1. 📖 소개
이 Codelab에서는 에이전트 개발 키트 (ADK)에서 멀티모달 도구 상호작용을 설계하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 이는 상담사가 업로드된 파일을 도구의 입력으로 참조하고 도구 응답에서 생성된 파일 콘텐츠도 이해해야 하는 특정 흐름입니다. 따라서 아래 스크린샷과 같은 상호작용이 가능합니다. 이 튜토리얼에서는 사용자가 제품 쇼케이스에 더 나은 사진을 편집할 수 있도록 지원하는 에이전트를 개발합니다.
Codelab을 통해 다음과 같이 단계별 접근 방식을 사용합니다.
- Google Cloud 프로젝트 준비
- 코딩 환경의 작업 디렉터리 설정
- ADK를 사용하여 에이전트 초기화
- Gemini 2.5 Flash Image로 구동되는 사진을 수정하는 데 사용할 수 있는 도구 설계
- 사용자 이미지 업로드를 처리하고, 아티팩트로 저장하고, 에이전트에 컨텍스트로 추가하는 콜백 함수를 설계합니다.
- 도구 응답으로 생성된 이미지를 처리하고, 아티팩트로 저장하고, 에이전트에 컨텍스트로 추가하는 콜백 함수를 설계합니다.
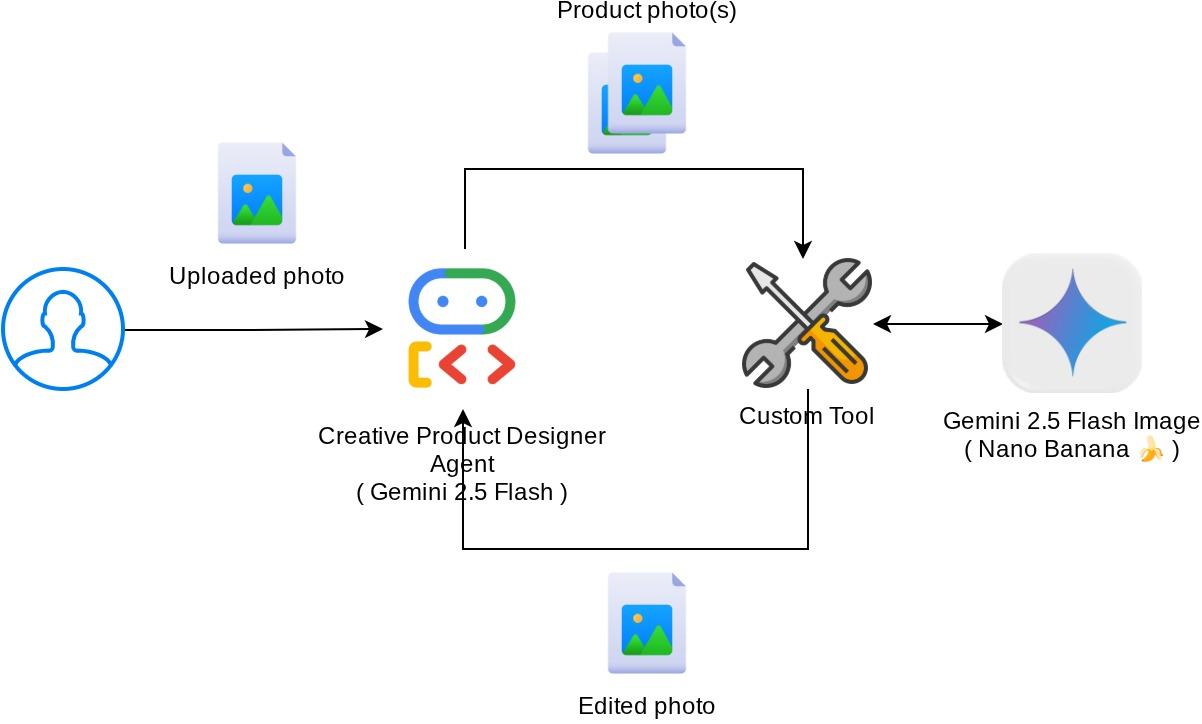
아키텍처 개요
이 Codelab의 전체 상호작용은 다음 다이어그램에 나와 있습니다.
기본 요건
- Python 사용에 능숙함
- (선택사항) 에이전트 개발 키트 (ADK)에 관한 기본 Codelabs
학습할 내용
- 콜백 컨텍스트를 활용하여 아티팩트 서비스에 액세스하는 방법
- 적절한 멀티모달 데이터 전파를 사용하여 도구를 설계하는 방법
- before_model_callback을 통해 아티팩트 컨텍스트를 추가하도록 에이전트 llm 요청을 수정하는 방법
- Gemini 2.5 Flash Image를 사용하여 이미지를 수정하는 방법
필요한 항목
- Chrome 웹브라우저
- Gmail 계정
- 결제 계정이 사용 설정된 Cloud 프로젝트
이 Codelab은 초보자를 포함한 모든 수준의 개발자를 대상으로 하며 샘플 애플리케이션에서 Python을 사용합니다. 하지만 제시된 개념을 이해하는 데 Python 지식이 필요하지는 않습니다.
2. 🚀 워크숍 개발 설정 준비
1단계: Cloud Console에서 활성 프로젝트 선택하기
Google Cloud 콘솔의 프로젝트 선택기 페이지에서 Google Cloud 프로젝트를 선택하거나 만듭니다 (콘솔의 왼쪽 상단 섹션 참고).

클릭하면 다음 예와 같이 모든 프로젝트 목록이 표시됩니다.
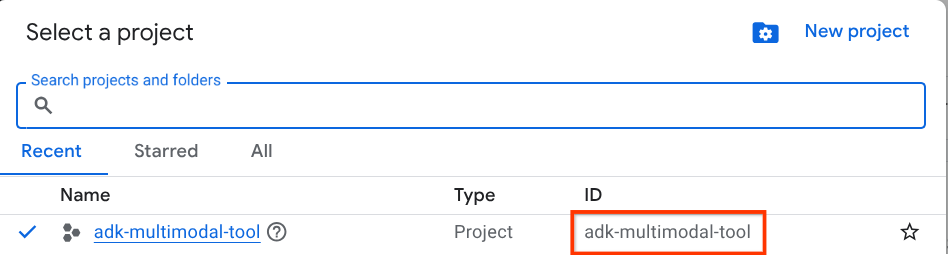
빨간색 상자로 표시된 값이 프로젝트 ID이며 이 값은 튜토리얼 전체에서 사용됩니다.
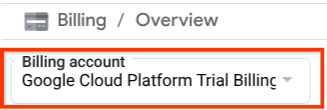
Cloud 프로젝트에 결제가 사용 설정되어 있는지 확인합니다. 이를 확인하려면 왼쪽 상단 표시줄에 있는 햄버거 아이콘 ☰을 클릭하여 탐색 메뉴를 표시하고 결제 메뉴를 찾습니다.

결제 / 개요 제목 ( 클라우드 콘솔의 왼쪽 상단 섹션) 아래에 'Google Cloud Platform 무료 체험판 결제 계정'이 표시되면 이 튜토리얼에서 프로젝트를 사용할 준비가 된 것입니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 이 튜토리얼의 시작 부분으로 돌아가서 체험판 결제 계정을 사용하세요.
