1. 事前準備
在本程式碼研究室中,您將更新在先前「開始使用行動裝置文字分類程式碼研究室」中建立的應用程式。
必要條件
- 本程式碼研究室是為熟悉機器學習技術的新手開發人員而設計,
- 程式碼研究室是序列課程的一部分。如果您尚未完成「建構基本訊息樣式」應用程式,或「建立垃圾留言機器學習模型」,請立即停止相關程序。
課程內容 [制定或學習]
- 我們會說明如何在上述步驟中將自訂模型整合至您的應用程式。
軟硬體需求
- Android Studio,iOS 適用的 CocoaPods
2. 開啟現有 Android 應用程式
您可以依照程式碼研究室 1 的指示取得程式碼,或是複製這個存放區,然後從 TextClassificationStep1 載入應用程式。
git clone https://github.com/googlecodelabs/odml-pathways
您可以在 TextClassificationOnMobile->Android 路徑中找到這個 ID。
已完成的程式碼也可做為 TextClassificationStep2 使用。
開啟後,您就可以繼續進行步驟 2。
3. 匯入模型檔案和中繼資料
在「建構垃圾留言機器學習模型」程式碼研究室中,您已建立 .TFLITE 模型。
模型檔案已下載完成。如果您沒有這個模型,可以到本程式碼研究室的存放區中取得,也可以前往這裡取得模型。
建立資產目錄,將這個檔案新增至專案。
- 使用專案導覽工具,確認已選取頂端的「Android」。
- 在「app」資料夾上按一下滑鼠右鍵。選取「新增」>目錄:
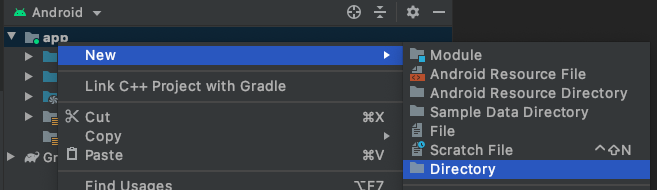
- 在「New Directory」對話方塊中,選取「src/main/assets」。
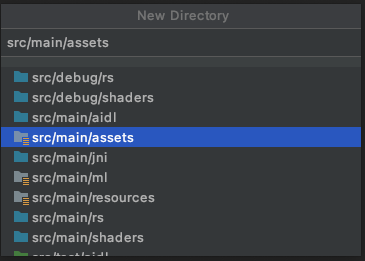
您將在應用程式中看到新的 assets 資料夾。
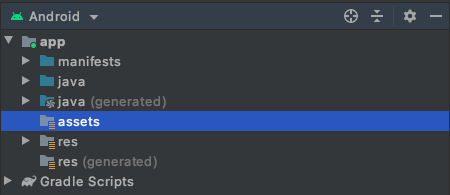
- 在資產上按一下滑鼠右鍵。
- 隨即開啟的選單會顯示「在 Finder 中顯示」 (Mac 使用者)。選取應用程式。(Windows 會顯示「在檔案總管中顯示」,而 Ubuntu 會顯示「在檔案中顯示」)。
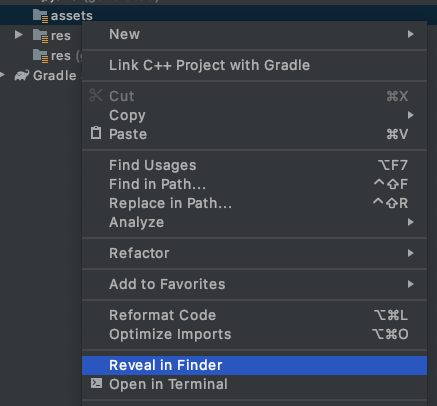
系統會隨即啟動 Finder,顯示檔案位置,例如 Windows 系統的檔案總管、Linux 的檔案。
- 將
labels.txt、model.tflite和vocab檔案複製到這個目錄。
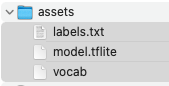
- 返回 Android Studio 後,您就可以在 assets 資料夾中看到這些內容。

4. 請更新 build.gradle,以便使用 TensorFlow Lite
如要使用 TensorFlow Lite,以及支援 TensorFlow Lite 的 TensorFlow Lite 工作程式庫,你必須更新 build.gradle 檔案。
Android 專案通常有多個專案,因此請務必找出「應用程式」等級 1。在 Android 檢視畫面的專案總管中,找到「Gradle Scripts」部分。正確的專案會加上 .app 標籤,如下所示:

您需要對這個檔案進行兩項變更。第一個位於底部的「dependencies」部分。為 TensorFlow Lite 工作程式庫新增文字 implementation,如下所示:
implementation 'org.tensorflow:tensorflow-lite-task-text:0.1.0'
版本號碼可能在寫入後變更,因此請務必前往 https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/inference_with_metadata/task_library/nl_classifier 查看最新資訊。
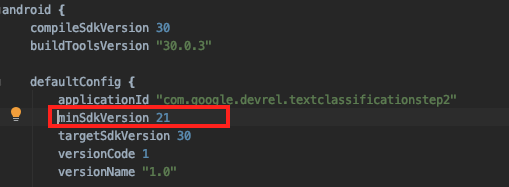
工作程式庫也需要 SDK 21 以上版本。在 android > 找到這項設定default config,然後變更為 21:
