1. 簡介
Google Antigravity 是 Google 推出的代理 IDE,在本程式碼研究室中,我們將使用 Antigravity 建構 Agent Skills,這是一種輕量級的開放格式,可透過專業知識和工作流程擴充 AI 服務專員功能。您將瞭解代理程式技能、優點和建構方式。接著,您將建構多項 Agent Skills,包括 Git 格式化工具、範本產生器、工具程式碼架構等,全都可在 Antigravity 中使用。
需求條件:
- 已安裝及設定 Google Antigravity。
- 對 Google Antigravity 有基本瞭解。建議先完成「開始使用 Google Antigravity」程式碼實驗室。
2. 為何要使用技能
現代 AI 代理已從簡單的接聽程式,演變成複雜的推理程式,可與本機檔案系統和外部工具 (透過 MCP 伺服器) 整合。不過,如果隨意將整個程式碼集和數百種工具載入代理程式,就會導致內容飽和和「工具膨脹」。即使上下文窗口很大,將 4 萬到 5 萬個未使用的工具權杖傾印到作用中記憶體,也會導致高延遲、浪費資金,以及「上下文腐敗」,也就是模型會因不相關的資料而感到困惑。
解決方案:Agent Skills
為解決這個問題,Anthropic 推出代理程式技能,將架構從單體式內容載入轉移至漸進式揭露。不必在工作階段開始時,強迫模型「記憶」每個特定工作流程 (例如資料庫遷移或安全稽核),而是將這些功能封裝成可探索的模組化單元。
運作方式
模型一開始只會接觸到輕量的「選單」中繼資料。只有在使用者意圖與技能完全相符時,才會載入大量程序知識 (指令和指令碼)。這可確保要求重構驗證中介軟體的開發人員取得安全環境,不必載入不相關的 CSS 管道,讓環境保持精簡、快速且符合成本效益。
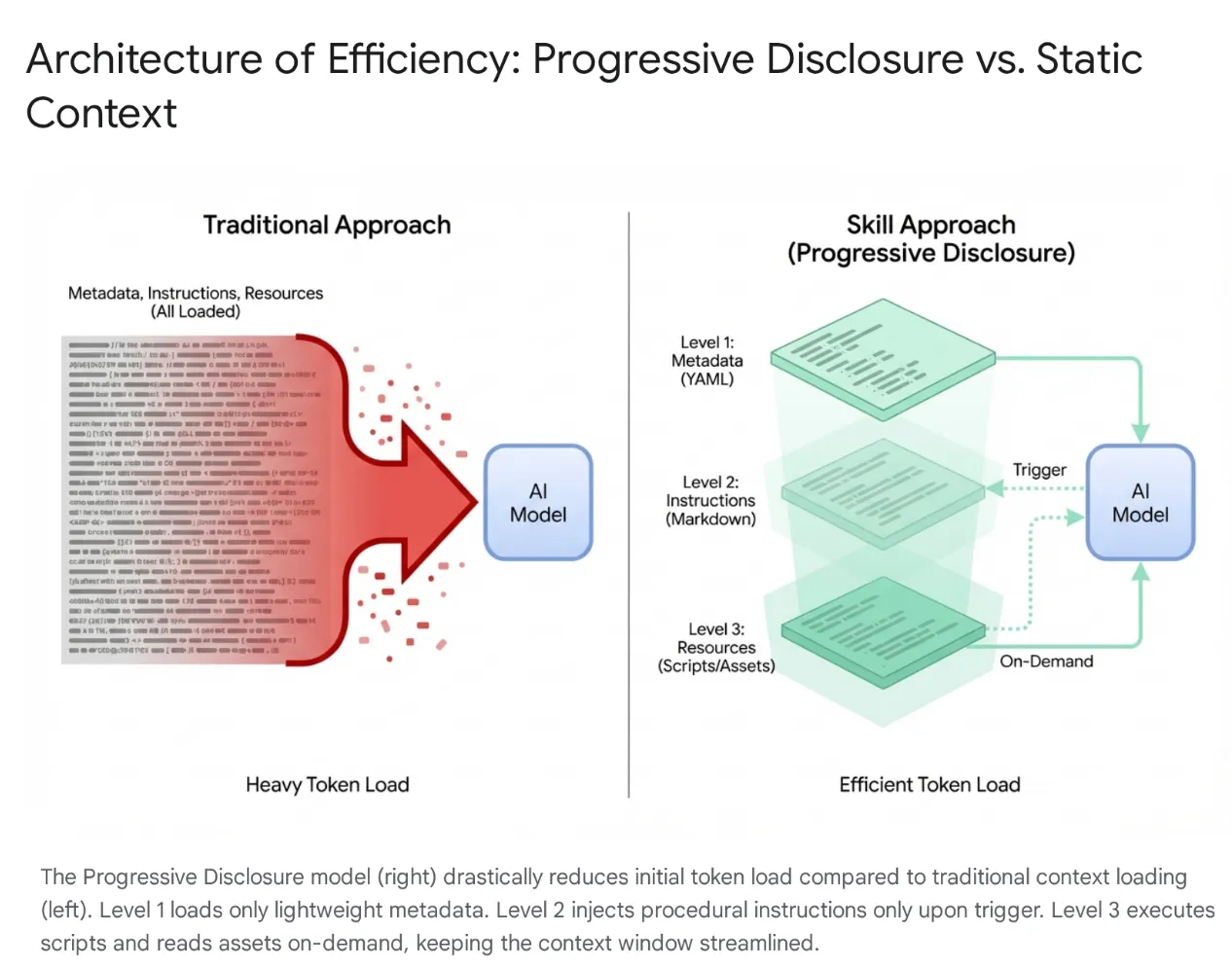
3. Agent Skills 和 Antigravity
在 Antigravity 生態系統中,如果 Agent Manager 是大腦,Editor 是畫布,技能就是專門的訓練模組,可彌合通才 Gemini 3 模型與特定情境之間的差距。當使用者要求執行相關工作時,代理程式就能「裝備」一組定義的指令和通訊協定,例如資料庫遷移標準或安全檢查。透過動態載入這些執行通訊協定,Skills 可有效將 AI 從一般程式設計師轉變為專家,嚴格遵守機構的編碼最佳做法和安全標準。
什麼是 Antigravity 中的技能?
在 Google Antigravity 中,技能是指以目錄為基礎的套件,內含定義檔 (SKILL.md) 和選用的支援資產 (指令碼、參照、範本)。
這是隨需擴充功能的機制。
- 隨選:與一律會載入的系統提示不同,只有在代理程式判斷技能與使用者目前的要求相關時,才會載入代理程式的環境。這項做法可最佳化內容視窗,避免代理程式受到無關指令干擾。在有數十種工具的大型專案中,這種選擇性載入對於效能和推理準確度至關重要。
- 功能擴充:技能不僅能提供指示,還能執行動作。透過 Python 或 Bash 指令碼組合,技能可讓代理程式在本機或外部網路執行複雜的多步驟動作,使用者不必手動執行指令。這項功能可讓代理程式從文字生成器變成工具使用者。
技能與生態系統 (工具、規則和工作流程)
Model Context Protocol (MCP) 就像代理的「雙手」,可與 GitHub 或 PostgreSQL 等外部系統建立持續性連線,而 Skills 則像「大腦」,負責指揮代理。
MCP 會處理有狀態的基礎架構,而 Skills 則是輕量級的暫時性工作定義,可封裝使用這些工具的方法。採用無伺服器方法後,代理程式就能執行臨時工作 (例如產生修訂記錄或遷移),不必為了執行持續性程序而產生作業負擔,且只會在工作處於活動狀態時載入內容,並在工作完成後立即釋出。
