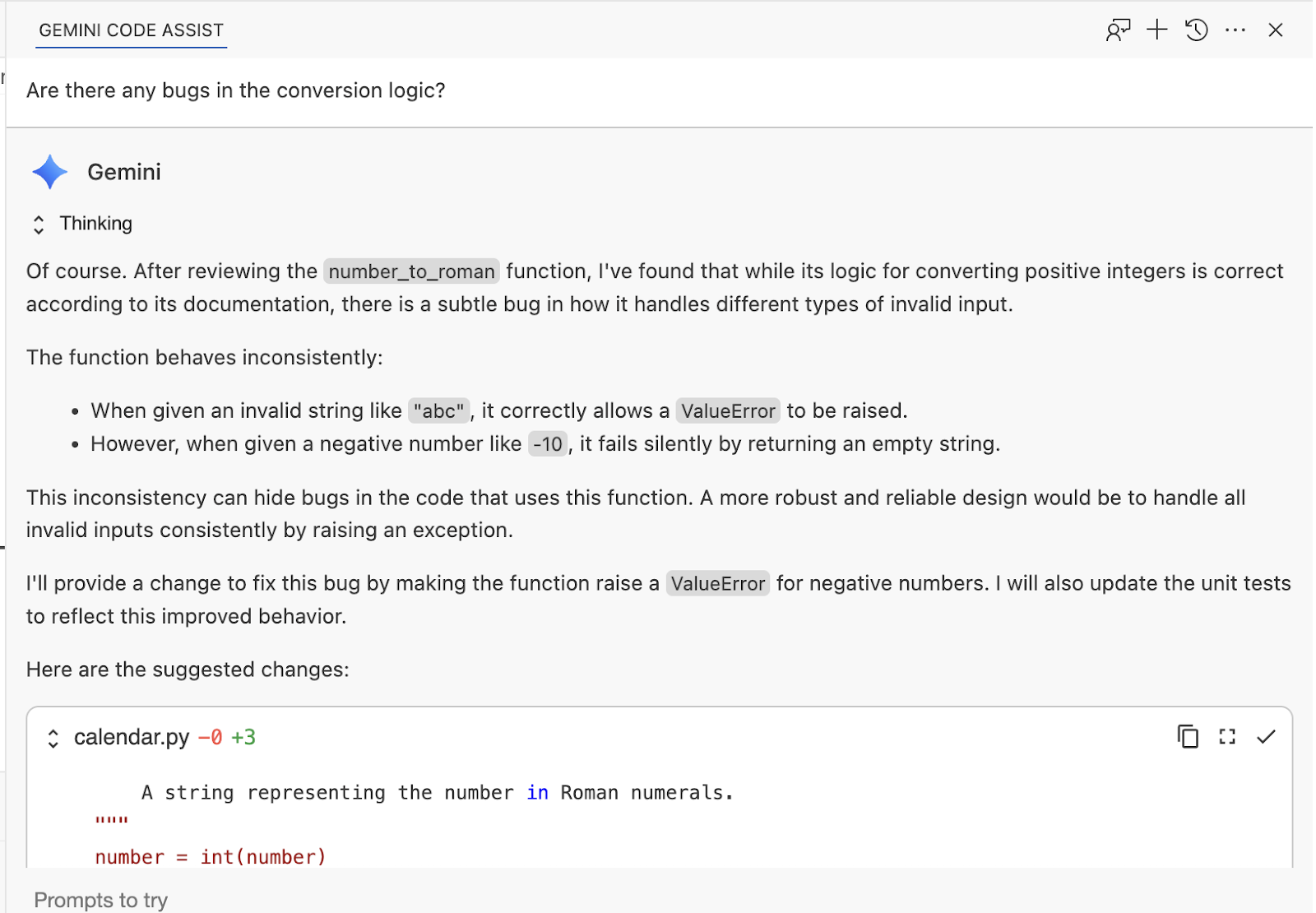
Are there any bugs in the conversion logic?
Review suggested changes and accept them in the chat:
Re-run unit tests to validate the changes:
python3 test_calendar.py
If you see error messages, you can select the error and add it into the context for Gemini to help with troubleshooting and fixing.