現在您已擁有所有依附元件,可以開始編寫程式了!
5. 新增輔助類別
如要區分應用程式使用該模型的推論邏輯,請建立另一個類別來處理模型推論。命名為「協助者」類別
- 在
MainActivity程式碼所在的套件名稱上按一下滑鼠右鍵。 - 選取新增 >套件。
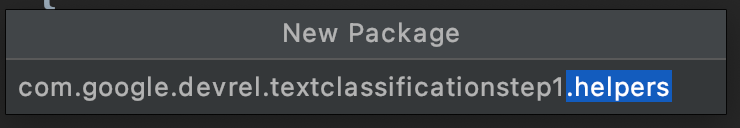
- 畫面中央會顯示一個對話方塊,要求你輸入套件名稱。請在目前套件名稱的結尾處新增。(在這個例子中稱為小幫手)。
- 完成後,在專案探索工具中的「helpers」資料夾上按一下滑鼠右鍵。
- 選取新增 >Java 類別,並命名為
TextClassificationClient。您將在下一個步驟編輯此檔案。
您的 TextClassificationClient 輔助類別看起來會像這樣 (但套件名稱可能不同)。
package com.google.devrel.textclassificationstep1.helpers;
public class TextClassificationClient {
}
- 使用下列程式碼更新檔案:
package com.google.devrel.textclassificationstep2.helpers;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import org.tensorflow.lite.support.label.Category;
import org.tensorflow.lite.task.text.nlclassifier.NLClassifier;
public class TextClassificationClient {
private static final String MODEL_PATH = "model.tflite";
private static final String TAG = "CommentSpam";
private final Context context;
NLClassifier classifier;
public TextClassificationClient(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public void load() {
try {
classifier = NLClassifier.createFromFile(context, MODEL_PATH);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getMessage());
}
}
public void unload() {
classifier.close();
classifier = null;
}
public List<Category> classify(String text) {
List<Category> apiResults = classifier.classify(text);
return apiResults;
}
}
這個類別將為 TensorFlow Lite 解譯器提供包裝函式、載入模型,並簡化管理應用程式和模型之間資料互換的複雜程度。
在 load() 方法中,系統會從模型路徑將新的 NLClassifier 類型例項化。模型路徑就是模型的名稱 model.tflite。NLClassifier 類型屬於文字工作程式庫的一部分,可協助您使用正確的序列長度將字串轉換為符記,將字串傳遞至模型,然後剖析結果。
(詳情請參閱「建立垃圾留言機器學習模型」)。
分類會在分類方法中執行,也就是傳遞字串,且傳回 List。使用機器學習模型對要判斷字串是否為垃圾內容時,通常會傳回所有答案,並指派機率。舉例來說,如果您傳送的郵件看起來像是垃圾內容,系統會傳回包含 2 個答案的清單。一個機率為垃圾郵件,但機率不高。「垃圾郵件/非垃圾郵件」屬於類別,因此傳回的 List 會包含這些機率。您稍後就會剖析出這些內容。
現在您已擁有輔助類別,請返回 MainActivity 進行更新,以便將文字分類。下一個步驟將會用到!
