1. 概览
在当今这个数据丰富的世界中,从非结构化内容(尤其是视频)中提取有意义的洞见是一项非常重要的需求。试想一下,您需要分析数百或数千个视频网址,总结其内容,提取关键技术,甚至为教育材料生成问答对。逐个执行此操作不仅耗时,而且效率低下。这正是现代云架构的优势所在。
在本实验中,我们将逐步介绍如何使用 Google Cloud 的强大服务套件(包括 Cloud Run、BigQuery 和 Google 的生成式 AI [Gemini])来处理视频内容,从而实现可扩缩的无服务器解决方案。我们将详细介绍我们从处理单个网址到在大型数据集中编排并行执行的历程,所有这些操作均无需管理复杂的消息队列和集成。
面临的挑战
我们的任务是处理大量视频内容,重点是实践实验室会话。目标是分析每个视频并生成结构化摘要,包括章节标题、简介背景信息、分步说明、所用技术和相关问答对。我们需要高效存储此输出,以便日后用于制作教育材料。
最初,我们有一个简单的基于 HTTP 的 Cloud Run 服务,每次只能处理一个网址。这种方法非常适合测试和临时分析。不过,当需要处理数千个来自 BigQuery 的网址时,这种单请求单响应模式的局限性就显现出来了。如果采用顺序处理,则需要数天甚至数周的时间。
机会是将手动或缓慢的顺序流程转变为自动化的并行工作流。通过利用云,我们旨在:
- 并行处理数据:大幅缩短大型数据集的处理时间。
- 利用现有的 AI 功能:利用 Gemini 的强大功能进行复杂的内容分析。
- 维护无服务器架构:避免管理服务器或复杂的基础设施。
- 集中数据:将 BigQuery 用作输入网址的单一可信来源,以及处理后结果的可靠目标位置。
- 构建稳健的流水线:创建一个可应对故障且易于管理和监控的系统。
目标
使用 Cloud Run 作业编排并行 AI 处理:
我们的解决方案以充当编排器的 Cloud Run 作业为中心。它会智能地从 BigQuery 读取批量的网址,将这些网址调度到我们现有的已部署 Cloud Run 服务(该服务负责处理单个网址的 AI 处理),然后汇总结果并将其写回 BigQuery。这种方法可让我们:
- 将编排与处理分离:作业管理工作流,而单独的服务专注于 AI 任务。
- 利用 Cloud Run 作业的并行性:作业可以扩缩多个容器实例,以并发方式调用 AI 服务。
- 降低复杂性:我们通过让作业直接管理并发 HTTP 调用来实现并行性,从而简化架构。
使用场景
Code Vipassana 会议视频中的 AI 赋能的分析洞见
我们的具体用例是分析 Code Vipassana 实践实验室的 Google Cloud 会议视频。目标是自动生成结构化文档(图书章节大纲),包括:
- 章节标题:每个视频片段的简明标题
- 简介背景信息:说明视频在更广泛的学习路线中的相关性
- 构建内容:会话的核心任务或目标
- 使用的技术:提及的云服务和其他技术列表
- 分步说明:任务的执行方式,包括代码段
- 源代码/演示网址:视频中提供的链接
- 问答环节:生成相关问题和答案,用于知识检查。
流程
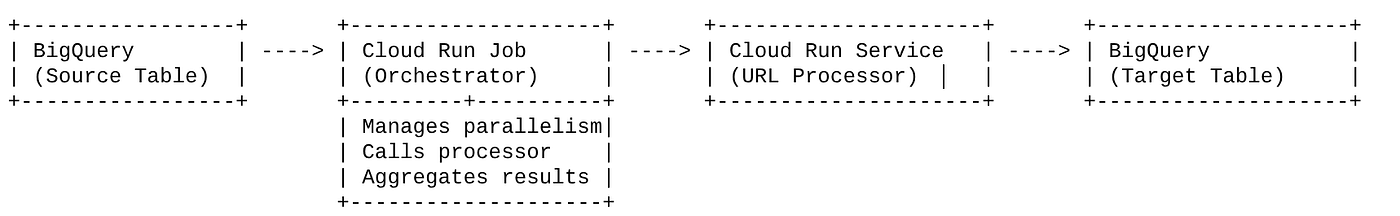
架构流程
Cloud Run 是什么?什么是 Cloud Run 作业?