9. Refactor UI
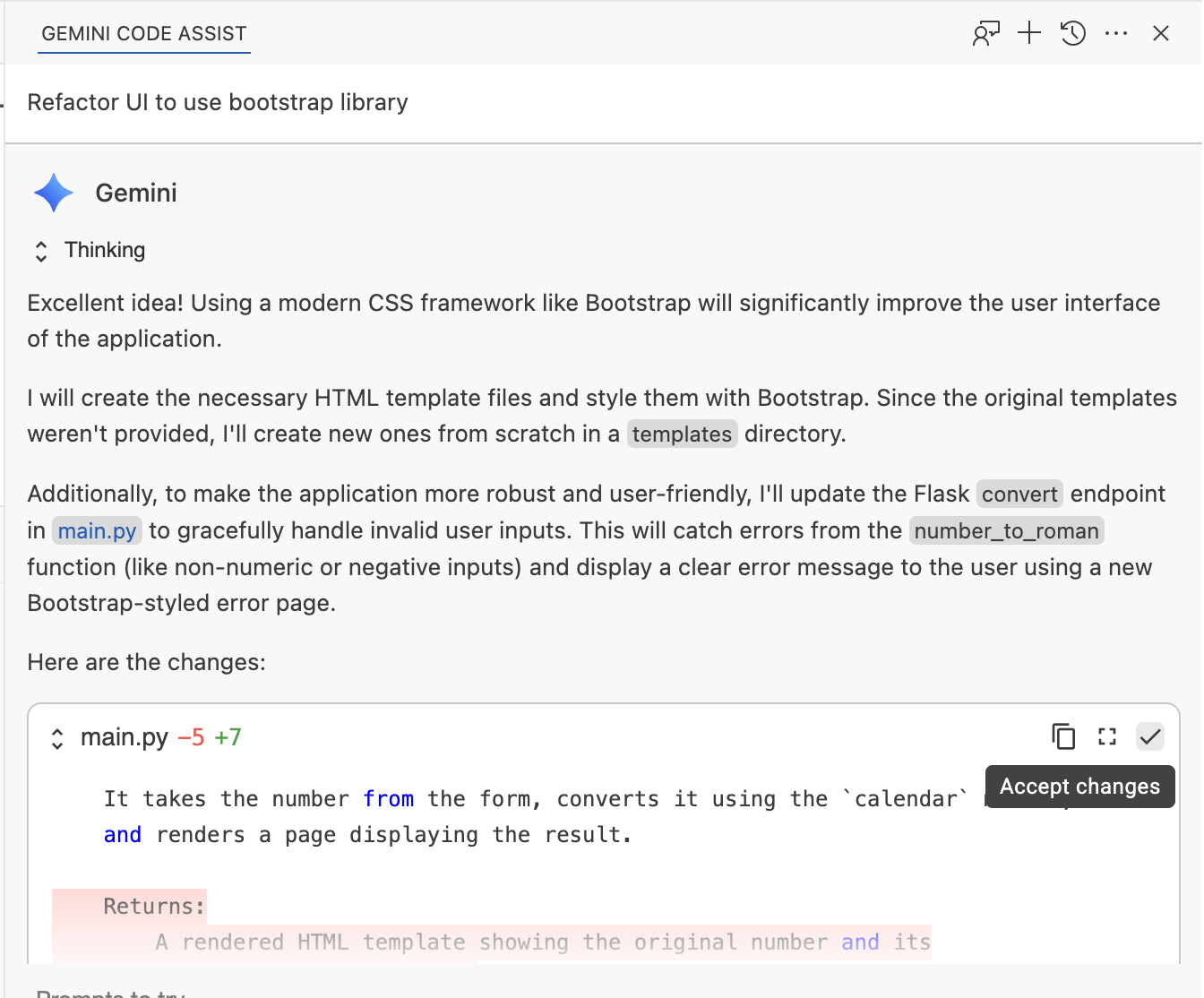
In the chat window send this prompt:
Refactor UI to use bootstrap library
Review and accept the changes:
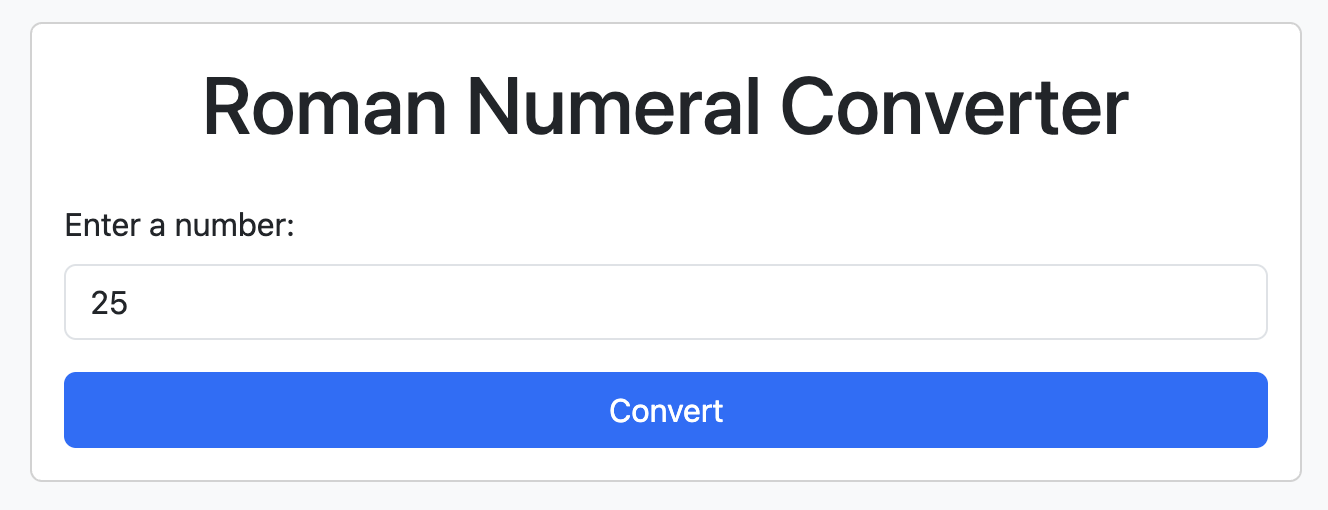
