1. खास जानकारी
गोपनीय GKE (सीजीकेई) नोड, यह पक्का करते हैं कि वर्कलोड का डेटा एन्क्रिप्ट (सुरक्षित) करके इस्तेमाल किया जा रहा है. vTPM डिवाइस को CGKE (सीजीकेई) वर्कलोड के बारे में बताने से वर्कलोड, vTPM की सुविधाओं का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं. इस कोडलैब में, आपको vTPM की दो सुविधाओं के बारे में बताया गया है.
- vTPM रिमोट अटेस्टेशन, रिमोट पार्टी को यह पुष्टि करने की अनुमति देता है कि वर्कलोड होस्ट करने वाले CGKE नोड, गोपनीय वीएम (सीवीएम) पर चल रहे हैं या नहीं.
- vTPM की अनुमति देना और vTPM को सील करना.
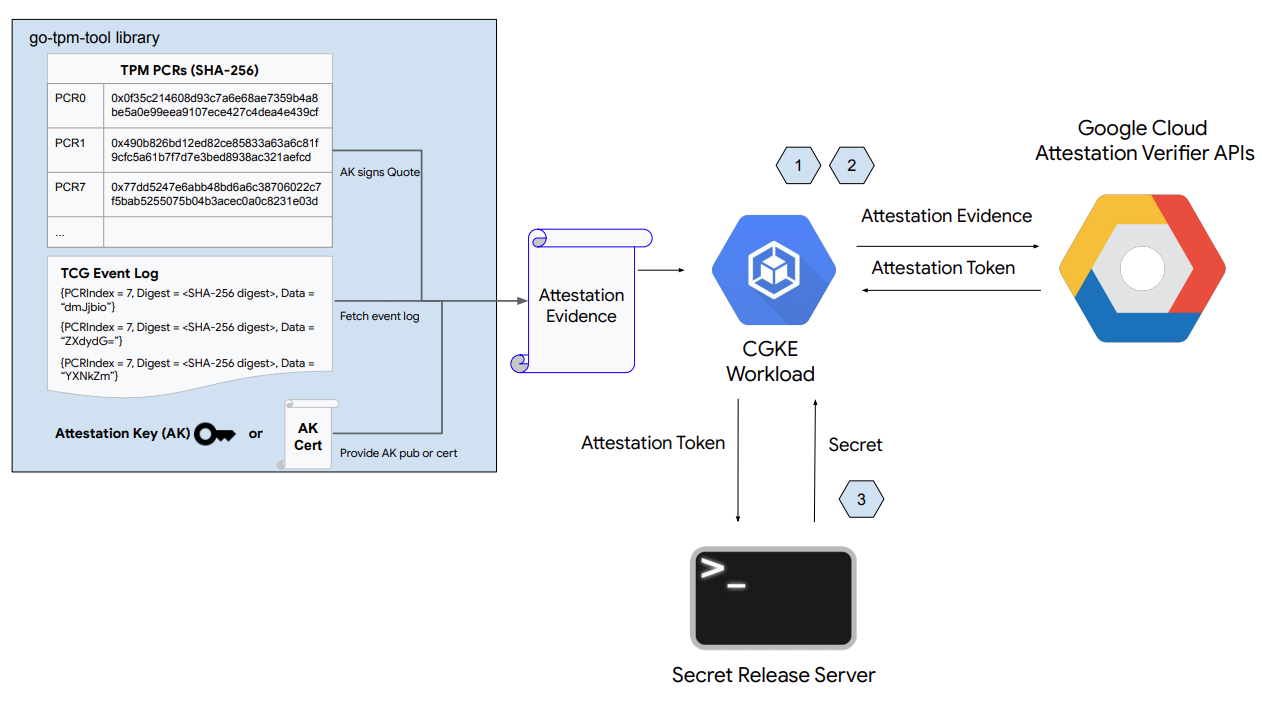
जैसा कि ऊपर दिए गए चित्र में दिखाया गया है, इस कोडलैब के पहले हिस्से में ये चरण शामिल हैं:
- CGKE नोड सेटअप करते हैं और vTPM डिवाइस को चुने गए वर्कलोड के लिए दिखाते हैं.
- वर्कलोड को होस्ट करने वाले CGKE नोड को दूर से प्रमाणित करने के लिए, वर्कलोड डिप्लॉय करें.
- सीक्रेट रिलीज़ वेब सर्वर सेटअप.