Cloud Run
全托管式无服务器平台,支持运行无状态容器。它非常适合可根据传入请求自动扩缩的 Web 服务、API 和微服务。您提供容器映像,Cloud Run 会处理其余事宜,包括部署、扩缩和管理基础架构。它擅长处理同步的请求-响应工作负载。
Cloud Run 作业
对 Cloud Run 服务进行补充的产品。Cloud Run 作业专为需要完成然后停止的批处理任务而设计。它们非常适合数据处理、ETL、机器学习批处理推理以及任何涉及处理数据集而非处理实时请求的任务。其主要特点是能够横向扩缩并发运行的容器实例(任务)数量,以处理一批工作,并且可以通过各种事件源触发,也可以手动触发。
主要区别
Cloud Run 服务适用于长时间运行的请求驱动型应用。Cloud Run 作业适用于运行直至完成的有限的、以任务为导向的批处理。
构建内容
Retail Search 应用
在此过程中,您将:
- 创建 BigQuery 数据集、表并提取数据(代码 Vipassana 元数据)
- 创建 Python Cloud Run Functions 函数以实现生成式 AI 功能(将视频转换为图书章节 JSON)
- 为数据到 AI 流水线创建 Python 应用 - 从 BigQuery 读取数据,调用 Cloud Run 函数端点以获取数据洞见,并将上下文写回 BigQuery
- 构建应用并将其容器化
- 使用此容器配置 Cloud Run 作业
- 执行并监控作业
- 报告结果
要求
2. 准备工作
创建项目
- 在 Google Cloud Console 的项目选择器页面上,选择或创建一个 Google Cloud 项目。
- 确保您的 Cloud 项目已启用结算功能。了解如何检查项目是否已启用结算功能。
Google Cloud 赠金:如果您想获得 Google Cloud 赠金来帮助您入门,请使用此链接 兑换赠金。您可以按照 此处的说明兑换。
- 您将使用 Cloud Shell,它是在 Google Cloud 中运行的命令行环境。点击 Google Cloud 控制台顶部的“激活 Cloud Shell”。

- 连接到 Cloud Shell 后,您可以使用以下命令检查自己是否已通过身份验证,以及项目是否已设置为您的项目 ID:
gcloud auth list
- 在 Cloud Shell 中运行以下命令,以确认 gcloud 命令了解您的项目。
gcloud config list project
- 如果项目未设置,请使用以下命令进行设置:
gcloud config set project <YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
- 启用必需的 API:点击此链接并启用相应的 API。
或者,您也可以使用 gcloud 命令来完成此操作。如需了解 gcloud 命令和用法,请参阅文档。
3. 数据库/数据仓库设置
BigQuery 是我们数据流水线的主干。它具有无服务器、扩缩能力极强的特性,非常适合存储输入数据和存放处理后的结果。
- 数据存储:BigQuery 充当我们的数据仓库。它会存储视频网址列表、视频状态(例如,PENDING、PROCESSING、COMPLETED),以及最终生成的上下文。它是唯一可信的来源,用于确定哪些视频需要处理。
- 目的地:AI 生成的数据洞见会保留在此处,以便下游应用或人工审核人员轻松查询。我们的数据集包含视频会话详细信息,尤其是“Code Vipassana Seasons”内容,其中通常包含详细的技术演示。
- 源表:包含以下记录的 BigQuery 表(例如 post_session_labs):
- id:每个会话/行的唯一标识符。
- url:视频的网址(例如,YouTube 链接或可访问的云端硬盘链接)。
- status:一个字符串,用于指示处理状态(例如,PENDING、PROCESSING、COMPLETED、FAILED_PROCESSING)。
- context:用于存储 AI 生成的摘要的字符串字段。
- 数据提取:在此方案中,数据是通过 INSERT 脚本提取到 BigQuery 中的。对于我们的流水线,BigQuery 是起点。
前往 BigQuery 控制台,打开一个新标签页,然后执行以下 SQL 语句:
--1. Create your dataset for the project
CREATE SCHEMA `<<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>>.cv_metadata`
OPTIONS(
location = 'us-central1', -- Specify the location (e.g., 'US', 'EU', 'asia-east1')
description = 'Code Vipassana Sessions Metadata' -- Optional: Add a description
);
--2. Create table
create table cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id STRING, descr STRING, url STRING, context STRING, status STRING);
4. 数据注入
现在,我们来添加一个包含商店数据的表格。在 BigQuery Studio 中前往某个标签页,然后执行以下 SQL 语句以插入示例记录:
--Insert sample data
insert into cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id,descr,url) values('10-1','Gen AI to Agents, where do I begin? Get started with building a single agent application on ADK Python SDK','https://youtu.be/tyqnQQXpxtI');
insert into cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id,descr,url) values('10-2','Build an E2E multi-agent kitchen renovation app on ADK in Python with AlloyDB data and multiple tools','https://youtu.be/RdrMo2lNh0o');
insert into cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id,descr,url) values('10-3','Augment your multiagent app with tools from MCP Toolbox for AlloyDB','https://youtu.be/9VVNh77Q3ZU?si=oQ4fhAX59Y3D5iWa');
insert into cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id,descr,url) values('10-4','Build an agentic MCP client application using MCP Toolbox for BigQuery','https://youtu.be/HmluMag5s20');
insert into cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id,descr,url) values('10-5','Build a travel agent using ADK & MCP Toolbox for Cloud SQL','https://youtu.be/IWg5CH6ZNs0');
insert into cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id,descr,url) values('10-6','Build an E2E Patent Analysis Agent using ADK and Advanced Vector Search with AlloyDB','https://youtu.be/yCXJ3sk3Lxc');
insert into cv_metadata.post_session_labs(id,descr,url) values('10-7','Getting Started with MCP, ADK and A2A','https://youtu.be/JcQ_DyWc0X0');
update cv_metadata.post_session_labs set status = ‘PENDING' where id is not null;
5. 创建视频数据分析函数
我们必须创建并部署 Cloud Run 函数,以实现从视频网址创建结构化图书章节的核心功能。为了能够将此功能作为独立的端点工具箱工具进行访问,我们刚刚创建并部署了一个 Cloud Run 函数。或者,您也可以选择将此作为 Cloud Run 作业的实际 Python 应用中的一个单独函数来包含:
- 在 Google Cloud 控制台中,前往 Cloud Run 页面
- 点击“编写函数”。
- 在“服务名称”字段中,输入一个名称以描述您的函数。服务名称只能以字母开头,最多可以包含 49 个字符(包括字母、数字或连字符)。服务名称不能以连字符结尾,并且在每个区域和项目中必须唯一。服务名称一旦指定便无法更改,并且公开显示。( generate-video-insights**)**
- 在“区域”列表中,使用默认值,或选择要在其中部署函数的区域。(选择 us-central1)
- 在“运行时”列表中,使用默认值,或选择一个运行时版本。(选择 Python 3.11)
- 在“身份验证”部分中,选择“允许公开访问”
- 点击“创建”按钮
- 系统会创建该函数,并加载模板 main.py 和 requirements.txt
- 将这些文件替换为此项目代码库中的文件:main.py 和 requirements.txt
重要提示:在 main.py 中,请务必将 <<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>> 替换为您的项目 ID。
- 部署并保存端点,以便您可以在 Cloud Run 作业的来源中使用该端点。
您的端点应如下所示(或类似):https://generate-video-insights-<<YOUR_POJECT_NUMBER>>.us-central1.run.app
此 Cloud Run 函数包含哪些内容?