從功能上來說,技能介於「規則」(被動、隨時啟用的防護措施) 和「工作流程」(主動、使用者觸發的巨集) 之間。不同於需要特定指令的工作流程 (例如 /test),技能是由服務專員觸發:模型會自動偵測使用者的意圖,並動態提供所需專業知識。這種架構可實現強大的組合性;舉例來說,全域規則可以在資料庫變更期間強制使用「安全遷移」技能,或是單一工作流程可以協調多項技能,建構穩固的部署管道。
4. 建立技能
在 Antigravity 中建立技能時,必須遵循特定目錄結構和檔案格式。這項標準化作業可確保技能可攜性,並讓代理程式可靠地剖析及執行技能。設計刻意簡化,採用 Markdown 和 YAML 等廣為人知的格式,降低開發人員擴充 IDE 功能的門檻。
目錄結構
技能可定義於兩個範圍,允許專案和使用者專屬的自訂項目:
- Workspace 範圍:位於
<workspace-root>/.agent/skills/。這些技能僅適用於特定專案。這項功能非常適合專案專屬指令碼,例如部署至特定環境、管理該應用程式的資料庫,或是為專有架構產生樣板程式碼。 - 全球範圍:位於
~/.gemini/antigravity/skills/。這些技能適用於使用者電腦上的所有專案。這類工具適合用於一般公用程式,例如「格式化 JSON」、「產生 UUID」、「檢查程式碼樣式」,或與個人生產力工具整合。
典型的 Skill 目錄如下所示:
my-skill/
├── SKILL.md # The definition file
├── scripts/ # [Optional] Python, Bash, or Node scripts
├── run.py
└── util.sh
├── references/ # [Optional] Documentation or templates
└── api-docs.md
└── assets/ # [Optional] Static assets (images, logos)
這種結構可有效區隔疑慮。邏輯 (scripts) 與指令 (SKILL.md) 和知識 (references) 分開,反映標準軟體工程實務。
SKILL.md 定義檔
SKILL.md 檔案是技能的大腦,這項資訊會告知代理程式技能內容、使用時機和執行方式。
這項服務包含兩個部分:
- YAML 前頁內容
- Markdown 內文。
YAML Frontmatter
這是中繼資料層。這是代理程式高階路由器編列索引的唯一技能部分。使用者傳送提示時,代理程式會根據所有可用技能的說明欄位,進行提示的語意比對。
---
name: database-inspector
description: Use this skill when the user asks to query the database, check table schemas, or inspect user data in the local PostgreSQL instance.
---
關鍵欄位:
- 名稱:非必填。範圍內的名稱不得重複。可使用小寫字母和連字號 (例如
postgres-query、pr-reviewer)。如果未提供,系統會預設為目錄名稱。 - 說明:這是必填欄位,也是最重要的欄位。這項功能就像「觸發字詞」,該字串必須清楚易懂,大型語言模型才能辨識語義相關性。「資料庫工具」等籠統的說明不夠充分,例如「針對本機 PostgreSQL 資料庫執行唯讀 SQL 查詢,以擷取使用者或交易資料。Use this for debugging data states" ensures the skill is picked up correctly.