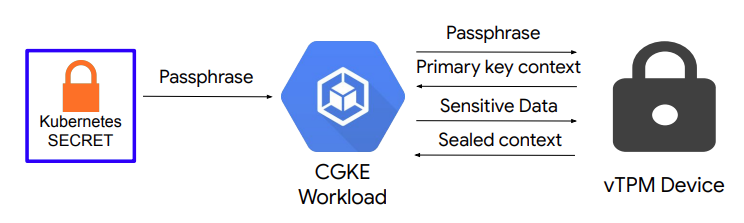
जैसा कि ऊपर दिए गए चित्र में दिखाया गया है, इस कोडलैब के दूसरे हिस्से में ये शामिल हैं:
- CGKE नोड पर vTPM की अनुमति का सेटअप और vTPM की सीलिंग.
आपको इनके बारे में जानकारी मिलेगी
- vTPM डिवाइस को CGKE (CGKE) के वर्कलोड में कैसे दिखाया जाए.
- CGKE (सीजीके) वर्कलोड पर, गोपनीय कंप्यूटिंग एपीआई (प्रमाणित करने की पुष्टि करने वाली सेवा) की मदद से दूर से प्रमाणित करने का तरीका.
- vTPM की अनुमति सेट अप करने और vTPM को सील करने का तरीका.
आपको इन चीज़ों की ज़रूरत होगी
- Google Cloud Platform प्रोजेक्ट
- ब्राउज़र, जैसे Chrome या Firefox
- Google Compute Engine ( कोडलैब), गोपनीय वीएम, गोपनीय GKE नोड, और Artifact Registry की बुनियादी जानकारी
2. सेटअप और ज़रूरी शर्तें:
ज़रूरी एपीआई चालू करने के लिए, Cloud कंसोल या अपने लोकल डेवलपमेंट एनवायरमेंट में यहां दिया गया कमांड चलाएं:
gcloud auth login
gcloud services enable \
cloudapis.googleapis.com \
cloudshell.googleapis.com \
container.googleapis.com \
containerregistry.googleapis.com \
confidentialcomputing.googleapis.com \
iamcredentials.googleapis.com \
compute.googleapis.com
3. CGKE नोड सेट अप करना और चुने गए वर्कलोड के लिए vTPM डिवाइस दिखाना
इससे कोडलैब का पहला हिस्सा शुरू होता है. इस चरण में, CGKE क्लस्टर शुरू किया जाता है और डिवाइस प्लगिन लागू किया जाता है, ताकि CVM vTPM डिवाइस को वर्कलोड में दिखाया जा सके. कमांड देने के लिए, Cloud Console या अपने लोकल डेवलपमेंट एनवायरमेंट पर जाएं.
1). CGKE क्लस्टर बनाएं और वर्कलोड आइडेंटिटी पूल का इस्तेमाल करें. इससे CGKE वर्कलोड को GCP गोपनीय कंप्यूटिंग एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करने की अनुमति मिल जाएगी. वर्कलोड आइडेंटिटी पूल ज़रूरी है, क्योंकि सीजीकेई वर्कलोड को GCP के संसाधनों को ऐक्सेस करने की ज़रूरत होती है. साथ ही, GCP के संसाधनों को ऐक्सेस करने के लिए, CGKE (जीजीकेई) वर्कलोड के लिए एक पहचान बताना ज़रूरी है.
gcloud container clusters create cgke-attestation-codelab \
--machine-type=n2d-standard-2 \
--enable-confidential-nodes \
--zone us-central1-c \
--workload-pool=${PROJECT_ID}.svc.id.goog \
--workload-metadata=GKE_METADATA
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
2). CGKE क्लस्टर को अनुमति देने के लिए, डिवाइस प्लगिन चालू करें, ताकि vTPM डिवाइस को वर्कलोड में दिखाया जा सके. हम एक नया संसाधन - google.com/cc बनाने के लिए kubernetes डिवाइस प्लगिन का इस्तेमाल करते हैं. नए संसाधन से जुड़ा कोई भी वर्कलोड, वर्कर नोड पर vTPM डिवाइस देख सकेगा.
gcloud container clusters get-credentials cgke-attestation-codelab --zone us-central1-c --project ${PROJECT_ID}
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/google/cc-device-plugin/main/manifests/cc-device-plugin.yaml
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
नीचे दिए गए निर्देश से, आपको डिप्लॉय किए गए cc-device- प्लग इन देखने की सुविधा मिलती है.
kubectl get pods -A | grep "cc-device-plugin"
ध्यान दें: मिला-जुला मोड वाले GKE (गोपनीय और गोपनीय GKE कर्मचारी दोनों नोड) क्लस्टर के मामले में, यह सुझाव दिया जाता है कि ऑपरेटर सिर्फ़ गोपनीय GKE (जीकेई) वर्कर नोड पर cc-डिवाइस-प्लग इन का इस्तेमाल करे.