Start the application or reload the page if the app is already running.
In the terminal start the app if its not running:
python3 main.py
Reload the page and check the changes.
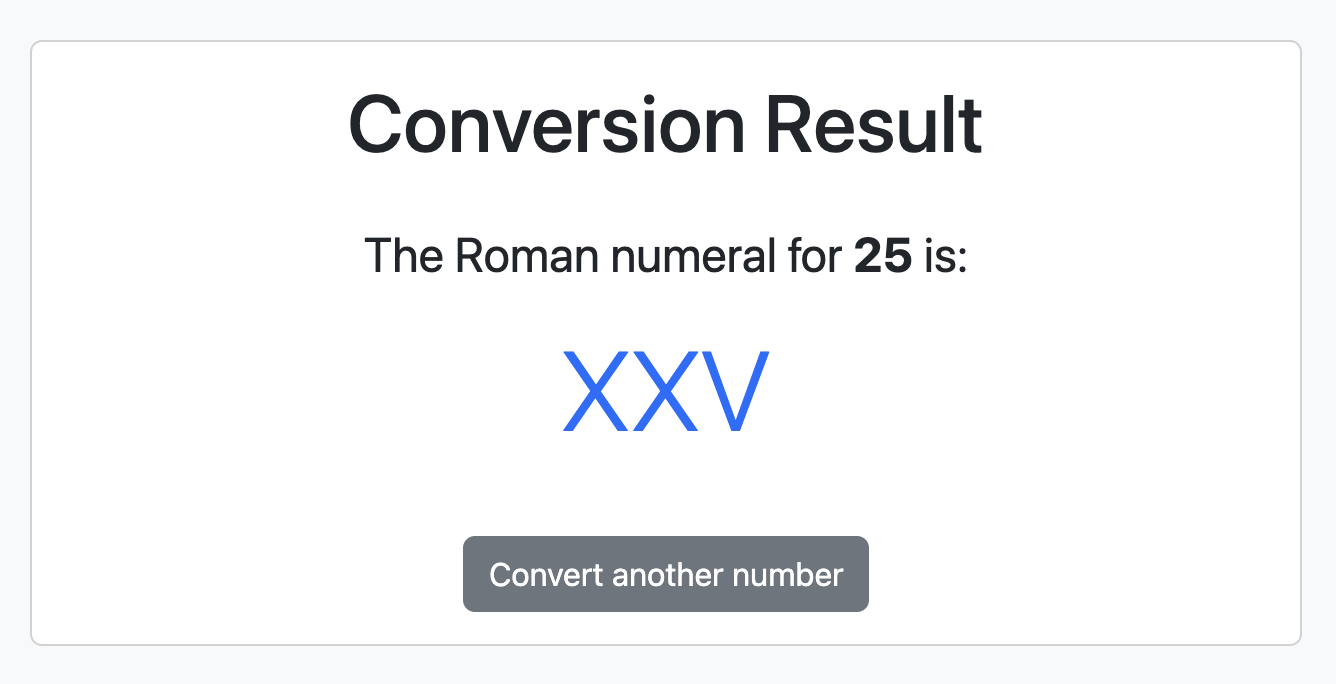
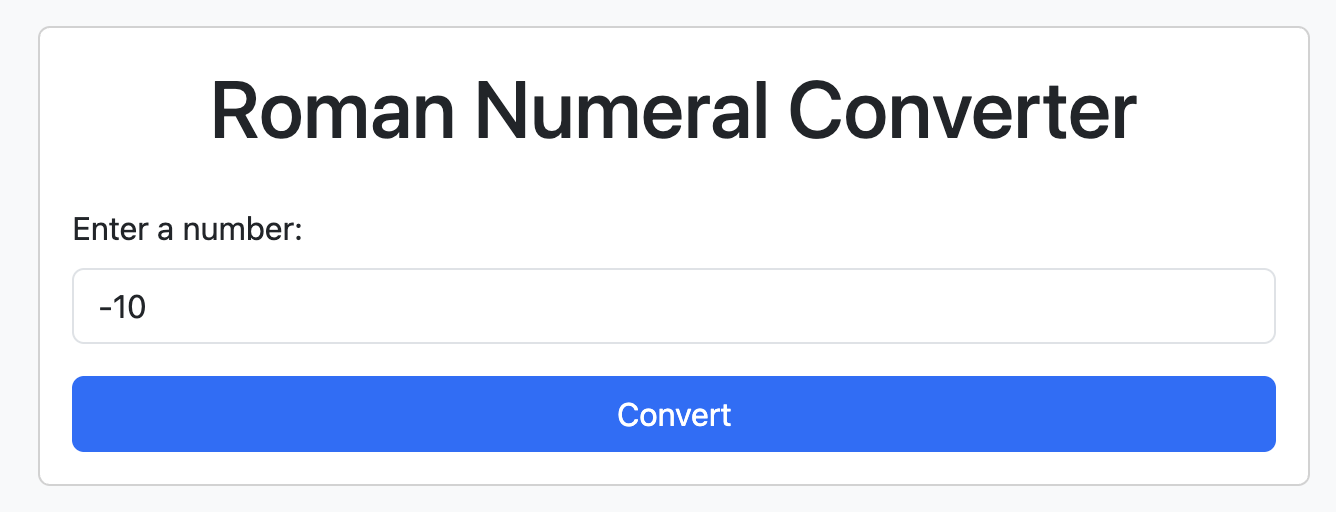
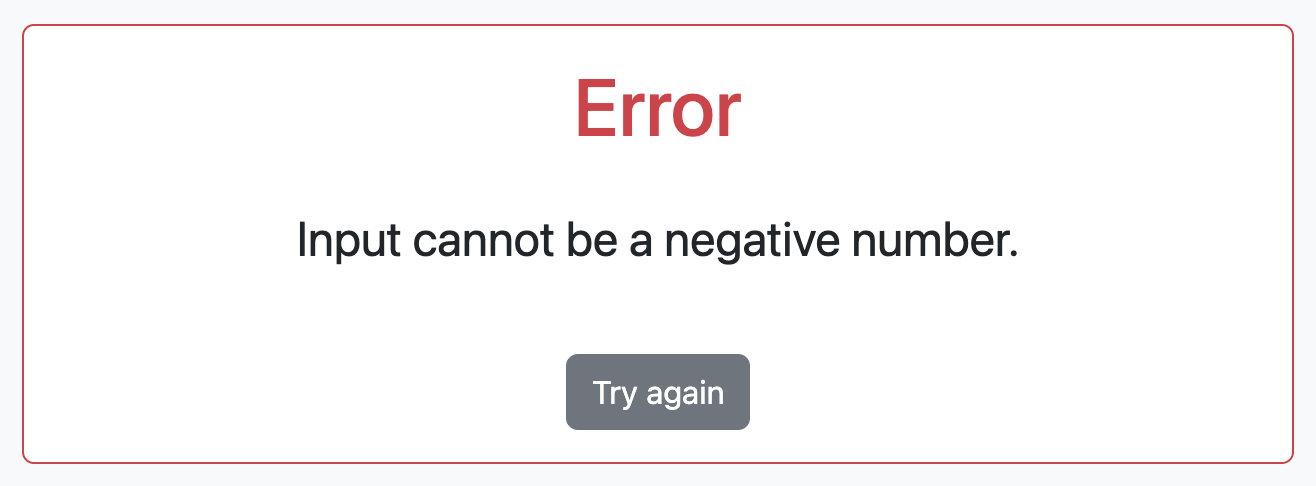
Try sending a negative number to verify the error page.