Markdown 內文
主體包含指令。這是儲存至檔案的「提示工程」。啟用技能後,這項內容會插入代理程式的背景資訊視窗。
主體應包含:
- 目標:清楚說明技能的用途。
- 說明:逐步邏輯。
- 範例:少量樣本的輸入和輸出內容,可引導模型提升成效。
- 限制:「請勿」規則 (例如「請勿執行 DELETE 查詢」)。
SKILL.md 內文範例:
Database Inspector
Goal
To safely query the local database and provide insights on the current data state.
Instructions
- Analyze the user's natural language request to understand the data need.
- Formulate a valid SQL query.
- CRITICAL: Only SELECT statements are allowed.
- Use the script scripts/query_runner.py to execute the SQL.
- Command: python scripts/query_runner.py "SELECT * FROM..."
- Present the results in a Markdown table.
Constraints
- Never output raw user passwords or API keys.
- If the query returns > 50 rows, summarize the data instead of listing it all.
整合指令碼
技能最實用的功能之一,就是能將執行作業委派給指令碼。這項功能可讓代理程式執行 LLM 無法直接執行的動作 (例如執行二進位檔、進行複雜的數學運算,或與舊版系統互動)。
腳本會放在 scripts/ 子目錄中。SKILL.md 會依相對路徑參照這些檔案。
5. 編寫技能
本節的目標是建構整合至 Antigravity 的技能,並逐步顯示各種功能,例如資源/指令碼等。
您可以從 Github 存放區下載技能:https://github.com/rominirani/antigravity-skills。
我們可以將這些技能放在 ~/.gemini/antigravity/skills 資料夾或 /.agent/skills 資料夾中。
第 1 級:基本路由器 ( git-commit-formatter )
我們將此視為技能的「Hello World」。
開發人員通常會編寫草率的提交訊息,例如「wip」、「fix bug」、「updates」。手動強制執行「傳統式提交」很麻煩,而且經常會忘記。我們來實作一項 Skill,強制執行 Conventional Commits 規格。只要指示代理程式遵守規則,就能讓它擔任執行者。
git-commit-formatter/
└── SKILL.md (Instructions only)
SKILL.md 檔案如下所示:
---
name: git-commit-formatter
description: Formats git commit messages according to Conventional Commits specification. Use this when the user asks to commit changes or write a commit message.