6. 分類文字
建議您先在 MainActivity 中匯入剛建立的輔助程式!
- 與其他匯入作業在
MainActivity.kt頂端,新增:
import com.google.devrel.textclassificationstep2.helpers.TextClassificationClient
import org.tensorflow.lite.support.label.Category
- 接下來,請建立輔助程式。在
onCreate中,緊接在setContentView行後方加入下列幾行內容,以例項化並載入輔助類別:
val client = TextClassificationClient(applicationContext)
client.load()
目前按鈕的 onClickListener 應如下所示:
btnSendText.setOnClickListener {
var toSend:String = txtInput.text.toString()
txtOutput.text = toSend
}
- 更新程式碼,如下所示:
btnSendText.setOnClickListener {
var toSend:String = txtInput.text.toString()
var results:List<Category> = client.classify(toSend)
val score = results[1].score
if(score>0.8){
txtOutput.text = "Your message was detected as spam with a score of " + score.toString() + " and not sent!"
} else {
txtOutput.text = "Message sent! \nSpam score was:" + score.toString()
}
txtInput.text.clear()
}
這項功能會改變功能,從只輸出使用者輸入內容,再到先分類。
- 在這一行中,您會擷取使用者輸入的字串,並將字串傳送至模型,傳回結果:
var results:List<Category> = client.classify(toSend)
只有 2 個類別:False 和 True
. (TensorFlow 會依字母順序排列,因此 False 為項目 0,True 值則為項目 1)。
- 如要取得值為
True的機率分數,請查看結果 [1].score,如下所示:
val score = results[1].score
- 選取門檻值 (本例中為 0.8);此時,當 True 類別的分數超過門檻值 (0.8),即表示郵件為垃圾郵件。否則這不是垃圾郵件,而是可以安全傳送的郵件:
if(score>0.8){
txtOutput.text = "Your message was detected as spam with a score of " + score.toString() + " and not sent!"
} else {
txtOutput.text = "Message sent! \nSpam score was:" + score.toString()
}
- 請在這裡查看模型的實際運作情形。「造訪我的網誌來購買商品!」訊息被標記為高可能垃圾內容:

相反地,「Ok,有趣的教學課程,謝謝!」被視為垃圾郵件的可能性極低:
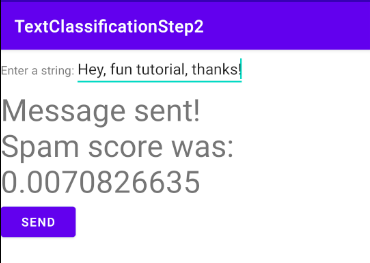
7. 更新 iOS 應用程式即可使用 TensorFlow Lite 模型
您可以依照程式碼研究室 1 的指示取得程式碼,或是複製這個存放區,然後從 TextClassificationStep1 載入應用程式。您可以在 TextClassificationOnMobile->iOS 路徑中找到這個 ID。
已完成的程式碼也可做為 TextClassificationStep2 使用。
在「建構垃圾留言機器學習模型」程式碼研究室中,您已建立非常簡單的應用程式,讓使用者在 UITextView 中輸入訊息,並將訊息傳送至沒有任何篩選功能的輸出內容。
您現在可以更新應用程式,在傳送前使用 TensorFlow Lite 模型偵測文字中的垃圾留言。只要在輸出標籤中轉譯文字,即可模擬這個應用程式中的傳送作業 (但實際的應用程式可能會使用公布欄、即時通訊等類似功能)。
首先,您需要從步驟 1 取得的應用程式,可以從存放區複製。
如要整合 TensorFlow Lite,請使用 CocoaPods。如果尚未安裝,請按照 https://cocoapods.org/ 中的操作說明安裝。
- 安裝 CocoaPods 後,請在與 TextClassification 應用程式
.xcproject相同的目錄中,建立名稱為 Podfile 的檔案。這個檔案的內容應如下所示:
target 'TextClassificationStep2' do
use_frameworks!