用于视频处理的 Gemini 2.5 Flash
对于理解和总结视频内容这一核心任务,我们利用了 Google 的 Gemini 2.5 Flash 模型。Gemini 模型是强大的多模态 AI 模型,能够理解和处理各种类型的输入,包括文本,以及通过特定集成处理视频。
在我们的设置中,我们没有直接将视频文件提供给 Gemini。相反,我们发送了一个包含视频网址的文本提示,并指示 Gemini 如何分析该网址处视频的(假设)内容。虽然 Gemini 2.5 Flash 能够处理多模态输入,但此特定流水线使用基于文本的提示来描述视频的性质(实践实验会话),并请求结构化的 JSON 输出。这利用了 Gemini 的高级推理和自然语言理解能力,可根据提示的上下文推断和合成信息。
Gemini 提示:引导 AI
精心设计的提示对于 AI 模型至关重要。我们的提示旨在提取非常具体的信息,并将其结构化为 JSON 格式,以便我们的应用轻松解析。
PROMPT_TEMPLATE = """
In the video at the following URL: {youtube_url}, which is a hands-on lab session:
Ignore the credits set-up part particularly the coupon code and credits link aspect should not be included in your analysis or the extaction of context. Also exclude any credentials that are explicit in the video.
Take only the first 30-40 minutes of the video without throwing any error.
Analyze the rest of the content of the video.
Extract and synthesize information to create a book chapter section with the following structure, formatted as a JSON string:
1. **chapter_title:** A concise and engaging title for the chapter.
2. **introduction_context:** Briefly explain the relevance of this video segment within a broader learning context.
3. **what_will_build:** Clearly state the specific task or goal accomplished in this video segment.
4. **technologies_and_services:** List all mentioned Google Cloud services and any other relevant technologies (e.g., programming languages, tools, frameworks).
5. **how_we_did_it:** Provide a clear, numbered step-by-step guide of the actions performed. Include any exact commands or code snippets as they appear in the video. Format code/commands using markdown backticks (e.g., `my-command`).
6. **source_code_url:** Provide a URL to the source code repository if mentioned or implied. If not available, use "N/A".
7. **demo_url:** Provide a URL to a demo if mentioned or implied. If not available, use "N/A".
8. **qa_segment:** Generate 10–15 relevant questions based on the content of this segment, along with concise answers. Ensure the questions are thought-provoking and test understanding of the material.
REMEMBER: Ignore the credits set-up part particularly the coupon code and credits link aspect should not be included in your analysis or the extaction of context. Also exclude any credentials that are explicit in the video.
Format the entire output as a JSON string. Ensure all keys and string values are enclosed in double quotes.
Example structure:
...
"""
此提示非常具体,可引导 Gemini 扮演某种教育者的角色。请求 JSON 字符串可确保输出结构化且机器可读。
以下是用于分析视频输入并返回其上下文的代码:
def process_videos_batch(video_url: str, PROMPT_TEMPLATE: str) -> str:
"""
Processes a video URL, generates chapter content using Gemini
"""
formatted_prompt = PROMPT_TEMPLATE.format(youtube_url=video_url)
try:
client = genai.Client(vertexai=True,project='<<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>>',location='us-central1',http_options=HttpOptions(api_version="v1"))
response = client.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
contents=formatted_prompt,
)
print(response.text)
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred during content generation: {e}")
return f"Error processing video: {e}"
print(response.text)
return response.text
上述代码段展示了相应使用场景的核心功能。它会接收视频网址,并通过 Vertex AI 客户端利用 Gemini 模型分析视频内容,并根据提示提取相关数据洞见。然后,系统会返回提取的上下文以供进一步处理。这表示一个同步操作,其中 Cloud Run 作业会等待服务完成。
6. 流水线应用开发 (Python)
我们的中央流水线逻辑位于应用的源代码中,该源代码将容器化为 Cloud Run 作业,从而编排整个并行执行过程。以下是关键部分:
编排器在管理工作流和确保数据完整性方面的作用:
# ... (imports and configuration) ...
def process_batch_from_bq(request_or_trigger_data=None):
# ... (initial checks for config) ...
BATCH_SIZE = 5 # Fetch 5 URLs at a time per job instance
query = f"""
SELECT url, id
FROM `{BIGQUERY_PROJECT}.{BIGQUERY_DATASET}.{BIGQUERY_TABLE_SOURCE}`
WHERE status = 'PENDING'
LIMIT {BATCH_SIZE}
"""
try:
logging.info(f"Fetching up to {BATCH_SIZE} pending URLs from BigQuery...")
