1. 简介
Google Antigravity 是 Google 推出的智能体 IDE。在此 Codelab 中,我们将使用 Antigravity 构建智能体技能,这是一种轻量级开放格式,用于通过专业知识和工作流扩展 AI 智能体功能。您将能够了解智能体技能是什么、其优势以及如何构建。然后,您将构建多个代理技能,包括 Git 格式化程序、模板生成器、工具代码框架等,所有这些都可以在 Antigravity 中使用。
前提条件:
- 已安装并配置 Google Antigravity。
- 对 Google Antigravity 有基本的了解。建议您先完成 Codelab:Google Antigravity 入门指南。
2. 为何要学习技能
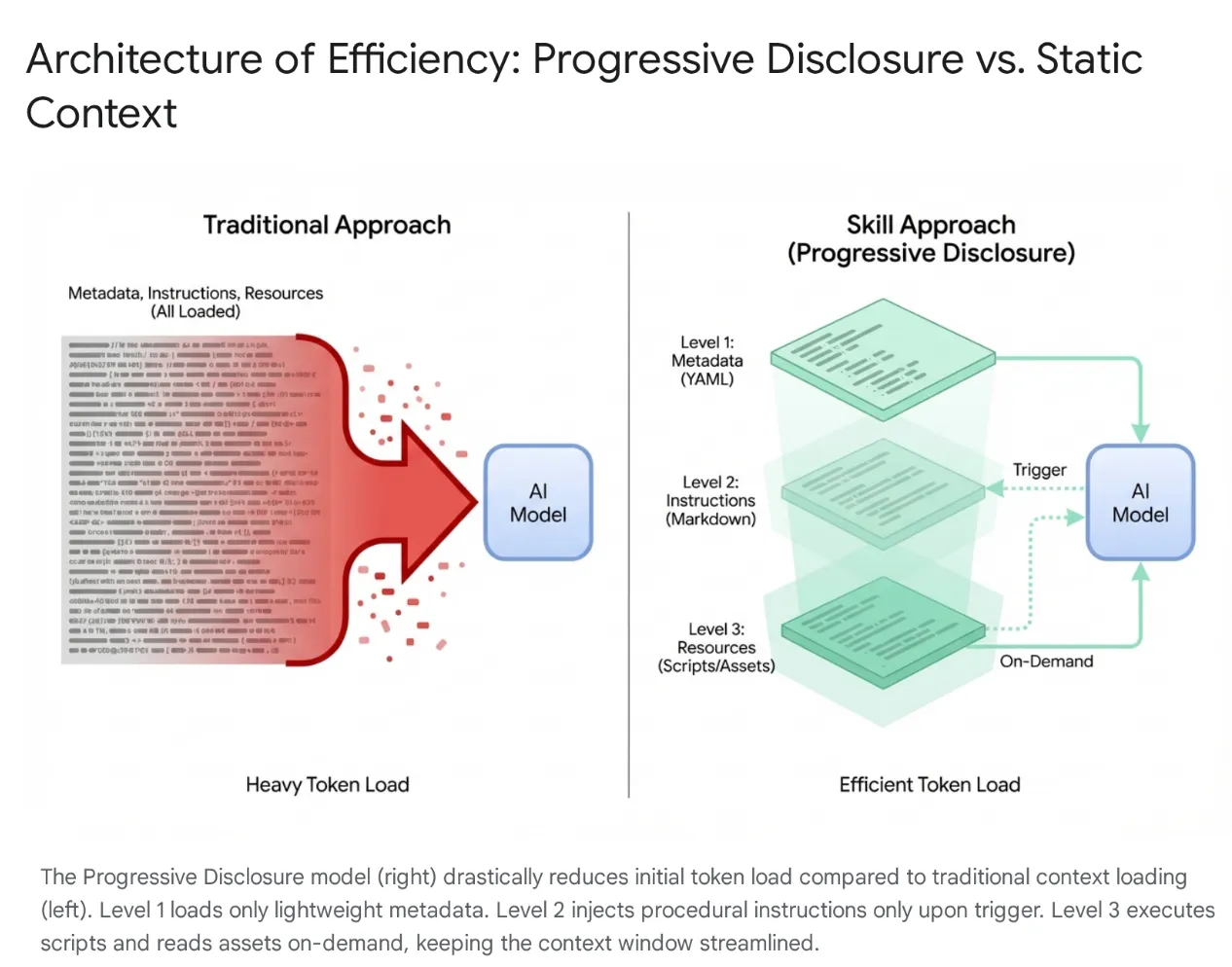
现代 AI 智能体已从简单的监听器发展为复杂的推理器,可与本地文件系统和外部工具(通过 MCP 服务器)集成。不过,如果随意为代理加载整个代码库和数百种工具,会导致上下文饱和和“工具膨胀”。即使上下文窗口很大,将 4 万到 5 万个未使用的工具令牌转储到活动内存中也会导致高延迟、资金浪费和“上下文腐烂”,即模型会被无关数据混淆。
解决方案:Agent Skills
为解决此问题,Anthropic 推出了智能体技能,将架构从单体上下文加载转变为逐步披露。这些功能被打包成模块化、可发现的单元,而不是在会话开始时强制模型“记住”每个特定的工作流(例如数据库迁移或安全审核)。
工作方式
模型最初仅会接触到轻量级的元数据“菜单”。它仅在用户意图与技能完全匹配时才加载繁琐的程序性知识(指令和脚本)。这样可确保请求重构身份验证中间件的开发者获得安全上下文,而无需加载无关的 CSS 流水线,从而保持上下文精简、快速且经济高效。
3. Agent Skills 和反重力
在 Antigravity 生态系统中,如果说 Agent Manager 是大脑,Editor 是画布,那么 Skill 就是专门的训练模块,可弥合通才 Gemini 3 模型与您的特定情境之间的差距。它们允许代理仅在请求相关任务时“配备”一组已定义的指令和协议,例如数据库迁移标准或安全检查。通过动态加载这些执行协议,技能可有效地将 AI 从通用程序员转变为严格遵守组织编纂的最佳实践和安全标准的专家。
什么是 Antigravity 中的技能?
在 Google Antigravity 的背景下,技能是指基于目录的软件包,其中包含定义文件 (SKILL.md) 和可选的支持资源(脚本、参考、模板)。
它是一种按需扩展功能的机制。
- 按需:与始终加载的系统提示不同,技能仅在代理确定其与用户当前请求相关时才加载到代理的上下文中。这样可以优化上下文窗口,防止代理受到无关指令的干扰。在包含数十种工具的大型项目中,这种选择性加载对于性能和推理准确性至关重要。
- 功能扩展:技能不仅可以发出指令,还可以执行操作。通过捆绑 Python 或 Bash 脚本,技能可以使代理能够对本地机器或外部网络执行复杂的多步操作,而无需用户手动运行命令。这会将代理从文本生成器转变为工具用户。
技能与生态系统(工具、规则和工作流)
虽然 Model Context Protocol (MCP) 充当智能体的“手”,可提供与 GitHub 或 PostgreSQL 等外部系统的持久连接,但技能充当“大脑”,可指导智能体执行操作。
MCP 处理有状态的基础设施,而技能是轻量级、短暂的任务定义,用于封装使用这些工具的方法。这种无服务器方法可让代理执行临时任务(例如生成更改日志或迁移),而无需运行持久进程的运营开销,仅在任务处于活动状态时加载上下文,并在任务完成后立即释放上下文。