# Pods for NLPClassifier
pod 'TensorFlowLiteSwift'
end
應用程式名稱應列於第一行,而非「TextClassificationStep2」。
使用終端機前往該目錄,然後執行 pod install。如果成功,您將有一個名為 Pod 的新目錄,以及為您建立新的 .xcworkspace 檔案。您將在未來使用此 API,而非 .xcproject。
如果失敗,請確認 .xcproject 所在的目錄中已有 Podfile。Podfile 通常位於錯誤的目錄中,或目標名稱錯誤,通常出乎意料。
8. 新增模型和 Vocab 檔案
使用 TensorFlow Lite Model Maker 建立模型時,您可以輸出模型 (格式為 model.tflite) 和詞彙 (格式為 vocab.txt)。
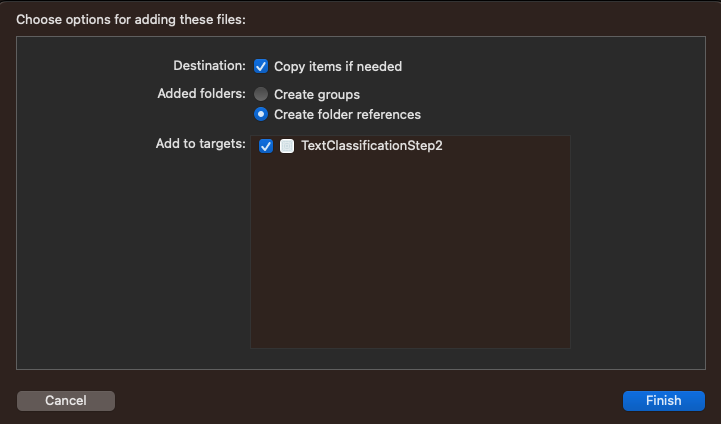
- 將這些檔案從 Finder 拖曳至專案視窗,即可新增至專案。確認已勾選 [新增至目標]:
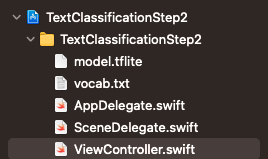
完成後,您應該會在專案中看到這些項目:
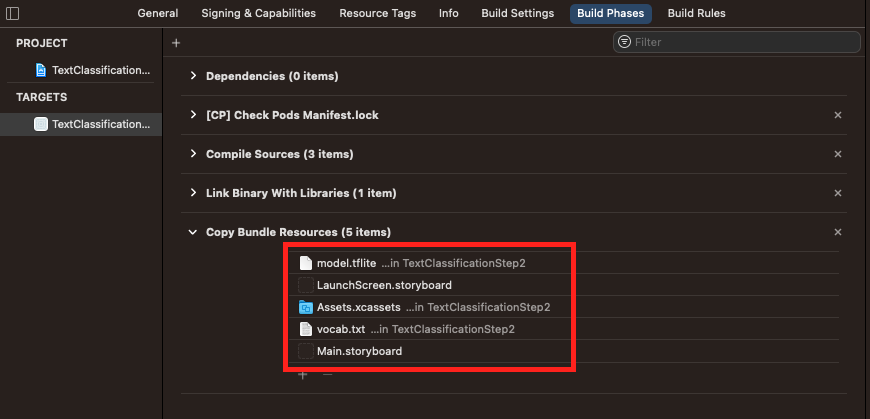
- 請選取您的專案 (在上方螢幕截圖中,藍色圖示為「TextClassificationStep2」TextClassificationStep2),然後查看「Build Phases」TextClassificationStep2分頁,確認是否已加入套件 (以便部署至裝置):
9. 載入單字
進行自然語言處理分類時,系統會使用編碼成向量的字詞訓練模型。模型將經過訓練的一組特定名稱和值對字詞進行編碼。請注意,大多數模型都有不同的詞彙,因此請務必在訓練時,使用產生的模型詞彙。這是您剛才新增至應用程式的 vocab.txt 檔案。
您可以在 Xcode 中開啟檔案,查看這些編碼方式。例如「歌曲」已編碼為 6 和 "love"12。順序其實就是頻率順序,因此「I」是資料集中最常見的字詞,後面接著「check」。
當使用者輸入字詞時,建議您先以這個詞彙對它們進行編碼,再傳送給模型加以分類。
我們就來探索這個程式碼吧!請先載入詞彙。
- 定義類別層級變數來儲存字典:
var words_dictionary = [String : Int]()
- 然後,在類別中建立
func,將詞彙載入這個字典:
func loadVocab(){
// This func will take the file at vocab.txt and load it into a has table
// called words_dictionary. This will be used to tokenize the words before passing them
// to the model trained by TensorFlow Lite Model Maker
if let filePath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "vocab", ofType: "txt") {
do {
let dictionary_contents = try String(contentsOfFile: filePath)
let lines = dictionary_contents.split(whereSeparator: \.isNewline)
for line in lines{
let tokens = line.components(separatedBy: " ")
let key = String(tokens[0])
let value = Int(tokens[1])
words_dictionary[key] = value
}
} catch {
print("Error vocab could not be loaded")
}
} else {
print("Error -- vocab file not found")
}
}
- 您可以從
viewDidLoad內呼叫此函式來執行:
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