---
Git Commit Formatter Skill
When writing a git commit message, you MUST follow the Conventional Commits specification.
Format
`<type>[optional scope]: <description>`
Allowed Types
- **feat**: A new feature
- **fix**: A bug fix
- **docs**: Documentation only changes
- **style**: Changes that do not affect the meaning of the code (white-space, formatting, etc)
- **refactor**: A code change that neither fixes a bug nor adds a feature
- **perf**: A code change that improves performance
- **test**: Adding missing tests or correcting existing tests
- **chore**: Changes to the build process or auxiliary tools and libraries such as documentation generation
Instructions
1. Analyze the changes to determine the primary `type`.
2. Identify the `scope` if applicable (e.g., specific component or file).
3. Write a concise `description` in an imperative mood (e.g., "add feature" not "added feature").
4. If there are breaking changes, add a footer starting with `BREAKING CHANGE:`.
Example
`feat(auth): implement login with google`
如何執行這個範例:
- 對工作區中的任何檔案進行小幅變更。
- 開啟對話並輸入:Commit these changes.
- 代理程式不會只執行 git commit,這項技能會先啟用 git-commit-formatter 技能。
- 結果:系統會建議採用傳統的 Git 提交訊息。
舉例來說,我讓 Antigravity 在 Python 範例檔案中新增一些註解,結果產生了類似 docs: add detailed comments to demo_primes.py.
第 2 級:資產使用率 (license-header-adder)
這是「參考」模式。
公司專案中的每個來源檔案可能都需要特定的 20 行 Apache 2.0 授權標頭。直接將這段靜態文字放入提示 (或 SKILL.md) 中,會浪費資源。每次為技能建立索引時,都會消耗權杖,且模型可能會在法律文件中「產生」錯字。
將靜態文字卸載至 resources/ 資料夾中的純文字檔。這項技能會指示代理程式僅在必要時讀取這個檔案。
license-header-adder/
├── SKILL.md
└── resources/
└── HEADER_TEMPLATE.txt (The heavy text)
SKILL.md 檔案如下所示:
---
name: license-header-adder
description: Adds the standard open-source license header to new source files. Use involves creating new code files that require copyright attribution.
---
# License Header Adder Skill
This skill ensures that all new source files have the correct copyright header.
## Instructions
1. **Read the Template**:
First, read the content of the header template file located at `resources/HEADER_TEMPLATE.txt`.
2. **Prepend to File**:
When creating a new file (e.g., `.py`, `.java`, `.js`, `.ts`, `.go`), prepend the `target_file` content with the template content.
3. **Modify Comment Syntax**:
- For C-style languages (Java, JS, TS, C++), keep the `/* ... */` block as is.
- For Python, Shell, or YAML, convert the block to use `#` comments.
- For HTML/XML, use `<!-- ... -->`.
如何執行這個範例:
- 建立新的虛擬 Python 檔案:
touch my_script.py - 類型:
Add the license header to my_script.py。 - 服務專員會朗讀
license-header-adder/resources/HEADER_TEMPLATE.txt。 - 系統會將內容逐字貼到檔案中。
第 3 級:透過範例學習 (json-to-pydantic)
「少量樣本」模式。
將鬆散資料 (例如 JSON API 回應) 轉換為嚴格程式碼 (例如 Pydantic 模型) 時,需要做出數十項決策。我們應該如何命名類別?我們應該使用 Optional 嗎?snake_case 或 camelCase?以英文撰寫這 50 條規則既繁瑣又容易出錯。
LLM 是模式比對引擎。
向他們展示黃金範例 (Input -> Output) 通常比冗長的指示更有效。
json-to-pydantic/
├── SKILL.md
└── examples/
├── input_data.json (The Before State)
└── output_model.py (The After State)
SKILL.md 檔案如下所示:
---
name: json-to-pydantic
description: Converts JSON data snippets into Python Pydantic data models.
---
# JSON to Pydantic Skill
This skill helps convert raw JSON data or API responses into structured, strongly-typed Python classes using Pydantic.