从功能上讲,技能介于“规则”(被动、始终开启的护栏)和“工作流”(主动、用户触发的宏)之间,具有独特的中间地位。与需要特定命令的工作流(例如/test),技能是由代理触发的:模型会自动检测用户意图,并动态配备所需的特定专业知识。此架构可实现强大的可组合性;例如,全局规则可以在数据库更改期间强制使用“安全迁移”技能,或者单个工作流可以编排多个技能来构建稳健的部署流水线。
4. 创建技能
在 Antigravity 中创建技能需要遵循特定的目录结构和文件格式。这种标准化可确保技能的可移植性,并确保代理能够可靠地解析和执行技能。该设计有意采用简单的方式,依赖于 Markdown 和 YAML 等广为人知的格式,从而降低了希望扩展 IDE 功能的开发者的入门门槛。
目录结构
技能可以在两个范围内定义,从而实现项目级和用户级自定义:
- 工作区范围:位于
<workspace-root>/.agent/skills/。这些技能只能在特定项目中提供。这非常适合项目专用脚本,例如部署到特定环境、管理相应应用的数据库,或为专有框架生成样板代码。 - 全球范围:位于
~/.gemini/antigravity/skills/。这些技能可在用户机器上的所有项目中使用。这适用于“格式化 JSON”“生成 UUID”“检查代码样式”等通用实用程序,或与个人效率工具集成。
典型的技能目录如下所示:
my-skill/
├── SKILL.md # The definition file
├── scripts/ # [Optional] Python, Bash, or Node scripts
├── run.py
└── util.sh
├── references/ # [Optional] Documentation or templates
└── api-docs.md
└── assets/ # [Optional] Static assets (images, logos)
这种结构可有效分离关注点。逻辑 (scripts) 与指令 (SKILL.md) 和知识 (references) 分开,这与标准软件工程实践相符。
SKILL.md 定义文件
SKILL.md 文件是技能的核心。它会告知代理技能是什么、何时使用以及如何执行。
它由两部分组成:
- YAML 前言
- Markdown 正文。
YAML 前言
这是元数据层。它是技能中唯一会被代理的高级路由器编入索引的部分。当用户发送提示时,代理会根据所有可用技能的说明字段对提示进行语义匹配。
---
name: database-inspector
description: Use this skill when the user asks to query the database, check table schemas, or inspect user data in the local PostgreSQL instance.
---
关键字段:
- name:此属性不是必需的。在相应范围内必须是唯一的。允许使用小写字母和连字符(例如
postgres-query、pr-reviewer)。如果未提供,则默认为目录名称。 - 说明:此字段为必填字段,也是最重要的字段。它充当“触发短语”。它必须具有足够的描述性,以便 LLM 识别语义相关性。“数据库工具”等模糊的说明是不够的。精确的描述,例如“针对本地 PostgreSQL 数据库执行只读 SQL 查询,以检索用户或交易数据。使用此技能调试数据状态”可确保技能被正确识别。