(ज़रूरी नहीं). CGKE पॉड प्रोमेथस मॉनिटरिंग की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करें. मॉनिटरिंग चालू करके, डिवाइस प्लगिन की स्थिति के बारे में जाना जा सकता है.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/google/cc-device-plugin/main/manifests/cc-device-plugin-pod-monitoring.yaml
https://console.cloud.google.com/monitoring/metrics-explorer पर जाएं और cc-device-plugin मेट्रिक ढूंढें या PROMQL का इस्तेमाल करें. उदाहरण के लिए, नीचे दिया गया PROMQL कमांड, हर cc-डिवाइस-प्लग इन प्रोसेस के लिए सीपीयू सेकंड दिखाता है.
rate(process_cpu_seconds_total[${__interval}])
4. वर्कलोड को डिप्लॉय करना और वर्कलोड पर दूर से प्रमाणित करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करना
इस चरण में, पिछले चरण में बनाए गए CGKE क्लस्टर में वर्कलोड बनाया और डिप्लॉय किया जाता है. साथ ही, वर्कर नोड पर प्रमाणित करने वाला टोकन (OIDC टोकन) पाने के लिए, vTPM रिमोट अटेस्टेशन किया जाता है.
1). ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर इमेज बनाएं और उसे Artifact Registry में भेजें. ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर इमेज में go-tpm टूल होता है, जो प्रमाणित करने से जुड़े सबूत इकट्ठा कर सकता है. साथ ही, इसे प्रमाणित करने वाले टोकन (OIDC टोकन) के लिए, प्रमाणित करने की पुष्टि करने वाली सेवा को भेज सकता है.
- ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर इमेज के लिए Dockerfile बनाएं.
Dockerfile
FROM golang:1.21.0 as builder
WORKDIR /
RUN git clone https://github.com/google/go-tpm-tools.git
WORKDIR /go-tpm-tools/cmd/gotpm
RUN CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux go build -o /gotpm
FROM debian:trixie
WORKDIR /
RUN apt-get update -y
RUN DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive apt-get install -y ca-certificates
RUN rm -rf /etc/apt/sources.list.d
COPY --from=builder /gotpm /gotpm
CMD ["tail", "-f", "/dev/null"]
- एक Artifact Registry बनाएं.
gcloud artifacts repositories create codelab-repo \
--repository-format=docker \
--location=us
- ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर इमेज को Artifact Registry में भेजें.
docker build -t us-docker.pkg.dev/${PROJECT_ID}/codelab-repo/go-tpm:latest .
docker push us-docker.pkg.dev/${PROJECT_ID}/codelab-repo/go-tpm:latest
2). GCP के संसाधनों पर GCP के सेवा खाते की अनुमतियां इनहेरिट करने के लिए, Kubernetes सेवा खाता सेट अप करें.
- Kubernetes सेवा खाता
codelab-ksaबनाएं.
kubectl create serviceaccount codelab-ksa \
--namespace default
Confidential_Computing_Workload_Userभूमिका बनाएं और गोपनीय कंप्यूटिंग एपीआई को ऐक्सेस करने के लिए, भूमिका की अनुमतियां दें.
gcloud iam roles create Confidential_Computing_Workload_User --project=<project-id> \
--title="CGKE Workload User" --description="Grants the ability to generate an attestation token in a GKE workload." \
--permissions="confidentialcomputing.challenges.create,confidentialcomputing.challenges.verify,confidentialcomputing.locations.get,confidentialcomputing.locations.list" --stage=GA
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
- GCP सेवा खाता
codelab-csaबनाएं और उसे इस भूमिका के साथ बाइंड करें.Confidential_Computing_Workload_User. So that codelab-csaके पास, गोपनीय कंप्यूटिंग एपीआई को ऐक्सेस करने की अनुमतियां होनी चाहिए.
gcloud iam service-accounts create codelab-csa \
--project=<project-id>
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding <project-id> \
--member "serviceAccount:codelab-csa@<project-id>.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role "projects/<project-id>/roles/Confidential_Computing_Workload_User"
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding codelab-csa@<project-id>.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:<project-id>.svc.id.goog[default/codelab-ksa]"
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
- Kubernetes सेवा खाते
codelab-ksaको GCP सेवा खातेcodelab-csaसे बाइंड करें. इससेcodelab-ksaके पास गोपनीय कंप्यूटिंग एपीआई को ऐक्सेस करने की अनुमतियां होती हैं.