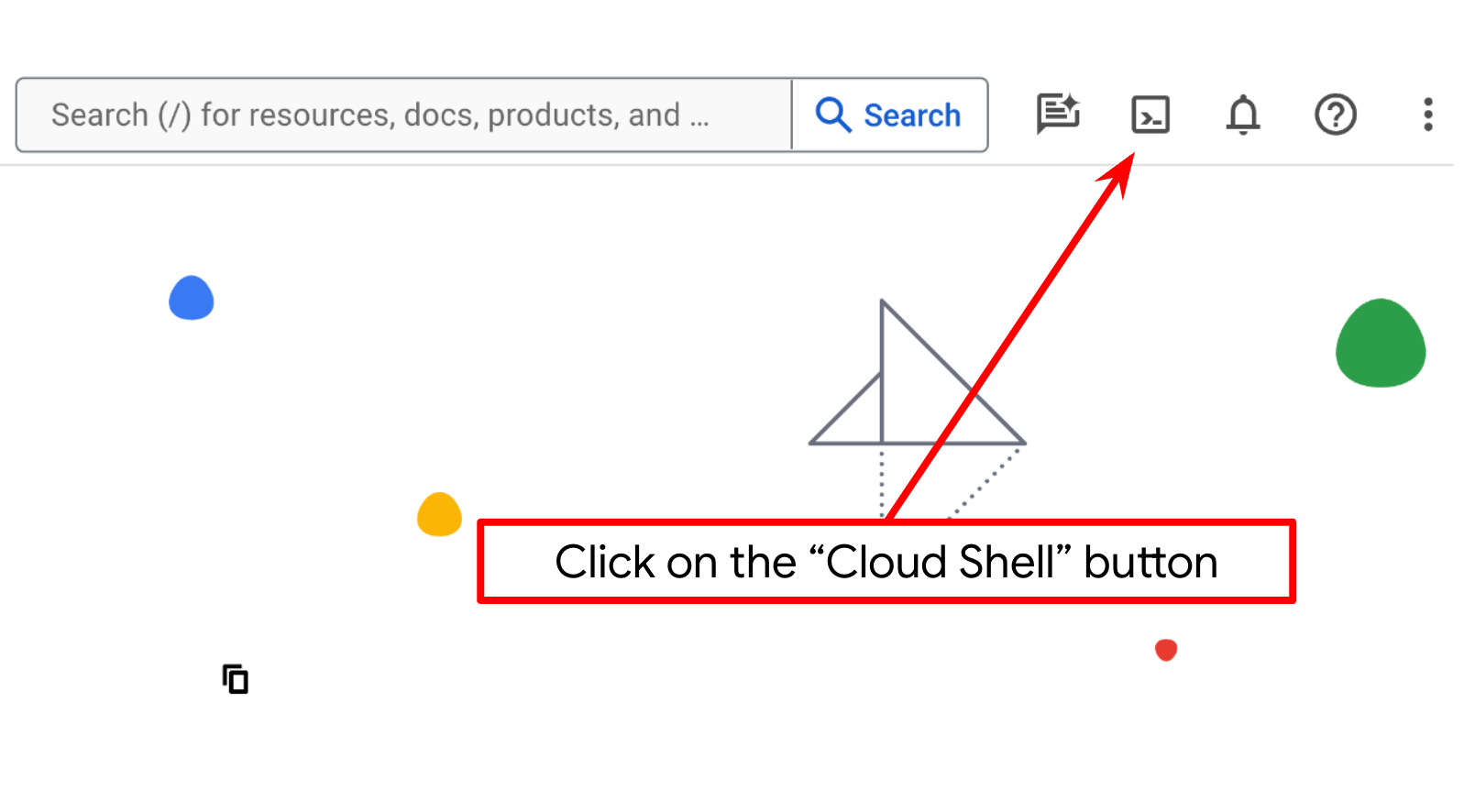
2단계: Cloud Shell 익히기
튜토리얼의 대부분에서 Cloud Shell을 사용합니다. Google Cloud 콘솔 상단에서 Cloud Shell 활성화를 클릭합니다. 승인하라는 메시지가 표시되면 승인을 클릭합니다.
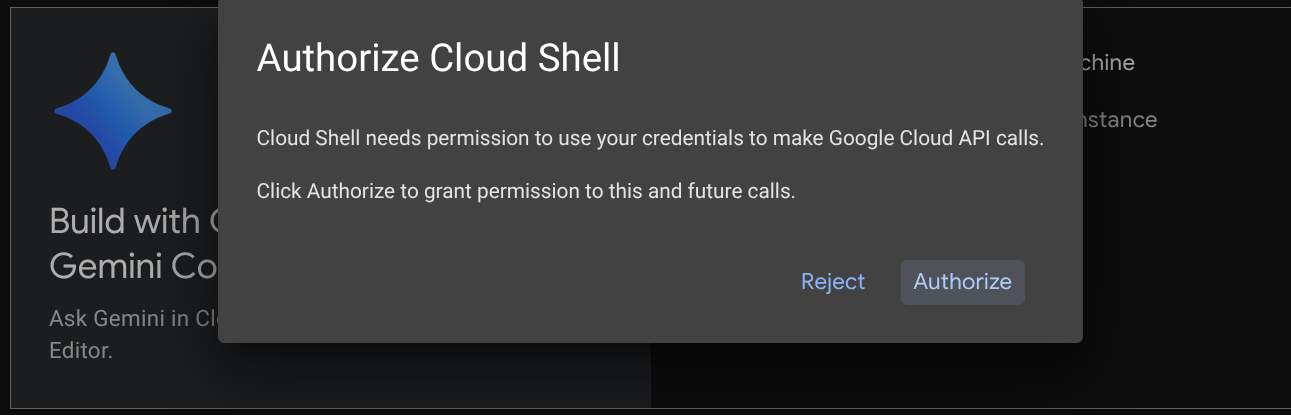
Cloud Shell에 연결되면 셸 ( 또는 터미널)이 계정으로 이미 인증되었는지 확인해야 합니다.
gcloud auth list
아래 예시 출력과 같이 개인 Gmail이 표시되면 모든 것이 정상입니다.
Credentialed Accounts
ACTIVE: *
ACCOUNT: alvinprayuda@gmail.com
To set the active account, run:
$ gcloud config set account `ACCOUNT`
그렇지 않은 경우 브라우저를 새로고침하고 메시지가 표시되면 승인을 클릭하세요 ( 연결 문제로 인해 중단될 수 있음).
다음으로, 셸이 이미 보유한 올바른 프로젝트 ID로 구성되어 있는지 확인해야 합니다. 터미널에서 $아이콘 앞에 괄호 안에 값이 표시되면(아래 스크린샷에서 값은 'adk-multimodal-tool'임) 이 값은 활성 셸 세션에 구성된 프로젝트를 보여줍니다.

표시된 값이 이미 올바른 경우 다음 명령어를 건너뛸 수 있습니다. 하지만 올바르지 않거나 누락된 경우 다음 명령어를 실행합니다.
gcloud config set project <YOUR_PROJECT_ID>
그런 다음 GitHub에서 이 Codelab의 템플릿 작업 디렉터리를 클론하고 다음 명령어를 실행합니다. adk-multimodal-tool 디렉터리에 작업 디렉터리가 생성됩니다.
git clone https://github.com/alphinside/adk-mcp-multimodal.git adk-multimodal-tool
3단계: Cloud Shell 편집기 숙지 및 애플리케이션 작업 디렉터리 설정
이제 코드 편집기를 설정하여 코딩 작업을 할 수 있습니다. 이를 위해 Cloud Shell 편집기를 사용합니다.
편집기 열기 버튼을 클릭하면 Cloud Shell 편집기 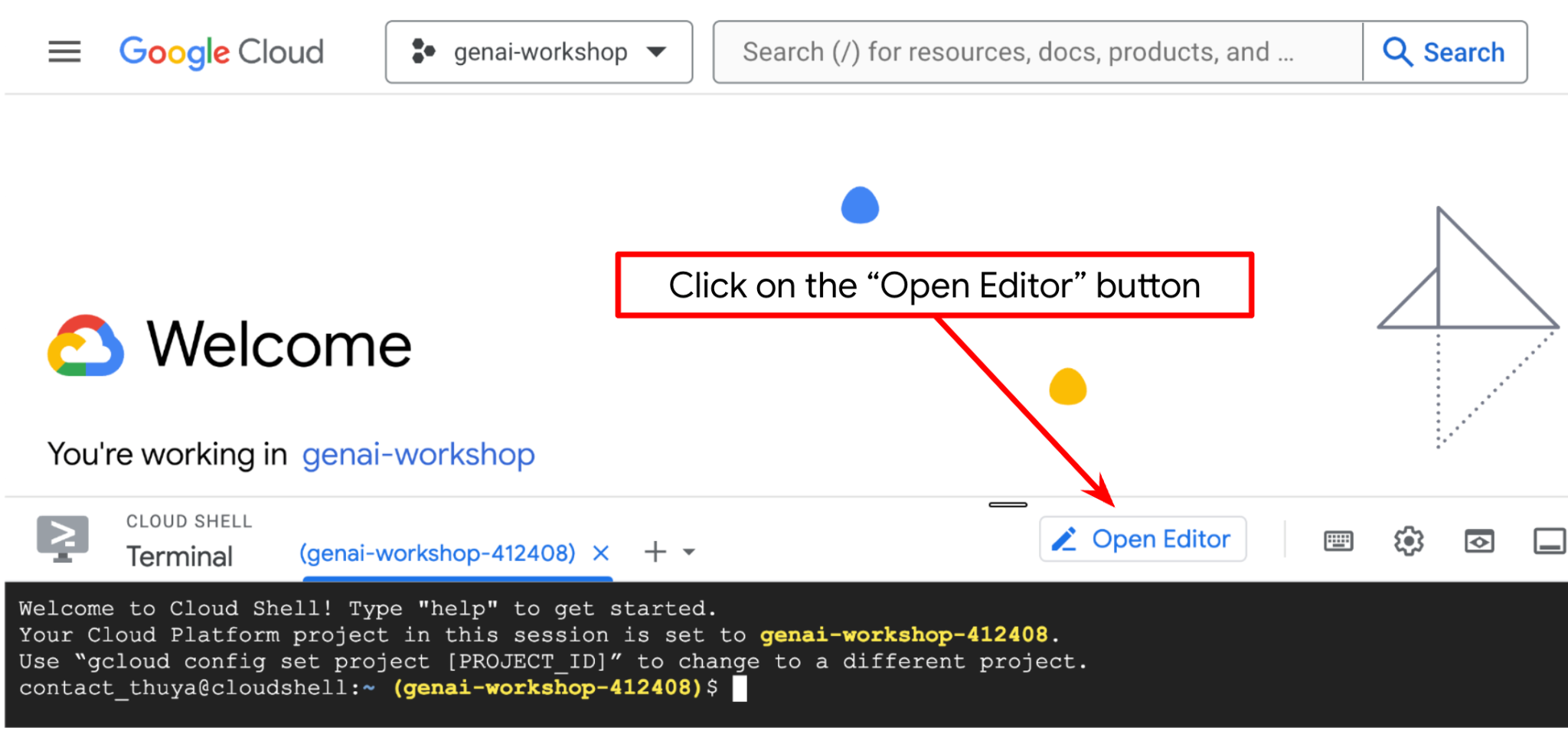 가 열립니다.