txtInput.delegate = self
loadVocab()
}
10. 將字串轉換為符記序列
使用者將以句子的形式輸入字詞,這些內容會成為字串。系統會將句子中的每個字詞 (如果字典中存在) 編碼為詞彙中定義的字詞鍵/值。
自然語言處理模型通常接受固定序列長度。使用 ragged tensors 建構的模型有些例外狀況,但大多數情況下都能修正。您在建立模型時指定了這個長度。請務必在 iOS 應用程式中使用相同的長度。
先前在 Colab 中用於 TensorFlow Lite Model Maker 的預設設定為 20,因此你也要在這裡設定:
let SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 20
新增這個 func,這會擷取字串、將其轉換為小寫,並移除所有標點符號:
func convert_sentence(sentence: String) -> [Int32]{
// This func will split a sentence into individual words, while stripping punctuation
// If the word is present in the dictionary it's value from the dictionary will be added to
// the sequence. Otherwise we'll continue
// Initialize the sequence to be all 0s, and the length to be determined
// by the const SEQUENCE_LENGTH. This should be the same length as the
// sequences that the model was trained for
var sequence = [Int32](repeating: 0, count: SEQUENCE_LENGTH)
var words : [String] = []
sentence.enumerateSubstrings(
in: sentence.startIndex..<sentence.endIndex,options: .byWords) {
(substring, _, _, _) -> () in words.append(substring!) }
var thisWord = 0
for word in words{
if (thisWord>=SEQUENCE_LENGTH){
break
}
let seekword = word.lowercased()
if let val = words_dictionary[seekword]{
sequence[thisWord]=Int32(val)
thisWord = thisWord + 1
}
}
return sequence
}
請注意,序列會是 Int32 的介面。請務必刻意選擇,因為在將值傳遞至 TensorFlow Lite 時,您會處理低階記憶體,而且 TensorFlow Lite 會將字串序列中的整數視為 32 位元整數。讓您更輕鬆地將字串傳送至模型。
11. 執行分類
如要將句子分類,您必須先根據語句中的字詞,將語句轉換為一串符記。這項作業已在步驟 9 中完成。
現在您要擷取語句並傳遞至模型,讓模型對語句進行推論,然後剖析結果。
這項操作會使用 TensorFlow Lite 翻譯,您必須匯入:
import TensorFlowLite
從序列中擷取 func,這是 Int32 類型的陣列:
func classify(sequence: [Int32]){
// Model Path is the location of the model in the bundle
let modelPath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "model", ofType: "tflite")
var interpreter: Interpreter
do{
interpreter = try Interpreter(modelPath: modelPath!)