rows = bq_client.query(query).result() # job_should_wait=True is default for result()
pending_urls_data = []
for row in rows:
pending_urls_data.append({"url": row.url, "id": row.id})
if not pending_urls_data:
logging.info("No pending URLs found. Job finished.")
return "No pending URLs found. Job finished.", 200
row_ids_to_process = [item["id"] for item in pending_urls_data]
# --- Mark as PROCESSING to prevent duplicate work ---
update_status_query = f"""
UPDATE `{BIGQUERY_PROJECT}.{BIGQUERY_DATASET}.{BIGQUERY_TABLE_SOURCE}`
SET status = 'PROCESSING'
WHERE id IN UNNEST(@row_ids_to_process)
"""
status_update_job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig(
query_parameters=[
bigquery.ArrayQueryParameter("row_ids_to_process", "STRING", values=row_ids_to_process)
]
)
update_status_job = bq_client.query(update_status_query, job_config=status_update_job_config)
update_status_job.result()
logging.info(f"Marked {len(row_ids_to_process)} URLs as 'PROCESSING'.")
# ... (rest of the code for parallel processing and writing) ...
except Exception as e:
# ... (error handling) ...
上述代码段首先从 BigQuery 源表中提取一批状态为“PENDING”的视频网址。然后,它会将这些网址的状态更新为 BigQuery 中的“PROCESSING”,以防止重复处理。
使用 ThreadPoolExecutor 并调用处理器服务进行并行处理:
# ... (inside process_batch_from_bq function) ...
# --- Step 3: Call the external URL Processor Service in parallel ---
processed_results = {}
futures = []
# ThreadPoolExecutor for I/O-bound tasks (HTTP requests to the processor service)
# MAX_CONCURRENT_TASKS_PER_INSTANCE controls parallelism within one job instance.
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=MAX_CONCURRENT_TASKS_PER_INSTANCE) as executor:
for item in pending_urls_data:
url = item["url"]
row_id = item["id"]
# Submit the task: call the processor service for this URL
future = executor.submit(call_url_processor_service, url)
futures.append((row_id, future))
# Collect results as they complete
for row_id, future in futures:
try:
content = future.result(timeout=URL_PROCESSOR_TIMEOUT_SECONDS)
# Check if the processor service returned an error message
if content.startswith("ERROR:"):
processed_results[row_id] = {"context": content, "status": "FAILED_PROCESSING"}
else:
processed_results[row_id] = {"context": content, "status": "COMPLETED"}
except TimeoutError:
logging.warning(f"URL processing timed out (service call for row ID {row_id}). Marking as FAILED.")
processed_results[row_id] = {"context": f"ERROR: Processing timed out for '{row_id}'.", "status": "FAILED_PROCESSING"}
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Exception during future result retrieval for row ID {row_id}: {e}")
processed_results[row_id] = {"context": f"ERROR: Unexpected error during result retrieval for '{row_id}'. Details: {e}", "status": "FAILED_PROCESSING"}
这部分代码利用 ThreadPoolExecutor 实现对所提取视频网址的并行处理。对于每个网址,它都会提交一个任务来异步调用 Cloud Run 服务(网址处理器)。这样,Cloud Run 作业就可以高效地同时处理多个视频,从而提升整个流水线的性能。该代码段还处理了处理器服务可能出现的超时和错误。
从 BigQuery 读取数据以及向 BigQuery 写入数据
与 BigQuery 的核心互动涉及提取待处理的网址,然后使用处理后的结果更新这些网址。
# ... (inside process_batch_from_bq) ...
BATCH_SIZE = 5
query = f"""
SELECT url, id
FROM `{BIGQUERY_PROJECT}.{BIGQUERY_DATASET}.{BIGQUERY_TABLE_SOURCE}`
WHERE status = 'PENDING'
LIMIT {BATCH_SIZE}
"""
rows = bq_client.query(query).result()
pending_urls_data = []
for row in rows:
pending_urls_data.append({"url": row.url, "id": row.id})
# ... (rest of fetching and marking as PROCESSING) ...
将结果写回 BigQuery:
# --- Step 4: Write results back to BigQuery ---
logging.info(f"Writing {len(processed_results)} results back to BigQuery...")
successful_updates = 0
for row_id, data in processed_results.items():
if update_bq_row(row_id, data["context"], data["status"]):
successful_updates += 1
logging.info(f"Finished processing. {successful_updates} out of {len(processed_results)} rows updated successfully.")
# ... (return statement) ...
# --- Helper to update a single row in BigQuery ---
def update_bq_row(row_id, context, status="COMPLETED"):
"""Updates a specific row in the target BigQuery table."""