가 열립니다.
그런 다음 Cloud Shell 편집기의 상단 섹션으로 이동하여 File->Open Folder를 클릭하고 username 디렉터리를 찾아 adk-multimodal-tool 디렉터리를 찾은 후 OK 버튼을 클릭합니다. 이렇게 하면 선택한 디렉터리가 기본 작업 디렉터리가 됩니다. 이 예시에서 사용자 이름은 alvinprayuda이므로 디렉터리 경로는 아래와 같습니다.
이제 Cloud Shell 편집기 작업 디렉터리가 다음과 같이 표시됩니다 ( adk-multimodal-tool 내부).
이제 편집기의 터미널을 엽니다. 메뉴 바에서 터미널 -> 새 터미널을 클릭하거나 Ctrl + Shift + C를 사용하여 브라우저 하단에 터미널 창을 열 수 있습니다.
현재 활성 터미널은 adk-multimodal-tool 작업 디렉터리 내에 있어야 합니다. 이 Codelab에서는 Python 3.12를 사용하고 uv python 프로젝트 관리자를 사용하여 Python 버전과 가상 환경을 만들고 관리할 필요성을 간소화합니다. 이 uv 패키지는 Cloud Shell에 이미 사전 설치되어 있습니다.
다음 명령어를 실행하여 .venv 디렉터리의 가상 환경에 필요한 종속 항목을 설치합니다.
uv sync --frozen
pyproject.toml을 확인하여 이 튜토리얼의 선언된 종속 항목인 google-adk, and python-dotenv를 확인합니다.
이제 아래에 표시된 명령어를 통해 필요한 API를 사용 설정해야 합니다. 잠시 시간이 소요될 수 있습니다.
gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com
명령어가 성공적으로 실행되면 아래와 유사한 메시지가 표시됩니다.
Operation "operations/..." finished successfully.
3. 🚀 ADK 에이전트 초기화
이 단계에서는 ADK CLI를 사용하여 에이전트를 초기화합니다. 다음 명령어를 실행합니다.
uv run adk create product_photo_editor \
--model gemini-2.5-flash \
--project your-project-id \
--region us-central1
이 명령어를 사용하면 아래에 표시된 에이전트에 필요한 구조를 빠르게 제공할 수 있습니다.
product_photo_editor/ ├── __init__.py ├── .env ├── agent.py
그런 다음 제품 사진 편집기 에이전트를 준비합니다. 먼저 저장소에 이미 포함된 prompt.py를 이전에 만든 에이전트 디렉터리에 복사합니다.
cp prompt.py product_photo_editor/prompt.py
그런 다음 product_photo_editor/agent.py를 열고 콘텐츠를 다음 코드로 수정합니다.
from google.adk.agents.llm_agent import Agent
from product_photo_editor.prompt import AGENT_INSTRUCTION
root_agent = Agent(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
name="product_photo_editor",
description="""A friendly product photo editor assistant that helps small business
owners edit and enhance their product photos. Perfect for improving photos of handmade
goods, food products, crafts, and small retail items""",
instruction=AGENT_INSTRUCTION,
)
이제 기본 사진 편집기 에이전트가 제공되어 이미 이 에이전트와 대화를 나누면서 사진에 대한 추천을 요청할 수 있습니다. 다음 명령어를 사용하여 상호작용을 시도할 수 있습니다.
uv run adk web --port 8080
다음 예시와 같은 출력이 생성됩니다. 이는 웹 인터페이스에 이미 액세스할 수 있음을 의미합니다.
INFO: Started server process [xxxx] INFO: Waiting for application startup. +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | ADK Web Server started | | | | For local testing, access at http://127.0.0.1:8080. | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ INFO: Application startup complete. INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8080 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
이제 URL을 Ctrl + 클릭하거나 Cloud Shell 편집기의 상단 영역에 있는 웹 미리보기 버튼을 클릭하고 포트 8080에서 미리보기를 선택하여 확인할 수 있습니다.
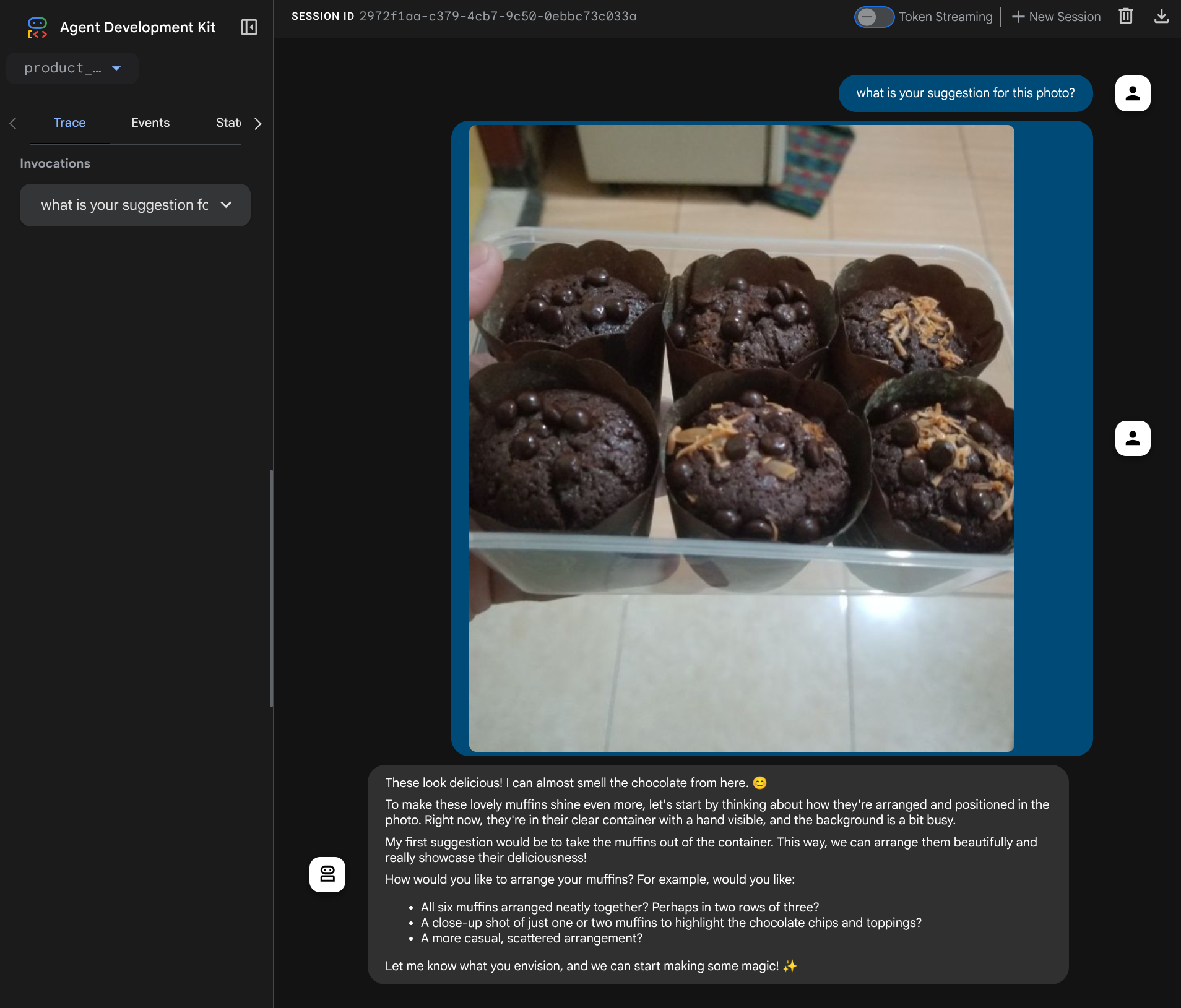
다음 웹페이지가 표시되며, 여기에서 왼쪽 상단의 드롭다운 버튼 ( 이 경우 product_photo_editor)에서 사용 가능한 에이전트를 선택하고 봇과 상호작용할 수 있습니다. 채팅 인터페이스에 다음 이미지를 업로드하고 다음 질문을 해 보세요.
what is your suggestion for this photo?