Markdown 正文
正文包含指令。这是保存到文件中的“提示工程”。当技能被激活时,此内容会被注入到代理的上下文窗口中。
正文应包含:
- 目标:清晰说明技能的用途。
- 说明:分步逻辑。
- 示例:用于引导模型表现的输入和输出少样本示例。
- 限制:“禁止”规则(例如,“不运行 DELETE 查询”)。
SKILL.md 正文示例:
Database Inspector
Goal
To safely query the local database and provide insights on the current data state.
Instructions
- Analyze the user's natural language request to understand the data need.
- Formulate a valid SQL query.
- CRITICAL: Only SELECT statements are allowed.
- Use the script scripts/query_runner.py to execute the SQL.
- Command: python scripts/query_runner.py "SELECT * FROM..."
- Present the results in a Markdown table.
Constraints
- Never output raw user passwords or API keys.
- If the query returns > 50 rows, summarize the data instead of listing it all.
脚本集成
技能最强大的功能之一是能够将执行操作委托给脚本。这使得代理能够执行 LLM 难以或无法直接执行的操作(例如二进制执行、复杂的数学计算或与旧版系统互动)。
脚本放置在 scripts/ 子目录中。SKILL.md 通过相对路径引用它们。
5. 创作技能
本部分的目标是构建集成到 Antigravity 中的技能,并逐步展示各种功能,例如资源/脚本等。
您可以从以下 GitHub 代码库下载技能:https://github.com/rominirani/antigravity-skills。
我们可以考虑将这些技能放在 ~/.gemini/antigravity/skills 文件夹或 /.agent/skills 文件夹中。
级别 1:基本路由器 ( git-commit-formatter )
让我们将此视为技能的“Hello World”。
开发者经常会编写懒惰的提交消息,例如“wip”“修复 bug”“更新”。手动强制执行“常规提交”既繁琐又容易忘记。我们来实现一个强制执行 Conventional Commits 规范的技能。只需向智能体说明规则,即可让其充当执行者。
git-commit-formatter/
└── SKILL.md (Instructions only)
SKILL.md 文件如下所示:
---
name: git-commit-formatter
description: Formats git commit messages according to Conventional Commits specification. Use this when the user asks to commit changes or write a commit message.