# ... (checks for config) ...
update_query = f"""
UPDATE `{BIGQUERY_PROJECT}.{BIGQUERY_DATASET}.{BIGQUERY_TABLE_TARGET}`
SET
context = @context,
status = @status
WHERE id = @row_id
"""
# Correctly defining query parameters for the UPDATE statement
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig(
query_parameters=[
bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter("context", "STRING", value=context),
bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter("status", "STRING", value=status),
# Assuming 'id' column is STRING. Adjust if it's INT64.
bigquery.ScalarQueryParameter("row_id", "STRING", value=row_id)
]
)
try:
update_job = bq_client.query(update_query, job_config=job_config)
update_job.result() # Wait for the job to complete
logging.info(f"Successfully updated BigQuery row ID {row_id} with status {status}.")
return True
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Failed to update BigQuery row ID {row_id}: {e}")
return False
上面的代码段重点介绍了 Cloud Run 作业与 BigQuery 之间的数据交互。它从源表中检索一批“PENDING”视频网址及其 ID。处理完网址后,此代码段演示了如何使用 UPDATE 查询将提取的上下文和状态(“COMPLETED”或“FAILED_PROCESSING”)写回目标 BigQuery 表。此代码段可完成数据处理循环。它还包含 update_bq_row 辅助函数,该函数展示了如何定义 update 语句的参数。
应用设置
应用结构为单个 Python 脚本,该脚本将容器化。它利用 Google Cloud 客户端库和 functions-framework 来定义其入口点。
- 依赖项:google-cloud-bigquery、requests
- 配置:所有关键设置(BigQuery 项目/数据集/表、网址处理器服务网址)均从环境变量加载,从而使应用具有可移植性和安全性
- 核心逻辑:process_batch_from_bq 函数负责编排整个工作流程
- 外部服务集成:call_url_processor_service 函数处理与单独的 Cloud Run 服务的通信
- BigQuery 互动:bq_client 用于提取网址和更新结果,并具有适当的参数处理功能
- 并行性:concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor 管理对外部服务的并发调用
- 入口点:名为 main.py 的 Python 代码充当启动批处理的入口点。
现在,我们来设置应用:
- 您可以先前往 Cloud Shell 终端并克隆代码库:
git clone https://github.com/AbiramiSukumaran/video-context-crj
- 前往 Cloud Shell 编辑器,您可以在其中看到新创建的文件夹 video-context-crj
- 删除以下内容,因为这些步骤已在前面的部分中完成:
- 删除 Cloud_Run_Function 文件夹
- 导航到项目文件夹 video-context-crj,您应该会看到以下项目结构:
7. Dockerfile 设置和容器化
为了将此逻辑部署为 Cloud Run 作业,我们需要将其容器化。容器化是将应用代码、依赖项和运行时打包到可移植映像中的过程。
请务必将 Dockerfile 中的占位符(粗体文本)替换为您的值:
# Use an official Python runtime as a parent image
FROM python:3.12-alpine
# Set the working directory in the container
WORKDIR /app
# Copy the requirements file into the container
COPY requirements.txt .
# Install any needed packages specified in requirements.txt
RUN pip install --trusted-host pypi.python.org -r requirements.txt
# Copy the rest of the application code
COPY . .
# Define environment variables for configuration (these will be overridden during deployment)
ENV BIGQUERY_PROJECT="YOUR-project"
ENV BIGQUERY_DATASET="YOUR-dataset"
ENV BIGQUERY_TABLE_SOURCE="YOUR-source-table"
ENV URL_PROCESSOR_SERVICE_URL="ENDPOINT FOR VIDEO PROCESSING"
ENV BIGQUERY_TABLE_TARGET = "YOUR-destination-table"
ENTRYPOINT ["python", "main.py"]
上面的 Dockerfile 代码段定义了基础映像,安装了依赖项,复制了我们的代码,并设置了使用 functions-framework 运行应用的命令,其中包含正确的目标函数 (process_batch_from_bq)。然后,将此映像推送到 Artifact Registry。
容器化
如需将其容器化,请前往 Cloud Shell 终端并执行以下命令(请务必替换 <<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>> 占位符):
export CONTAINER_IMAGE="gcr.io/<<YOUR_PROJECT_ID>>/batch-url-processor-orchestrator:latest"
gcloud builds submit --tag $CONTAINER_IMAGE .