kubectl annotate serviceaccount codelab-ksa \
--namespace default \
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account=codelab-csa@<project-id>.iam.gserviceaccount.com
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
3). डेमो ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, ऐप्लिकेशन डिप्लॉयमेंट yaml बनाएं. चुने गए वर्कलोड के लिए, Kubernetes सेवा खाता codelab-ksa असाइन करें.
deploy.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: go-tpm-demo
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: go-tpm-demo
spec:
serviceAccountName: codelab-ksa
nodeSelector:
iam.gke.io/gke-metadata-server-enabled: "true"
containers:
- name: go-tpm
image: us-docker.pkg.dev/<project-id>/codelab-repo/go-tpm:latest
resources:
limits:
google.com/cc: 1
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
4). CGKE (सीजीकेई) क्लस्टर में डिप्लॉयमेंट को लागू करें.
kubectl create -f deploy.yaml
5). प्रमाणित करने वाला टोकन (OIDC टोकन) फ़ेच करने के लिए, वर्कलोड से कनेक्ट करें और दूर से प्रमाणित करने की सुविधा को लॉन्च करें
kubectl exec -it go-tpm-demo -- /bin/bash ./gotpm token --event-log=/run/cc-device-plugin/binary_bios_measurements > attestation_token
दावे देखने के लिए, jwt.io में जाकर पुष्टि करने वाले टोकन को डिकोड किया जा सकता है!
5. सीक्रेट रिलीज़ वेब सर्वर सेट अप करना
इस चरण में, पिछले एसएसएच सेशन से बाहर निकलें और दूसरी वीएम सेट अप करें. इस वीएम पर, आपने सीक्रेट रिलीज़ वेब सर्वर सेट अप किया है. वेब सर्वर, मिले सर्टिफ़िकेशन टोकन और उसके दावों की पुष्टि करता है. अगर पुष्टि हो जाती है, तो यह अनुरोध अनुरोध करने वाले को भेज दिया जाता है.
1). Cloud Console या अपने लोकल डेवलपमेंट एनवायरमेंट पर जाएं. वर्चुअल मशीन बनाएं.
gcloud config set project <project-id>
gcloud compute instances create cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server \
--machine-type=n2d-standard-2 \
--zone=us-central1-c \
--image=ubuntu-2204-jammy-v20240228 \
--image-project=ubuntu-os-cloud
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
2). एसएसएच की मदद से, अपनी नई वर्चुअल मशीन (वीएम) का इस्तेमाल करें.
gcloud compute ssh --zone us-central1-c cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server
3). Go वातावरण को सेट अप करें.
wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.22.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.22.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin
4). सीक्रेट रिलीज़ वेब सर्वर का सोर्स कोड स्टोर करने वाली नीचे दी गई दो फ़ाइलें बनाएं (नैनो की मदद से कॉपी चिपकाएं).
main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"strings"
"time"
"log"
"github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4"
)
const (
theSecret = "This is the super secret information!"
)
func homePage(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
tokenString := r.Header.Get("Authorization")
if tokenString != "" {
tokenString, err := extractToken(tokenString)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
tokenBytes := []byte(tokenString)
// A method to return a public key from the well-known endpoint
keyFunc := getRSAPublicKeyFromJWKsFile
token, err := decodeAndValidateToken(tokenBytes, keyFunc)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "Invalid JWT Token", http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
if ok, err := isValid(token.Claims.(jwt.MapClaims)); ok {
fmt.Fprintln(w, theSecret)
} else {
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "Error validating JWT claims: "+err.Error(), http.StatusUnauthorized)
} else {
http.Error(w, "Invalid JWT token Claims", http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
}
} else {
http.Error(w, "Authorization token required", http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
}
func extractToken(tokenString string) (string, error) {
if strings.HasPrefix(tokenString, "Bearer ") {
return strings.TrimPrefix(tokenString, "Bearer "), nil
}
return "", fmt.Errorf("invalid token format")
}
func isValid(claims jwt.MapClaims) (bool, error) {
// 1. Evaluating Standard Claims:
subject, ok := claims["sub"].(string)
if !ok {
return false, fmt.Errorf("missing or invalid 'sub' claim")
}
fmt.Println("Subject:", subject)
// e.g. "sub":"https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/<project_id>/zones/<project_zone>/instances/<instance_name>"
issuedAt, ok := claims["iat"].(float64)
if !ok {
return false, fmt.Errorf("missing or invalid 'iat' claim")