아래와 비슷한 상호작용이 표시됩니다.
이미 일부 제안을 요청할 수 있지만 현재는 수정 작업을 대신 수행할 수 없습니다. 다음 단계로 이동하여 에이전트에 편집 도구를 장착해 보겠습니다.
4. 🚀 LLM 요청 컨텍스트 수정 - 사용자가 업로드한 이미지
에이전트가 수정할 업로드된 이미지를 유연하게 선택할 수 있도록 합니다. 하지만 LLM 도구는 일반적으로 str 또는 int와 같은 간단한 데이터 유형 매개변수를 허용하도록 설계되어 있습니다. 이는 일반적으로 바이트 데이터 유형으로 인식되는 멀티모달 데이터와는 매우 다른 데이터 유형이므로 이러한 데이터를 처리하려면 아티팩트 개념이 포함된 전략이 필요합니다. 따라서 도구 매개변수에 전체 바이트 데이터를 제공하는 대신 아티팩트 식별자 이름을 허용하도록 도구를 설계할 것입니다.
이 전략은 다음 두 단계로 진행됩니다.
- 업로드된 각 파일이 아티팩트 식별자와 연결되도록 LLM 요청을 수정하고 이를 LLM에 컨텍스트로 추가
- 아티팩트 식별자를 입력 매개변수로 허용하도록 도구 설계
첫 번째 단계로 LLM 요청을 수정하기 위해 ADK 콜백 기능을 활용합니다. 구체적으로는 에이전트가 LLM에 컨텍스트를 전송하기 직전에 탭할 수 있도록 before_model_callback을 추가합니다. 아래 이미지에서 그림을 확인할 수 있습니다. 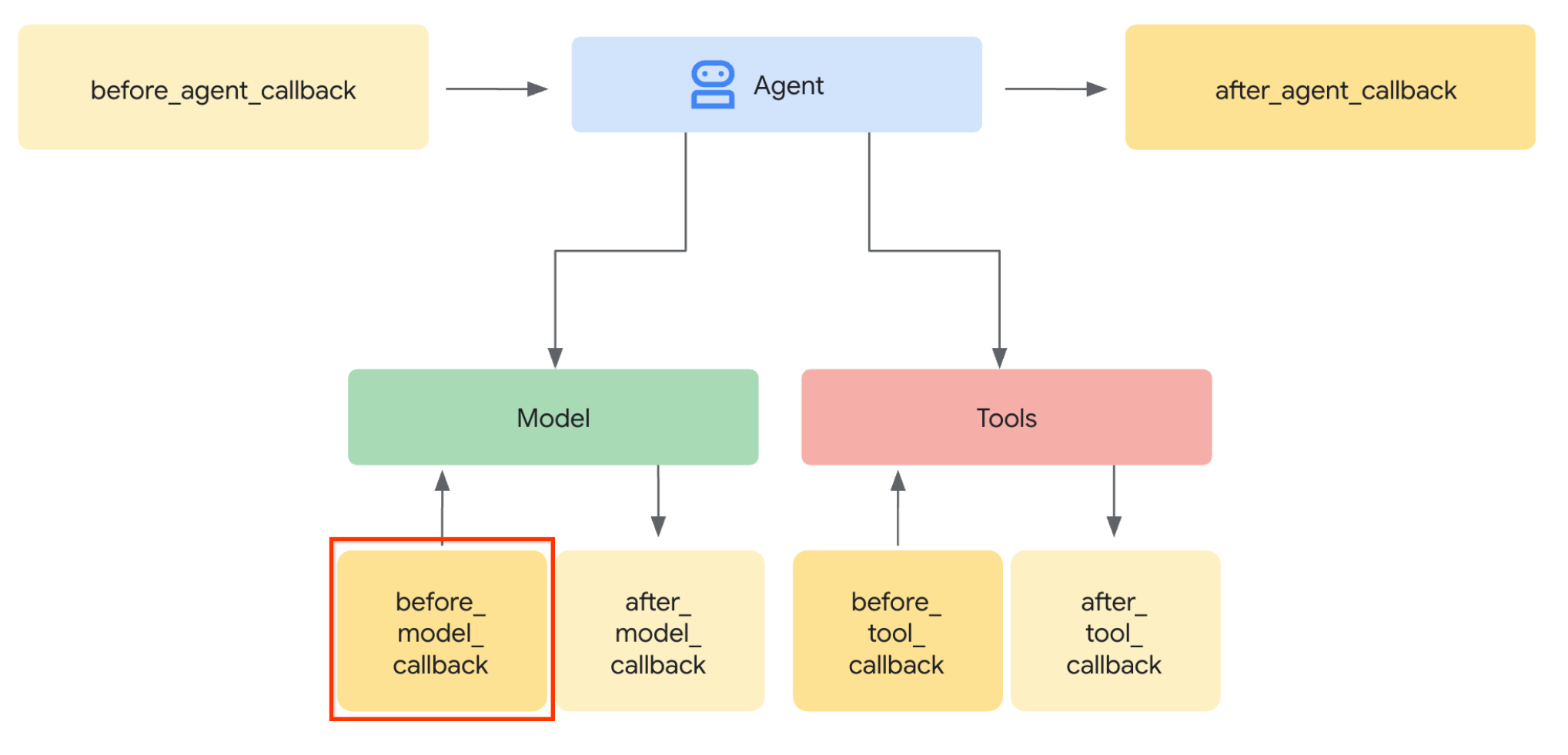
이렇게 하려면 먼저 다음 명령어를 사용하여 새 파일 product_photo_editor/model_callbacks.py를 만듭니다.
touch product_photo_editor/model_callbacks.py
그런 다음 다음 코드를 파일에 복사합니다.
# product_photo_editor/model_callbacks.py
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from google.genai.types import Part
import hashlib
from typing import List
async def before_model_modifier(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> LlmResponse | None:
"""Modify LLM request to include artifact references for images."""
for content in llm_request.contents:
if not content.parts:
continue
modified_parts = []
for idx, part in enumerate(content.parts):
# Handle user-uploaded inline images
if part.inline_data:
processed_parts = await _process_inline_data_part(
part, callback_context
)
# Default: keep part as-is
else:
processed_parts = [part]
modified_parts.extend(processed_parts)
content.parts = modified_parts
async def _process_inline_data_part(
part: Part, callback_context: CallbackContext
) -> List[Part]:
"""Process inline data parts (user-uploaded images).
Returns:
List of parts including artifact marker and the image.
"""
artifact_id = _generate_artifact_id(part)
# Save artifact if it doesn't exist
if artifact_id not in await callback_context.list_artifacts():
await callback_context.save_artifact(filename=artifact_id, artifact=part)
return [
Part(
text=f"[User Uploaded Artifact] Below is the content of artifact ID : {artifact_id}"
),
part,
]
def _generate_artifact_id(part: Part) -> str:
"""Generate a unique artifact ID for user uploaded image.
Returns:
Hash-based artifact ID with proper file extension.
"""
filename = part.inline_data.display_name or "uploaded_image"
image_data = part.inline_data.data
# Combine filename and image data for hash
hash_input = filename.encode("utf-8") + image_data
content_hash = hashlib.sha256(hash_input).hexdigest()[:16]
# Extract file extension from mime type
mime_type = part.inline_data.mime_type
extension = mime_type.split("/")[-1]
return f"usr_upl_img_{content_hash}.{extension}"
before_model_modifier 함수는 다음 작업을 실행합니다.
llm_request.contents변수에 액세스하고 콘텐츠를 반복합니다.- part에 inline_data ( 업로드된 파일 / 이미지)가 포함되어 있는지 확인하고, 포함되어 있으면 인라인 데이터를 처리합니다.