10. Refactor Backend
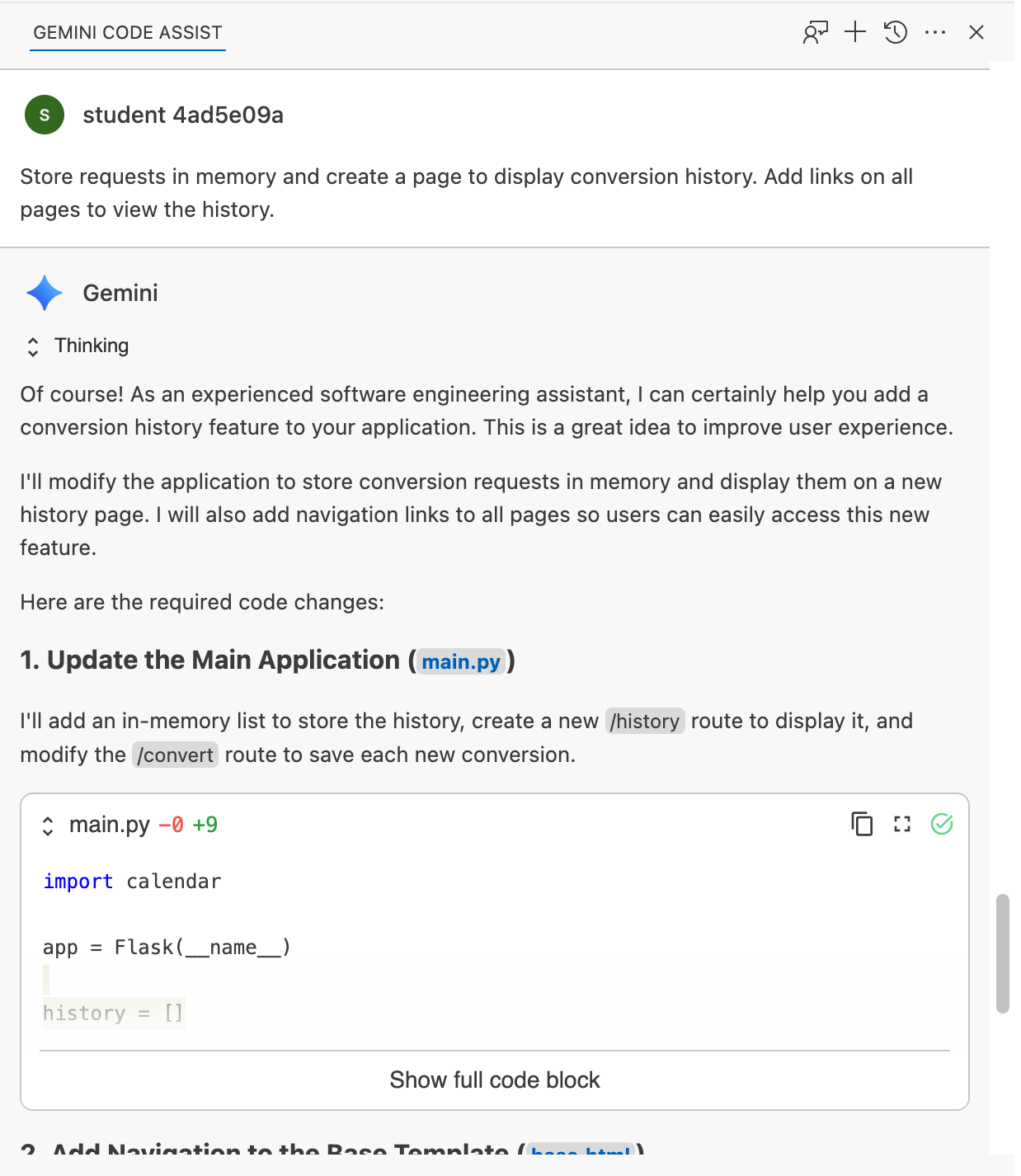
In the chat window send this prompt:
Store requests in memory and create a page to display conversion history. Add links on all pages to view the history.