容器映像创建完成后,您应该会看到以下输出:
我们的容器现已创建并保存在 Artifact Registry 中。我们可以继续执行下一步了。
8. Cloud Run 作业创建
部署作业涉及构建容器映像,然后创建 Cloud Run 作业资源。
我们已创建容器映像并将其存储在 Artifact Registry 中。现在,我们来创建作业。
- 前往 Cloud Run 作业控制台,然后点击“部署容器”:

- 选择我们刚刚创建的容器映像:
- 输入其他配置详细信息,如下所示:

- 按如下方式设置任务容量:
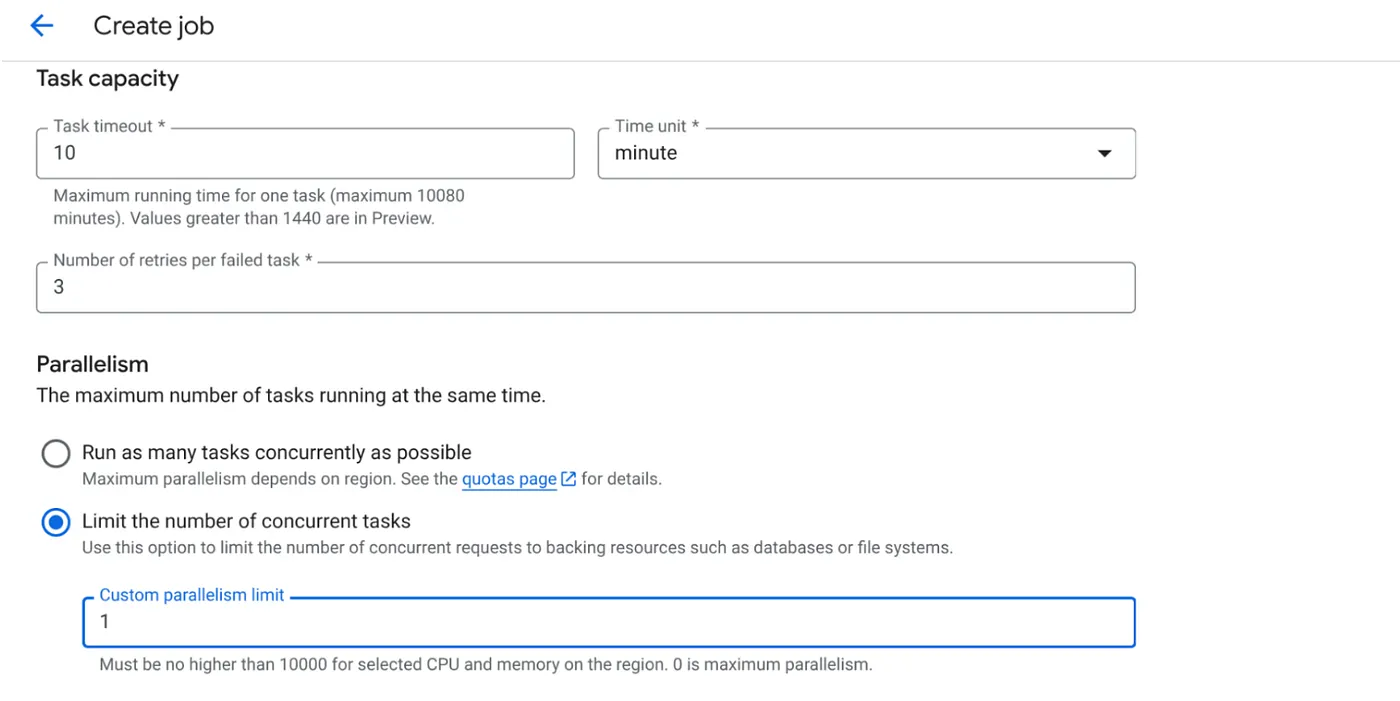
由于我们有数据库写入操作,并且代码中已处理并行化(max_instances 和任务并发性),因此我们将并发任务数设置为 1。不过,您可以根据自己的需求随意增加此值。此处的目的是让任务按照配置运行完成,同时在并行性中设置并发级别。
- 点击“创建”
您的 Cloud Run 作业将成功创建。
运作方式
作业的容器实例开始运行。它会查询 BigQuery 以获取一小批(BATCH_SIZE)标记为 PENDING 的网址。它会立即将这些已提取网址的状态在 BigQuery 中更新为 PROCESSING,以防止其他作业实例提取这些网址。它会创建一个 ThreadPoolExecutor,并为批处理中的每个网址提交一个任务。每个任务都会调用 call_url_processor_service 函数。当 call_url_processor_service 请求完成(或超时/失败)时,系统会收集其结果(AI 生成的上下文或错误消息),并将其映射回原始 row_id。当批处理的所有任务都完成后,作业会遍历收集的结果,并更新 BigQuery 中每个相应行的上下文和状态字段。如果成功,作业实例会正常退出。如果遇到未处理的错误,它会引发异常,从而可能会触发 Cloud Run 作业进行重试(具体取决于作业配置)。
Cloud Run 作业的适用场景:编排
这正是 Cloud Run 作业的真正优势所在。
无服务器批处理:我们获得了一个代管式基础架构,该基础架构可以根据需要启动任意数量的容器实例(最多 MAX_INSTANCES),以并发处理数据。
并行性控制:我们定义了 MAX_INSTANCES(总体上可以并行运行多少个作业)和 TASK_CONCURRENCY(每个作业实例并行执行多少个操作)。这样可以精细地控制吞吐量和资源利用率。
容错能力:如果作业实例在运行中途失败,您可以将 Cloud Run 作业配置为重试整个作业或特定任务,从而确保数据处理不会丢失。
简化架构:通过直接在作业中编排 HTTP 调用并使用 BigQuery 进行状态管理,我们避免了设置和管理 Pub/Sub、其主题、订阅和确认逻辑的复杂性。
MAX_INSTANCES 与 TASK_CONCURRENCY 的对比:
MAX_INSTANCES::整个作业执行过程中可以并发运行的作业实例总数。这是您同时处理多个网址的主要并行化手段。
TASK_CONCURRENCY::单个作业实例将执行的并行操作(对处理器服务的调用)数量。这有助于使一个实例的 CPU/网络达到饱和状态。
9. 执行和监控 Cloud Run 作业
视频元数据
在点击“执行”之前,我们先查看一下数据状态。
前往 BigQuery Studio 并运行以下查询:
Select id, descr, url, status from cv_metadata.post_session_labs where status = ‘PENDING'
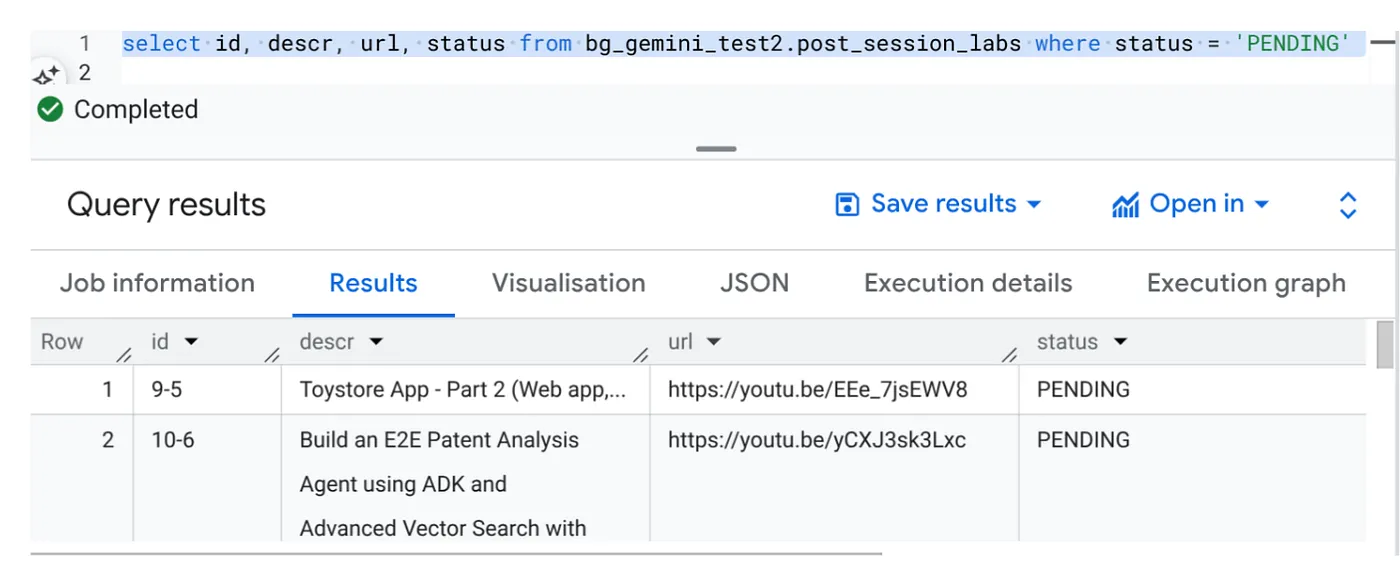
我们有一些包含视频网址且状态为“待处理”的示例记录。我们的目标是以提示中说明的格式,使用视频中的数据洞见填充“context”字段。
作业触发器
接下来,点击 Cloud Run 作业控制台中作业上的“执行”按钮来执行作业,您应该能够在控制台中看到作业的进度和状态:
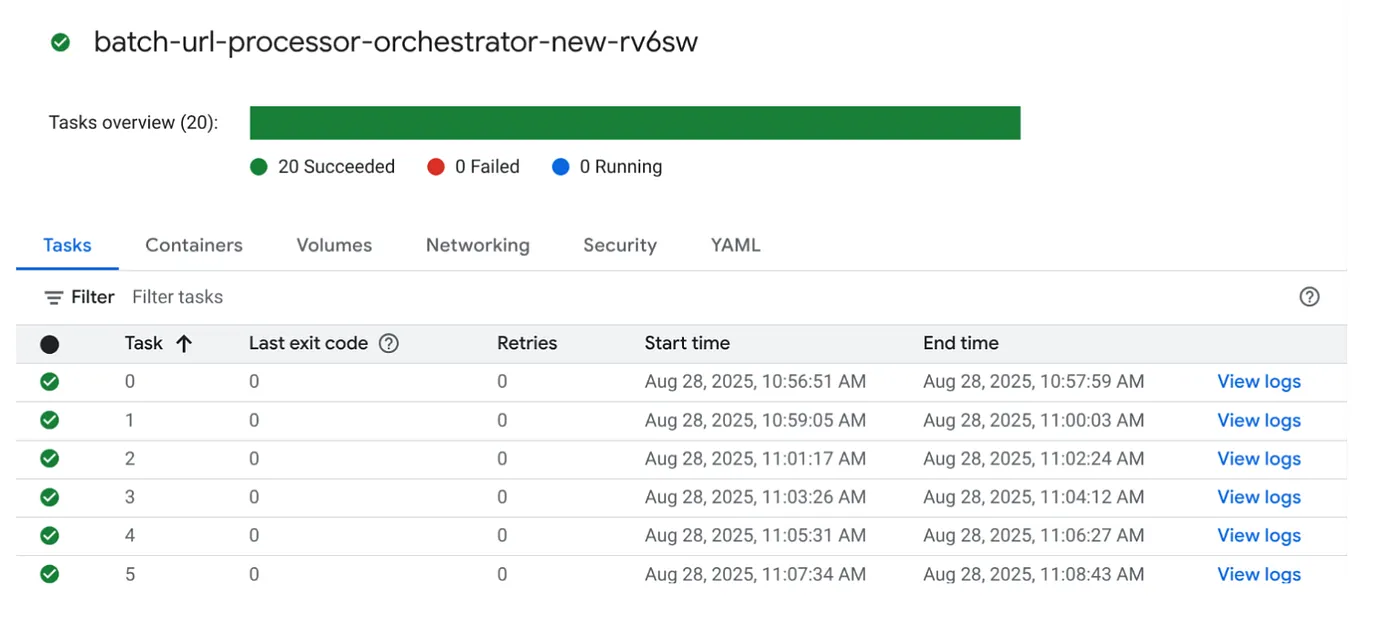