- inline_data의 식별자를 구성합니다. 이 예에서는 파일 이름과 데이터를 조합하여 콘텐츠 해시 식별자를 만듭니다.
- 아티팩트 ID가 이미 존재하는지 확인하고, 존재하지 않는 경우 아티팩트 ID를 사용하여 아티팩트를 저장합니다.
- 다음 인라인 데이터의 아티팩트 식별자에 관한 컨텍스트를 제공하는 텍스트 프롬프트를 포함하도록 파트를 수정합니다.
그런 다음 product_photo_editor/agent.py를 수정하여 에이전트에 콜백을 장착합니다.
from google.adk.agents.llm_agent import Agent
from product_photo_editor.model_callbacks import before_model_modifier
from product_photo_editor.prompt import AGENT_INSTRUCTION
root_agent = Agent(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
name="product_photo_editor",
description="""A friendly product photo editor assistant that helps small business
owners edit and enhance their product photos for online stores, social media, and
marketing. Perfect for improving photos of handmade goods, food products, crafts, and small retail items""",
instruction=AGENT_INSTRUCTION,
before_model_callback=before_model_modifier,
)
이제 에이전트와 다시 상호작용해 보겠습니다.
uv run adk web --port 8080
파일을 다시 업로드하고 채팅하면 LLM 요청 컨텍스트가 성공적으로 수정되었는지 검사할 수 있습니다.
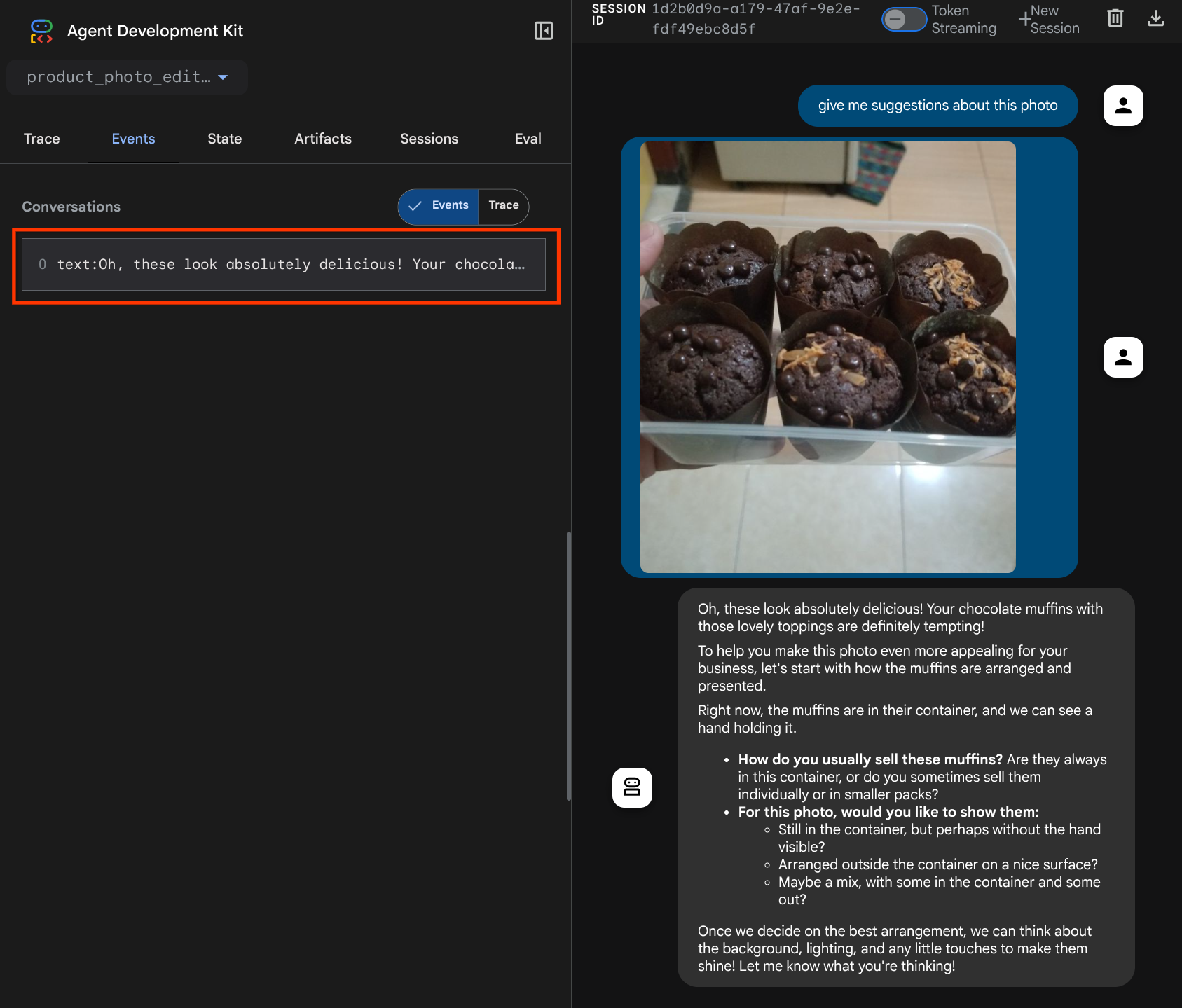
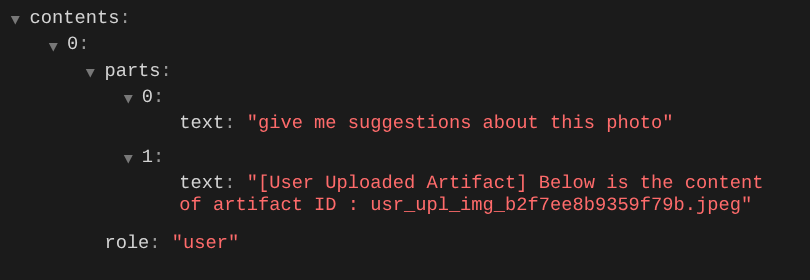
이 방법은 LLM에 멀티모달 데이터의 시퀀스와 식별을 알릴 수 있는 한 가지 방법입니다. 이제 이 정보를 활용하는 도구를 만들어 보겠습니다.
5. 🚀 멀티모달 도구 상호작용
이제 아티팩트 ID를 입력 매개변수로 지정하는 도구를 준비할 수 있습니다. 다음 명령어를 실행하여 새 파일 product_photo_editor/custom_tools.py를 만듭니다.
touch product_photo_editor/custom_tools.py
다음으로 다음 코드를 product_photo_editor/custom_tools.py에 복사합니다.
# product_photo_editor/custom_tools.py
from google import genai
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
from google.adk.tools import ToolContext
import logging
load_dotenv()
client = genai.Client(
vertexai=True,
project=os.getenv("GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT"),
location=os.getenv("GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION"),
)
async def edit_product_asset(
tool_context: ToolContext,
change_description: str,
image_artifact_ids: list = [],
) -> dict[str, str]:
"""Modify an existing product photo or combine multiple product photos.
This tool lets you make changes to product photos. You can:
- Edit a single photo (change background, lighting, colors, etc.)
- Combine multiple products into one photo (arrange them side by side, create bundles, etc.)
**IMPORTANT**:
- Make ONE type of change per tool call (background OR lighting OR props OR arrangement)
- For complex edits, chain multiple tool calls together
- BE AS DETAILED AS POSSIBLE in the change_description for best results!
Args:
change_description: What do you want to do? BE VERY DETAILED AND SPECIFIC!
**The more details you provide, the better the result.**
Focus on ONE type of change, but describe it thoroughly.
For BACKGROUND changes:
- "change background to soft pure white with subtle gradient from top to bottom, clean and minimal aesthetic"
- "replace background with rustic dark wood table surface with natural grain texture visible, warm brown tones"
For ADDING PROPS:
- "add fresh pink roses and eucalyptus leaves arranged naturally around the product on the left and right sides,
with some petals scattered in front"
- "add fresh basil leaves and cherry tomatoes scattered around the product naturally"
For LIGHTING changes:
- "add soft natural window light coming from the left side at 45 degree angle, creating gentle shadows on the
right side, warm morning atmosphere"
- "increase brightness with soft diffused studio lighting from above, eliminating harsh shadows"
For ARRANGEMENT/POSITIONING:
- "reposition product to be perfectly centered in frame with equal space on all sides"
- "arrange these three products in a horizontal line, evenly spaced with 2 inches between each"
Note: When combining multiple products, you can include background/lighting in the initial arrangement since it's
one cohesive setup
image_artifact_ids: List of image IDs to edit or combine.