} catch _{
print("Error loading model!")
return
}
這項操作會從套件中載入模型檔案,並透過它叫用解譯器。
下一步會將序列中儲存的基礎記憶體複製到名為 myData, 的緩衝區,以便傳遞給張量。導入 TensorFlow Lite Pod 和解譯器時,你可以使用 Tensor 類型。
請以像這樣的程式碼開始 (仍在 func 分類中):
let tSequence = Array(sequence)
let myData = Data(copyingBufferOf: tSequence.map { Int32($0) })
let outputTensor: Tensor
如果您在 copyingBufferOf 上收到錯誤訊息,請不用擔心。稍後會導入為擴充功能。
現在我們要在解譯器上分配張量,將剛剛建立的資料緩衝區複製到輸入張量,然後叫用解譯器來執行推論:
do {
// Allocate memory for the model's input `Tensor`s.
try interpreter.allocateTensors()
// Copy the data to the input `Tensor`.
try interpreter.copy(myData, toInputAt: 0)
// Run inference by invoking the `Interpreter`.
try interpreter.invoke()
叫用完成後,您可以查看翻譯後的輸出內容來查看結果。
您必須讀取並轉換這些原始值 (每個神經元 4 個位元組)。這個特定模型有 2 個輸出神經元,因此您需要在 8 個位元組內讀取 8 個位元組,將轉換為 Float32 以剖析。您正在處理低層級記憶體,因此 unsafeData。
// Get the output `Tensor` to process the inference results.
outputTensor = try interpreter.output(at: 0)
// Turn the output tensor into an array. This will have 2 values
// Value at index 0 is the probability of negative sentiment
// Value at index 1 is the probability of positive sentiment
let resultsArray = outputTensor.data
let results: [Float32] = [Float32](unsafeData: resultsArray) ?? []
現在,我們可以相對輕易剖析資料,藉此判斷垃圾內容的品質。模型有 2 項輸出結果,第一組可能為訊息非垃圾郵件,第二個為非垃圾郵件。因此,您可以查看 results[1] 來找出垃圾內容的值:
let positiveSpamValue = results[1]
var outputString = ""
if(positiveSpamValue>0.8){
outputString = "Message not sent. Spam detected with probability: " + String(positiveSpamValue)
} else {
outputString = "Message sent!"
}
txtOutput.text = outputString
為了方便起見,以下是完整方法:
func classify(sequence: [Int32]){
// Model Path is the location of the model in the bundle
let modelPath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "model", ofType: "tflite")
var interpreter: Interpreter
do{
interpreter = try Interpreter(modelPath: modelPath!)
} catch _{
print("Error loading model!")
Return
}
let tSequence = Array(sequence)
let myData = Data(copyingBufferOf: tSequence.map { Int32($0) })
let outputTensor: Tensor
do {
// Allocate memory for the model's input `Tensor`s.
try interpreter.allocateTensors()
// Copy the data to the input `Tensor`.
try interpreter.copy(myData, toInputAt: 0)
// Run inference by invoking the `Interpreter`.
try interpreter.invoke()
// Get the output `Tensor` to process the inference results.
outputTensor = try interpreter.output(at: 0)
// Turn the output tensor into an array. This will have 2 values
// Value at index 0 is the probability of negative sentiment
// Value at index 1 is the probability of positive sentiment
let resultsArray = outputTensor.data
let results: [Float32] = [Float32](unsafeData: resultsArray) ?? []
let positiveSpamValue = results[1]
var outputString = ""
if(positiveSpamValue>0.8){
outputString = "Message not sent. Spam detected with probability: " +
String(positiveSpamValue)
} else {
outputString = "Message sent!"
}
txtOutput.text = outputString
} catch let error {
print("Failed to invoke the interpreter with error: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}
}
12. 新增 Swift 擴充功能
上述程式碼使用了資料類型的擴充功能,可讓您將 Int32 陣列的原始位元複製到 Data。以下是該擴充功能的程式碼:
extension Data {
/// Creates a new buffer by copying the buffer pointer of the given array.
///
/// - Warning: The given array's element type `T` must be trivial in that it can be copied bit
/// for bit with no indirection or reference-counting operations; otherwise, reinterpreting
/// data from the resulting buffer has undefined behavior.