---
Git Commit Formatter Skill
When writing a git commit message, you MUST follow the Conventional Commits specification.
Format
`<type>[optional scope]: <description>`
Allowed Types
- **feat**: A new feature
- **fix**: A bug fix
- **docs**: Documentation only changes
- **style**: Changes that do not affect the meaning of the code (white-space, formatting, etc)
- **refactor**: A code change that neither fixes a bug nor adds a feature
- **perf**: A code change that improves performance
- **test**: Adding missing tests or correcting existing tests
- **chore**: Changes to the build process or auxiliary tools and libraries such as documentation generation
Instructions
1. Analyze the changes to determine the primary `type`.
2. Identify the `scope` if applicable (e.g., specific component or file).
3. Write a concise `description` in an imperative mood (e.g., "add feature" not "added feature").
4. If there are breaking changes, add a footer starting with `BREAKING CHANGE:`.
Example
`feat(auth): implement login with google`
如何运行此示例:
- 对工作区中的任意文件进行小幅更改。
- 打开对话,然后输入:提交这些更改。
- 代理不会只运行 git commit。它会先激活 git-commit-formatter 技能。
- 结果:系统将建议一条常规 Git 提交消息。
例如,我让 Antigravity 向一个示例 Python 文件添加了一些注释,最终生成了类似 docs: add detailed comments to demo_primes.py. 的 Git 提交消息
第 2 级:资源利用率 (license-header-adder)
这是“参考”模式。
公司项目中的每个源文件可能都需要一个特定的 20 行 Apache 2.0 许可标头。将此静态文本直接放入提示(或 SKILL.md)中会浪费资源。每次为技能编制索引时,模型都会消耗令牌,并且可能会在法律文本中“幻觉”出拼写错误。
将静态文本分流到 resources/ 文件夹中的纯文本文件。该技能会指示代理仅在需要时读取此文件。
license-header-adder/
├── SKILL.md
└── resources/
└── HEADER_TEMPLATE.txt (The heavy text)
SKILL.md 文件如下所示:
---
name: license-header-adder
description: Adds the standard open-source license header to new source files. Use involves creating new code files that require copyright attribution.
---
# License Header Adder Skill
This skill ensures that all new source files have the correct copyright header.
## Instructions
1. **Read the Template**:
First, read the content of the header template file located at `resources/HEADER_TEMPLATE.txt`.
2. **Prepend to File**:
When creating a new file (e.g., `.py`, `.java`, `.js`, `.ts`, `.go`), prepend the `target_file` content with the template content.
3. **Modify Comment Syntax**:
- For C-style languages (Java, JS, TS, C++), keep the `/* ... */` block as is.
- For Python, Shell, or YAML, convert the block to use `#` comments.
- For HTML/XML, use `<!-- ... -->`.
如何运行此示例:
- 创建一个新的虚拟 Python 文件:
touch my_script.py - 类型:
Add the license header to my_script.py。 - 代理将读取
license-header-adder/resources/HEADER_TEMPLATE.txt。 - 它会将内容原封不动地粘贴到您的文件中。
第 3 级:通过示例学习(json-to-pydantic)
“少样本”模式。
将松散的数据(例如 JSON API 响应)转换为严格的代码(例如 Pydantic 模型)需要做出数十项决策。我们应该如何命名这些类?我们应该使用 Optional 吗?snake_case还是camelCase?用英语写出这 50 条规则既繁琐又容易出错。
LLM 是模式匹配引擎。
向模型展示一个黄金示例(Input -> Output)通常比冗长的指令更有效。
json-to-pydantic/
├── SKILL.md
└── examples/
├── input_data.json (The Before State)
└── output_model.py (The After State)
SKILL.md 文件如下所示:
---
name: json-to-pydantic
description: Converts JSON data snippets into Python Pydantic data models.