}
fmt.Println("Issued At:", time.Unix(int64(issuedAt), 0))
// 2. Evaluating Remote Attestation Claims:
hwModel, ok := claims["hwmodel"].(string)
if !ok || hwModel != "GCP_AMD_SEV" {
return false, fmt.Errorf("missing or invalid 'hwModel'")
}
fmt.Println("hwmodel:", hwModel)
swName, ok := claims["swname"].(string)
if !ok || swName != "GCE" {
return false, fmt.Errorf("missing or invalid 'hwModel'")
}
fmt.Println("swname:", swName)
return true, nil
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", homePage)
fmt.Println("Server listening on :8080")
err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Server failed to start: %v", err)
}
}
helper.go
package main
import (
"crypto/rsa"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"math/big"
"net/http"
"github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4"
)
const (
socketPath = "/run/container_launcher/teeserver.sock"
expectedIssuer = "https://confidentialcomputing.googleapis.com"
wellKnownPath = "/.well-known/openid-configuration"
)
type jwksFile struct {
Keys []jwk `json:"keys"`
}
type jwk struct {
N string `json:"n"` // "nMMTBwJ7H6Id8zUCZd-L7uoNyz9b7lvoyse9izD9l2rtOhWLWbiG-7pKeYJyHeEpilHP4KdQMfUo8JCwhd-OMW0be_XtEu3jXEFjuq2YnPSPFk326eTfENtUc6qJohyMnfKkcOcY_kTE11jM81-fsqtBKjO_KiSkcmAO4wJJb8pHOjue3JCP09ZANL1uN4TuxbM2ibcyf25ODt3WQn54SRQTV0wn098Y5VDU-dzyeKYBNfL14iP0LiXBRfHd4YtEaGV9SBUuVhXdhx1eF0efztCNNz0GSLS2AEPLQduVuFoUImP4s51YdO9TPeeQ3hI8aGpOdC0syxmZ7LsL0rHE1Q",
E string `json:"e"` // "AQAB" or 65537 as an int
Kid string `json:"kid"` // "1f12fa916c3a0ef585894b4b420ad17dc9d6cdf5",
// Unused fields:
// Alg string `json:"alg"` // "RS256",
// Kty string `json:"kty"` // "RSA",
// Use string `json:"use"` // "sig",
}
type wellKnown struct {
JwksURI string `json:"jwks_uri"` // "https://www.googleapis.com/service_accounts/v1/metadata/jwk/signer@confidentialspace-sign.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
// Unused fields:
// Iss string `json:"issuer"` // "https://confidentialcomputing.googleapis.com"
// Subject_types_supported string `json:"subject_types_supported"` // [ "public" ]
// Response_types_supported string `json:"response_types_supported"` // [ "id_token" ]
// Claims_supported string `json:"claims_supported"` // [ "sub", "aud", "exp", "iat", "iss", "jti", "nbf", "dbgstat", "eat_nonce", "google_service_accounts", "hwmodel", "oemid", "secboot", "submods", "swname", "swversion" ]
// Id_token_signing_alg_values_supported string `json:"id_token_signing_alg_values_supported"` // [ "RS256" ]
// Scopes_supported string `json:"scopes_supported"` // [ "openid" ]
}
func getWellKnownFile() (wellKnown, error) {
httpClient := http.Client{}
resp, err := httpClient.Get(expectedIssuer + wellKnownPath)
if err != nil {
return wellKnown{}, fmt.Errorf("failed to get raw .well-known response: %w", err)
}
wellKnownJSON, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return wellKnown{}, fmt.Errorf("failed to read .well-known response: %w", err)
}
wk := wellKnown{}
json.Unmarshal(wellKnownJSON, &wk)
return wk, nil
}
func getJWKFile() (jwksFile, error) {
wk, err := getWellKnownFile()
if err != nil {
return jwksFile{}, fmt.Errorf("failed to get .well-known json: %w", err)
}
// Get JWK URI from .wellknown
uri := wk.JwksURI
fmt.Printf("jwks URI: %v\n", uri)
httpClient := http.Client{}
resp, err := httpClient.Get(uri)
if err != nil {
return jwksFile{}, fmt.Errorf("failed to get raw JWK response: %w", err)
}
jwkbytes, err := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
return jwksFile{}, fmt.Errorf("failed to read JWK body: %w", err)
}
file := jwksFile{}
err = json.Unmarshal(jwkbytes, &file)
if err != nil {
return jwksFile{}, fmt.Errorf("failed to unmarshall JWK content: %w", err)
}
return file, nil
}
// N and E are 'base64urlUInt' encoded: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7518#section-6.3
func base64urlUIntDecode(s string) (*big.Int, error) {
b, err := base64.RawURLEncoding.DecodeString(s)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
z := new(big.Int)
z.SetBytes(b)
return z, nil
}
func getRSAPublicKeyFromJWKsFile(t *jwt.Token) (any, error) {
keysfile, err := getJWKFile()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to fetch the JWK file: %w", err)
}
// Multiple keys are present in this endpoint to allow for key rotation.