您可以在“可观测性”中的“日志”标记中查看有关作业和任务的监控步骤和其他详细信息。
10. 结果分析
作业完成后,您应该能够在表格中看到每个视频网址的上下文已更新:
输出上下文(针对其中一条记录)
{
"chapter_title": "Building a Travel Agent with ADK and MCP Toolbox",
"introduction_context": "This chapter section is derived from a hands-on lab session focused on building a travel agent. It details the process of integrating various Google Cloud services and tools to create an intelligent agent capable of querying a database and interacting with users.",
"what_will_build": "The goal is to build and deploy a travel agent that can answer user queries about hotels using the Agent Development Kit (ADK) and the MCP Toolbox for Databases, connecting to a PostgreSQL database.",
"technologies_and_services": [
"Google Cloud Platform",
"Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL",
"Agent Development Kit (ADK)",
"MCP Toolbox for Databases",
"Cloud Shell",
"Cloud Run",
"Python",
"Docker"
],
"how_we_did_it": [
"Provision a Cloud SQL instance for PostgreSQL with the 'hoteldb-instance'.",
"Prepare the 'hotels' database by creating a table with relevant schema and populating it with sample data.",
"Set up the MCP Toolbox for Databases by downloading and configuring the necessary components.",
"Install the Agent Development Kit (ADK) and its dependencies.",
"Create a new agent using the ADK, specifying the model (Gemini 2.0-flash) and backend (Vertex AI).",
"Modify the agent's code to connect to the PostgreSQL database via the MCP Toolbox.",
"Run the agent locally to test its functionality and ability to interact with the database.",
"Deploy the agent to Cloud Run for cloud-based access and further testing.",
"Interact with the deployed agent through a web console or command line to query hotel information."
],
"source_code_url": "N/A",