---
# JSON to Pydantic Skill
This skill helps convert raw JSON data or API responses into structured, strongly-typed Python classes using Pydantic.
Instructions
1. **Analyze the Input**: Look at the JSON object provided by the user.
2. **Infer Types**:
- `string` -> `str`
- `number` -> `int` or `float`
- `boolean` -> `bool`
- `array` -> `List[Type]`
- `null` -> `Optional[Type]`
- Nested Objects -> Create a separate sub-class.
3. **Follow the Example**:
Review `examples/` to see how to structure the output code. notice how nested dictionaries like `preferences` are extracted into their own class.
- Input: `examples/input_data.json`
- Output: `examples/output_model.py`
Style Guidelines
- Use `PascalCase` for class names.
- Use type hints (`List`, `Optional`) from `typing` module.
- If a field can be missing or null, default it to `None`.
在 /examples 文件夹中,包含 JSON 文件和输出文件(即 Python 文件)。这两种情况如下所示:
input_data.json
{
"user_id": 12345,
"username": "jdoe_88",
"is_active": true,
"preferences": {
"theme": "dark",
"notifications": [
"email",
"push"
]
},
"last_login": "2024-03-15T10:30:00Z",
"meta_tags": null
}
output_model.py
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List, Optional
class Preferences(BaseModel):
theme: str
notifications: List[str]
class User(BaseModel):
user_id: int
username: str
is_active: bool
preferences: Preferences
last_login: Optional[str] = None
meta_tags: Optional[List[str]] = None
如何运行此示例:
- 向代理提供 JSON 代码段(将其粘贴到对话中或指向相应文件)。
{ "product": "Widget", "cost": 10.99, "stock": null }
- 类型:
Convert this JSON to a Pydantic model。 - 代理会查看技能文件夹中的
examples对。 - 它会生成一个 Python 类,该类可完美模仿
output_model.py的编码风格、导入和结构,包括将 null 股票处理为 Optional。
示例输出 (product_model.py) 如下所示:
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Optional
class Product(BaseModel):
product: str
cost: float
stock: Optional[int] = None
级别 4:过程逻辑 (database-schema-validator)
这是“工具使用”模式。
如果您向 LLM 询问“此架构是否安全?”,即使缺少关键主键,它也可能会说一切正常,仅仅是因为 SQL 看起来正确。
让我们将此检查委托给确定性脚本。我们使用技能来路由代理,以运行我们编写的 Python 脚本。该脚本提供二元(True/False)真实值。
database-schema-validator/
├── SKILL.md
└── scripts/
└── validate_schema.py (The Validator)
SKILL.md 文件如下所示:
---
name: database-schema-validator
description: Validates SQL schema files for compliance with internal safety and naming policies.
---
# Database Schema Validator Skill
This skill ensures that all SQL files provided by the user comply with our strict database standards.
Policies Enforced
1. **Safety**: No `DROP TABLE` statements.
2. **Naming**: All tables must use `snake_case`.
3. **Structure**: Every table must have an `id` column as PRIMARY KEY.
Instructions
1. **Do not read the file manually** to check for errors. The rules are complex and easily missed by eye.
2. **Run the Validation Script**:
Use the `run_command` tool to execute the python script provided in the `scripts/` folder against the user's file.
`python scripts/validate_schema.py <path_to_user_file>`
3. **Interpret Output**:
- If the script returns **exit code 0**: Tell the user the schema looks good.
- If the script returns **exit code 1**: Report the specific error messages printed by the script to the user and suggest fixes.
validate_schema.py 文件如下所示:
import sys
import re
def validate_schema(filename):
"""
Validates a SQL schema file against internal policy:
1. Table names must be snake_case.
2. Every table must have a primary key named 'id'.
3. No 'DROP TABLE' statements allowed (safety).
"""
try:
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
content = f.read()
lines = content.split('\n')
errors = []
# Check 1: No DROP TABLE
if re.search(r'DROP TABLE', content, re.IGNORECASE):
errors.append("ERROR: 'DROP TABLE' statements are forbidden.")