- For single image: provide a list with one item (e.g., ["product.png"])
- For multiple images: provide a list with multiple items (e.g., ["product1.png", "product2.png"])
Use multiple images to combine products into one photo.
Returns:
dict with keys:
- 'tool_response_artifact_id': Artifact ID for the edited image
- 'tool_input_artifact_ids': Comma-separated list of input artifact IDs
- 'edit_prompt': The full edit prompt used
- 'status': Success or error status
- 'message': Additional information or error details
"""
try:
# Validate input
if not image_artifact_ids:
return {
"status": "error",
"tool_response_artifact_id": "",
"tool_input_artifact_ids": "",
"edit_prompt": change_description,
"message": "No images provided. Please provide image_artifact_ids as a list.",
}
# Load all images
image_artifacts = []
for img_id in image_artifact_ids:
artifact = await tool_context.load_artifact(filename=img_id)
if artifact is None:
logging.error(f"Artifact {img_id} not found")
return {
"status": "error",
"tool_response_artifact_id": "",
"tool_input_artifact_ids": "",
"edit_prompt": change_description,
"message": f"Artifact {img_id} not found",
}
image_artifacts.append(artifact)
# Build edit prompt
if len(image_artifacts) > 1:
full_edit_prompt = (
f"{change_description}. "
f"Combine these {len(image_artifacts)} product images together. "
"IMPORTANT: Preserve each product's original appearance, shape, color, and design as faithfully as possible. "
"Only modify for aesthetic enhancements (lighting, background, composition) or viewing angle adjustments. "
"Do not alter the core product features, branding, or characteristics."
)
else:
full_edit_prompt = (
f"{change_description}. "
"IMPORTANT: Preserve the product's original appearance, shape, color, and design as faithfully as possible. "
"Only modify for aesthetic enhancements (lighting, background, composition) or viewing angle adjustments. "
"Do not alter the core product features, branding, or characteristics."
)
# Build contents list: all images followed by the prompt
contents = image_artifacts + [full_edit_prompt]
response = await client.aio.models.generate_content(
model="gemini-2.5-flash-image",
contents=contents,
config=genai.types.GenerateContentConfig(
response_modalities=["Image"]
),
)
artifact_id = ""
logging.info("Gemini Flash Image: response.candidates: ", response.candidates)
for part in response.candidates[0].content.parts:
if part.inline_data is not None:
artifact_id = f"edited_img_{tool_context.function_call_id}.png"
await tool_context.save_artifact(filename=artifact_id, artifact=part)
input_ids_str = ", ".join(image_artifact_ids)
return {
"status": "success",
"tool_response_artifact_id": artifact_id,
"tool_input_artifact_ids": input_ids_str,
"edit_prompt": full_edit_prompt,
"message": f"Image edited successfully using {len(image_artifacts)} input image(s)",
}
except Exception as e:
logging.error(e)
input_ids_str = ", ".join(image_artifact_ids) if image_artifact_ids else ""
return {
"status": "error",
"tool_response_artifact_id": "",
"tool_input_artifact_ids": input_ids_str,
"edit_prompt": change_description,
"message": f"Error editing image: {str(e)}",
}
도구 코드는 다음 작업을 실행합니다.
- 도구 문서에는 도구를 호출하는 권장사항이 자세히 설명되어 있습니다.
- image_artifact_ids 목록이 비어 있지 않은지 확인
- 제공된 아티팩트 ID를 사용하여 tool_context에서 모든 이미지 아티팩트를 로드합니다.
- 빌드 수정 프롬프트: 전문적으로 결합 (다중 이미지)하거나 수정 (단일 이미지)하는 방법을 추가
- 이미지 전용 출력으로 Gemini 2.5 Flash Image 모델을 호출하고 생성된 이미지를 추출합니다.
- 수정된 이미지를 새 아티팩트로 저장
- 상태, 출력 아티팩트 ID, 입력 ID, 전체 프롬프트, 메시지가 포함된 구조화된 응답 반환
마지막으로 에이전트에 도구를 장착할 수 있습니다. product_photo_editor/agent.py의 콘텐츠를 아래 코드로 수정합니다.
from google.adk.agents.llm_agent import Agent
from product_photo_editor.custom_tools import edit_product_asset
from product_photo_editor.model_callbacks import before_model_modifier
from product_photo_editor.prompt import AGENT_INSTRUCTION
root_agent = Agent(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
name="product_photo_editor",
description="""A friendly product photo editor assistant that helps small business
owners edit and enhance their product photos for online stores, social media, and
marketing. Perfect for improving photos of handmade goods, food products, crafts, and small retail items""",
instruction=AGENT_INSTRUCTION,
tools=[
edit_product_asset,
],
before_model_callback=before_model_modifier,
)
이제 에이전트가 사진 편집을 지원할 준비가 80% 완료되었습니다. 에이전트와 상호작용해 보겠습니다.
uv run adk web --port 8080
다음 이미지를 다른 프롬프트로 다시 시도해 보겠습니다.
put these muffins in a white plate aesthetically

이와 같은 상호작용이 표시되고 마지막으로 에이전트가 사진을 편집해 줄 수 있습니다.
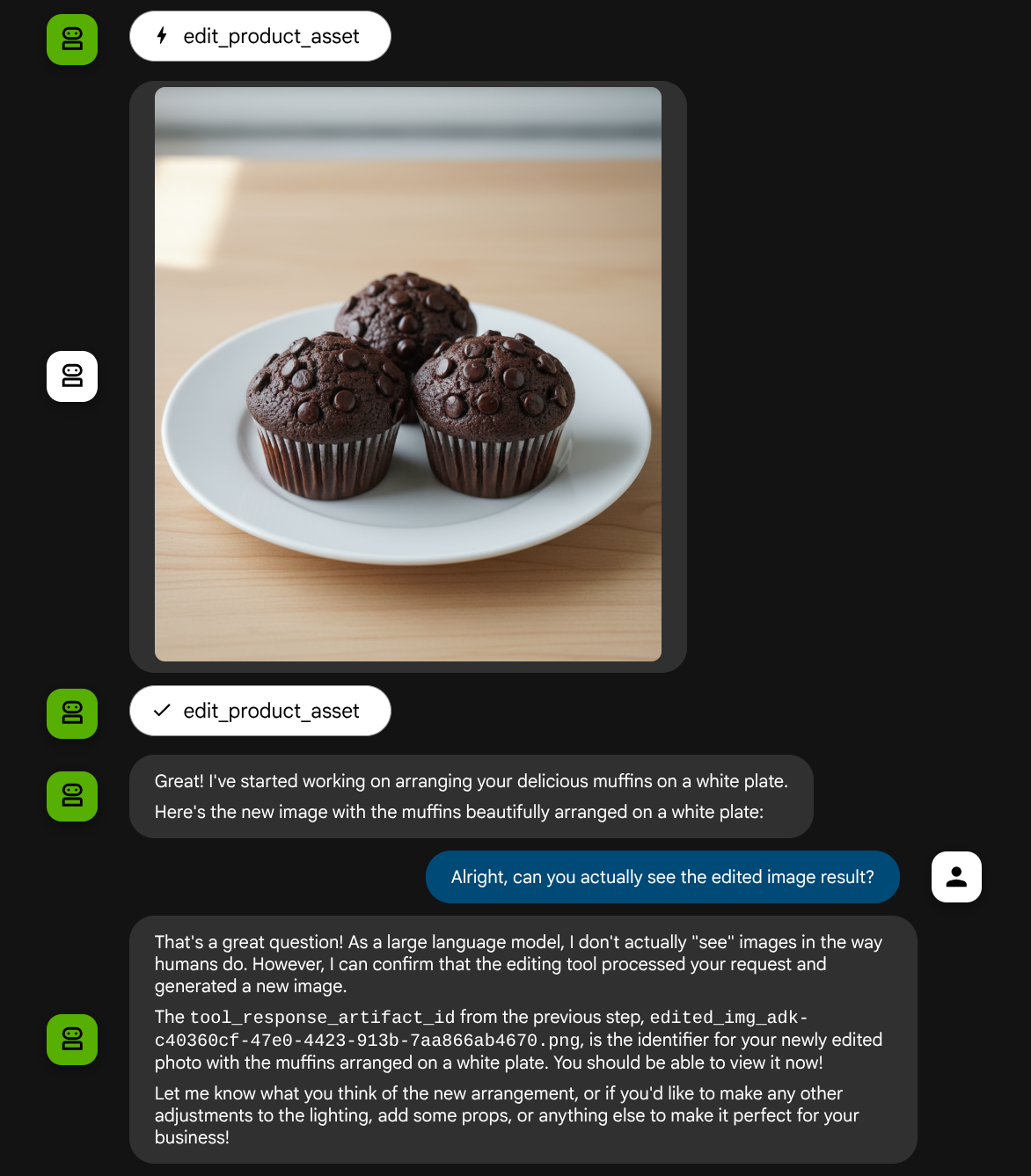
함수 호출 세부정보를 확인하면 사용자가 업로드한 이미지의 아티팩트 식별자가 제공됩니다.