"demo_url": "N/A",
"qa_segment": [
{
"question": "What is the primary purpose of the MCP Toolbox for Databases?",
"answer": "The MCP Toolbox for Databases is an open-source MCP server designed to help users develop tools faster, more securely, and by handling complexities like connection pooling, authentication, and more."
},
{
"question": "Which Google Cloud service is used to create the database for the travel agent?",
"answer": "Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL is used to create the database."
},
{
"question": "What is the role of the Agent Development Kit (ADK)?",
"answer": "The ADK helps build Generative AI tools that allow agents to access data in a database. It enables agents to perform actions, interact with users, utilize external tools, and coordinate with other agents."
},
{
"question": "What command is used to create the initial agent application using ADK?",
"answer": "The command `adk create hotel-agent-app` is used to create the agent application."
},
....
现在,您应该能够验证此 JSON 结构,以实现更高级的代理用例。
为什么采用这种方法?
此架构可提供显著的战略优势:
- 经济实惠:无服务器服务意味着您只需按使用量付费。Cloud Run 作业在不使用时会缩减至零。
- 可伸缩性:通过调整 Cloud Run 作业实例和并发设置,轻松处理数万个网址。
- 敏捷性:只需更新所含的应用及其服务,即可快速开发和部署新的处理逻辑或 AI 模型。
- 降低了运维开销:无需修补或管理服务器;Google 会处理基础架构。
- 普及 AI:无需深厚的 ML Ops 专业知识即可使用高级 AI 处理功能来处理批处理任务。
11. 清理
为避免系统因本博文中使用的资源向您的 Google Cloud 账号收取费用,请按照以下步骤操作:
- 在 Google Cloud 控制台中,前往资源管理器页面。
- 在项目列表中,选择要删除的项目,然后点击删除。
- 在对话框中输入项目 ID,然后点击关停以删除项目。
12. 恭喜
恭喜!通过围绕 Cloud Run 作业设计解决方案,并利用 BigQuery 的数据管理功能和外部 Cloud Run 服务的 AI 处理功能,您构建了一个可扩缩性极强、经济实惠且易于维护的系统。此模式可解耦处理逻辑,在无需复杂基础架构的情况下实现并行执行,并显著缩短获得数据洞见的时间。
我们建议您探索 Cloud Run 作业,以满足自己的批量处理需求。无论是扩缩 AI 分析、运行 ETL 流水线,还是执行定期数据任务,这种无服务器方法都能提供强大而高效的解决方案。如需自行开始,请查看此页面。
如果您有兴趣以无服务器和智能体方式构建和部署所有应用,请报名参加 Code Vipassana,该活动旨在加速开发数据驱动的生成式智能体应用!