// This method finds the key that was used for signing to pass to the validator.
kid := t.Header["kid"]
for _, key := range keysfile.Keys {
if key.Kid != kid {
continue // Select the key used for signing
}
n, err := base64urlUIntDecode(key.N)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to decode key.N %w", err)
}
e, err := base64urlUIntDecode(key.E)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to decode key.E %w", err)
}
// The parser expects an rsa.PublicKey: https://github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/blob/main/rsa.go#L53
// or an array of keys. We chose to show passing a single key in this example as its possible
// not all validators accept multiple keys for validation.
return &rsa.PublicKey{
N: n,
E: int(e.Int64()),
}, nil
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to find key with kid '%v' from well-known endpoint", kid)
}
func decodeAndValidateToken(tokenBytes []byte, keyFunc func(t *jwt.Token) (any, error)) (*jwt.Token, error) {
var err error
fmt.Println("Unmarshalling token and checking its validity...")
token, err := jwt.NewParser().Parse(string(tokenBytes), keyFunc)
fmt.Printf("Token valid: %v\n", token.Valid)
if token.Valid {
return token, nil
}
if ve, ok := err.(*jwt.ValidationError); ok {
if ve.Errors&jwt.ValidationErrorMalformed != 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("token format invalid. Please contact the Confidential Space team for assistance")
}
if ve.Errors&(jwt.ValidationErrorNotValidYet) != 0 {
// If device time is not synchronized with the Attestation Service you may need to account for that here.
return nil, errors.New("token is not active yet")
}
if ve.Errors&(jwt.ValidationErrorExpired) != 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("token is expired")
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unknown validation error: %v", err)
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("couldn't handle this token or couldn't read a validation error: %v", err)
}
5). वेब सर्वर बनाने और उसे चलाने के लिए, यहां दिए गए निर्देशों का पालन करें. इससे :8080 पोर्ट पर सीक्रेट रिलीज़ वेबसर्वर शुरू होता है.
go mod init google.com/codelab go mod tidy go get github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 go build ./codelab
समस्या हल करना: आपको नीचे दी गई चेतावनी दिख सकती है. go mod tidy: को चलाते समय, इसे अनदेखा किया जा सकता है
go: finding module for package github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 go: downloading github.com/golang-jwt/jwt v3.2.2+incompatible go: downloading github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 v4.5.0 go: found github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 in github.com/golang-jwt/jwt/v4 v4.5.0 go: google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible: import path "google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible" should not have @version go: google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible/cmd/jwt: import path "google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible/cmd/jwt" should not have @version go: google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible/request: import path "google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible/request" should not have @version go: google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible/test: import path "google.com/codelab/go/pkg/mod/github.com/golang-jwt/jwt@v3.2.2+incompatible/test" should not have @version
6). कोई दूसरा Cloud Console टैब या लोकल डेवलपमेंट एनवायरमेंट सेशन शुरू करें और नीचे दिया गया निर्देश चलाएं. इससे आपको cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server-internal-ip मिलेगा.
gcloud compute instances describe cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server --format='get(networkInterfaces[0].networkIP)' --zone=us-central1-c
7). प्रमाणित करने वाला टोकन (OIDC टोकन) पाने के लिए, अपने CGKE (CGKE) के वर्कलोड से कनेक्ट करें और दूर से प्रमाणित करने की सुविधा लॉन्च करें. इसके बाद, attestation-token और cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server-internal-ip के कॉन्टेंट को यहां दिए गए निर्देश में जोड़ें. इससे आपको सीक्रेट रिलीज़ वेब सर्वर के पास रखा गया सीक्रेट फ़ेच हो जाएगा!
kubectl exec -it go-tpm-demo -- /bin/bash ./gotpm token --event-log=/run/cc-device-plugin/binary_bios_measurements > attestation_token curl http://<cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server-internal-ip>:8080 -H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat ./attestation_token)"
इन्हें बदलें:
cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server-internal-ip,cgke-attestation-codelab-web-serverवीएम इंस्टेंस का इंटरनल आईपी है.
6. vTPM CGKE (सीजीकेई) नोड पर सीलिंग करना
यह चरण, इस कोडलैब का दूसरा हिस्सा शुरू करता है. इस चरण में, CGKE नोड पर vTPM मालिक की अनुमति का सेट अप किया जाता है और vTPM मालिक के लंबे पासवर्ड के साथ वर्कलोड को डिप्लॉय किया जाता है. इसके बाद, vTPM को सील करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करके, वर्कलोड में डेटा को सील करने और अनसील करने के लिए vTPM प्राइमरी पासकोड बनाया जा सकता है.