Instructions
1. **Analyze the Input**: Look at the JSON object provided by the user.
2. **Infer Types**:
- `string` -> `str`
- `number` -> `int` or `float`
- `boolean` -> `bool`
- `array` -> `List[Type]`
- `null` -> `Optional[Type]`
- Nested Objects -> Create a separate sub-class.
3. **Follow the Example**:
Review `examples/` to see how to structure the output code. notice how nested dictionaries like `preferences` are extracted into their own class.
- Input: `examples/input_data.json`
- Output: `examples/output_model.py`
Style Guidelines
- Use `PascalCase` for class names.
- Use type hints (`List`, `Optional`) from `typing` module.
- If a field can be missing or null, default it to `None`.
/examples 資料夾中會有 JSON 檔案和輸出檔案 (即 Python 檔案)。兩者如下所示:
input_data.json
{
"user_id": 12345,
"username": "jdoe_88",
"is_active": true,
"preferences": {
"theme": "dark",
"notifications": [
"email",
"push"
]
},
"last_login": "2024-03-15T10:30:00Z",
"meta_tags": null
}
output_model.py
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List, Optional
class Preferences(BaseModel):
theme: str
notifications: List[str]
class User(BaseModel):
user_id: int
username: str
is_active: bool
preferences: Preferences
last_login: Optional[str] = None
meta_tags: Optional[List[str]] = None
如何執行這個範例:
- 將 JSON 程式碼片段提供給服務專員 (貼到即時通訊中或指向檔案)。
{ "product": "Widget", "cost": 10.99, "stock": null }
- 類型:
Convert this JSON to a Pydantic model。 - 代理程式會查看技能資料夾中的
examples配對。 - 這個外掛程式會生成 Python 類別,完美模仿
output_model.py的程式碼樣式、匯入項目和結構,包括將空值庫存處理為 Optional。
輸出範例 (product_model.py) 如下所示:
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import Optional
class Product(BaseModel):
product: str
cost: float
stock: Optional[int] = None
第 4 級:程序邏輯 (database-schema-validator)
這是「工具使用」模式。
如果您詢問 LLM「這個結構定義是否安全?」,即使缺少重要的主鍵,LLM 也可能會說一切正常,因為 SQL 看起來正確無誤。
我們將這項檢查委派給確定性指令碼。我們會使用技能將專員導向我們編寫的 Python 指令碼。指令碼會提供二元 (True/False) 真實值。
database-schema-validator/
├── SKILL.md
└── scripts/
└── validate_schema.py (The Validator)
SKILL.md 檔案如下所示:
---
name: database-schema-validator
description: Validates SQL schema files for compliance with internal safety and naming policies.
---
# Database Schema Validator Skill
This skill ensures that all SQL files provided by the user comply with our strict database standards.
Policies Enforced
1. **Safety**: No `DROP TABLE` statements.
2. **Naming**: All tables must use `snake_case`.
3. **Structure**: Every table must have an `id` column as PRIMARY KEY.
Instructions
1. **Do not read the file manually** to check for errors. The rules are complex and easily missed by eye.
2. **Run the Validation Script**:
Use the `run_command` tool to execute the python script provided in the `scripts/` folder against the user's file.
`python scripts/validate_schema.py <path_to_user_file>`
3. **Interpret Output**:
- If the script returns **exit code 0**: Tell the user the schema looks good.
- If the script returns **exit code 1**: Report the specific error messages printed by the script to the user and suggest fixes.
validate_schema.py 檔案如下所示:
import sys
import re
def validate_schema(filename):
"""
Validates a SQL schema file against internal policy:
1. Table names must be snake_case.
2. Every table must have a primary key named 'id'.
3. No 'DROP TABLE' statements allowed (safety).
"""
try:
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
content = f.read()
lines = content.split('\n')
errors = []
# Check 1: No DROP TABLE
if re.search(r'DROP TABLE', content, re.IGNORECASE):
errors.append("ERROR: 'DROP TABLE' statements are forbidden.")
# Check 2 & 3: CREATE TABLE checks
table_defs = re.finditer(r'CREATE TABLE\s+(?P<name>\w+)\s*\((?P<body>.*?)\);', content, re.DOTALL | re.IGNORECASE)
for match in table_defs:
table_name = match.group('name')
body = match.group('body')
# Snake case check
if not re.match(r'^[a-z][a-z0-9_]*$', table_name):
errors.append(f"ERROR: Table '{table_name}' must be snake_case.")