# Check 2 & 3: CREATE TABLE checks
table_defs = re.finditer(r'CREATE TABLE\s+(?P<name>\w+)\s*\((?P<body>.*?)\);', content, re.DOTALL | re.IGNORECASE)
for match in table_defs:
table_name = match.group('name')
body = match.group('body')
# Snake case check
if not re.match(r'^[a-z][a-z0-9_]*$', table_name):
errors.append(f"ERROR: Table '{table_name}' must be snake_case.")
# Primary key check
if not re.search(r'\bid\b.*PRIMARY KEY', body, re.IGNORECASE):
errors.append(f"ERROR: Table '{table_name}' is missing a primary key named 'id'.")
if errors:
for err in errors:
print(err)
sys.exit(1)
else:
print("Schema validation passed.")
sys.exit(0)
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Error: File '{filename}' not found.")
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage: python validate_schema.py <schema_file>")
sys.exit(1)
validate_schema(sys.argv[1])
如何运行此示例:
- 创建错误的 SQL 文件
bad_schema.sql:CREATE TABLE users (name TEXT); - 类型:
Validate bad_schema.sql。 - 代理不会猜测。它将调用脚本,但脚本会失败(退出代码 1),并向我们报告“验证失败,因为表‘users’缺少主键”。
第 5 级:架构师 (adk-tool-scaffold)
此模式涵盖了技能中的大部分功能。
复杂的任务通常需要一系列操作,这些操作会结合我们之前介绍的所有内容:创建文件、遵循模板和编写逻辑。为 ADK(智能体开发套件)创建新工具需要所有这些信息。
我们结合了:
- 脚本(用于处理文件创建/框架搭建)
- 模板(用于处理资源中的样板)
- 示例(用于引导逻辑生成)。
adk-tool-scaffold/
├── SKILL.md
├── resources/
│ └── ToolTemplate.py.hbs (Jinja2 Template)
├── scripts/
│ └── scaffold_tool.py (Generator Script)
└── examples/
└── WeatherTool.py (Reference Implementation)
SKILL.md 文件如下所示。您可以参考 技能代码库,查看脚本、资源和示例文件夹中的文件。对于此特定技能,请前往 adk-tool-scaffold 技能。
---
name: adk-tool-scaffold
description: Scaffolds a new custom Tool class for the Agent Development Kit (ADK).
---
# ADK Tool Scaffold Skill
This skill automates the creation of standard `BaseTool` implementations for the Agent Development Kit.
Instructions
1. **Identify the Tool Name**:
Extract the name of the tool the user wants to build (e.g., "StockPrice", "EmailSender").
2. **Review the Example**:
Check `examples/WeatherTool.py` to understand the expected structure of an ADK tool (imports, inheritance, schema).
3. **Run the Scaffolder**:
Execute the python script to generate the initial file.
`python scripts/scaffold_tool.py <ToolName>`
4. **Refine**:
After generation, you must edit the file to:
- Update the `execute` method with real logic.
- Define the JSON schema in `get_schema`.
Example Usage
User: "Create a tool to search Wikipedia."
Agent:
1. Runs `python scripts/scaffold_tool.py WikipediaSearch`
2. Editing `WikipediaSearchTool.py` to add the `requests` logic and `query` argument schema.
如何运行此示例:
- 类型:
Create a new ADK tool called StockPrice to fetch data from an API。 - 第 1 步(框架):代理运行 Python 脚本。这会立即创建具有正确类结构、导入和类名称
StockPriceTool的StockPriceTool.py。 - 第 2 步(实现):代理“读取”刚刚创建的文件。它会看到
# TODO: Implement logic. - 第 3 步(指导):不确定如何为工具实参定义 JSON 架构。它会检查
examples/WeatherTool.py。 - 完成:它会修改文件以添加
requests.get(...),并在架构中定义 ticker 实参,完全符合 ADK 样式。
6. 恭喜
您已成功完成有关反重力技能的实验,并构建了以下技能:
- Git 提交格式设置工具。
- 许可标头添加器。
- JSON 到 Pydantic。
- 数据库架构验证器。
- ADK 工具框架。
代理技能无疑是一种绝佳的方式,可让 Antigravity 以您的方式编写代码、遵循规则并使用您的工具。