1). CGKE नोड पर vTPM मालिक की अनुमति सेट अप करें.
- एक बार इस्तेमाल की जाने वाली जॉब कंटेनर इमेज बनाएं. एक बार इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला जॉब, सभी vTPM के लिए मालिक का पासवर्ड सेट करता है. कंटेनर इमेज बनाने के लिए डॉक फ़ाइल यहां दी गई है.
Dockerfile
FROM debian:latest
RUN echo 'debconf debconf/frontend select Noninteractive' | debconf-set-selections
RUN apt-get update
RUN apt -y install \
autoconf-archive \
libcmocka0 \
libcmocka-dev \
net-tools \
build-essential \
git \
pkg-config \
gcc \
g++ \
m4 \
libtool \
automake \
libgcrypt20-dev \
libssl-dev \
uthash-dev \
autoconf \
uuid-dev \
libcurl4-openssl-dev \
libjson-c-dev
RUN mkdir /src
WORKDIR /src
RUN git clone https://github.com/tpm2-software/tpm2-tss
WORKDIR /src/tpm2-tss
RUN ./bootstrap
RUN ./configure --prefix=/usr/local
RUN make all install
WORKDIR /src
RUN git clone https://github.com/tpm2-software/tpm2-tools
WORKDIR /src/tpm2-tools
RUN apt-get -y install libcurl4 libcurl4-openssl-dev pandoc man-db
RUN ./bootstrap
RUN ./configure --prefix=/usr/local
RUN make all install
RUN apt-get -y install vim
ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/bash"]
- आर्टफ़ैक्ट रजिस्ट्री में, एक बार इस्तेमाल की जाने वाली जॉब कंटेनर इमेज बनाएं और पुश करें.
docker build -t us-docker.pkg.dev/<project-id>/codelab-repo/tpm-tools:latest . docker push us-docker.pkg.dev/<project-id>/codelab-repo/tpm-tools:latest
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
- Kubernetes जॉब के ज़रिए, वन-टाइम जॉब लागू करें. (चेतावनी: यह जॉब हर CVM पर vTPM को हटा देता है, अगर आपका CVM डिस्क को एन्क्रिप्ट करने के लिए vTPM का इस्तेमाल करता है, तो फिर से चालू करने के बाद यह जॉब आपके CVM को इस्तेमाल करने लायक नहीं बना देगा. यह देखा जा सकता है कि आपकी डिस्क में
lsblk -fनिर्देश के साथ FSTYPEcrypto_LUKSहै या नहीं)
tpm-tools-task.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: tpm-tools-task
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: tpm-tools
image: us-docker.pkg.dev/<project-id>/codelab-repo/tpm-tools:latest
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args: ["tpm2_clear; tpm2_changeauth -c owner this_is_passphrase"]
resources:
limits:
google.com/cc: 1
restartPolicy: Never
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
- एक बार इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला जॉब लॉन्च करें. यह जॉब सभी वर्कर नोड पर vTPM मालिक का लंबा पासवर्ड सेट करता है.
kubectl create -f tpm-tools-task.yaml
2). vTPM के मालिक का लंबा पासवर्ड होल्ड करने के लिए, Kubernetes सीक्रेट बनाएं.
kubectl create secret generic tpm-secret --from-literal=passphrase='this_is_passphrase'
3). एक डेमो ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर बनाएं और उसमें लंबा पासवर्ड पास करें. डेमो ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर में, vTPM के साथ इंटरैक्ट करने के लिए tpm2 टूल होते हैं.
- डेमो ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर के लिए, डिप्लॉयमेंट yaml फ़ाइल बनाएं.
deploy_demo.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: tpm-tools-demo
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: tpm-tools-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: tpm-tools
image: us-docker.pkg.dev/<project-id>/codelab-repo/tpm-tools:latest
command: ["tail", "-f", "/dev/null"]
resources:
limits:
google.com/cc: 1
volumeMounts:
- name: secret-volume
mountPath: "/etc/tpmsecret"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: secret-volume
secret:
secretName: tpm-secret
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
- डेमो ऐप्लिकेशन डिप्लॉय करें.
kubectl create -f deploy_demo.yaml
4). डेमो ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर में vTPM को सील करें.
- डेमो ऐप्लिकेशन कंटेनर से कनेक्ट करें और लंबे पासवर्ड से एक प्राथमिक कुंजी सेट करें.
kubectl exec -it tpm-tools-demo -- /bin/bash tpm2_createprimary -C o -c primary.ctx -P $(cat /etc/tpmsecret/passphrase)
tpm2_createprimary, तय हैरारकी और टेंप्लेट के आधार पर मुख्य ऑब्जेक्ट जनरेट करने के लिए, vTPM से इंटरैक्ट करता है.