/// - Parameter array: An array with elements of type `T`.
init<T>(copyingBufferOf array: [T]) {
self = array.withUnsafeBufferPointer(Data.init)
}
}
處理低階記憶體時,請使用「不安全」而上述程式碼則需要初始化不安全的資料陣列。這項擴充功能可讓您:
extension Array {
/// Creates a new array from the bytes of the given unsafe data.
///
/// - Warning: The array's `Element` type must be trivial in that it can be copied bit for bit
/// with no indirection or reference-counting operations; otherwise, copying the raw bytes in
/// the `unsafeData`'s buffer to a new array returns an unsafe copy.
/// - Note: Returns `nil` if `unsafeData.count` is not a multiple of
/// `MemoryLayout<Element>.stride`.
/// - Parameter unsafeData: The data containing the bytes to turn into an array.
init?(unsafeData: Data) {
guard unsafeData.count % MemoryLayout<Element>.stride == 0 else { return nil }
#if swift(>=5.0)
self = unsafeData.withUnsafeBytes { .init($0.bindMemory(to: Element.self)) }
#else
self = unsafeData.withUnsafeBytes {
.init(UnsafeBufferPointer<Element>(
start: $0,
count: unsafeData.count / MemoryLayout<Element>.stride
))
}
#endif // swift(>=5.0)
}
}
13. 執行 iOS 應用程式
執行並測試應用程式。
如果一切順利,裝置上應會顯示這個應用程式,如下所示:
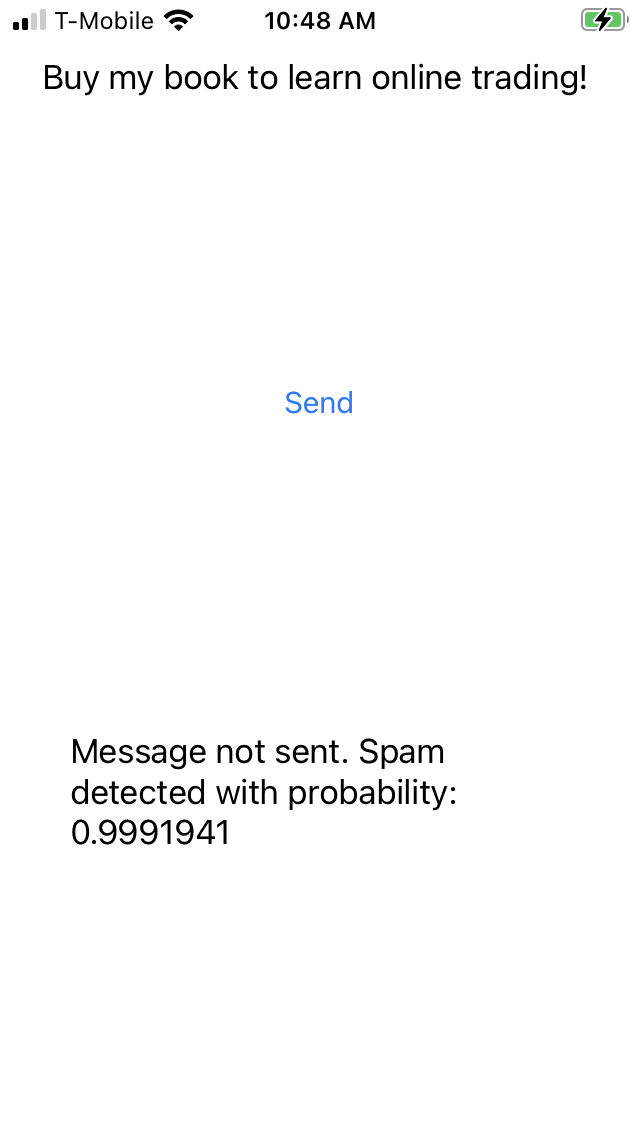
「購買我的書即可學習線上交易!」訊息的網頁在訊息傳送時,應用程式會傳回偵測到垃圾內容的快訊,警示機率為 0 .99%!
14. 恭喜!
現在,您已經開發出一個非常簡單的應用程式,能使用用來篩選垃圾網誌上的資料模型,進一步篩選垃圾留言。
一般開發人員生命週期的下一步,是探索如何根據自家社群取得的資料自訂模型。做法將在下個課程活動中說明。