# Primary key check
if not re.search(r'\bid\b.*PRIMARY KEY', body, re.IGNORECASE):
errors.append(f"ERROR: Table '{table_name}' is missing a primary key named 'id'.")
if errors:
for err in errors:
print(err)
sys.exit(1)
else:
print("Schema validation passed.")
sys.exit(0)
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Error: File '{filename}' not found.")
sys.exit(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage: python validate_schema.py <schema_file>")
sys.exit(1)
validate_schema(sys.argv[1])
如何執行這個範例:
- 建立錯誤的 SQL 檔案
bad_schema.sql:CREATE TABLE users (name TEXT); - 類型:
Validate bad_schema.sql。 - 代理程式不會猜測。這會叫用指令碼,但指令碼會失敗 (結束代碼 1),並向我們回報「驗證失敗,因為資料表『users』缺少主鍵」。
第 5 級:架構師 (adk-tool-scaffold)
這個模式涵蓋 Skills 提供的大部分功能。
複雜的工作通常需要一連串的作業,結合我們所見的一切:建立檔案、遵循範本和編寫邏輯。為 ADK (Agent Development Kit) 建立新工具時,需要上述所有項目。
我們會合併:
- 指令碼 (用於處理檔案建立/架構)
- 範本 (處理資源中的樣板)
- 範例 (引導邏輯生成)。
adk-tool-scaffold/
├── SKILL.md
├── resources/
│ └── ToolTemplate.py.hbs (Jinja2 Template)
├── scripts/
│ └── scaffold_tool.py (Generator Script)
└── examples/
└── WeatherTool.py (Reference Implementation)
SKILL.md 檔案如下所示。您可以參閱 技能存放區,查看指令碼、資源和範例資料夾中的檔案。如要使用這項技能,請前往 adk-tool-scaffold 技能。
---
name: adk-tool-scaffold
description: Scaffolds a new custom Tool class for the Agent Development Kit (ADK).
---
# ADK Tool Scaffold Skill
This skill automates the creation of standard `BaseTool` implementations for the Agent Development Kit.
Instructions
1. **Identify the Tool Name**:
Extract the name of the tool the user wants to build (e.g., "StockPrice", "EmailSender").
2. **Review the Example**:
Check `examples/WeatherTool.py` to understand the expected structure of an ADK tool (imports, inheritance, schema).
3. **Run the Scaffolder**:
Execute the python script to generate the initial file.
`python scripts/scaffold_tool.py <ToolName>`
4. **Refine**:
After generation, you must edit the file to:
- Update the `execute` method with real logic.
- Define the JSON schema in `get_schema`.
Example Usage
User: "Create a tool to search Wikipedia."
Agent:
1. Runs `python scripts/scaffold_tool.py WikipediaSearch`
2. Editing `WikipediaSearchTool.py` to add the `requests` logic and `query` argument schema.
如何執行這個範例:
- 類型:
Create a new ADK tool called StockPrice to fetch data from an API。 - 步驟 1 (支架):代理程式會執行 Python 指令碼。這會立即建立
StockPriceTool.py,其中包含正確的類別結構、匯入項目和類別名稱StockPriceTool。 - 步驟 2 (實作):代理程式「讀取」剛建立的檔案。看到
# TODO: Implement logic. - 步驟 3 (指引):不確定如何定義工具引數的 JSON 結構定義。小幫手會檢查
examples/WeatherTool.py。 - 完成:編輯檔案以新增
requests.get(...),並在結構定義中定義股票代號引數,完全符合 ADK 樣式。
6. 恭喜
您已順利完成 Antigravity Skills 實驗室,並建構下列 Skills:
- Git 修訂版本格式轉換程式。
- 授權標頭新增器。
- JSON 轉成 Pydantic。
- 資料庫結構定義驗證工具。
- ADK 工具架構。
代理程式技能絕對是讓 Antigravity 按照您的方式編寫程式碼、遵守規則及使用工具的絕佳方式。
參考文件
- 程式碼研究室:開始使用 Google Antigravity
- 官方網站:https://antigravity.google/
- 說明文件:https://antigravity.google/docs
- 下載:https://antigravity.google/download
- Antigravity Skills 說明文件:https://antigravity.google/docs/skills