- -C o: इससे पता चलता है कि मुख्य पासकोड, TPM के मालिक के क्रम के तहत बनाया जाएगा.
- -cprimary.ctx: बनाए गए मुख्य ऑब्जेक्ट के संदर्भ (हैंडल और उससे जुड़ा डेटा) को app.ctx फ़ाइल में सेव करता है. यह कॉन्टेक्स्ट, बाद के ऑपरेशन के लिए ज़रूरी है.
मुख्य कुंजी बनाने के लिए, वर्कलोड में मालिक के गलत लंबे पासवर्ड का इस्तेमाल नहीं किया जा सकता.
tpm2_createprimary -C o -P गलत_passphrase
यह निर्देश नीचे दी गई गड़बड़ियां दिखाता है:
WARNING:esys:src/tss2-esys/api/Esys_CreatePrimary.c:401:Esys_CreatePrimary_Finish() Received TPM Error ERROR:esys:src/tss2-esys/api/Esys_CreatePrimary.c:135:Esys_CreatePrimary() Esys Finish ErrorCode (0x000009a2) ERROR: Esys_CreatePrimary(0x9A2) - tpm:session(1):authorization failure without DA implications ERROR: Unable to run tpm2_createprimary
- इसके बाद, बनाई गई प्राथमिक कुंजी का इस्तेमाल डेटा को सील करने और अनसील करने के लिए किया जा सकता है.
echo "This is my secret message" > secret.txt tpm2_create -C primary.ctx -u sealed.pub -r sealed.priv -i secret.txt tpm2_load -C primary.ctx -u sealed.pub -r sealed.priv -c sealed.ctx tpm2_unseal -c sealed.ctx -o unsealed.txt
tpm2_create मनचाहे क्रिप्टोग्राफ़िक ऑब्जेक्ट को जनरेट करने के लिए, vTPM से इंटरैक्ट करता है.
- -Cprimary.ctx: उस प्राथमिक कुंजी संदर्भ का उपयोग करता है, जिसे हमने पहले बनाया था.
- -u सीलल्ड.पब: सीलिंग की के सार्वजनिक हिस्से (अनसीलिंग के लिए ज़रूरी है) को सील किए गए.pub में स्टोर करता है.
- -r सीलल्ड.प्रिव: सीलिंग कुंजी के निजी हिस्से को सीलल्ड.प्रिव में स्टोर करता है.
- -isecret.txt: वह फ़ाइल जिसमें सील किया जाने वाला सीक्रेट है.
tpm2_load: सार्वजनिक और निजी हिस्सों (लॉक किया गया.pub, सील किया गया.priv) का इस्तेमाल करके टीपीएम में सीलिंग कुंजी को लोड करता है और इसके कॉन्टेक्स्ट को सील किए गए.ctx में सेव करता है.
tpm2_unseal: vTPM सीलिंग ऑब्जेक्ट का इस्तेमाल करके, पहले एन्क्रिप्ट (सुरक्षित) किए गए डेटा को डिक्रिप्ट (अनसील) करने के लिए किया जाता है.
ध्यान दें: primary.ctx, sealed.priv फ़ाइलों का इस्तेमाल सिर्फ़ एक vTPM डिवाइस पर किया जा सकता है. इसके अलावा, जिस भी व्यक्ति के पास vTPM डिवाइस और इन फ़ाइलों का ऐक्सेस है वह सील किए गए डेटा को ऐक्सेस कर सकता है. आगे से, डेटा को सील करने के लिए पीसीआर वैल्यू पर बनी नीति का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. हालांकि, यह कोडलैब इस नीति के दायरे से बाहर है.
7. साफ़-सफ़ाई सेवा
Cloud Console या अपने लोकल डेवलपमेंट एनवायरमेंट में, यहां दिए गए कमांड चलाएं:
gcloud config set project <project-id> # Delete the CGKE cluster gcloud container clusters delete cgke-attestation-codelab --zone us-central1-c # Delete the Artifact Registry gcloud artifacts repositories delete codelab-repo --location=us # Delete the web server VM instance gcloud compute instances delete cgke-attestation-codelab-web-server --zone=us-central1-c # Delete the GCP service account gcloud iam service-accounts delete codelab-csa@<project-id>.iam.gserviceaccount.com # Delete the role gcloud iam roles delete Confidential_Computing_Workload_User
इन्हें बदलें:
project-id, प्रोजेक्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर है.
8. आगे क्या करना है
गोपनीय GKE नोड के बारे में ज़्यादा जानें.