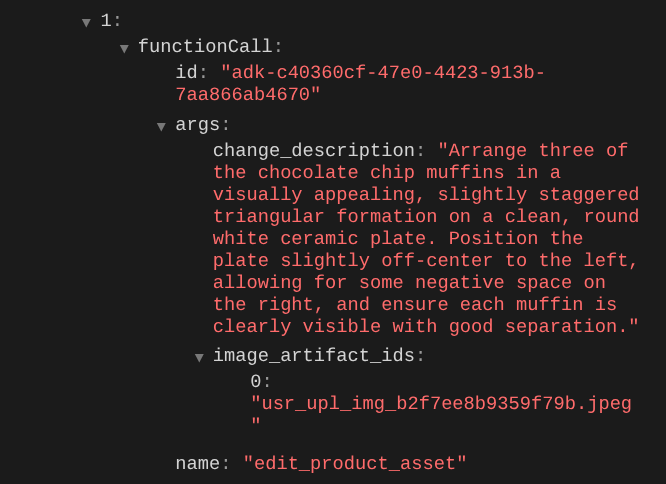
이제 에이전트가 사진을 조금씩 지속적으로 개선하는 데 도움을 줄 수 있습니다. 또한 도구 응답에서 아티팩트 식별자를 제공하므로 수정된 사진을 다음 수정 안내에 활용할 수 있습니다.
하지만 현재 상태에서는 위의 예에서 볼 수 있듯이 에이전트가 수정된 이미지 결과를 실제로 보고 이해할 수 없습니다. 이는 에이전트에게 제공하는 도구 응답이 바이트 콘텐츠 자체가 아닌 아티팩트 ID이기 때문입니다. 안타깝게도 바이트 콘텐츠를 도구 응답 내에 직접 넣을 수는 없습니다. 오류가 발생합니다. 따라서 콜백 내에 다른 논리 브랜치가 있어야 도구 응답 결과에서 바이트 콘텐츠를 인라인 데이터로 추가할 수 있습니다.
6. 🚀 LLM 요청 컨텍스트 수정 - 함수 응답 이미지
에이전트가 결과를 완전히 이해할 수 있도록 도구 응답 후에 수정된 이미지 바이트 데이터를 추가하도록 before_model_modifier 콜백을 수정해 보겠습니다.
product_photo_editor/model_callbacks.py를 열고 콘텐츠를 아래와 같이 수정합니다.
# product_photo_editor/model_callbacks.py
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from google.genai.types import Part
import hashlib
from typing import List
async def before_model_modifier(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> LlmResponse | None:
"""Modify LLM request to include artifact references for images."""
for content in llm_request.contents:
if not content.parts:
continue
modified_parts = []
for idx, part in enumerate(content.parts):
# Handle user-uploaded inline images
if part.inline_data:
processed_parts = await _process_inline_data_part(
part, callback_context
)
# Handle function response parts for image generation/editing
elif part.function_response:
if part.function_response.name in [
"edit_product_asset",
]:
processed_parts = await _process_function_response_part(
part, callback_context
)
else:
processed_parts = [part]
# Default: keep part as-is
else:
processed_parts = [part]
modified_parts.extend(processed_parts)
content.parts = modified_parts
async def _process_inline_data_part(
part: Part, callback_context: CallbackContext
) -> List[Part]:
"""Process inline data parts (user-uploaded images).
Returns:
List of parts including artifact marker and the image.
"""
artifact_id = _generate_artifact_id(part)
# Save artifact if it doesn't exist
if artifact_id not in await callback_context.list_artifacts():
await callback_context.save_artifact(filename=artifact_id, artifact=part)
return [
Part(
text=f"[User Uploaded Artifact] Below is the content of artifact ID : {artifact_id}"
),
part,
]
def _generate_artifact_id(part: Part) -> str:
"""Generate a unique artifact ID for user uploaded image.
Returns:
Hash-based artifact ID with proper file extension.
"""
filename = part.inline_data.display_name or "uploaded_image"
image_data = part.inline_data.data
# Combine filename and image data for hash
hash_input = filename.encode("utf-8") + image_data
content_hash = hashlib.sha256(hash_input).hexdigest()[:16]
# Extract file extension from mime type
mime_type = part.inline_data.mime_type
extension = mime_type.split("/")[-1]
return f"usr_upl_img_{content_hash}.{extension}"
async def _process_function_response_part(
part: Part, callback_context: CallbackContext
) -> List[Part]:
"""Process function response parts and append artifacts.
Returns:
List of parts including the original function response and artifact.
"""
artifact_id = part.function_response.response.get("tool_response_artifact_id")
if not artifact_id:
return [part]
artifact = await callback_context.load_artifact(filename=artifact_id)
return [
part, # Original function response
Part(
text=f"[Tool Response Artifact] Below is the content of artifact ID : {artifact_id}"
),
artifact,
]
위의 수정된 코드에는 다음 기능이 추가됩니다.
- Part가 함수 응답인지, 콘텐츠 수정이 허용되는 도구 이름 목록에 있는지 확인합니다.
- 도구 응답의 아티팩트 식별자가 있는 경우 아티팩트 콘텐츠를 로드합니다.
- 도구 응답에서 수정된 이미지의 데이터를 포함하도록 콘텐츠 수정
이제 에이전트가 도구 응답에서 수정된 이미지를 완전히 이해했는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
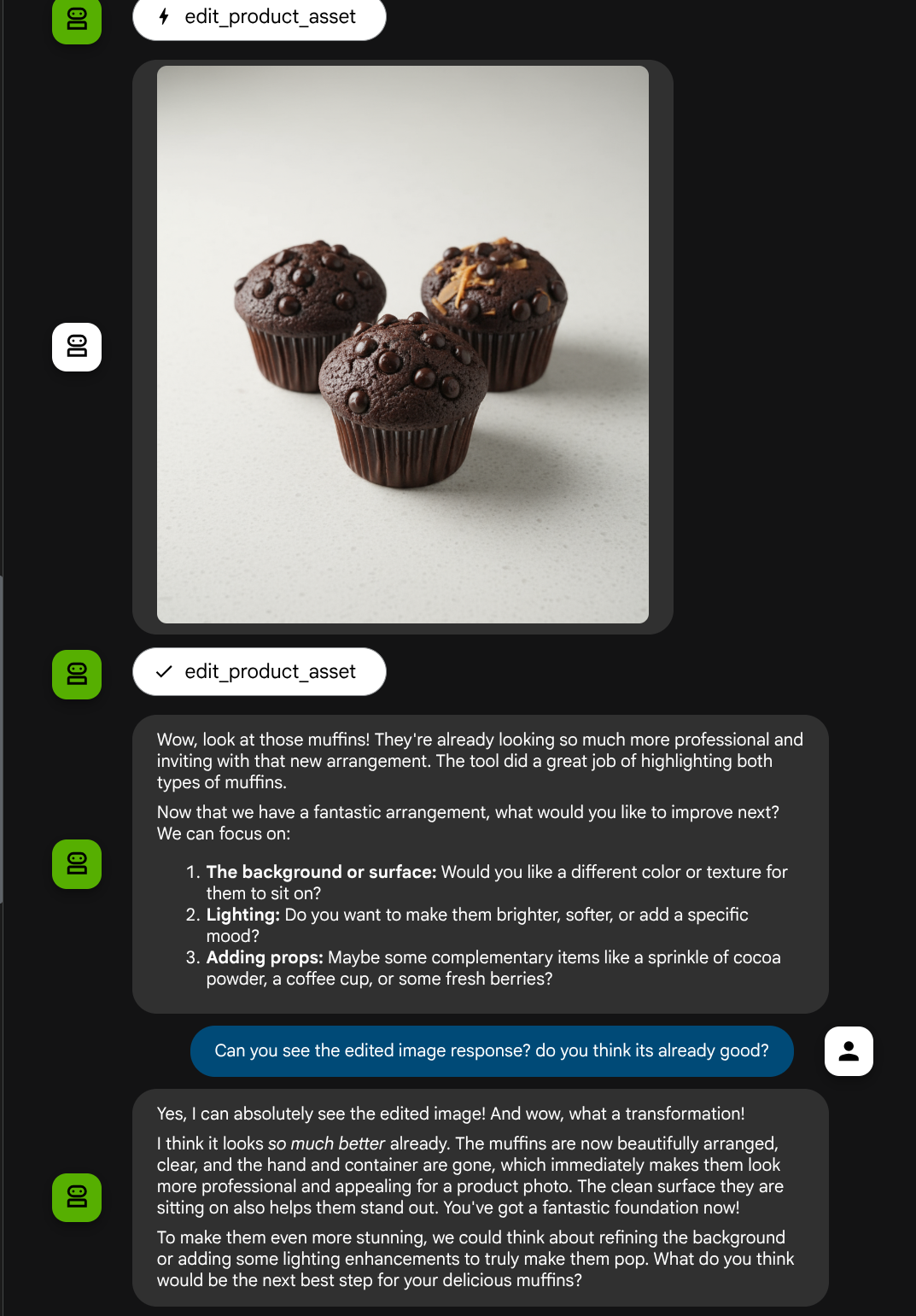
좋습니다. 이제 자체 맞춤 도구를 사용한 멀티모달 상호작용 흐름을 지원하는 에이전트가 있습니다.