Review and accept the changes in the chat:
Start the application by running this command in the terminal:
python3 main.py
Access the application and submit multiple requests before reviewing the history page.
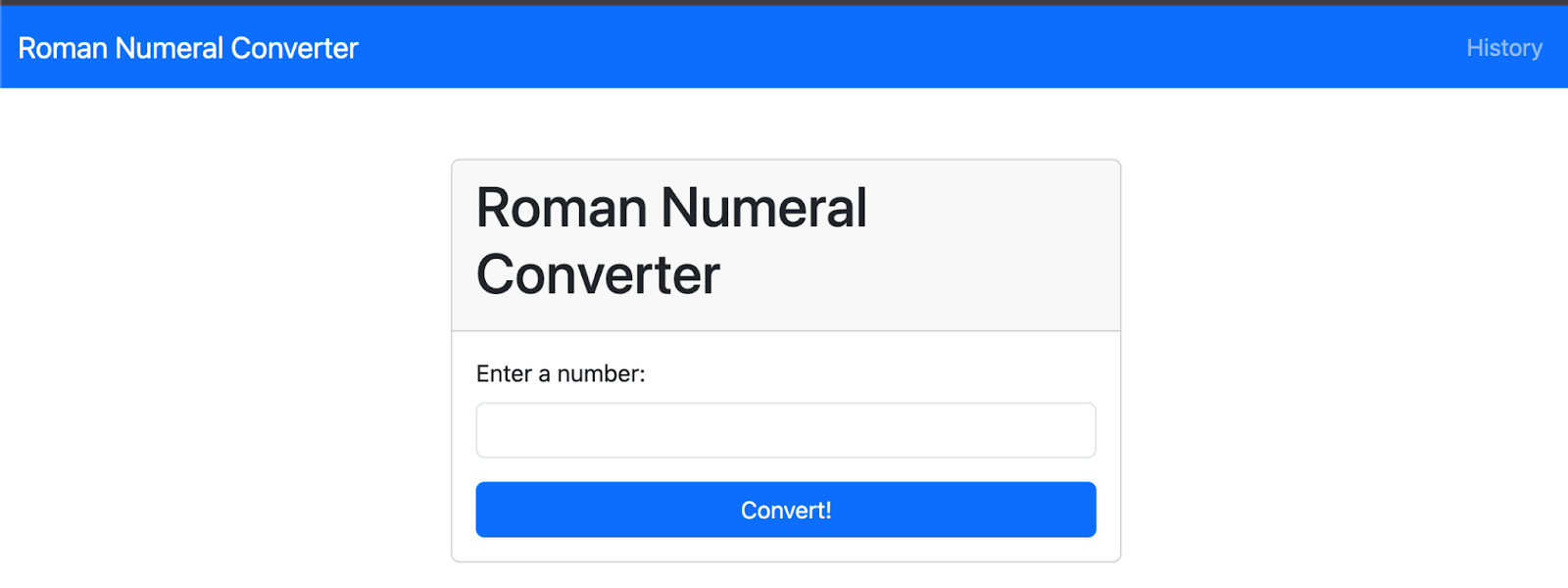
Review the history of conversion requests.
11. Conclusion for Gemini Code Assist
You've now seen how Gemini Code Assist can significantly streamline various development tasks, from understanding existing code to generating documentation, unit tests, and refactoring both UI and backend components. Its ability to comprehend context and provide relevant suggestions makes it a powerful tool for developers.
We encourage you to experiment further with Gemini Code Assist. Try different prompts, explore its capabilities with your own codebases, and discover how it can enhance your daily development workflow. The more you interact with it, the more you'll uncover its potential to accelerate your productivity and improve code quality.
12. Congratulations!
Congratulations, you finished the codelab!
What we've covered:
- Using Gemini Code Assist for common developer tasks
What's next:
- More hands-on sessions are coming!
Clean up
To avoid incurring charges to your Google Cloud account for the resources used in this tutorial, either delete the project that contains the resources, or keep the project and delete the individual resources.
Deleting the project
The easiest way to eliminate billing is to delete the project that you created for the tutorial.
©2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