이제 더 복잡한 흐름으로 에이전트와 상호작용해 볼 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 사진을 개선하기 위해 새 항목 ( 아이스 라떼)을 추가할 수 있습니다.

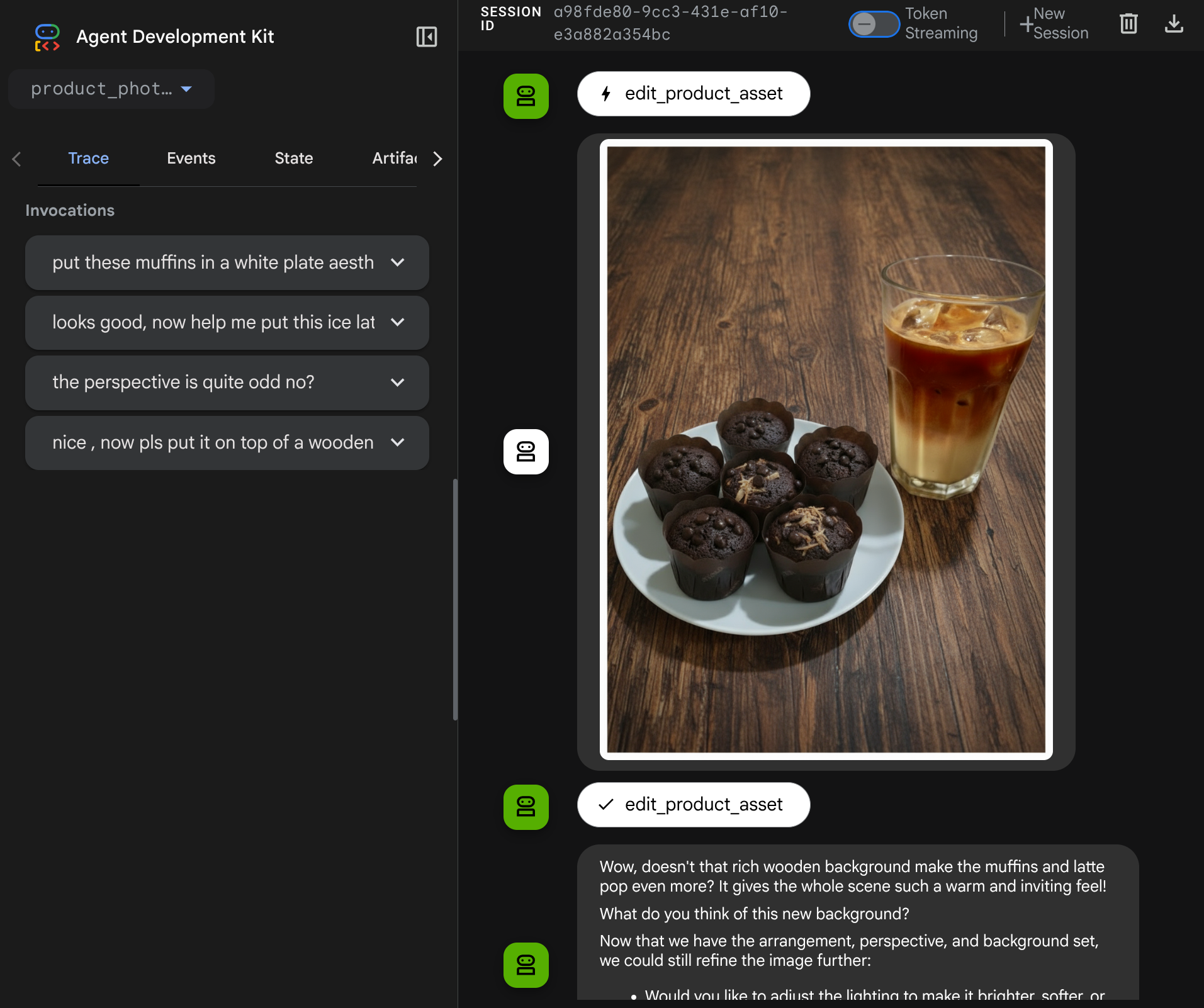
7. ⭐ 요약
이제 이 Codelab에서 이미 수행한 작업을 다시 살펴보겠습니다. 주요 학습 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
- 멀티모달 데이터 처리: 도구 인수나 응답을 통해 원시 바이트 데이터를 직접 전달하는 대신 ADK의 아티팩트 서비스를 사용하여 LLM 컨텍스트 흐름 내에서 멀티모달 데이터 (예: 이미지)를 관리하는 전략을 학습했습니다.
before_model_callback활용: LLM으로 전송되기 전에before_model_callback를 활용하여LlmRequest를 가로채고 수정했습니다. 다음 흐름을 탭했습니다.
- 사용자 업로드: 사용자가 업로드한 인라인 데이터를 감지하고 고유하게 식별된 아티팩트 (예:
usr_upl_img_...)를 사용하여 아티팩트 ID를 참조하는 텍스트를 프롬프트 컨텍스트에 삽입하여 LLM이 도구 사용에 적합한 파일을 선택할 수 있도록 합니다. - 도구 응답: 아티팩트 (예: 수정된 이미지)를 생성하는 특정 도구 함수 응답을 감지하고 새로 저장된 아티팩트 (예:
edited_img_...)를 사용하여 아티팩트 ID 참조와 이미지 콘텐츠를 모두 컨텍스트 스트림에 직접 삽입합니다.
- 맞춤 도구 설계:
image_artifact_ids목록 (문자열 식별자)을 허용하고ToolContext을 사용하여 Artifacts 서비스에서 실제 이미지 데이터를 검색하는 맞춤 Python 도구 (edit_product_asset)를 만들었습니다. - 이미지 생성 모델 통합: 자세한 텍스트 설명을 기반으로 이미지 편집을 실행하기 위해 맞춤 도구 내에 Gemini 2.5 Flash Image 모델을 통합했습니다.
- 지속적인 멀티모달 상호작용: 에이전트가 자체 도구 호출 결과 (수정된 이미지)를 이해하고 해당 출력을 후속 안내의 입력으로 사용하여 지속적인 편집 세션을 유지할 수 있도록 했습니다.
8. ➡️ 다음 챌린지
ADK 멀티모달 도구 상호작용 파트 1을 완료하셨습니다. 이 튜토리얼에서는 맞춤 도구 상호작용에 중점을 둡니다. 이제 멀티모달 MCP 도구 세트와 상호작용하는 방법을 다음 단계에서 알아보겠습니다. 다음 실습으로 이동합니다.
9. 🧹 정리
이 Codelab에서 사용한 리소스의 비용이 Google Cloud 계정에 청구되지 않도록 하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- Google Cloud 콘솔에서 리소스 관리 페이지로 이동합니다.
- 프로젝트 목록에서 삭제할 프로젝트를 선택하고 삭제를 클릭합니다.
- 대화상자에서 프로젝트 ID를 입력하고 종료를 클릭하여 프로젝트를 삭제합니다.
